Biosensors to Diagnose Chagas Disease: A Brief Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
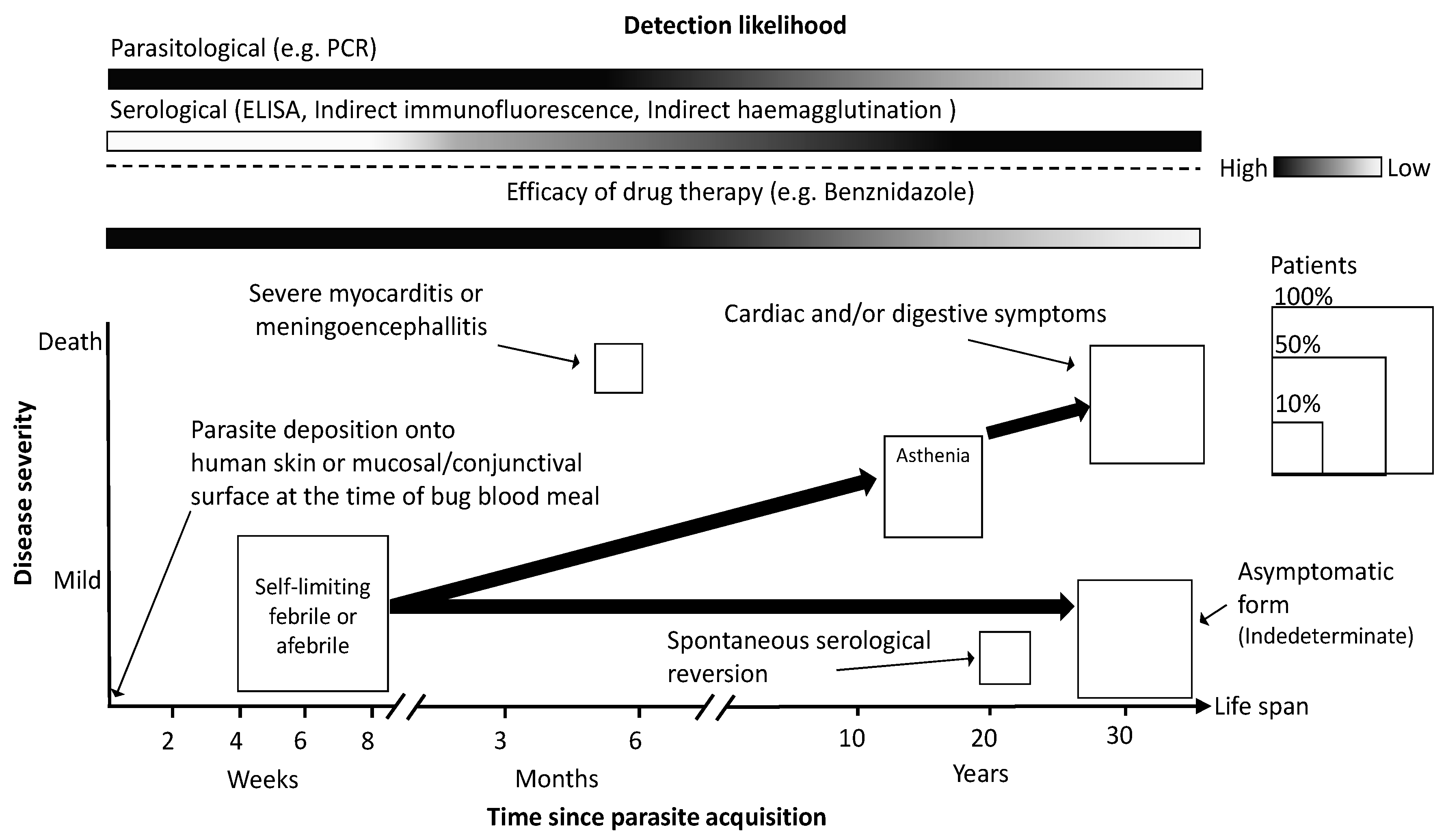
2. Brief Description of CD and Current Needs
3. Current Detection Technologies and Their Limitations
4. Biosensing Research Efforts for Chagas Diagnosis
5. Biosensors and Their Contribution to Reducing the CD Burden
6. Infrastructure Requirements
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chagas, C. Nova tripanozomiaze humana: Estudos sobre a morfolojia e o ciclo evolutivo do Schizotrypanum cruzi n. gen., n. sp., ajente etiolojico de nova entidade morbida do homem. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1909, 1, 159–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotez, P.J.; Bottazzi, M.E.; Franco-Paredes, C.; Ault, S.K.; Periago, M.R. The neglected tropical diseases of Latin America and the Caribbean: A review of disease burden and distribution and a roadmap for control and elimination. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Health Estimates 2015: Burden of Disease by Cause, Age, Sex, by Country and by Region, 2000–2015; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gascon, J.; Vilasanjuan, R.; Lucas, A. The need for global collaboration to tackle hidden public health crisis of Chagas disease. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2014, 12, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarleton, R.L.; Gürtler, R.E.; Urbina, J.A.; Ramsey, J.; Viotti, R. Chagas disease and the london declaration on neglected tropical diseases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luz, J.G.G.; Souto, D.E.P.; Machado-Assis, G.F.; de Lana, M.; Kubota, L.T.; Luz, R.C.S.; Damos, F.S.; Martins, H.R. Development and Evaluation of a SPR-based Immunosensor for Detection of Anti-Trypanosoma cruzi Antibodies in Human Serum. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 212, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Camargo, C.L.; Albajar-Viñas, P.; Wilkins, P.P.; Nieto, J.; Leiby, D.A.; Paris, L.; Scollo, K.; Flórez, C.; Guzmán-Bracho, C.; Luquetti, A.O.; et al. Comparative evaluation of 11 commercialized rapid diagnostic tests for detecting Trypanosoma cruzi antibodies in serum banks in areas of endemicity and nonendemicity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2506–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Control of Chagas Disease Second Report of the WHO Expert Committee; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002; Volume 905. [Google Scholar]
- Coura, J.R. The main sceneries of chagas disease transmission. The vectors, blood and oral transmissions—A comprehensive review. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, C.J.; Lymbery, A.J.; Thompson, R.C.A. Chagas disease: The challenge of polyparasitism? Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, J.M.; Elizondo-Cano, M.; Sanchez-González, G.; Peña-Nieves, A.; Figueroa-Lara, A. Opportunity cost for early treatment of Chagas disease in Mexico. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, X.-N. Preventing the transmission of American trypanosomiasis and its spread into non-endemic countries. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2015, 4, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manne, J.M.; Snively, C.S.; Ramsey, J.M.; Salgado, M.O.; Bärnighausen, T.; Reich, M.R. Barriers to treatment access for Chagas disease in Mexico. