Techniques for Interface Stress Measurements within Prosthetic Sockets of Transtibial Amputees: A Review of the Past 50 Years of Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Evolution of Transtibial Socket Designs
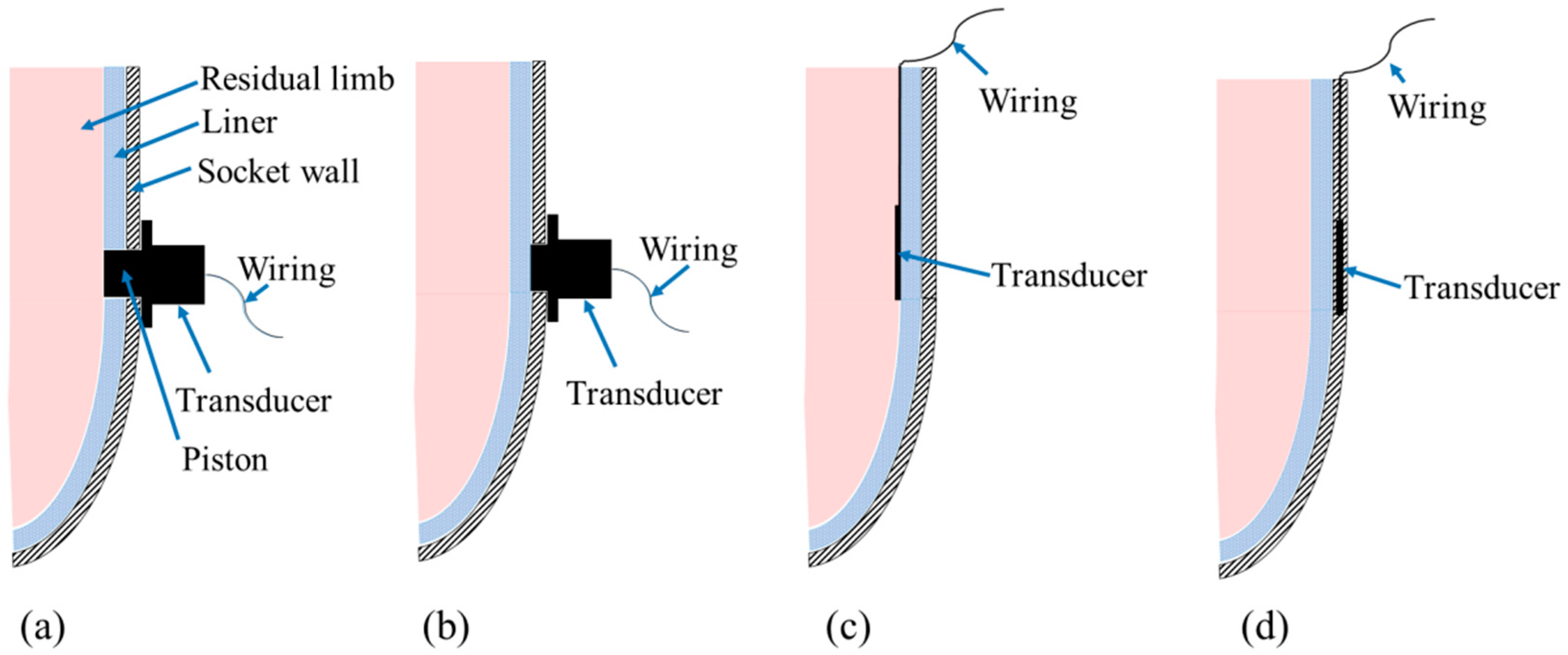
3. Transducer Mounting Techniques
3.1. Transducers Mounted on Socket Wall
3.2. Transducers Inserted in Socket
3.3. Transducers Embedded in Socket Wall
4. Types of Transducers
4.1. Strain Gauge-Based Transducers
4.2. Piezoresistive Transducers
4.3. Capacitive Transducers
4.4. Optical Sensors
5. Prosthetic Interface Stress Measurement in Different Socket Designs
5.1. PTB Sockets
5.2. TSB Sockets
5.3. PTB vs. TSB Sockets
6. Effect of Liner Materials and Suspension Systems
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PTB | Patellar Tendon Bearing |
| TSB | Total Tendon Bearing |
| PT | Patellar Tendon |
| SCSP | Supracondylar Suprapatellar |
| SC | Supracondylar |
| RP | Rapid Prototyping |
| CAD/CAM | Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing |
| 2/3D | Two/Three Dimensional |
| SG | Strain Gauge |
| F-Socket | Force-Socket |
| FOS | Fiber Optical Sensor |
| FBG | Fiber Bragg Grating |
| PFBG | Polymer Fiber Bragg Grating |
| EMI | Electromagnetic Interference |
| GF | Gauge Factor |
| FSR | Force Sensing Resistor |
| PCB | Printed Circuit Board |
| LED | Light Emitting Diode |
| PCast | Pressure Casting |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
References
- Laszczak, P.; Jiang, L.; Bader, D.L.; Moser, D.; Zahedi, S. Development and validation of a 3D-printed interfacial stress sensor for prosthetic applications. Med. Eng. Phys. 2015, 37, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirouzi, G.; Abu Osman, N.; Eshraghi, A.; Ali, S.; Gholizadeh, H.; Wan Abas, W. Review of the socket design and interface pressure measurement for transtibial prosthesis. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 849073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Fakih, E.; Osman, A.; Azuan, N.; Mahamd Adikan, F.; Eshraghi, A.; Jahanshahi, P. Development and validation of fiber bragg grating sensing pad for interface pressure measurements within prosthetic sockets. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, S.; Lee, P.V.; Goh, J.C. Engineering a trans-tibial prosthetic socket for the lower limb amputee. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2011, 40, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reiber, G.E. Who is at risk of limb loss and what to do about it? J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1994, 31, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dou, P.; Jia, X.; Suo, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, M. Pressure distribution at the stump/socket interface in transtibial amputees during walking on stairs, slope and non-flat road. Clin. Biomech. 2006, 21, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, J. Interface mechanics in external prosthetics: Review of interface stress measurement techniques. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1995, 33, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver-Thorn, M.B.; Steege, J.W.; Childress, D.S. A review of prosthetic interface stress investigations. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1996, 33, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Polliack, A.; Sieh, R.; Craig, D.; Landsberger, S.; McNeil, D.; Ayyappa, E. Scientific validation of two commercial pressure sensor systems for prosthetic socket fit. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2000, 24, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Turner-Smith, A.; Tanner, A.; Roberts, V. Clinical investigation of the pressure and shear stress on the trans-tibial stump with a prosthesis. Med. Eng. Phys. 1998, 20, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, B.J.; Sanders, J.E. Considerations for development of sensing and monitoring tools to facilitate treatment and care of persons with lower limb loss. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2014, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radcliffe, C.W.; Foort, J. The Patellar-Tendon-Bearing Below-Knee Prosthesis; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.L.; Chang, C.H.; Hsu, A.T.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, S.I.; Chang, G.L. A proposal for the pre-evaluation protocol of below-knee socket design-integration pain tolerance with finite element analysis. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2003, 26, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radcliffe, C.W. The biomechanics of below-knee prostheses in normal, level, bipedal walking. Artif. Limbs 1962, 6, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ng, P.; Lee, P.; Goh, J. Prosthetic sockets fabrication using rapid prototyping technology. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2002, 8, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Osman, N.A.; Spence, W.D.; Solomonidis, S.E.; Paul, J.P.; Weir, A.M. The patellar tendon bar! Is it a necessary feature? Med. Eng. Phys. 2010, 32, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, K.L.; Boone, D.A.; Laing, L.S.; Mathews, D.E.; Smith, D.G. Quantification of prosthetic outcomes: Elastomeric gel liner with locking pin suspension versus polyethylene foam liner with neoprene sleeve suspension. