A Context-Recognition-Aided PDR Localization Method Based on the Hidden Markov Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
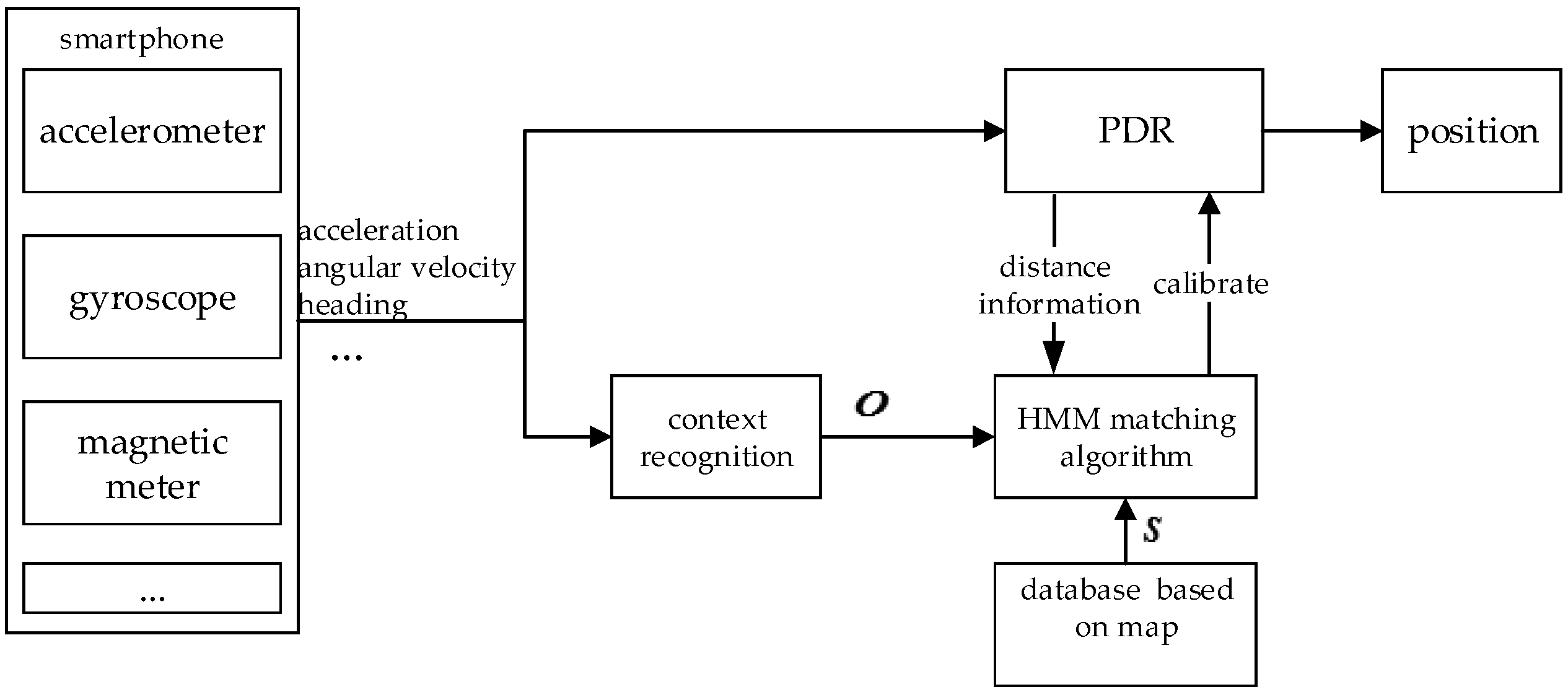
2. The Structure of Context-Recognition-Aided PDR Localization Method Based on HMM
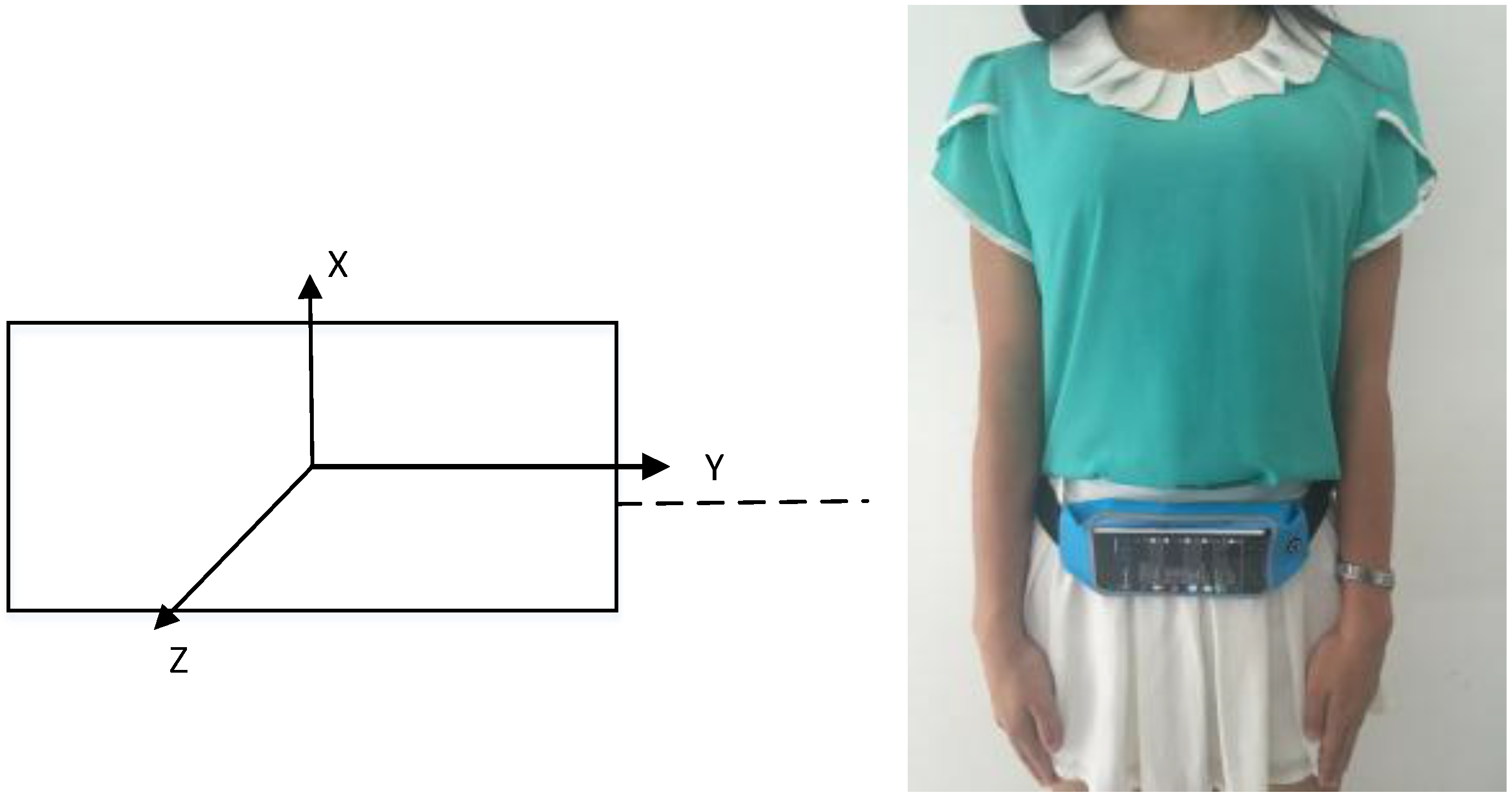
3. Context Recognition
4. HMM Matching Algorithm
4.1. The HMM Matching Algorithm Model
4.2. Matching Procedure Based on HMM
5. Experiments and Discussion
5.1. Determination of Threshold in HMM Algorithm
5.2. Determination of the Starting Point
5.3. Localization Accuracy
5.4. Robustness of the Method
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, X.Y.; Tao, W.Y.; Chung, M.O.; Pan, Z.J. On the dynamic RSS feedbacks of indoor fingerprinting databases for localization reliability improvement. Sensors 2016, 16, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W. Research and Implementation of Indoor Positioning Based on the Android Mobile Phone. Master’s Thesis, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wei, D.Y.; Yuan, H.; Ouyang, G.Z. A novel method of WiFi fingerprint positioning using spatial multi-points matching. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Alcalá de Henares, Spain, 4–5 October 2016.