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmunis, G.A.; Yadon, Z.E. Chagas disease: A Latin American health problem becoming a world health problem. Acta Trop. 2010, 115, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conners, E.E.; Vinetz, J.M.; Weeks, J.R.; Brouwer, K.C. A global systematic review of Chagas disease prevalence among migrants. Acta Trop. 2016, 156, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena-Méndez, A.; Aldasoro, E.; de Lazzari, E.; Sicuri, E.; Brown, M.; Moore, D.A.J.; Gascon, J.; Muñoz, J. Prevalence of Chagas Disease in Latin-American Migrants Living in Europe: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bern, C.; Montgomery, S.; Herwaldt, B.; Rassi, A., Jr.; Marin-Neto, J.A.; Dantas, R.O.; Maguire, J.H.; Acquatella, H.; Morillo, C.; et al. Kirchhoff LV Evaluation and treatment of Chagas disease in the United States: A systematic review. JAMA 2007, 298, 2171–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, M.L.Y.; Mach, K.E.; Wong, P.K.; Liao, J.C. Advances and challenges in biosensor-based diagnosis of infectious diseases. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, A. Clinical and epidemiological aspects of Chagas disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2001, 1, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassi, A.; Rassi, A.; Marin-Neto, J.A. Chagas disease. Lancet 2010, 375, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bern, C. Chagas’ Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassi, A.; Rassi, A.; Marin-Neto, J.A. Chagas Disease. In Neglected Tropical Diseases-Latin America and the Caribbean; Franco-Paredes, C., Santos-Preciado, J.I., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 45–71. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2163–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillo, C.A.; Marin-Neto, J.A.; Avezum, A.; Sosa-Estani, S.; Rassi, A., Jr.; Rosas, F.; Villena, E.; Quiroz, R.; Bonilla, R.; Britto, C.; et al. Randomized Trial of Benznidazole for Chronic Chagas’ Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherst, R.W. Global Change and Human Vulnerability to Vector-Borne Diseases Global Change and Human Vulnerability to Vector-Borne Diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 136–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Githeko, A.K.; Lindsay, S.W.; Confalonieri, U.E.; Patz, J.A. Climate change and vector-borne diseases: A regional analysis. Bull. World Health Organ. 2000, 78, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coura, J.R. Chagas disease: Control, elimination and eradication. Is it possible? Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2013, 108, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luz, J.G.G.; Souto, D.E.P.; Machado-Assis, G.F.; de Lana, M.; Luz, R.C.S.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Damos, F.S.; Martins, H.R. Applicability of a novel immunoassay based on surface plasmon resonance for the diagnosis of Chagas disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 454, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasil, P.E.; De Castro, L.; Hasslocher-Moreno, A.M.; Sangenis, L.H.; Braga, J.U. ELISA versus PCR for diagnosis of chronic Chagas disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.V.; Bertolino, F.A.; Fernández-Baldo, M.A.; Messina, G.A.; Salinas, E.; Sanz, M.I.; Raba, J. A microfluidic device based on a screen-printed carbon electrode with electrodeposited gold nanoparticles for the detection of IgG anti-Trypanosoma cruzi antibodies. Analyst 2011, 136, 4745–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, L.F.; Flórez, O.; Rincón, G.; González, C.I. Comparison of seven diagnostic tests to detect Trypanosoma cruzi infection in patients in chronic phase of Chagas disease. Colomb. Med. (Cali) 2014, 45, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, T.; Falconar, A.K.; Luquetti, A.O.; Costales, J.A.; Grijalva, M.J.; Lewis, M.D.; Messenger, L.A.; Tran, T.T.; Ramirez, J.D.; Guhl, F.; et al. Development of Peptide-Based Lineage-Specific Serology for Chronic Chagas Disease: Geographical and Clinical Distribution of Epitope Recognition. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.A.P.; Colli, W.; Da Costa, P.I.; Yamanaka, H. Immunosensor for the diagnosis of Chagas’ disease. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belluzo, M.S.; Ribone, M.É.; Camussone, C.; Marcipar, I.S.; Lagier, C.M. Favorably orienting recombinant proteins to develop amperometric biosensors to diagnose Chagas’ disease. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 408, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.A.P.; Colli, W.; Alves, M.J.M.; Oliveira, D.R.; Costa, P.I.; Güell, A.G.; Sanz, F.; Benedetti, A.V.; Yamanaka, H. Investigation of the interaction between Tc85-11 protein and antibody anti-T. cruzi by AFM and amperometric measurements. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 5046–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinicius Foguel, M.; Pilondos Santos, G.; Aparecido Pupim Ferreira, A.; Yamanaka, H.; Vicente Benedetti, A. Amperometric immunosensor for Chagas’ disease using gold CD-R Transducer. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 2555–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, C.A.; Kovalczuk, E.; Inaba, J.; Viana, A.G.; Pessoa, C.A.; Wohnrath, K.; Garcia, J.R. Development of a Nano-particle enhanced impedimetric biosensor for Chagas’ Disease Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the XLII Annual Meeting of SBBq, Parana, Brazil, 18–21 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Salinas, E.; Torriero, A.; Battaglini, F.; Sanz, M.; Olisina, R.; Raba, J. Continuous-flow/stopped-flow system for enzyme immunoassay using a rotating bioreactor: Determination of Chagas disease. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coltro, W.K.T.; Neves, R.D.S.; Motheo, A.D.J.; Da Silva, J.A.F.; Carrilho, E. Microfluidic devices with integrated dual-capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection to monitor binding events in real time. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortina, M.E.; Melli, L.J.; Roberti, M.; Mass, M.; Longinotti, G.; Tropea, S.; Lloret, P.; Serantes, D.A.R.; Salomón, F.; Lloret, M.; et al. Electrochemical magnetic microbeads-based biosensor for point-of-care serodiagnosis of infectious diseases. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachse, K.; Frey, J. PCR Detection of Microbial Pathogens: Methods and Protocols. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Totowa, N., Ed.; Humana Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Diguta, C.; Rousseaux, S.; Weidmann, S.; Bretin, N.; Vincent, B.; Guilloux-Benatier, M.A.H. Development of a qPCR assay for specific quantification of Botrytis cinerea on grapes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 313, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janissen, R.; Sahoo, P.K.; Santos, C.A.; da Silva, A.M.; von Zuben, A.A.G.; Souto, D.E.P.; Costa, A.D.T.; Celedon, P.; Zanchin, N.I.T.; Almeida, D.B.; et al. InP Nanowire Biosensor with Tailored Biofunctionalization: Ultrasensitive and Highly Selective Disease Biomarker Detection. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5938–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thacker, J.; Casale, E.; Tucker, C. Immunoassays (ELISA) for rapid, quantitative analysis in the food-processing industry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 2680–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Mayo, M.; Bruno, J.; Bronk, B.; Batt, C.; Chambers, P. A review of molecular recognition technologies for detection of biological threat agents. