Embedded Ultrasonic Transducers for Active and Passive Concrete Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. A novel Ultrasonic Transducer to Be Embedded in Concrete
2.1. Transducer Design and Description

2.2. Installation


2.3. Characterization



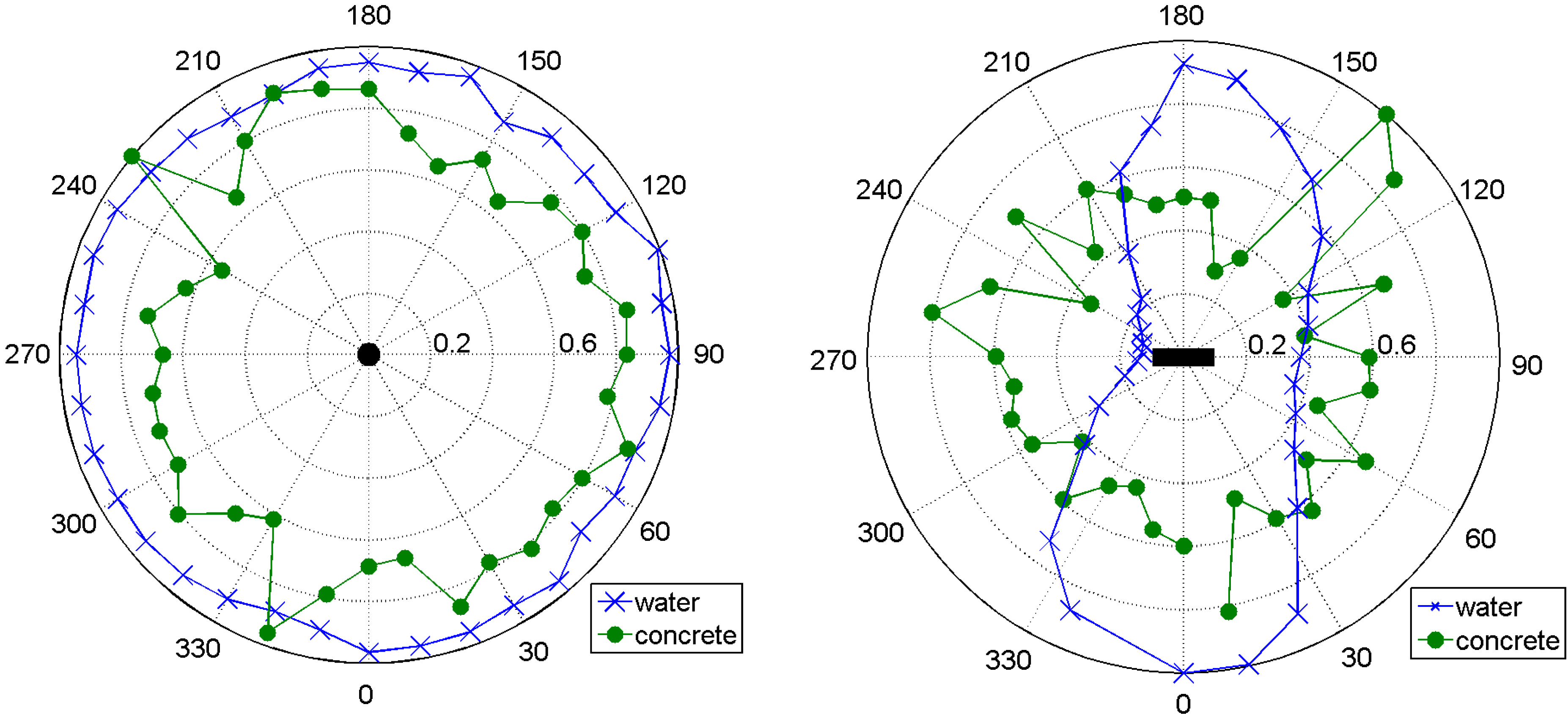

3. Short Notes on Ultrasonic Transmission Experiments
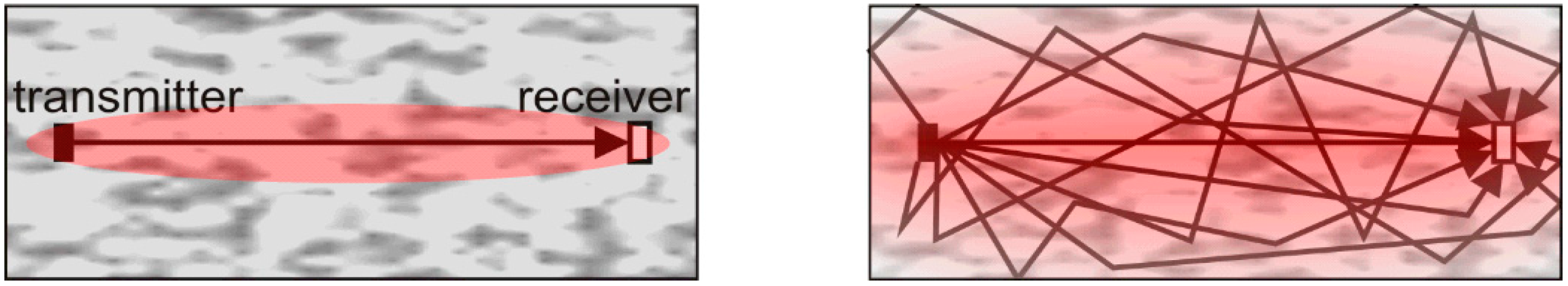
3.1. Wave Propagation in Concrete
3.2. Data Evaluation
4. Application Examples
4.1. Monitoring of Load Changes


