A Low Cost Compact Measurement System Constructed Using a Smart Electrochemical Sensor for the Real-Time Discrimination of Fruit Ripening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Principle of the Smart Electrochemical Ethylene Sensor
3. Monitoring of the Ethylene Gas with a Smart Electrochemical Sensor
4. Measurements and Results
4.1. Establishment of the Standard Curve for the Quantification of the Ethylene Gas Concentrations
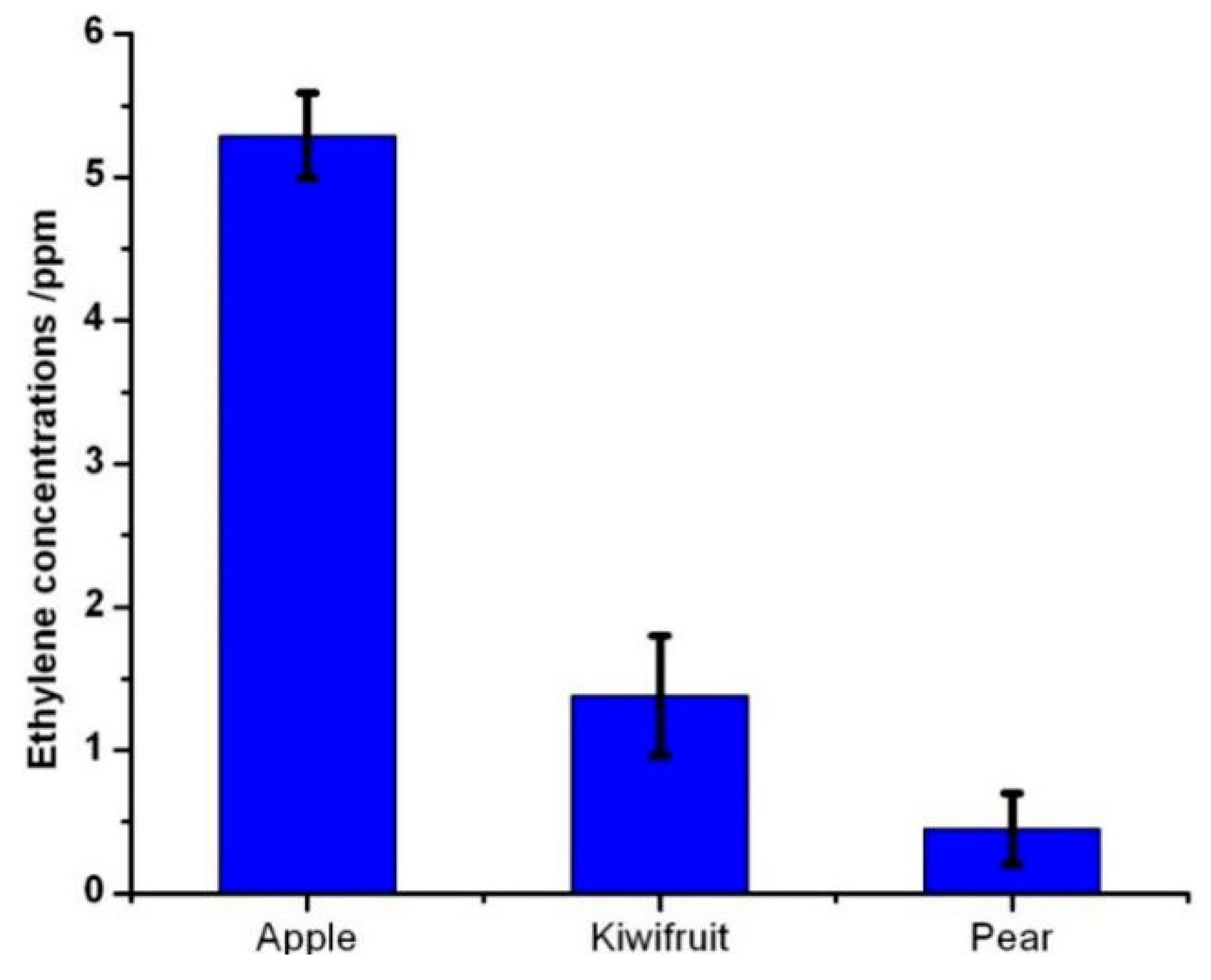
4.2. Measurement of the Ethylene Concentrations Released from the Fruits
4.3. Selectivity and Regeneration
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, G.; Fiori, G.; Noferini, M.; Ziosi, V. Internal fruit quality: How to influence it, how to define it. Acta Hortic. 2006, 712, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboni, T.; Cannac, M.; Chiaramonti, N. Effect of cold storage and ozone treatment on physicochemical parameters, soluble sugars and organic acids in Actinidia deliciosa. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 946–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, S.A.; Ismail, N.; Noor, M.A.M.; Ahmad, H. Some physical and chemical properties of ambarella (Spondias cytherea Sonn.) at three different stages of maturity. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2005, 18, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moing, A.; Renaud, C.; Gaudillere, M.; Raymond, P.; Roudeillac, P.; Denoyes, B. Biochemical Changes during Fruit Development of Four Strawberry Cultivars. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2001, 126, 394–403. [Google Scholar]
- Guadarrama, Á.; Andrade, S. Physical, Chemical and Biochemical Changes of Sweetsop (Annona squamosa L.) and Golden Apple (Spondias citherea Sonner) Fruits during Ripening. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. B 2012, 2, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Seager, N.G.; Haslemore, R.M. Rapid Estimation of Fruit Starch and Soluble Sugar Concentrations in Kiwifruit. HortScinece 1993, 28, 948–950. [Google Scholar]
- Nicola, B.M.; Beullens, K.; Bobelyn, E.; Peirs, A.; Saeys, W.; Theron, K.I.; Lammertyn, J. Nondestructive measurement of fruit and vegetable quality by means of NIR spectroscopy: A review. Postharvest. Biol. Technol. 2007, 46, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonora, E.; Stefanelli, D.; Costa, G. Nectarine fruit ripening and quality assessed using the index of absorbance difference. Int. J. Agron. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.B.; Golic, M.; Greensill, C.V. 2004 Sorting of fruit using near infrared spectroscopy: Application to a range of fruit and vegetables for soluble solids and dry matter content. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2004, 12, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, J.; Li, T.Q.; Wu, X.X.; Svanberg, S.; Svanberg, K. Studies of tropical fruit ripening using three different spectroscopic techniques. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burg, S.P.; Burg, E.A. Role of Ethylene in Fruit Ripening. Plant Physiol. 