- Huang, C.M.; Hsieh, T.H.; Lin, S.Y. A signal-aware fingerprinting-based positioning technique in cellular networks. In Proceedings of the 2011 14th International Conference on Network-Based Information Systems (NBiS), Tirana, Albania, 7–9 September 2011; pp. 325–332.
- Yao, T.J.; Wei, D.Y.; Yuan, H. Research on the feedback correction-based fusion method for WLAN and PDR positioning. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 37, 446–453. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, A.R.; Seco, F.; Zampella, F.; Prieto, J.C.; Guevara, J. PDR with a foot-mounted IMU and ramp detection. Sensors 2011, 11, 9393–9410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.W.; Jang, H.J.; Hwang, D.H.; Park, C. A step, stride and heading determination for the pedestrian navigation system. J. Global Pos. Syst. 2004, 3, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiang, G.; Wang, Y. An improved pedestrian navigation algorithm. J. Chongqing Univ. Post Telecommun. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2016, 28, 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, G.; Lu, M.; Jiang, F. Bumping: A bump-aided inertial navigation method for indoor vehicles using smartphones. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2014, 25, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.R.J.; Granja, F.S.; Honorato, J.C.P. Pedestrian indoor navigation by aiding a foot-mounted IMU with RFID Signal Strength measurements. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Zurich, Switzerland, 15–17 September 2010.
- Dao, T.K.; Nguyen, H.L.; Pham, T.T. User localization in complex environments by multimodal combination of GPS, Wi-Fi, RFID, and Pedometer Technologies. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, A.; Wang, J.; Gao, J. An indoor localization method based on pedestrian dead reckoning aided by map matching. J. Geom. Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 529–532. [Google Scholar]
- Woodman, O.; Harle, R. Pedestrian localization for indoor environments. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Seoul, Korea, 21–24 September 2008; pp. 114–123.
- Feng, T.; Du, W. A map matching algorithm based on ideal hidden markov model. Nat. Sci. J. Hainan Univ. 2014, 32, 212–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, A.; Zhao, W. An indoor location system based on Bluetooth-corrected and map-matching aided pedestrian dead reckoning algorithm. Sci. Surv. Mapping 2016, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z. Map matching technology and its application in ITS. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2005, 41, 225–228. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.J. Research on Positioning Method for Pedestrian Based on WLAN/Bluetooth and PDR in Complex Scenarios. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.H.; Wei, D.Y.; Lai, Q.F.; Li, W.; Yuan, H. Smartphone-based integrated PDR/GPS/Bluetooth pedestrian location. Adv. Space Res. 2016. accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, K.; Nadales, M.J.V.; Robertson, P. Reliable real-time recognition of motion related human activities using MEMS inertial sensors. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation, Portland, OR, USA, 21–24 September 2010; pp. 2919–2932.
- Nadales, M.J.V. Recognition of Human Motion Related Activities from Sensors. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Malaga, Malaga, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, D.U.; Kim, S.J.; Chung, W.Y. Classification of posture and movement using a 3-axis accelerometer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Convergence Information Technology, Gyeongju, Korea, 21–23 November 2007; pp. 837–844.
