Centrifugal Microfluidic System for Nucleic Acid Amplification and Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. System Design and Construction



2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. PCR Reagents
2.4. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PCR Chamber Design and Fluid Control


3.2. Temperature Control

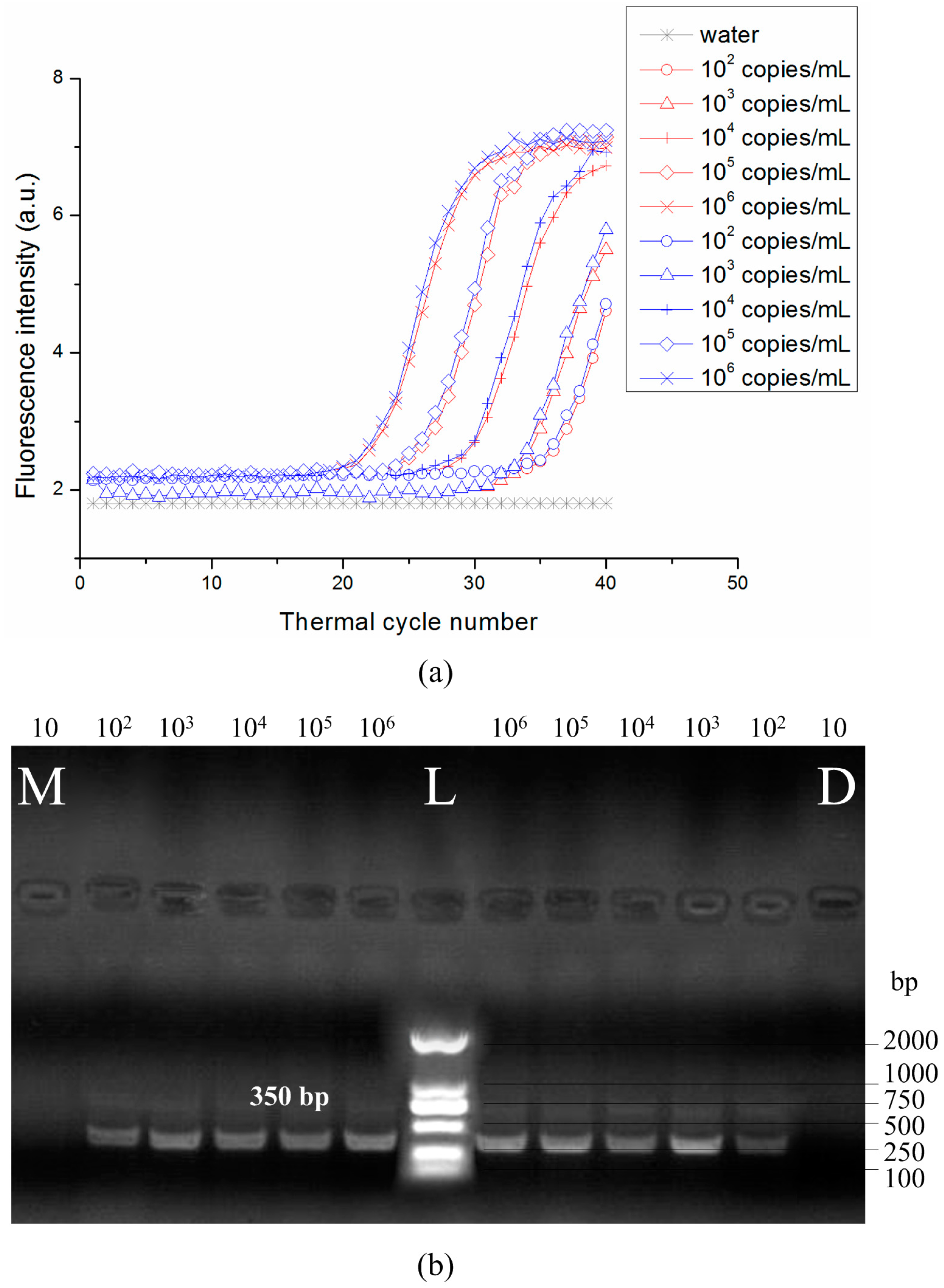
3.3. DNA Amplification and Quantification
| Denaturation Time (s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 5 | 3 | 2 | |
| Ct (Mean ± SD) | 32.2 ± 0.48 | 32.3 ± 0.49 | 32.3 ± 0.48 | 33.4 ± 0.72 |
| Annealing Time (s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 10 | 9 | |
| Ct (Mean ± SD) | 32.2 ± 0.49 | 32.3 ± 0.51 | 32.9 ± 0.68 |
| Extension Time (s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 10 | 5 | 4 | |
| Ct (Mean ± SD) | 32.2 ± 0.48 | 32.3 ± 0.50 | 32.3 ± 0.51 | 33.2 ± 0.67 |