1962, 37, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannetta, P.P.M.; Laarhoven, L.J.; Medina-Escobar, N.; James, E.K.; McManus, M.T.; Davies, H.V.; Harren, F.J.M. Ethylene and carbon dioxide production by developing strawberries show a correlative pattern that is indicative of ripening climacteric fruit. Physiol. Plant. 2006, 127, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, C.S.; Giovannoni, J.J. Ethylene and Fruit Ripening. J. Plant Growth Reg. 2007, 26, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranamornkith, T.; East, A.; Heyes, J. Influence of exogenous ethylene during refrigerated storage on storability and quality of Actinidia chinensis (cv. Hort16A). Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2012, 64, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.T.; Martin, A.J.P. Gas-liquid partition chromatography: The separation and micro-estimaton of volatile fatty acids from formic acid to dodecanoic acid. Biochem. J. 1952, 50, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.H.; Cui, D.F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.L.; Cai, H.Y.; Li, H. Fabrication and characterization of MEMS-based gas chromatography column with embedded micro-posts for separation of environmental carcinogens. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1291, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dow, A.B.A.; Sklorz, A.; Lang, W. A microfluidic preconcentrator for enhanced monitoring of ethylene gas. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 167, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristescu, S.M.; Mandon, J.; Arslanov, D.; Pessemier, J.D.; Hermans, C.; Harren, F.J.M. Current methods for detecting ethylene in plants. Ann. Bot. 2013, 111, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sklorz, A.; Janen, S.; Lang, W. Application of a miniaturised packed gas chromatography column and a SnO2 gas detector for analysis of low molecular weight hydrocarbons with focus on ethylene detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 180, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, A.M.; Nijem, N.; Chabal, Y.J.; Balkus, K.J. Selective detection of olefinsusing a luminescent silver-functionalized metal organic framework, RPM3. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 174, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Choo, C.-K.; Sumi, S.; Kamitani, Y.; Fujii, T.; Satoh, K. C60/Zeolite semi-conductor electrode and the gas sensing. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 4155–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoli, A.; Steffens, C.; Paschoalin, R.T.; Correa, A.A.; Alves, W.F.; Leite, F.L.; Herrmann, P.S.P. Low-cost gas sensors produced by the graphite line-patterning technique applied to monitoring banana ripeness. Sensors 2011, 11, 6425–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brezmes, J.; Llobet, E.; Vilanova, X.; Saiz, G.; Correig, X. Fruit ripeness monitoring using an Electronic Nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 69, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobet, E.; Hines, E.L.; Gardner, J.W.; Franco, S. Non-destructive banana ripeness determination using aneural network-based electronic nose. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harren, F.J.M.; Bijnen, J.; Reuss, F.G.C.; Voesenek, L.A.C.J.; Blom, C.W.P.M. Sensitive intracavity photoacoustic measurements with a CO2 waveguide laser. Appl. Phys. B. 1990, 50, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gouw, J.A.; Hekkert, S.T.L.; Mellqvist, J.; Warneke, C.; Atlas, E.L.; Fehsenfeld, F.C.; Fried, A.; Frost, G.J.; Harren, F.J.M.; Holloway, J.S.; et al. Airborne measurements of ethene from industrial sources using laser photo-acoustic spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2437–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijnen, F.G.C.; Reuss, J.; Harrena, F.J.M. Geometrical optimization of a longitudinal resonant photoacoustic cell for sensitive and fast trace gas detection. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1996, 67, 2914–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevenbergen, M.A.G.; Wouters, D.; Dam, V.T.; Brongersma, S.H.; Crego-Calama, M. Electrochemical sensing of ethylene employing a thin ionic-liquid layer. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6300–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birgit, E.; Jan, M.S.; Timothy, M.S. Selective detection of ethylene gas using carbon nanotube-based devices: Utility in determination of fruit ripeness. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Der-tau, C.; Howard, H.C. On the conductivity of phosphoric acid electrolyte. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1989, 19, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, S.; Schmitt, K.; Blanke, M.; Bauersfeld, M.L.; Wlenstein, J.; Lang, W. Ethylene detection in fruit supply chains. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2014, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Chang, K.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Sun, X.; Lu, Z.; Sun, H.; Guo, Q.; et al. A Low Cost Compact Measurement System Constructed Using a Smart Electrochemical Sensor for the Real-Time Discrimination of Fruit Ripening. Sensors 2016, 16, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040501
Ma L, Wang L, Chen R, Chang K, Wang S, Hu X, Sun X, Lu Z, Sun H, Guo Q, et al. A Low Cost Compact Measurement System Constructed Using a Smart Electrochemical Sensor for the Real-Time Discrimination of Fruit Ripening. Sensors. 2016; 16(4):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040501
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Liuzheng, Ling Wang, Ruipeng Chen, Keke Chang, Shun Wang, Xinran Hu, Xiaohui Sun, Zhaohui Lu, Haifeng Sun, Qingqian Guo, and et al. 2016. "A Low Cost Compact Measurement System Constructed Using a Smart Electrochemical Sensor for the Real-Time Discrimination of Fruit Ripening" Sensors 16, no. 4: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040501
APA StyleMa, L., Wang, L., Chen, R., Chang, K., Wang, S., Hu, X., Sun, X., Lu, Z., Sun, H., Guo, Q., Jiang, M., & Hu, J. (2016). A Low Cost Compact Measurement System Constructed Using a Smart Electrochemical Sensor for the Real-Time Discrimination of Fruit Ripening. Sensors, 16(4), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040501