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2004, 41, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewell, P.; Noroozi, S.; Vinney, J.; Andrews, S. Developments in the trans-tibial prosthetic socket fitting process: A review of past and present research. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2000, 24, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaioannou, G.; Tsiokos, D.; Fiedler, G.; Mitrogiannis, C.; Avdeev, I.; Wood, J.; McKinney, R. Dynamic radiography imaging as a tool in the design and validation of a novel intelligent amputee socket. In Computational Vision and Medical Image Processing: Recent Trends; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 91–112. [Google Scholar]
- Breakey, J.W. Criteria for use of supracondylar and supracondylar suprapatellar suspension for below-knee prostheses. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1973, 27, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Taft, C. The patellar-tendon-supracondylar (pts) prosthesis: Report of a preliminary study. Inter-Clin. Inform. Bull. 1968, 7, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Girling, J.; Cummings, G. Artificial-limb fabrication without the use of commercially available components. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1972, 4, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chino, N.; Pearson, J.; Cockrell, J.; Mikishko, H.; Koepke, G. Negative pressures during swing phase in below-knee prostheses with rubber sleeve suspension. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1975, 56, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baars, E.; Geertzen, J. Literature review of the possible advantages of silicon liner socket use in trans-tibial prostheses. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2005, 29, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari, M.R.; Meier, M.R. Systematic review of effects of current transtibial prosthetic socket designs—Part 1: Qualitative outcomes. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2015, 52, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdik, J. The below knee suction socket. Orthop. Prosthet. Appl. J. 1955, 9, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Friel, K. Componentry for lower extremity prostheses. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2005, 13, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foort, J. The patellar-tendon-bearing prosthesis for below-knee amputees, a review of technique and criteria. Artif. Limbs 1965, 9, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yigiter, K.; Sener, G.; Bayar, K. Comparison of the effects of patellar tendon bearing and total surface bearing sockets on prosthetic fitting and rehabilitation. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2002, 26, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristinsson, Ö. The iceross concept: A discussion of a philosophy. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1993, 17, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fergason, J.; Smith, D.G. Socket considerations for the patient with a transtibial amputation. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1999, 361, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshraghi, A.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Gholizadeh, H.; Ali, S.; Sævarsson, S.K.; Abas, W.A.B.W. An experimental study of the interface pressure profile during level walking of a new suspension system for lower limb amputees. Clin. Biomech. 2013, 28, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, M.L. Below knee prosthetic socket designs and suspension systems. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 11, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eshraghi, A.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Gholizadeh, H.; Karimi, M.; Ali, S. Pistoning assessment in lower limb prosthetic sockets. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2012, 36, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirouzi, G.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Oshkour, A.A.; Ali, S.; Gholizadeh, H.; Wan Abas, W.A. Development of an air pneumatic suspension system for transtibial prostheses. Sensors 2014, 14, 16754–16765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshraghi, A.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Karimi, M.T.; Gholizadeh, H.; Ali, S.; Abas, W.A.B.W. Quantitative and qualitative comparison of a new prosthetic suspension system with two existing suspension systems for lower limb amputees. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.C.; Lee, P.V.S.; Tam, K.F.; Lye, S.L. Automation of prosthetic socket design and fabrication using computer aided design/computer aided engineering and rapid prototyping techniques. In Proceedings of the 1st National Symposium of Prosthetics and Orthotics, Singapore, 28 November 1998; pp. 19–22.
