Cotton Fabric Coated with Conducting Polymers and its Application in Monitoring of Carnivorous Plant Response
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Cotton Coating with Conducting Polymers
2.2. Characterization
2.3. FTIR and Raman Spectra
2.4. Plant Material and Culture Condition
2.5. Monitoring the Electrical Response from Plant
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Coating of Cotton with Conducting Polymers
3.2. FTIR and Raman Spectra
3.3. Electrical Properties
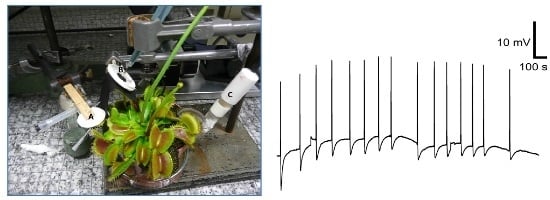
3.4. Response to Plant Stimulation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sapurina, I.; Stejskal, J. Mechanism of the oxidative polymerization of aniline and the formation of supramolecular polyaniline structures. Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 1295–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Sapurina, I.; Trchová, M. Polyaniline nanostructures and the role of aniline oligomers in their formation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1420–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Jing, X.L.; Li, Y. Self-assembly of aniline oligomers and their induced polyaniline supramolecular structures. Chem. Pap. 2013, 67, 891–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, S.; Khastgir, D.; Singha, N.K. Progress in preparation and applications of polyaniline. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 783–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćirić-Marjanović, G. Recent advances in polyaniline research: Polymerization mechanisms, structural aspects, properties and applications. Synth. Met. 2013, 177, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Trchová, M.; Bober, P.; Humpolíček, P.; Kašpárková, V.; Sapurina, I.; Shishov, M.A.; Varga, M. Conducting Polymers: Polyaniline. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology; Wiley Online Library, Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Guimard, N.K.; Gomez, N.; Schmidt, C.E. Conducting polymers in biomedical engineering. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 876–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, T.H.; Rai, R.; Boccaccini, A.R. Tissue engineering of electrically responsive tissues using polyaniline based polymers: A review. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9068–9086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Ansari, U.; Murtaza, N. Real-time wound management through integrated pH sensors: A review. Sens. Rev. 2015, 35, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Gilbert, R.G. Polyaniline. Preparation of a conducting polymer (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirase, R.; Shikata, T.; Shirai, M. Selective formation of polyaniline on wool by chemical polymerization, using potassium iodate. Synth. Met. 2004, 146, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.H.; Oh, K.W.; Kang, T.J. Preparation of conducting nylon-6 electrospun fiber webs by the in situ polymerization of polyaniline. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.J.; Deogaonkar, S.C. A novel method of in situ chemical polymerization of polyaniline for synthesis of electrically conductive cotton fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2012, 82, 1517–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.P.; Gao, B.; Wang, B.B.; Wei, J.T.; Zhao, C. A new nanocomposite: Carbon cloth based polyaniline for an electrochemical supercapacitor. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 111, 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Xu, Z.H.; Men, X.H.; Zhu, X.T. Fabrication of super-repellent cotton fabrics with rapid reversible wettability switching of diverse liquids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 276, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, F.Z.; Usta, I. Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of polyester fabrics with polyaniline deposition. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubidoust, F.; Wicaksono, D.H.B.; Chandren, S.; Nur, H. Effect of graphene oxide on the structural and electrochemical behavior of polypyrrole deposited on cotton fabric. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1075, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bober, P.; Stejskal, J.; Šeděnková, I.; Trchová, M.; Martinková, L.; Marek, J. The deposition of globular polypyrrole and polypyrrole nanotubes on cotton fabric. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 156, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Rani, N.; Saxena, P.; Bhandari, H.; Dhawan, S.K. Development of polyaniline/zinc oxide nanocomposite impregnated fabric as an electrostatic charge dissipative material. Polym. Int. 2015, 64, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, G.G.; Campbell, T.E.; Innis, P.C. Putting function into fashion: Organic conducting polymer fibres and textiles. Fibers Polym. 