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, Y.C.; Huang, M.Y.; Young, K.C.; Chang, T.T.; Wu, C.Y. A rapid micro-polymerase chain reaction system for hepatitis C virus amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 71, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Park, S.H.; Yang, H.; Chung, K.H.; Yoon, T.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.T. Bulk-micromachined submicroliter-volume PCR chip with very rapid thermal response and low power consumption. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.Y.; Cao, W.B.; Wu, J.B.; Wen, W.J.; Chang, D.C.; Sheng, P. Design and integration of an all-in-one biomicrofluidic chip. Biomicrofluidics 2008, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.B.; Michael, G.M.; Chen, D.F.; Liu, C.C.; Haim, H.B. A large volume, portable, real-time PCR reactor. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3170–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, D.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, Y.; Cho, H.J.; Sung, S.W.; Oh, K.W.; Cha, J.; Lim, G. Precise temperature control and rapid thermal cycling in a micromachined DNA polymerase chain reaction chip. Micromech. Microeng. 2002, 12, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsumi, Y.; Hitaka, Y.; Matsui, K.; Takeo, M.; Negoro, S.; Ukita, Y. Planar microreactor for biochemical application made from silicon and polymer films. Microsyst. Technol. 2007, 13, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, M.U.; Manz, A. Chemical amplification: Continuous-flow PCR on a chip. Science 1998, 280, 1046–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Wang, X.S.; Chen, T.; Ma, X.M.; Zuo, T.C. Fabrication and characterization of a polymethyl methacrylate continuous-flow PCR microfluidic chip using CO2 laser ablation. Microsyst. Technol. 2009, 15, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.H.; Ramalingam, N.; Xian-Dui, D.; Ngin, T.S.; Xianting, Z.; Kuan, A.T.L.; Hai-Qing, G. Real-time PCR microfluidic devices with concurrent electrochemical detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2131–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagatani, N.; Yamanaka, K.; Ushijima, H.; Koketsu, R.; Sasaki, T.; Ikuta, K.; Tamiya, E. Detection of influenza virus using a lateral flow immunoassay for amplified DNA by a microfluidic RT-PCR chip. Analyst 2012, 137, 3422–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, N. Multichannel oscillatory-flow PCR micro-fluidic chip with controllable temperature gradient. Microsyst. Technol. 2014, 21, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gransee, R.; Schneider, T.; Elyorgun, D.; Strobach, X.; Schunck, T.; Gatscha, T.; Höth, J. Fluorescence detection in Lab-on-a-chip systems using ultrafast nucleic acid amplification methods. In Proceedings of the Smart Biomedical and Physiological Sensor Technology XI, Baltimore, MD, USA, 5 May 2014.
- Almassian, D.R.; Cockrell, L.M.; Nelson, W.M. Portable nucleic acid thermocyclers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8769–8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madou, M.; Zoval, J.; Jia, G.; Kido, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, N. Lab on a CD. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 8, 601–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorkin, R.; Park, J.; Siegrist, J.; Amasia, M.; Lee, B.S.; Park, J.M.; Cho, Y.K. Centrifugal microfluidics for biomedical applications. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1758–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducree, J.; Haeberle, S.; Lutz, S.; Pausch, S.; Stetten, F.V.; Zengerle, R. The centrifugal microfluidic Bio-Disk platform. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, S103–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, R.; Kirby, D.; Glynn, M.; Nwankire, C.; O’Sullivan, M.; Siegrist, J.; Kinahan, D.; Aguirre, G.; Kijanka, G.; Gorkin, R.A.; et al. Centrifugal microfluidics for cell analysis. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2012, 16, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strohmeier, O.; Emperle, A.; Roth, G.; Mark, D.; Zengerle, R.; Stetten, F. Centrifugal gas-phase transition magnetophoresis (GTM)—A generic method for automation of magnetic bead based assays on the centrifugal microfluidic platform and application to DNA purification. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Ho, H.P.; Chen, Q.; Yang, A.K.L.; Kwok, H.C.; Wu, S.Y.; Zhang, X. A lab-in-a-droplet bioassay strategy for centrifugal microfluidics with density difference pumping, power to disc and bidirectional flow control. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3698–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasia, M.; Cozzens, M.; Madou, M. Centrifugal microfluidic platform for rapid PCR amplification using integrated thermoelectric heating and ice-valving. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, G.J.; Arnold, T.E.; Carvalho, B.L.; Duffy, D.C.; Sheppard, N.F. Centrifugal microfluidics: Applications. In Micro Total Analysis Systems 2000; Springer Netherlands: Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.H.; Jung, J.H.; Zhang, H.; Lee, N.Y.; Seo, T.S. A rotary microsystem for simple, rapid and automatic RNA purification. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3875–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strohmeier, O.; Keller, M.; Schwemmer, F.; Zehnle, S.; Mark, D.; von Stetten, F.; Zengerle, R.; Paust, N. Centrifugal microfluidic platforms: Advanced unit operations and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6187–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucl. Acids Res. 2001, 29, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, L.J.; Wang, J.H.; Hsieh, T.M.; Chen, P.H.; Chen, P.J.; Lee, D.S.; Lee, G.B. A micro circulating PCR chip using a suction-type membrane for fluidic transport. Biomed. Microdev. 2009, 11, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, T.M.; Luo, C.H.; Huang, F.C.; Wang, J.H.; Chien, L.J.; Lee, G.B. Enhancement of thermal uniformity for a microthermal cycler and its application for polymerase chain reaction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 130, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Chien, L.J.; Hsieh, T.M.; Luo, C.H.; Chou, W.P.; Chen, P.H.; Lee, G.B. A miniaturized quantitative polymerase chain reaction system for DNA amplification and detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 141, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miao, B.; Peng, N.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Hu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C. Centrifugal Microfluidic System for Nucleic Acid Amplification and Detection. Sensors 2015, 15, 27954-27968. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151127954
Miao B, Peng N, Li L, Li Z, Hu F, Zhang Z, Wang C. Centrifugal Microfluidic System for Nucleic Acid Amplification and Detection. Sensors. 2015; 15(11):27954-27968. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151127954
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiao, Baogang, Niancai Peng, Lei Li, Zheng Li, Fei Hu, Zengming Zhang, and Chaohui Wang. 2015. "Centrifugal Microfluidic System for Nucleic Acid Amplification and Detection" Sensors 15, no. 11: 27954-27968. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151127954
APA StyleMiao, B., Peng, N., Li, L., Li, Z., Hu, F., Zhang, Z., & Wang, C. (2015). Centrifugal Microfluidic System for Nucleic Acid Amplification and Detection. Sensors, 15(11), 27954-27968. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151127954