- Comotti, C.; Regazzoni, D.; Rizzi, C.; Vitali, A. Multi-material design and 3D printing method of lower limb prosthetic sockets. In Proceedings of the 3rd 2015 Workshop on ICTs for improving Patients Rehabilitation Research Techniques, Lisbon, Portugal, 1–2 October 2015; pp. 42–45.
- Faustini, M.C.; Neptune, R.R.; Crawford, R.H.; Rogers, W.E.; Bosker, G. An experimental and theoretical framework for manufacturing prosthetic sockets for transtibial amputees. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2006, 14, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, B.; Bosker, G.; Faustini, M.; Walden, G.; Neptune, R.R.; Crawford, R. Case report: Variably compliant transtibial prosthetic socket fabricated using solid freeform fabrication. J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2008, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengeh, D.M.; Herr, H. A variable-impedance prosthetic socket for a transtibial amputee designed from magnetic resonance imaging data. J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2013, 25, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appoldt, F.; Bennett, L.; Contini, R. Stump-socket pressure in lower extremity prostheses. J. Biomech. 1968, 1, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, S.; Sanders, J. Standing interface stresses as a predictor of walking interface stresses in the trans-tibial prosthesis. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2001, 25, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Goh, J.; Lee, P.; Chong, S. Stump/socket pressure profiles of the pressure cast prosthetic socket. Clin. Biomech. 2003, 18, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.E.; Daly, C.H. Measurement of stresses in three orthogonal directions at the residual limb-prosthetic socket interface. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 1993, 1, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.; Solomonidis, S.; Spence, W. Stump-socket interface pressure as an aid to socket design in prostheses for trans-femoral amputees—A preliminary study. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H J. Eng. Med. 1997, 211, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amali, R.; Noroozi, S.; Vinney, J.; Sewell, P.; Andrews, S. Predicting interfacial loads between the prosthetic socket and the residual limb for below-knee amputees—A case study. Strain 2006, 42, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahandi, R.; Sewell, P.; Noroozi, S.; Hewitt, M. Remote monitoring of lower-limb prosthetic socket fit using wireless technologies. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2012, 36, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewell, P.; Noroozi, S.; Vinney, J.; Amali, R.; Andrews, S. Static and dynamic pressure prediction for prosthetic socket fitting assessment utilising an inverse problem approach. Artif. Intell. Med. 2012, 54, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonck, W.A.; Cockrell, J.L.; Koepke, G.H. Effect of liner materials on interface pressures in below-knee prostheses. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1970, 51, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frieden, J.; Cugnoni, J.; Botsis, J.; Gmür, T.; Ćorić, D. High-speed internal strain measurements in composite structures under dynamic load using embedded fbg sensors. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaroni, C.; Saccomandi, P.; Schena, E. Medical smart textiles based on fiber optic technology: An overview. J. Funct. Biomater. 2015, 6, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, L. A fiber bragg grating quasi-distributed sensing network with a wavelength-tunable chaotic fiber laser. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. Open Access J. 2014, 2, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwana, M.I.; Redmond, S.J.; Lovell, N.H. A review of tactile sensing technologies with applications in biomedical engineering. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 179, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeggel, S.; Tosi, D.; Duraibabu, D.; Leen, G.; McGrath, D.; Lewis, E. Optical fibre pressure sensors in medical applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 17115–17148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ştefănescu, D.M. Wheatstone bridge-the basic circuit for strain gauge force transducers. In Handbook of Force Transducers; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 347–360. [Google Scholar]
- Rae, J.W.; Cockrell, J.L. Interface pressure and stress distribution in prosthetic fitting. Bull. Prosthet. Res. 1971, 10, 64–111. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.; Porter, D.; Roberts, V.; Regan, J. Triaxial force transducer for investigating stresses at the stump/socket interface. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1992, 30, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appoldt, F.A.; Bennett, L.; Contini, R. Tangential pressure measurements in above-knee suction sockets. Bull. Prosthet. Res. 1970, 10, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Almassri, A.M.; Wan Hasan, W.; Ahmad, S.; Ishak, A.; Ghazali, A.; Talib, D.; Wada, C. Pressure sensor: State of the art, design, and application for robotic hand. J. Sens. 2015, 2015, 846487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, J.S.; Evans, K.R.; Hebert, J.S.; Marasco, P.D.; Carey, J.P. The effect of biomechanical variables on force sensitive resistor error: Implications for calibration and improved accuracy. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.-P.; Berglund, L.J.; An, K.-N. Validation of f-scan pressure sensor system: A technical note. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1998, 35, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Engsberg, J.; Springer, J.; Harder, J. Quantifying interface pressures in below-knee-amputee sockets. Assoc. Child. Prosth. Orthot. Clin. 1992, 27, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Houston, V.; Mason, C.; LaBlanc, K.; Beatties, A.; Garbarini, M.; Lorenze, E. Preliminary results with the DVA-tekscan BK prosthetic socket/residual limb stress measurement system. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Meeting American Academy of Orthotist and Prosthetist, Nashville, TN, USA, 23–26 March 1994; pp. 8–9.
