Improved Durability and Sensitivity of Bitterness-Sensing Membrane for Medicines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Sensor Electrode
2.3. Measurement System
2.4. Accelerated Deterioration Process
2.5. Effect of Membrane Components on the Deterioration Rate
2.6. Quantitative Analysis by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
2.7. Component Detection by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
2.8. Measurement of the Amount of Adsorbed Quinine Hydrochloride
2.9. Measurement of Surface Contact Angle
2.10. Fabrication of a Durable Bitterness Sensor
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Conditions of the Accelerated Deterioration Process
3.2. Relationship between Deterioration Rate and Lipid Mass Ratio
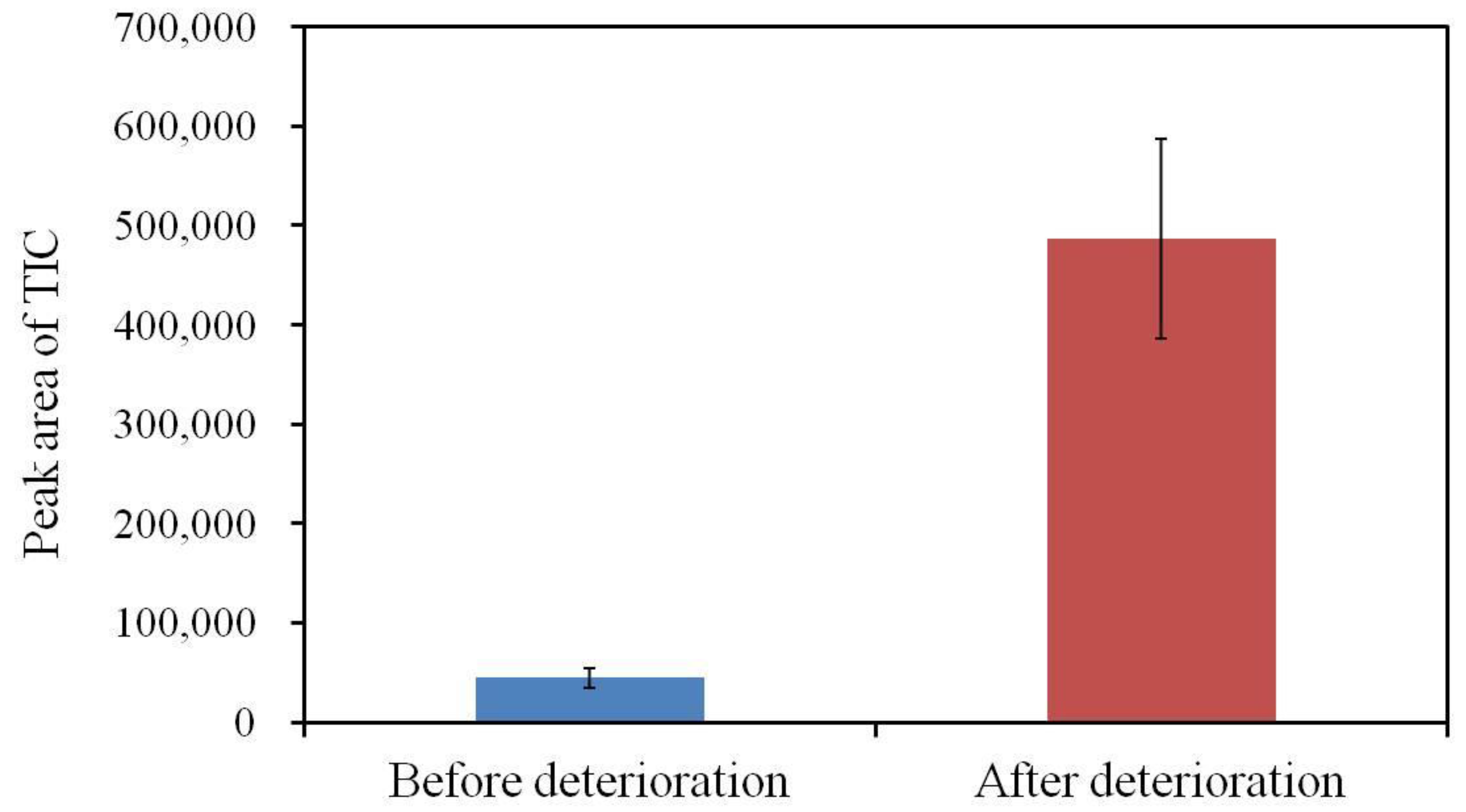
3.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis Results
3.4. GC-MS Analysis of the Membrane Components
3.5. Amount of Adsorbed Quinine Hydrochloride
3.6. Reference Potential and Contact Angle of Lipid Polymer Membrane
3.7. BT0 Sensor with Improved Durability and Sensitivity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawano, Y.; Ito, A.; Sasatsu, M.; Machida, Y. Preparation of orally disintegrating tablets with taste-masking function: Masking effect in granules prepared with correctives using the dry granulation method and evaluation of tablets prepared using the taste-masked granules. Yakugaku Zasshi 2010, 130, 81–86. (in Japanese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, V.; Kataria, M.; Kukkar, V.; Saharan, V. The latest trends in the taste assessment of pharmaceuticals. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R.; Tudu, B.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Bhattacharyya, N. A review on combined odor and taste sensor systems. J. Food Eng. 2016, 190, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, Y.; Toko, K. Electronic tongues—A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3001–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmanov, A.A.; Beauchamp, G.K. Taste receptor genes. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2007, 27, 389–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winquist, F. Voltammetric electronic tongues—Basic principles and applications. Microchim. Acta 2008, 163, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facure, M.H.M.; Mercante, L.A.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Correa, D.S. Detection of trace levels of organophosphate pesticides using an electronic tongue based on graphene hybrid nanocomposites. Talanta 2017, 167, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciosek, P.; Wroblewski, W. Sensor array for liquid sensing-electronic tongue systems. Analyst 2007, 132, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, I.; Rodrigues, N.; Dias, L.G.; Veloso, A.C.A.; Pereira, J.A.; Drunkler, D.A.; Peres, A.M. Sensory classification of table olives using an electronic tongue: Analysis of aqueous pastes and brines. Talanta 2017, 162, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Citterio, D.; Suzuki, K. Smart taste sensors. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3965–3972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nuñez, L.; Cetó, X.; Pividori, M.I.; Zanoni, M.V.B.; del Valle, M. Development and application of an electronic tongue for detection and monitoring of nitrate, nitrite and ammonium levels in waters. Microchem. J. 2013, 110, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daikuzonoa, C.M.; Dantas, C.A.R.; Volpati, D.; Constantino, C.J.L.; Piazzetta, M.H.O.; Gobbi, A.L.; Taylor, D.M.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Riul, A., Jr. Microfluidic electronic tongue. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.S.; Kwon, O.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, U.K.; Jang, J.; Park, T.H. Human Taste Receptor-Functionalized Field Effect Transistor as a Human-Like Nanobioelectronic Tongue. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.; Sun, Q.; Su, K.; Wan, H.; Li, H.; Xu, N.; Sun, F.; Zhuang, L.; Hu, N.; Wang, P. Recent achievements in electronic tongue and bioelectronic tongue as taste sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toko, K.; Hara, D.; Tahara, Y.; Yasuura, M.; Ikezaki, H. Relationship between the amount of bitter substances adsorbed onto lipid/polymer membrane and the electrical response of taste sensors. Sensors 2014, 14, 16274–16286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikezaki, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Toukubo, R.; Naito, Y.; Taniguchi, A.; Toko, K. Techniques to control sensitivity and selectivity of multichannel taste sensor using lipid membranes. Proc. Transducers 1999, 99, 1634–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Habara, M.; Ikezaki, H.; Toko, K. Selectivity control in a sweetness sensor using lipid/polymer membranes. Sens. Mater. 2005, 17, 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Del Valle, M. Electronic tongues employing electrochemical sensors. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1539–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Habara, M.; Ikezaki, H.; Chen, R.G.; Naito, Y.; Toko, K. Advanced taste sensors based on artificial lipids with global selectivity to basic taste qualities and high correlation to sensory scores. Sensors 2010, 10, 3411–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Fu, S.; Shi, Y.; Men, H. Automatic evaluation of sensory information for beer at a fuzzy level using electronic tongue and electronic nose. Sens. Mater. 2016, 28, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Dai, L.; Kang, B.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Gui, X.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Traditional human taste panel and taste sensors methods for bitter taste masking research on combined bitterness suppressants of berberine hydrochloride. Sens. Mater. 2017, 29, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Hamada, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ikezaki, H.; Toko, K. Development of an artificial lipid-based membrane sensor with high selectivity and sensitivity to the bitterness of drugs and with high correlation with sensory score. IEEJ Trans. 2009, 4, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akitomi, H.; Tahara, Y.; Yasuura, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ikezaki, H.; Toko, K. Quantification of tastes of amino acids using taste sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 179, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Wada, K.; Yoshida, M.; Hazakawa, K.; Abe, K.; Chen, R.G.; Habara, M.; Ikezaki, H.; Uchida, T. Quantitative evaluation of bitterness of H1-receptor antagonists and masking effect of acesulfame potassium, an artificial sweetener, using a taste sensor. Sens. Mater. 2013, 25, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, S.; Toko, K.; Wada, K.; Ohki, T. Quantification of suppression of bitterness using an electronic tongue. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 12, 2042–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Onitake, H.; Haraguchi, T.; Tahara, Y.; Yatabe, R.; Yoshida, M.; Uchida, T.; Ikezaki, H.; Toko, K. Quantitative prediction of bitterness masking effect of high-potency sweeteners using taste sensor Voltammetric electronic tongues—Basic principles and applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuura, M.; Okazaki, H.; Tahara, Y.; Ikezaki, H.; Toko, K. Development of sweetness sensor with selectivity to negatively charged high-potency sweeteners. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuura, M.; Tahara, Y.; Ikezaki, H.; Toko, K. Development of a sweetness sensor for positively charged high-potency sweeteners. Sensors 2014, 14, 7359–7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, Y.; Tahara, Y.; Toko, K. Study of the relationship between taste sensor response and the amount of epigallocatechin gallate adsorbed onto a lipid-polymer membrane. Sensors 2015, 15, 6241–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukagawa, T.; Tahara, Y.; Yasuura, M.; Habara, M.; Ikezaki, H.; Toko, K. Relationship between taste sensor response and amount of quinine adsorbed on lipid/polymer membrane. J. Innov. Electron. Commun. 2012, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, D.; Fukagawa, T.; Tahara, Y.; Yasuura, M.; Toko, K. Examination of amount of astringent substances adsorbed onto lipid/polymer membrane used in taste sensor. Sens. Lett. 2014, 12, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastl, M.; Hanke, S.; Back, W. Analytical investigations to evaluate bitter sensation using a taste sensing system. Brew. Sci. 2007, 60, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gastl, M.; Hanke, S.; Back, W. Drinkability—Balance and harmony of components as well as an incentive for continuing to drink. BRAUWELT Int. 2008, 3, 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Lyall, V.; Heck, G.L.; Vinnikova, A.K.; Ghosh, S.; Phan, T.H.; Alam, R.I.; Russell, O.F.; Malik, S.A.; Bigbee, J.W.; DeSimone, J.A. The mammalian amiloride-insensitive non-specific salt taste receptor is a vanilloid receptor-1 variant. J. Physiol. 2004, 588, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, Y.; Noda, J.; Yatabe, R.; Ikezaki, H.; Toko, K. Research on the changes to the lipid/polymer membrane used in the acidic bitterness sensor caused by preconditioning. Sensors 2016, 16, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffmann, C. The sense of taste. In Handbook of Physiology; Field, I.J., Ed.; American Physiological Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1959; Volume 1, pp. 507–533. [Google Scholar]












| LC instrument | Shimadzu LC-20A (Kyoto, Japan) |
| LC column | Cadenza CD-C18 (2.0 × 100 mm, 3 µm, Portland, OR, USA) |
| Column temperature | 50 °C |
| Mobile phase | A: 10 mmol/L Ammonium acetate/H2O |
| B: Acetonitrile | |
| Flow rate | 0.3 mL/min |
| Gradient conditions | <PADE> |
| 0.0 min → 10.0 min: B20% → B90% | |
| 10.0 min → 12.0 min: B90% | |
| 12.1 min → 20.0 min: B20% | |
| <BBPA/TBAC> | |
| 0.0 min → 5.0 min: B60% → B95% | |
| 5.0 min → 15.0 min: B95% | |
| 15.1 min → 20.0 min: B60% | |
| Injection volume | 1 µL |
| MS instrument | API 4000 (AB SCIEX) |
| Ionization | ESI |
| Polarity | <PADE> negative; <TBAC/BBPA> positive |
| Scan type | SRM |
| <PADE> Q1: m/z 377.3 → Q3: m/z 237.1 | |
| <BBPA> Q1: m/z 399.3 → Q3: m/z 273.2 | |
| <TBAC> Q1: m/z 403.3 → Q3: m/z 329.3 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Onitake, H.; Huang, Z.; Shiino, T.; Tahara, Y.; Yatabe, R.; Ikezaki, H.; Toko, K. Improved Durability and Sensitivity of Bitterness-Sensing Membrane for Medicines. Sensors 2017, 17, 2541. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112541
Wu X, Onitake H, Huang Z, Shiino T, Tahara Y, Yatabe R, Ikezaki H, Toko K. Improved Durability and Sensitivity of Bitterness-Sensing Membrane for Medicines. Sensors. 2017; 17(11):2541. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112541
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xiao, Hideya Onitake, Zhiqin Huang, Takeshi Shiino, Yusuke Tahara, Rui Yatabe, Hidekazu Ikezaki, and Kiyoshi Toko. 2017. "Improved Durability and Sensitivity of Bitterness-Sensing Membrane for Medicines" Sensors 17, no. 11: 2541. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112541
APA StyleWu, X., Onitake, H., Huang, Z., Shiino, T., Tahara, Y., Yatabe, R., Ikezaki, H., & Toko, K. (2017). Improved Durability and Sensitivity of Bitterness-Sensing Membrane for Medicines. Sensors, 17(11), 2541. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112541





