One-Pot Click Access to a Cyclodextrin Dimer-Based Novel Aggregation Induced Emission Sensor and Monomer-Based Chiral Stationary Phase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
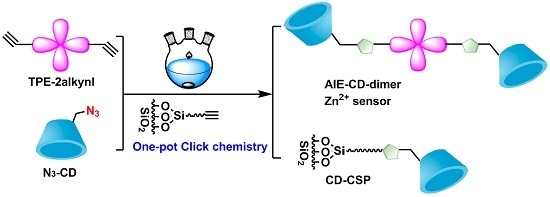
2.2. Synthesis of TPE-Triazole-CD and CSP via ‘One-Pot’ Click Chemistry
2.3. Instrumentation
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, D.W.; Ward, T.J.; Armstrong, R.D.; Beesley, T.E. Separation of drug stereoisomers by the formation of beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Science 1986, 232, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, M.L.; Reibenspies, J.H.; Darensbourg, M.Y. A cyclodextrin host/guest approach to a hydrogenase active site biomimetic cavity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8870–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Qi, L.; Qiao, J.; Chen, Y. Ratiometric fluorescent pattern for sensing proteins using aqueous polymer-pyrene/gamma-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1821–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tang, J.; Tang, W. Cyclodextrin clicked chiral stationary phases with functionalities-tuned enantioseparations in high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1406, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemma, S.M.; Scampicchio, M.; Mahon, P.J.; Sbarski, I.; Wang, J.; Kingshott, P. Controlled release of retinyl acetate from beta-cyclodextrin functionalized poly(vinyl alcohol) electrospun nanofibers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3481–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, C.; Li, R.; Guo, J.; Ding, L.; Zhong, W. New generation of beta-cyclodextrin-chitosan nanoparticles encapsulated quantum dots loaded with anticancer drug for tumor-target drug delivery and imaging of cancer cells. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Kong, J.; Yao, X.; Zhao, C.; Dong, Y.; Lu, X. Polydopamine-assisted attachment of beta-cyclodextrin on porous electrospun fibers for water purification under highly basic condition. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Shan, C.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Ma, H.; Luo, Y.; Song, H. Assembling of a functional cyclodextrin-decorated upconversion luminescence nanoplatform for cysteine-sensing. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14054–14056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, H.C.; Finn, M.G.; Sharpless, K.B. Click chemistry: Diverse chemical function from a few good reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2004–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, Y.; Han, C.; Zhan, J. Triazole-ester modified silver nanoparticles: Click synthesis and Cd2+ colorimetric sensing. Chem. Commun. 2009, 4812–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, R.K.; Dikundwar, A.G.; Row, T.N.G.; Rao, C.P. A lower rim triazole linked calix 4 arene conjugate as a fluorescence switch on sensor for Zn2+ in blood serum milieu. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4345–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, R.K.; Hinge, V.K.; Mahesh, K.; Rai, A.; Panda, D.; Rao, C.P. Cd2+ complex of a triazole-based calix 4 arene conjugate as a selective fluorescent chemosensor for cys. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6907–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, R.K.; Tabbasum, K.; Rai, A.; Panda, D.; Rao, C.P. Pyrophosphate sensing by a fluorescent Zn2+ bound triazole linked imino-thiophenyl conjugate of calix 4 arene in hepes buffer medium: Spectroscopy, microscopy, and cellular studies. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5117–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Gong, Y.; Mamuti, R.; Xing, W.; Zheng, H.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y. Chiral differentiation of novel isoxazoline derivatives on “clicked” thioether and triazole bridged cyclodextrin chiral stationary phases. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 30492–30499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Young, D.J.; Tan, T.T.Y.; Ng, S.-C. “Click” preparation of hindered cyclodextrin chiral stationary phases and their efficient resolution in high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7878–7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragg, W.; Shamsi, S.A. A novel positively charged achiral co-monomer for beta-cyclodextrin monolithic stationary phase: Improved chiral separation of acidic compounds using capillary electrochromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1267, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Ng, S.-C.; Tan, T.T.Y.; Wang, Y. Recent development of cyclodextrin chiral stationary phases and their applications in chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1269, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ong, T.-T.; Li, L.-S.; Tan, T.T.Y.; Ng, S.-C. Enantioseparation of a novel “click” chemistry derived native beta-cyclodextrin chiral stationary phase for high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 2388–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedehontaa-Hiaa, G.; Guerrouache, M.; Carbonnier, B.; Le Derf, F.; Morin, C.J. Layer-by-layer assemblies based on a cationic beta-cyclodextrin polymer: Chiral stationary phases for open-tubular electrochromatography. Chromatographia 2015, 78, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, G.; Tang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, D. Fluorescence turn-on detection of DNA and label-free fluorescence nuclease assay based on the aggregation-induced emission of silole. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6443–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Feng, X.; Tong, B.; Shi, J.; Chen, L.; Zhi, J.; Dong, Y. A novel “turn-on” fluorescent chemosensor for the selective detection of Al3+ based on aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Xu, B.; Dong, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; He, J.; Li, H.; Tian, W. Novel fluorescent ph sensors and a biological probe based on anthracene derivatives with aggregation-induced emission characteristics. Langmuir 2010, 26, 6838–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Dong, Y.Q.