- Buis, A.; Convery, P. Calibration problems encountered while monitoring stump/socket interface pressures with force sensing resistors: Techniques adopted to minimise inaccuracies. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1997, 21, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hachisuka, K.; Takahashi, M.; Ogata, H.; Ohmine, S.; Shitama, H.; Shinkoda, K. Properties of the flexible pressure sensor under laboratory conditions simulating the internal environment of the total surface bearing socket. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1998, 22, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Polliack, A.; Craig, D.; Sieh, R.; Landsberger, S.; McNeal, D. Laboratory and clinical tests of a prototype pressure sensor for clinical assessment of prosthetic socket fit. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2002, 26, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruda, E.M.; Sanchez, O.F.A.; Mejia, J.C.H.; Gomez, S.J.; Flautero, O.I.C. Design process of mechatronic device for measuring the stump stresses on a lower limb amputee. In Proceedings of the 22nd Intl Congress of Mechanical Engineering (COBEM 2013), Ribeirão Preto, Brazil, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 4620–4628.
- Lai, C.H.; Li-Tsang, C.W. Validation of the pliance x system in measuring interface pressure generated by pressure garment. Burns 2009, 35, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.I.; Alimusaj, M.; Fradet, L.; Siegel, J.; Braatz, F. Pressure characteristics at the stump/socket interface in transtibial amputees using an adaptive prosthetic foot. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari, M.R.; Tafti, N.; Aminian, G. Socket interface pressure and amputee reported outcomes for comfortable and uncomfortable conditions of patellar tendon bearing socket: A pilot study. Assist. Technol. 2015, 27, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwana, M.I.; Shashank, A.; Redmond, S.J.; Lovell, N.H. Characterization of a capacitive tactile shear sensor for application in robotic and upper limb prostheses. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 165, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, R., 3rd; Meeks, E., Jr.; Herman, R. Stump-socket fit of below-knee prostheses: Comparison of three methods of measurement. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1973, 54, 553–558. [Google Scholar]
- Sundara-Rajan, K.; Bestick, A.; Rowe, G.; Klute, G.; Ledoux, W.; Wang, H.; Mamishev, A. An interfacial stress sensor for biomechanical applications. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 085701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fakih, E.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Mahamd Adikan, F.R. The use of fiber bragg grating sensors in biomechanics and rehabilitation applications: The state-of-the-art and ongoing research topics. Sensors 2012, 12, 12890–12926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rossi, S.; Lenzi, T.; Vitiello, N.; Donati, M.; Persichetti, A.; Giovacchini, F.; Vecchi, F.; Carrozza, M.C. Development of an in-shoe pressure-sensitive device for gait analysis. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBC, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 5637–5640.
- Lincoln, L.S.; Quigley, M.; Rohrer, B.; Salisbury, C.; Wheeler, J. An optical 3d force sensor for biomedical devices. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Rome, Itally, 24–27 June 2012; pp. 1500–1505.
- Bae, J.; An, T.; Kim, Y.; Ryu, C. Analysis of digital load cell using 2.4 ghz band’s zig-bee. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, ICIEA, Singapore, 3–5 June 2008; pp. 1358–1361.
- Abu Osman, N.A.; Spence, W.D.; Solomonidis, S.E.; Paul, J.P.; Weir, A.M. Transducers for the determination of the pressure and shear stress distribution at the stump—Socket interface of trans-tibial amputees. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2010, 224, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.; Zachariah, S.; Jacobsen, A.; Fergason, J. Changes in interface pressures and shear stresses over time on trans-tibial amputee subjects ambulating with prosthetic limbs: Comparison of diurnal and six-month differences. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, J.; Fergason, J.; Zachariah, S.; Jacobsen, A. Case study: Interface pressure and shear stress changes with amputee weight loss: Case studies from two trans-tibial amputee subjects. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2002, 26, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, A.F.; Zhang, M.; Boone, D.A. State-of-the-art research in lower-limb prosthetic biomechanics-socket interface. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2001, 38, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goh, J.; Lee, P.; Chong, S. Static and dynamic pressure profiles of a patellar-tendon-bearing (PTB) socket. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H J. Eng. Med. 2003, 217, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossard, L.; Beck, J.; Dillon, M.; Evans, J. Development and preliminary testing of a device for the direct measurement of forces and moments in the prosthetic limb of transfemoral amputees during activities of daily living. J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2003, 15, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollinger, A.; Wanderley, M.M. Evaluation of commercial force-sensing resistors. In Proceedings of the International Conference on New Interfaces for Musical Expression, Paris, France, 4–8 June 2006.