- Marianne, N.; Bjørge, H.H.; Benedicte, P. Accelerometer-determined physical activity and walking capacity in persons with Down syndrome, Williams syndrome and Prader–Willi syndrome. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 4395–4403. [Google Scholar]
- Ru, C.G. Research on Sensor-Based Activity Recognition. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, S.X. Algorithm Research on Personal Navigation System Based on Particle Filter. Master’s Thesis, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.Y.; Liu, G.Z.; Li, H.L. A multiple visual models based perceptive analysis frame work for multilevel video summarization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2007, 17, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Liang, C.K.; Peng, Y.C. Integration of digital stabilizer with video codec for digital video cameras. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2007, 17, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Wu, J.; Wei, Z. Global motion video segmentation based on the change of integral brightness in rows (columns). In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Image and Signal Processing, Agadir, Morocco, 28–30 June 2012.
- Anliker, U.; Ward, J.A.; Lukowicz, P. AMON: A wearable multi-parameter medical monitoring and alert system. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2004, 8, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Inertial and Environmental Sensors in XiaoMi smartphone. Available online: http://www.sensorexpert.com.cn/Article/chouchouxiaomishouji_1.html (accessed on 8 November 2016).
- The Test of Sensors in XiaoMi3. Available online: http://it.21cn.com/market/a/2014/0106/09/25878912_2.shtml (accessed on 8 November 2016).
- AndroSensor. Available online: http://www.fivasim.com/androsensor.html (accessed on 7 November 2016).
- Porikli, F.; Li, X. Traffic congestion estimation using HMM models without vehicle tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Parma, Italy, 14–17 June 2004; pp. 188–193.
- Liu, N.; Lovell, B.C.; Kootsookos, P.J. Understanding HMM training for video gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Region 10 Conference on TENCON, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 21–24 November 2004.
- Wang, X.; Cong, Z.; Fang, L. Determination of real-time vehicle driving status using HMM. Acta Autom. Sin. 2013, 39, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoubin, G. An Introduction to hidden markov models and Bayesian networks. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2001, 15, 9–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hidden Markov Model. Available online: http://wwwR2.cs.cmu.ed/~aura/docdir/small00.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2016).
- Trogh, J.; Plets, D.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W. Advanced Real-Time Indoor Tracking Based on the Viterbi Algorithm and Semantic Data. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Movement | Mean/Rad·s−1 | Variance/Rad·s−1 |
|---|---|---|
| Turn left | −1.7425 | 0.4242 |
| Turn right | 2.2055 | 0.9155 |
| Walk straight | −0.0019 | 0.0021 |
| Parameter | Accelerometer | Gyroscope | Magnetic Meter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | MPU-6050 | MPU-6050 | AK8963 |
| Manufacturer | InvenSense | InvenSense | AKM |
| Measurement | acceleration | angular velocity | magnetic field |
| Range | ±20 m/s2 | ±35 rad/s | 0–9830 μT |
| Accuracy | 1.5 × 10−1 m/s2 | 3 × 10−3 rad/s | 3 μT |
| Scene | Correctness/% | Average Number of Contexts |
|---|---|---|
| garage | 100 | 2 |
| floor 8 | 100 | 2.067 |
| Scene | Correctness/% | Average Number of Contexts |
|---|---|---|
| Zero false rate | 100 | 2 |
| One missed detection | 92.3 | 3.917 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Wei, D.; Lai, Q.; Li, W.; Yuan, H. A Context-Recognition-Aided PDR Localization Method Based on the Hidden Markov Model. Sensors 2016, 16, 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16122030
Lu Y, Wei D, Lai Q, Li W, Yuan H. A Context-Recognition-Aided PDR Localization Method Based on the Hidden Markov Model. Sensors. 2016; 16(12):2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16122030
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yi, Dongyan Wei, Qifeng Lai, Wen Li, and Hong Yuan. 2016. "A Context-Recognition-Aided PDR Localization Method Based on the Hidden Markov Model" Sensors 16, no. 12: 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16122030
APA StyleLu, Y., Wei, D., Lai, Q., Li, W., & Yuan, H. (2016). A Context-Recognition-Aided PDR Localization Method Based on the Hidden Markov Model. Sensors, 16(12), 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16122030