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z.; Wong, K.S. Studies on the aggregation-induced emission of silole film and crystal by time-resolved fluorescence technique. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 402, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Chang, N.; Li, C.; Mei, J.; Deng, C.; Luo, X.; Liu, Z.; Bo, Z.; Dong, Y.Q.; Tang, B.Z. Locking the phenyl rings of tetraphenylethene step by step: Understanding the mechanism of aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10675–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Wang, H.; Hauke, C.E.; Cook, T.R.; Wang, M.; Saha, M.L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Huang, F.; et al. A suite of tetraphenylethylene-based discrete organoplatinum(ii) metallacycles: Controllable structure and stoichiometry, aggregation-induced emission, and nitroaromatics sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15276–15286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y. Click synthesis of a novel triazole bridged aie active cyclodextrin probe for specific detection of Cd2+. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 4298–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Mei, J.; Hu, R.R.; Sun, J.Z.; Qin, A.J.; Tang, B.Z. Click synthesis, aggregation-induced emission, e/z isomerization, self-organization, and multiple chromisms of pure stereoisomers of a tetraphenylethene-cored luminogen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9956–9966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Leung, N.L.C.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Together we shine, united we soar! Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11718–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitti, A.; Villafiorita-Monteleone, F.; Pacini, A.; Botta, C.; Virgili, T.; Forni, A.; Cariati, E.; Boiocchi, M.; Pasini, D. Structure-activity relationships for the solid state emission of a new family of “push-pull” pi-extended chromophores. Faraday Discuss. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, C.; Benedini, S.; Carlucci, L.; Forni, A.; Marinotto, D.; Nitti, A.; Pasini, D.; Righetto, S.; Cariati, E. Polymorphism-dependent aggregation induced emission of a push-pull dye and its multi-stimuli responsive behavior. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 2979–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluccini, C.; Sharma, A.K.; Caricato, M.; Sironi, A.; Cariati, E.; Righetto, S.; Tordin, E.; Botta, C.; Forni, A.; Pasini, D. Switching of emissive and NLO properties in push-pull chromophores with crescent PPV-like structures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.-F.; Zeng, J.; Lu, J.-W.; Zhang, Z.-B. Insights into the general and efficient cross mcmurry reactions between ketones. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 9873–9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Bian, N.; Cao, C.; Qiu, X.-L.; Qi, A.-D.; Han, B.-H. Glucosamine hydrochloride functionalized tetraphenylethylene: A novel fluorescent probe for alkaline phosphatase based on the aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4067–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J. ‘Click’ preparation of a novel ‘native-phenylcarbamoylated’ bilayer cyclodextrin stationary phase for enhanced chiral differentiation. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1381, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Xiao, Y.; Ng, C.H.; Oh, T.S.; Tan, T.T.Y.; Ng, S.C. Preparation of cyclodextrin chiral stationary phases by organic soluble catalytic ‘click’ chemistry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasini, D. The click reaction as an efficient tool for the construction of macrocyclic structures. Molecules 2013, 18, 9512–9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacini, A.; Caricato, M.; Ferrari, S.; Capsoni, D.; de Ilarduya, A.M.; Munoz-Guerra, S.; Pasini, D. Poly(gamma-glutamic acid) esters with reactive functional groups suitable for orthogonal conjugation strategies. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 4790–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricato, M.; Olmo, A.; Gargiulli, C.; Gattuso, G.; Pasini, D. A ‘clicked’ macrocyclic probe incorporating binol as the signalling unit for the chiroptical sensing of anions. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 7861–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, A.R. Industrial applications of cyclodextrins. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhao, R.; Tang, X.; Shi, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. One-Pot Click Access to a Cyclodextrin Dimer-Based Novel Aggregation Induced Emission Sensor and Monomer-Based Chiral Stationary Phase. Sensors 2016, 16, 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16121985
Li X, Zhao R, Tang X, Shi Y, Li C, Wang Y. One-Pot Click Access to a Cyclodextrin Dimer-Based Novel Aggregation Induced Emission Sensor and Monomer-Based Chiral Stationary Phase. Sensors. 2016; 16(12):1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16121985
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaoli, Rui Zhao, Xiaoying Tang, Yanyan Shi, Chunyi Li, and Yong Wang. 2016. "One-Pot Click Access to a Cyclodextrin Dimer-Based Novel Aggregation Induced Emission Sensor and Monomer-Based Chiral Stationary Phase" Sensors 16, no. 12: 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16121985
APA StyleLi, X., Zhao, R., Tang, X., Shi, Y., Li, C., & Wang, Y. (2016). One-Pot Click Access to a Cyclodextrin Dimer-Based Novel Aggregation Induced Emission Sensor and Monomer-Based Chiral Stationary Phase. Sensors, 16(12), 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16121985