- Kane, B.J.; Cutkosky, M.R.; Kovacs, G.T. A traction stress sensor array for use in high-resolution robotic tactile imaging. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2000, 9, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.-T.; Mallon, J.R., Jr.; Rastegar, A.J.; Pruitt, B.L. Review: Semiconductor piezoresistance for microsystems. IEEE Proc. 2009, 97, 513–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccomandi, P.; Schena, E.; Oddo, C.M.; Zollo, L.; Silvestri, S.; Guglielmelli, E. Microfabricated tactile sensors for biomedical applications: A review. Biosensors 2014, 4, 422–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchi, F.; Freschi, C.; Micera, S.; Sabatini, A.M.; Dario, P.; Sacchetti, R. Experimental evaluation of two commercial force sensors for applications in biomechanics and motor control. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual Conference of the International Functional Electrical Stimulation Society, Aalborg, Denmark, 18–20 June 2000; pp. 44–54.
- Zhang, H.; So, E. Hybrid resistive tactile sensing. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern. 2002, 32, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shem, K.L.; Breakey, J.W.; Werner, P.C. Pressures at the residual limb-socket interface in transtibial amputees with thigh lacer-side joints. J. Prosthet. Orthot. 1998, 10, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Eshraghi, A.; Gholizadeh, H.; Abas, W.A.B.B.W. Interface pressure in transtibial socket during ascent and descent on stairs and its effect on patient satisfaction. Clin. Biomech. 2013, 28, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolsley, C.; Hill, P. Review of interface pressure measurement to establish a protocol for their use in the assessment of patient support surfaces. J. Tissue Viability 2000, 10, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.-X.; Huang, Q.-A.; Qin, M.; Zhou, W. A novel capacitive pressure sensor based on sandwich structures. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2005, 14, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razian, M.; Pepper, M.G. Design, development, and characteristics of an in-shoe triaxial pressure measurement transducer utilizing a single element of piezoelectric copolymer film. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2003, 11, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugenholtz, P.G.; Gamble, W.J.; Monroe, G.R.; Polanyi, M. The use of fiberoptics in clinical cardiac catheterization ii. In vivo dye-dilution curves. Circulation 1965, 31, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roriz, P.; Frazão, O.; Lobo-Ribeiro, A.B.; Santos, J.L.; Simões, J.A. Review of fiber-optic pressure sensors for biomedical and biomechanical applications. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 050903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poeggel, S.; Duraibabu, D.; Kalli, K.; Leen, G.; Dooly, G.; Lewis, E.; Kelly, J.; Munroe, M. Recent improvement of medical optical fibre pressure and temperature sensors. Biosensors 2015, 5, 432–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Y.-J.; Webb, D.J.; Jackson, D.A.; Zhang, L.; Bennion, I. Optical in-fiber bragg grating sensor systems for medical applications. J. Biomed. Opt. 1998, 3, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo-Dinh, T. Biomedical Photonics Handbook: Biomedical Diagnostics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Keiser, G.; Xiong, F.; Cui, Y.; Shum, P.P. Review of diverse optical fibers used in biomedical research and clinical practice. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 080902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, V.; Singh, N.; Tiwari, U.; Kapur, P. Fiber grating sensors in medicine: Current and emerging applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 167, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.; Gomes, J.; Carmo, J.; Silva, A.; Correia, J. Low-cost/high-reproducibility flexible sensor based on photonics for strain measuring. Opt. Laser Technol. 2014, 56, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresvig, T.; Ludvigsen, P.; Steen, H.; Reikerås, O. Fibre optic bragg grating sensors: An alternative method to strain gauges for measuring deformation in bone. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Zhou, X. Pressure sensor based on the fiber-optic extrinsic fabry-perot interferometer. Photon. Sens. 2011, 1, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Iordachita, I.I.; He, X.; Taylor, R.H.; Kang, J.U. Miniature fiber-optic force sensor based on low-coherence fabry-pérot interferometry for vitreoretinal microsurgery. Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 1062–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelt, H.; Elsmann, T.; Habisreuther, T.; Schuster, K.; Rothhardt, M. Optical bragg grating sensor fibers for ultra-high temperature applications. In Proceedings of the 5th Asia Pacific Optical Sensors Conference, Jeju, Korea, 20–22 May 2015.
- Gao, R.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D. Filmed extrinsic fabry–perot interferometric sensors for the measurement of arbitrary refractive index of liquid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar Zawawi, M.; O’Keffe, S.; Lewis, E. Intensity-modulated fiber optic sensor for health monitoring applications: A comparative review. Sens. Rev. 2013, 33, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Zbyszewski, D.; Schaeffter, T.; Razavi, R.; Seneviratne, L.D.; Althoefer, K. Mri-compatible fiber-optic force sensors for catheterization procedures. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 1598–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roriz, P.; Carvalho, L.; Frazão, O.; Santos, J.L.; Simões, J.A. From conventional sensors to fibre optic sensors for strain and force measurements in biomechanics applications: A review. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sante, R. Fibre optic sensors for structural health monitoring of aircraft composite structures: Recent advances and applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 18666–18713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihailov, S.J. Fiber bragg grating sensors for harsh environments. Sensors 2012, 12, 1898–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udd, E.; Spillman, W.B., Jr. Fiber Optic Sensors: An Introduction for Engineers and Scientists; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Abushagur, A.A.; Arsad, N.; Reaz, M.I.; Bakar, A. Advances in bio-tactile sensors for minimally invasive surgery using the fibre bragg grating force sensor technique: A survey. Sensors 2014, 14, 6633–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quandt, B.M.; Scherer, L.J.; Boesel, L.F.; Wolf, M.; Bona, G.L.; Rossi, R.M. Body-monitoring and health supervision by means of optical fiber-based sensing systems in medical textiles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 330–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murukeshan, V.; Chan, P.; Ong, L.; Seah, L. Cure monitoring of smart composites using fiber bragg grating based embedded sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2000, 79, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellos, G.T.; Papaioannou, G.; Tsiokos, D.; Mitrogiannis, C.; Nianios, G.; Pleros, N. Two dimensional polymer-embedded quasi-distributed fbg pressure sensor for biomedical applications. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellos, G.T.; Tsiokos, D.; Pleros, N.; Papaioannou, G.; Childs, P.; Pissadakis, S. Enhanced durability fbg-based sensor pads for biomedical applications as human-machine interface surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Workshop on Biophotonics, Parma, Italy, 8–10 June 2011.