2007, 8, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.H.; Liu, W.J. Polyaniline/poly(ethylene terephthalate) conducting composite fabric with improved fastness to washing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 5775–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varesano, A.; Dall’Acqua, L.; Tonin, C. A study on the electrical conductivity decay of polypyrrole coated wool textiles. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2005, 89, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mičušík, M.; Nedelčev, T.; Omastová, M.; Krupa, I.; Olejníková, K.; Fedorko, P.; Chehimi, M.M. Conductive polymer-coated textiles: The role of fabric treatment by pyrrole-functionalized triethoxysilane. Synth. Met. 2007, 157, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.N.; Tian, M.W.; Qu, L.J.; Zhu, S.F.; Guo, X.Q.; Han, G.T.; Sun, K.K.; Hu, X.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Xu, X.Q. Functionalization of cotton fabric with graphene oxide nanosheet and polyaniline for conductive and UV blocking properties. Synth. Met. 2015, 202, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.T.; Zhang, B.W.; Wu, J.X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Ma, H.J.; Yu, M.; Li, L.F.; Li, J.Y. Electrical switchability and dry-wash durability of conductive textiles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11255-1–11255-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.Y.; Zhang, X.G.; Ye, X.G.; Yang, S.D. Preparation and enhanced capacitance of core-shell polypyrrole/polyaniline composite electrode for supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2008, 176, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.T.; Abbas, F.; Kausar, A.; Khan, M.R. New polyaniline/polypyrrole/polythiophene and functionalized multiwalled carbion nanotube-based nanocomposites: Layer-by-layer in situ polymerization. High Perform. Polym. 2013, 25, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Sumathi, C.; Dharuman, D. Polypyrrole-polyaniline-Au (PPY-PANi-Au) nano composite films for label-free electrochemical DNA sensing. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.L.; Qin, Z.Y.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, Y.Q. Controlled synthesis, core-shell structures and electrochemical properties of polyaniline/polypyrrole composite nanofibers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2129–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.; Sumathi, C.; Dharuman, V.; Wilson, J. Polypyrrole nanotubes-polyaniline composite for DNA detection using methylene blue as intercalator. Anal. Meth. 2013, 5, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; He, X.J.; Ye, S.H.; Tong, Y.X.; Li, G.R. Design of polypyrrole/polyaniline double-walled nanotube arrays for electrochemical energy storage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2014, 6, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stejskal, J.; Sapurina, I.; Trchová, M.; Šeděnková, I.; Kovářová, J.; Kopecká, J.; Prokeš, J. Coaxial conducting polymer nanotubes: Polypyrrole nanotubes coated with polyaniline or poly(p-phenylenediamine) and products of their carbonization. Chem. Pap. 2015, 69, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.G.; Xu, S.C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.X. Polypyrrole/polyaniline composites with enhanced performance for capacitive deionization. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 3248–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.J.; Zhu, L.G.; Xu, J.; Fang, D.; Bai, Z.K.; Xu, W.L. Investigations of poly(pyrrole)-coated cotton fabrics prepared in blends of anionic and cationic surfactants as flexible electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 103, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempien, Z.; Rybicki, T.; Rybicki, E.; Kozanecki, M.; Szynkowska, M.I. In-situ deposition of polyaniline and polypyrrole electroconductive layers on textile surfaces by the reactive ink-jet printing technique. Synth. Met. 2015, 202, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.G.; Zhang, L.X.; Sun, Y.Y.; Bai, Z.K.; Xu, J.; Liang, G.J.; Xu, W.L. Conductive cotton fabrics for heat generation prepared by mist polymerization. Fiber Polym. 2014, 15, 1804–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetiner, S. Dielectric and morphological studies of nanostructured polypyrrole-coated cotton fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazhini, B.K.; Prabu, H.G. Study on flame retardant and UV-protection properties of cotton fabric functionalized with ppy-ZnO-CNT nanocomposite. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 49062–49069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deogaonkar, S.C.; Bhat, N.V. Polymer based fabrics as transducers in ammonia & ethanol gas sensing. Fiber Polym. 2015, 16, 1803–1811. [Google Scholar]