4.2. Acoustic Emission

4.3. Time Reversal Experiment
4.4. Other Applications


5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karbhari, V.M.; Ansari, M. Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Infrastructure Systems; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-1-84569-392-3. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, M.; Mayer, K.; Friese, M.; Milmann, B.; Mielentz, F.; Ballier, G. Progress in ultrasonic tendon duct imaging. Eur. J. Environ. Civil Eng. 2011, 15, 461–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Gu, H.; Mo, Y.-L. Smart aggregates: Multi-functional sensors for concrete structures—A tutorial and a review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, S.H.; Zhu, J. Using piezoelectric sensors for ultrasonic pulse velocity measurements in concrete. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederleithinger, E.; Krompholz, R.; Müller, S.; Lautenschläger, R.; Kittler, J. 36 Jahre Talsperre Eibenstock—36 Jahre Überwachung des Eibenstock—36 Years Monitoring the concrete condition by Ultrasound, in German). Proceedings of 38. Dresdner Wasserbaukolloquium, Germany, 2015; Available online: http://www.researchgate.net/publication/274708685_36_Jahre_Talsperre_Eibenstock__36_Jahre_berwachung_des_Betonzustands_durch_Ultraschall (accessed on 24 April 2015).
- Wolf, J.; Mielentz, F.; Milmann, B.; Helmerich, R.; Köpp, C.; Wiggenhauser, H. Ultrasound based monitoring system for concrete monolithic objects. In Procedings of the 6th International Conference on Structural Health Monitoring of Intelligent Infrastructure (SHMII-6), Hong Kong, China, 9 December 2013.
- Wolf, J.; Niederleithinger, E.; Mielentz, F.; Grothe, S.; Wiggenhauser, H. Überwachung von Betonkonstruktionen mit eingebetteten Ultraschallsensoren. Bautechnik 2014, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Facaoaru, I. Recommendations for testing concrete by the ultrasonic pulse method. Mater. Constr. 1969, 2, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, G.I. Guide to Nondestructive Testing of Concrete. In Technical Report FHWA-SA-97-105; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- British Standards Institute (BSI). Testing Concrete in Structures. Determination of Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity. BS EN 12504-4:2004 (equivalent German version: DIN EN 12504–4:2004. Available online: http://shop.bsigroup.com/ProductDetail/?pid=000000000030102823 (accessed on 24 April 2015).
- Sayers, C.M. Stress-induced ultrasonic wave velocity anisotropy in fractured rock. Ultrasonics 1988, 26, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokouhi, P.; Zoega, A. Surface Wave Velocity-Stress Relationship in Uniaxially Loaded Concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2012, 109, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Suaris, W.; Fernando, V. Ultrasonic Pulse Attenuation as a Measure of Damage Growth during Cyclic Loading of Concrete. ACI Mater. J. 1987, 84, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.T. The Stress Effect on the Ultrasonic Velocity Variations of Concrete under Repeated Loading. ACI Mater. J. 1998, 95, 519–524. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Abraham, O.; Grondin, F.; Loukili, A.; Tournat, V.; Duff, A.-L.; Lascoup, B.; Durand, O. Study of stress-induced velocity variation in concrete under direct tensile force and monitoring of the damage level by using thermally-compensated Coda Wave Interferometry. Ultrasonics 2012, 52, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederleithinger, E.; Wunderlich, C. Influence of small temperature variations on the ultrasonic velocity in concrete. Rev. Prog. Quant. Nondestruct. Eval. 2013, 1511, 390–397. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Abraham, O.; Tournat, V.; Duff, A.L.; Lascoup, B.; Loukili, A.; Grondin, F.; Durand, O. Validation of a thermal bias control technique for Coda Wave Interferometry (CWI). Ultrasonics 2013, 53, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohdaira, E.; Masuzawa, N. Water content and its effect on ultrasound propagation in concrete—The possibility of NDE. Ultrasonics 2000, 38, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedenblad, G. Moisture Permeability of Some Porous Materials; Report TVBM (Intern 7000-Rapport). Byggnadstysik: DTH, Lyngby, September 1993. Available online: http://lup.lub.lu.se/luur/download?func=downloadFile&recordOId=1653173&fileOId=1653174 (accessed on 24 April 2015).