- Tsiokos, D.; Papaioannou, G.; Kanellos, G.T.; Pissadakis, S. Fiber Optic-Based Pressure Sensing Surface for Skin Health Management in Prosthetic and Rehabilitation Interventions; INTECH Open Access Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Fakih, E.A.; Osman, N.A.A.; Eshraghi, A.; Adikan, F.R.M. The capability of fiber bragg grating sensors to measure amputees’ trans-tibial stump/socket interface pressures. Sensors 2013, 13, 10348–10357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Tao, X.M.; Zhang, H.P.; Zhu, B. Soft fiber optic sensors for precision measurement of shear stress and pressure. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 1478–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rossi, S.M.M.; Vitiello, N.; Lenzi, T.; Ronsse, R.; Koopman, B.; Persichetti, A.; Vecchi, F.; Ijspeert, A.J.; Van der Kooij, H.; Carrozza, M.C. Sensing pressure distribution on a lower-limb exoskeleton physical human-machine interface. Sensors 2011, 11, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, M.; Vitiello, N.; De Rossi, S.M.M.; Lenzi, T.; Crea, S.; Persichetti, A.; Giovacchini, F.; Koopman, B.; Podobnik, J.; Munih, M. A flexible sensor technology for the distributed measurement of interaction pressure. Sensors 2013, 13, 1021–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missinne, J.; Bosnian, E.; Van Hoe, B.; Van Steenberge, G.; Van Daele, P.; Vanfleteren, J. Embedded flexible optical shear sensor. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Sensors, Kona, HI, USA, 1–4 November 2010; pp. 987–990.
- Wheeler, J. A Better Prosthesis: Sandia Invents Sensor to Learn About Fit; System to Make Fit Better. Available online: https://share.sandia.gov/news/resources/news_releases/prosthesic_sensor (accessed on 31 December 2015).
- Yousef, H.; Boukallel, M.; Althoefer, K. Tactile sensing for dexterous in-hand manipulation in robotics—A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 167, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.R.; Holmgren, G.; March, L.; Oberg, K. Pressures in critical regions of the below-knee patellar-tendon-bearing prosthesis. Bull. Prosthet. Res. 1973, 10, 52–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanders, J.; Boone, D.; Daly, C. The residual limb/prosthetic socket interface normal stress and shear stress. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual RESNA Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 15–20 June 1990; pp. 234–235.
- Sanders, J.; Daly, C.; Burgess, E. Clinical measurement of normal and shear stresses on a trans-tibial stump: Characteristics of wave-form shapes during walking. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1993, 17, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, J.E.; Lain, D.; Dralle, A.J.; Okumura, R. Interface pressures and shear stresses at thirteen socket sites on two persons with transtibial amputation. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1997, 34, 19–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goh, J.C.H.; Lee, P.V.S.; Chong, S.Y. Comparative study between patellar-tendon-bearing and pressure cast prosthetic sockets. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2004, 41, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Convery, P.; Buis, A. Conventional patellar-tendon-bearing (PTB) socket/stump interface dynamic pressure distributions recorded during the prosthetic stance phase of gait of a transtibial amputee. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1998, 22, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Convery, P.; Buis, A. Socket/stump interface dynamic pressure distributions recorded during the prosthetic stance phase of gait of a trans-tibial amputee wearing a hydrocast socket. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1999, 23, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dumbleton, T.; Buis, A.W.; McFadyen, A.; McHugh, B.F.; McKay, G.; Murray, K.D.; Sexton, S. Dynamic interface pressure distributions of two transtibial prosthetic socket concepts. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2009, 46, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Osman, N.A.A.; Mortaza, N.; Eshraghi, A.; Gholizadeh, H.; Abas, W.A.B.B.W. Clinical investigation of the interface pressure in the trans-tibial socket with dermo and seal-in x5 liner during walking and their effect on patient satisfaction. Clin. Biomech. 2012, 27, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Arifin, N.; Gholizadeh, H.; Abd Razak, N.A.; Wan Abas, W.A.B. Comparative study between dermo, pelite, and seal-in x5 liners: Effect on patient’s satisfaction and perceived problems. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Razak, A.; Hussain, S.; Abas, W. The effect of dermo and seal-in x5 prosthetic liners on pressure distributions and reported satisfaction during ramp ambulation in persons with transtibial limb loss. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 51, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Eshraghi, A.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Gholizadeh, H.; Ahmadian, J.; Rahmati, B.; Abas, W.A.B.W. Development and evaluation of new coupling system for lower limb prostheses with acoustic alarm system. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshraghi, A.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Gholizadeh, H.; Ali, S.; Abas, W.A.B.W. Interface stress in socket/residual limb with transtibial prosthetic suspension systems during locomotion on slopes and stairs. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 94, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Suo, S.; Meng, F.; Wang, R. Effects of alignment on interface pressure for transtibial amputee during walking. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2008, 3, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, J.E.; Daly, C.H. Normal and shear interface stresses in lower-limb prosthetics. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Seattle, WA, USA, 9–12 November 1989; pp. 1443–1444.