- Fromm, J.; Lautner, S. Electrical signals and their physiological significance in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziolek, C.; Grams, T.E.E.; Schreiber, U.; Matyssek, R.; Fromm, J. Transient knockout of photosynthesis mediated by electrical signals. New Phytol. 2004, 161, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, E.; Dziubinska, H.; Stolarz, M.; Trebacz, M. Effect of ion channel inhibitors on cold and electrically-induced action potentials in Dionaea muscipula. Biol. Plant. 2006, 50, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libiaková, M.; Floková, K.; Novák, O.; Slováková, L.; Pavlovič, A. Abundance of cysteine endopeptidase dionain in digestive fluid of Venus flytrap (Dionaea muscipula Ellis) is regulated by different stimuli from prey through jasmonates. PLos ONE 2014, 9, 104424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omastová, M.; Trchová, M.; Kovářová, J.; Stejskal, J. Synthesis and structural study of polypyrroles prepared in the presence of surfactants. Synth. Met. 2003, 138, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaváčková, V.; Krchňák, P.; Naus, J.; Novák, O.; Špundová, M.; Strnad, M. Electrical and chemical signals involved in short-term systemic photosynthetic responses of tobacco plants to local burning. Planta 2006, 225, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilík, P.; Hlaváčková, V.; Krchňák, P.; Nauš, J. A low-noise multi-channel device for monitoring of systemic electrical signal propagation in plants. Biol. Plant. 2010, 54, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Sapurina, I. Polyaniline: thin films and colloidal dispersions (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2005, 77, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Sapurina, I.; Prokeš, J.; Zemek, J. In-situ polymerized polyaniline films. Synth. Met. 1999, 105, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćirić-Marjanović, G.; Mentus, S.; Pašti, I.; Gavrilov, N.; Krstić, J.; Travas-Sejdic, J.; Strover, L.; Kopecká, J.; Morávková, Z.; Trchová, M.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and electrochemistry of nanotubular polypyrrole and polypyrrole-derived carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 14770–14784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecká, J.; Kopecký, D.; Vrňata, M.; Fitl, P.; Stejskal, J.; Trchová, M.; Bober, P.; Morávková, Z.; Prokeš, J.; Sapurina, I. Polypyrrole nanotubes: Mechanism of formation. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trchová, M.; Morávková, Z.; Bláha, M.; Stejskal, J. Raman spectroscopy of polyaniline and oligoaniline thin films. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 122, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocherginsky, N.M.; Wang, Z. The role of ionic conductivity and interface in electrical resistance, ion transport and transmembrane redox reactions through polyaniline membranes. Synth. Met. 2006, 156, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Bogomolova, O.E.; Blinova, N.V.; Trchová, M.; Šeděnková, I.; Prokeš, J.; Sapurina, I. Mixed electron and proton conductivity of polyaniline films in aqueous solutions of acids: beyond the 1000 S·cm−1 limit. Polym. Int. 2009, 58, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.X.; Yang, F.; Ding, G.Q.; Mya, K.Y.; Ma, J.; Lu, X.H. Covalent bonding of polyaniline on fullerene: Enhanced electrical, ionic conductivities and electrochromic performances. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 67, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Cotton | Sheet Resistivity, Ω□−1 | Conductivity of Related Powders, S·cm−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| as Prepared | after Dry Cleaning | ||
| +PANI | 6.3 × 104 | 5.0 × 105 | 2.2 |
| +PANI+PPy | 630 | 7.7 × 103 | 7.2 |
| +PPy | 1.7 × 103 | 5.0 × 103 | 4.2 |
| +PPy+PANI | 210 | 1.7 × 103 | 3.2 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bajgar, V.; Penhaker, M.; Martinková, L.; Pavlovič, A.; Bober, P.; Trchová, M.; Stejskal, J. Cotton Fabric Coated with Conducting Polymers and its Application in Monitoring of Carnivorous Plant Response. Sensors 2016, 16, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040498
Bajgar V, Penhaker M, Martinková L, Pavlovič A, Bober P, Trchová M, Stejskal J. Cotton Fabric Coated with Conducting Polymers and its Application in Monitoring of Carnivorous Plant Response. Sensors. 2016; 16(4):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040498
Chicago/Turabian StyleBajgar, Václav, Marek Penhaker, Lenka Martinková, Andrej Pavlovič, Patrycja Bober, Miroslava Trchová, and Jaroslav Stejskal. 2016. "Cotton Fabric Coated with Conducting Polymers and its Application in Monitoring of Carnivorous Plant Response" Sensors 16, no. 4: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040498