- Lencis, U. Moisture Effect on the Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity in Concrete Cured under Normal Conditions and at Elevated Temperature. Constr. Sci. 2013, 14, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payan, C.; Quiviger, A.; Garnier, J.F. Applying diffuse ultrasound under dynamic loading to improve closed crack characterization in concrete. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramamoorthy, S.K.; Kane, Y.; Turner, J.A. Ultrasound diffusion for crack depth determination in concrete. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 115, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payan, C.; Garnier, V. Determination of third order elastic constants in a complex solid applying coda wave interferometry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. Standard Test Method for Pulse Velocity through Concrete. ASTM C597-09. Available online: http://www.astm.org/Standards/C597.htm (accessed on 24 April 2015).
- Tronicke, J. The Influence of High Frequency Uncorrelated Noise on First-Break Arrival Times and Crosshole Traveltime Tomography. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2007, 12, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederleithinger, E.; Sens-Schönfelder, C.; Grothe, S.; Wiggenhauser, H. Coda Wave Interferometry Used to Localize Compressional Load Effects on a Concrete Specimen. In Proceedings of the 7 th European Workshop on Structiral Health Monitoring (EWSHM 2014), Nantes, France, 8–11 July 2014.
- Larose, E.; Hall, S. Monitoring stress related velocity variation in concrete with a 2 × 10−5 relative resolution using diffuse ultrasound. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 1853–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planes, T.; Larose, E.; Margerin, L.; Rossetto, L.; Sens-Schönfelder, C. Decorrelation and phaseshift of coda waves induced by local changes: Multiple scattering approach and numerical validation. Waves Random Complex Media 2014, 24, 99–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanu, C. Time-Lapse Monitoring of Localized Changes within Heterogeneous Media with Scattered Waves. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 5 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Jiang, L.; Liaw, P.K.; Brooks, C.R.; Seelev, R.; Klarstrom, D.L. Using Acoustic Emission in Fatigue and Fracture Materials Research. Memb. J. Miner. Metals Mater. Soc. 1998, 50. Available online: http://www.tms.org/pubs/journals/JOM/9811/Huang/Huang-9811.html (accessed on 24 April 2015).
- Große, C.U.; Schumacher, T. Anwendungen der Schallemissionsanalyse an Betonbauwerken. Bautechnik 2013, 90, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.E.; Douma, J.; Ulrich, T.J.; Snieder, R. Improving Spatio-Temporal Focusing and Source Reconstruction through Deconvolution. Wave Motion 2015, 52, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douma, J.; Niederleithinger, E.; Snieder, R. Locating Events Using Time Reversal and Deconvolution: Experimental Application and Analysis. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niederleithinger, E.; Wolf, J.; Mielentz, F.; Wiggenhauser, H.; Pirskawetz, S. Embedded Ultrasonic Transducers for Active and Passive Concrete Monitoring. Sensors 2015, 15, 9756-9772. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150509756
Niederleithinger E, Wolf J, Mielentz F, Wiggenhauser H, Pirskawetz S. Embedded Ultrasonic Transducers for Active and Passive Concrete Monitoring. Sensors. 2015; 15(5):9756-9772. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150509756
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiederleithinger, Ernst, Julia Wolf, Frank Mielentz, Herbert Wiggenhauser, and Stephan Pirskawetz. 2015. "Embedded Ultrasonic Transducers for Active and Passive Concrete Monitoring" Sensors 15, no. 5: 9756-9772. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150509756
APA StyleNiederleithinger, E., Wolf, J., Mielentz, F., Wiggenhauser, H., & Pirskawetz, S. (2015). Embedded Ultrasonic Transducers for Active and Passive Concrete Monitoring. Sensors, 15(5), 9756-9772. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150509756