- Beil, T.L.; Street, G.M. Comparison of interface pressures with pin and suction suspension systems. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2004, 41, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klute, G.K.; Glaister, B.C.; Berge, J.S. Prosthetic liners for lower limb amputees: A review of the literature. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2010, 34, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek, N.L.; Marks, M.B.; Marshall, S.C.; Chardon, J.P. Dermatologic conditions associated with use of a lower-extremity prosthesis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emrich, R.; Slater, K. Comparative analysis of below-knee prosthetic socket liner materials. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 1998, 22, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, A.; Morrison, J. Polyurethane gel liner usage in the oxford prosthetic service. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2001, 25, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Weg, F.; Van der Windt, D. A questionnaire survey of the effect of different interface types on patient satisfaction and perceived problems among trans-tibial amputees. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2005, 29, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane, H.; Orsi, K.; Reilly, P. Lower limb amputation part 3: Prosthetics-a 10 year literature review. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2001, 25, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholizadeh, H.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Eshraghi, A.; Ali, S.; Razak, N.A. Transtibial prosthesis suspension systems: Systematic review of literature. Clin. Biomech. 2014, 29, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Naqshbandi, M.M.; Eshraghi, A.; Kamyab, M.; Gholizadeh, H. Qualitative study of prosthetic suspension systems on transtibial amputees’ satisfaction and perceived problems with their prosthetic devices. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 1919–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonstra, A.; Van Duin, W.; Eisma, W. Silicone suction socket (3S) versus supracondylar PTB prosthesis with pelite liner: Transtibial amputees’ preferences. J. Prosthet. Orthot. 1996, 8, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.E.; Daly, C.H.; Cummings, W.R.; Reed, R.D.; Robert J MARKS, I. A measurement device to assist amputee prothetic fitting. J. Clin. Eng. 1994, 19, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.E.; Greve, J.M.; Mitchell, S.B.; Zachariah, S.G. Material properties of commonly-used interface materials and their static coefficients of friction with skin and socks. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1998, 35, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanders, J.E.; Nicholson, B.S.; Zachariah, S.G.; Cassisi, D.V. Testing of elastomeric liners used in limb prosthetics: Classification of 15 products by mechanical performance. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2004, 41, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutwell, E.; Stine, R.; Tucker, K. Effect of prosthetic gel liner thickness on gait biomechanics and pressure distribution within the transtibial socket. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2012, 49, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholizadeh, H.; Osman, N.A.A.; Kamyab, M.; Eshraghi, A.; Lúvíksdóttir, Á.G.; Abas, W.A.B.W. Clinical evaluation of two prosthetic suspension systems in a bilateral transtibial amputee. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Transducer Type | Ref. | Structure and Mounting Technique | Parameters to Measure | Merits | Demerits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diaphragm SG (Kulite sensor) | [50,57] |
|
|
|
|
| Piston-type SG | [42,45,58,59] |
|
|
|
|
| Single-point FSRs | [60,61] |
|
|
|
|
| Array of Piezoresistive | [60,62,63,64,65,66,67] |
|
|
|
|
| Capacitive (Single sensing element) | [68,69,70,71,72,73] |
|
|
|
|
| “Novel” Capacitive (Array) | [67,74] |
|
|
|
|
| 3-D printed Capacitive | [1] |
|
|
|
|
| Fibre-optics | [3,75] |
|
|
|
|
| Optoelectronic | [76,77] |
|
|
|
|
| Authors | Year | Objectives | Sensor Type | Mounting Method | Socket Type | Sites of Interest | No. of Subjects | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rae and Cockrell | 1971 | To compare the differences in interface peak pressures in sockets with no liner, sponge liner, and silicone liner at that time. | Diaphragm SG (Kulite) | Inserted in socket | PTB | Condylar flairs (MTC, LTC), PT, distal anterior region (Kick-point, KP) | - | [57] |
| Pearson et al. | 1973 | To compare interface pressures during standing and walking. | Diaphragm SG (Kulite) | Inserted in socket | PTB | PT, KP, MTC, and LTC | 10 | [128] |
| Chino et al. | 1975 | To investigate the effect of various suspension systems on the suction pressure between the apex of the stump and the socket during the swing phase. | Diaphragm SG (Kulite) | Inserted in socket | PTB | KP | 8 | [23] |
| Sanders et al. | 1990 | To design the instrumentation capable of measuring normal and shear stresses simultaneously in prosthetic sockets | Piston-type SG | Mounted on socket wall | - | - | - | [129] |
| Sanders et al. | 1993 | To report the characteristics of interface stress wave-form shapes and their effects on stump tissue mechanics | Piston-type SG | Mounted on socket wall | PTB | At discrete points at all socket aspects | 3 | [130] |
| Sanders et al. | 1997 | To investigate the magnitudes of maximal stance phase pressure, maximal shear stress, shear angle and changes in pressures for each of the 13 sites in sockets of two amputees. | Piston-type SG | Mounted on socket wall | PTB | 13 sites (anterior, lateral, and posterior) | 2 | [131] |
| Goh et al. | 2003 | To investigate pressure distribution in sockets fabricated using pressure casting (PCast) technique. | Piston-type SG | Mounted on socket wall | Hydrocast socket | 16 Discrete points | 5 | [44] |
| Goh et al. | 2004 | To compare pressure profile of PCast and PTB sockets | Piston-type SG | Mounted on socket wall | PTB & Hydrocast | 16 Discrete points | 4 | [132] |
| Abu Osman et al. | 2010 | To investigate the effect of varying the load (through the depth of indentation) on the patellar tendon bar on the pattern of pressure distribution at the stump–socket interface and if there is any correlation between varying the load on the patellar tendon and the pressure distribution at other sites in the socket | Piston-type SG | Mounted on socket wall | PTB | 16 sites including those in high curvature regions | 10 | [79] |
| Meier et al. | 1973 | To investigate pressures on the residual limbs of 8 transtibial amputees. | Capacitive | Inserted in socket | PTB | 5 sites | 8 | [73] |
| Dou et al. | 2006 | To measure pressures at five interesting sites of only one below-knee amputee socket during walking on stairs, flat, and non-flat roads | Capacitive | Inserted in socket | 5 sites | 1 | [6] | |
| Convery & Buis | 1998, 1999 | To compare the dynamic residual limb-socket interface pressure distributions in PTB and Hydrocast (TSB) sockets | Piezoresistive (F-Socket) | Attached to inner socket wall | PTB & Hydrocast | Overall impression of the interface | 1 | [133,134] |
| Dumbleton et al. | 2009 | To compare the dynamic interface pressure distribution and patient satisfaction between PTB sockets with Pelite liners and hydrostatic sockets with silicone liners | Piezoresistive (F-Socket) | Attached to inner socket wall | PTB & Hydrocast | Overall impression of the interface | 48 | [135] |
| Ali et al. | 2012 | To clinically investigate the interface pressure in TSB sockets with Dermo and Seal-In X5 liners during normal walking on level ground and their effect on patient satisfaction | Piezoresistive (F-Socket) | Attached in between the stump and liner | TSB | Overall impression of the interface | 9 | [136] |
| Ali et al. | 2014 | To compare the patients’ satisfaction and identify the perceived problems with the subjects’ prostheses while using three different suspension systems: Pelite, Dermo liner with shuttle lock, and Seal-In X5 liner | Piezoresistive (F-Socket) | Attached in between the stump and liner | TSB | Overall impression of the interface | 30 | [137] |
| Ali et al. | 2013, 2015 | To compare the interface pressure between the Dermo and Seal-In X5 liners during more amputees’ daily activities such as stair ascent and decent and ramp negotiation | Piezoresistive (F-Socket) | Attached in between the stump and liner | TSB | Overall impression of the interface | 10 | [92,138] |
| Eshraghi et al. | 2013 | To evaluate a patented magnetic-based suspension system in-situ with regard to the pistoning during walking | Piezoresistive (F-Socket) | Attached in between the stump and liner | TSB | Overall impression of the interface | - | [139] |
| Eshraghi et al. | 2013 | To experimentally investigate the interface pressures with the magnetic suspension system compared to the other two commonly used suspension systems: pin/lock and seal-in | Piezoresistive (F-Socket) | Attached in between the stump and liner | TSB | Overall impression of the interface | 12 | [32] |
| Eshraghi et al. | 2015 | To compare the effect of these three suspension systems on the interface pressures inside transtibial sockets during locomotion on stairs and ramps | Piezoresistive (F-Socket) | Attached in between the stump and liner | TSB | Overall impression of the interface | - | [140] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Fakih, E.A.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Mahmad Adikan, F.R. Techniques for Interface Stress Measurements within Prosthetic Sockets of Transtibial Amputees: A Review of the Past 50 Years of Research. Sensors 2016, 16, 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071119
Al-Fakih EA, Abu Osman NA, Mahmad Adikan FR. Techniques for Interface Stress Measurements within Prosthetic Sockets of Transtibial Amputees: A Review of the Past 50 Years of Research. Sensors. 2016; 16(7):1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071119
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Fakih, Ebrahim A., Noor Azuan Abu Osman, and Faisal Rafiq Mahmad Adikan. 2016. "Techniques for Interface Stress Measurements within Prosthetic Sockets of Transtibial Amputees: A Review of the Past 50 Years of Research" Sensors 16, no. 7: 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071119
APA StyleAl-Fakih, E. A., Abu Osman, N. A., & Mahmad Adikan, F. R. (2016). Techniques for Interface Stress Measurements within Prosthetic Sockets of Transtibial Amputees: A Review of the Past 50 Years of Research. Sensors, 16(7), 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071119