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 15, 549–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, P.; Ludwig, G.; Peruski, A.; Tuite, J.; Morse, S.; Peruski, L. Immunoassay of infectious agents. Biotechniques 2003, 35, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peruski, A.; Peruski, L. Immunological methods for detection and identification of infectious disease and biological warfare agents. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2003, 10, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barfield, C.A.; Barney, R.S.; Crudder, C.H.; Wilmoth, J.L.; Stevens, D.S.; Mora-Garcia, S.; Yanovsky, J. A Highly Sensitive Rapid Diagnostic Test for Chagas Disease That Utilizes a Recombinant Trypanosoma cruzi Antigen. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 58, 814–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regiart, M.; Pereira, S.V.; Bertolino, F.A.; Garcia, C.D.; Raba, J.; Aranda, P.R. An electrochemical immunosensor for anti-T. cruzi IgM antibodies, a biomarker for congenital Chagas disease, using a screen-printed electrode modified with gold nanoparticles and functionalized with shed acute phase antigen. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Brasil, P.E.A.A.; Castro, R.; de Castro, L. Commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay versus polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of chronic chagas disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2016, 111, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcerzak, A.; Rejmund, F.; Gutkiewicz, P.; Zienkiewicz, B.; Zhavnerko, G. Ultrasonic chemical sensor with organic monomolecular layer. Arch. Acoust. 2014, 31, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, D.V.; Gollob, K.J.; Dutra, W.O. Acute Chagas Disease: New Global Challenges for an Old Neglected Disease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarkatti, R.; de Araujo, F.F.; Gupta, C.; Debrabant, A. Aptamer Based, Non-PCR, Non-Serological Detection of Chagas Disease Biomarkers in Trypanosoma cruzi Infected Mice. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyara, M.; Chader, D.; Sage, E.; Sugiyama, D.; Nishikawa, H.; Bouvry, D.; Claër, L.; Hingorani, R.; Balderas, R.; Rohrer, J.; et al. Sialyl Lewis x (CD15s) identifies highly differentiated and most suppressive FOXP3(high) regulatory T cells in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7225–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinazo, M.-J.; Thomas, M.C.; Bua, J.; Perrone, A.; Schijman, A.-G.; Viotti, R.-J.; Ramsey, J.-M.; Ribeiro, I.; Sosa-Estani, S.; López, M.-C.; et al. Biological markers for evaluating therapeutic efficacy in Chagas disease, a systematic review. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2014, 12, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, G.R.; Gomes, J.A.S.; Fares, R.C.G.; de Souza Damásio, M.P.; Chaves, A.T.; Ferreira, K.S.; Nunes, M.C.P.; Medeiros, N.I.; Valente, V.A.A.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; et al. Plasma Cytokine Expression Is Associated with Cardiac Morbidity in Chagas Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaria, C.; Chatelain, E.; Jackson, Y.; Miao, Q.; Ward, B.J.; Chappuis, F.; Ndao, M. Serum biomarkers predictive of cure in Chagas disease patients after nifurtimox treatment. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, A.Y.; Valente Vda, C.; Coura, J.R.; Valente, S.A.; Junqueira, A.C.; Santos, L.C.; Ferreira, A.G., Jr.; de Macedo, R.C. Clinical Follow-Up of Responses to Treatment with Benznidazol in Amazon: A Cohort Study of Acute Chagas Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, S.M.; Deng, X.; Fernandes, F.; Cunha-Neto, E.; Ribeiro, A.L.; Adesina, B.; Beyer, A.I.; Contestable, P.; Custer, B.; Busch, M.P.; et al. Inflammatory and cardiac biomarkers are differentially expressed in clinical stages of Chagas disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 199, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.R.P.; Frade, A.F.; Santos, R.H.B.; Teixeira, P.C.; Baron, M.A.; Navarro, I.C.; Benvenuti, L.A.; Fiorelli, A.I.; Bocchi, E.A.; Stolf, N.A.; et al. MicroRNAs miR-1, miR-133a, miR-133b, miR-208a and miR-208b are dysregulated in Chronic Chagas disease Cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 175, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Sesquen, Y.E.; Gilman, R.H.; Paico, H.; Yauri, V.; Angulo, N.; Ccopa, F.; Bern, C. Cell Death and Serum Markers of Collagen Metabolism during Cardiac Remodeling in Cavia porcellus Experimentally Infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, R.T.; Waghabi, M.C.; Cardillo, F.; Mengel, J.; Antas, P.R.Z. Scrutinizing the Biomarkers for the Neglected Chagas Disease: How Remarkable! Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Araujo, F.F.; Nagarkatti, R.; Gupta, C.; Marino, A.P.; Debrabant, A. Aptamer-Based Detection of Disease Biomarkers in Mouse Models for Chagas Drug Discovery. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fares, R.C.G.; Gomes, J.A.; Garzoni, L.R.; Waghabi, M.C.; Saraiva, R.M.; Medeiros, N.I.; Oliveira-Prado, R.; Sangenis, L.H.; Chambela Mda, C.; de Araújo, F.F.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 are differentially expressed in patients with indeterminate and cardiac clinical forms of Chagas disease. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3600–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Methods | Drawbacks | Benefits | LOD * | Need of Labeling | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selective Media |
|
| NA | No | [41,42] |
| Biosensors |
|
| ~2 nM [43] | No | [6,18,28,30,33,34,35,36,37,43] |
| ELISA |
|
| ~30 nM [43] | Yes | [41,42,44,45,46,47] |
| Quantitative PCR |
|
| ~10 nM [43] | Yes | [40,42,45,46,47] |
| Rapid lateral flow test |
|
| ~20 nM | Yes | [7,48] |
| Phase of the Disease | Biomarker Name | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Acute | IL-12, IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, nitric oxide (NO), IL-17, IL-10, CD4+ T cells | [52] |
| Chronic | Aptamer, CCL2, MAL/TIRAP, CCR5, CD15s+ Treg cells, CD27+ T cells, CD28+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, TIMP-1, IMP-2, Troponin I, TGF-β, IL-10, APOA1, Fibronectin, MMP-2, MMP-9, ANP, BNP, N-terminal pro-BNP, IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, CKMB, miRNA-1, miRNA-133a, iRNA-133b, miRNA-208a, miRNA-208b, PIIINP, PICP, Syndecan-4, ICAM-1, Galectin-3, KMP11, HSP70, PAR2, Tgp63, Antigen 13, SAPA, Tc24 | [16,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64] |
| Product | Company Name | Transducer Technology | Dimensions (cm) | Weight (kg) | Sample Volume (µL) | Portability Rate * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q-Sense Omega Auto | Q-sense | Acoustic | 70 × 67 × 57 | 83 | 50 | 1 |
| Biacore X100 | General Electric | SPR | 59.6 × 56.3 × 59.3 | 47 | 20–30 | 3 |
| AWS A20-F20 | AWsensors | Acoustic | 77 × 75 × 45 | 60 | 50–1000 | 2 |
| OpenPlex | Horiba | SPRi | 49 × 30.4 × 48 | 15.6 | 200 | 4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rocha-Gaso, M.-I.; Villarreal-Gómez, L.-J.; Beyssen, D.; Sarry, F.; Reyna, M.-A.; Ibarra-Cerdeña, C.-N. Biosensors to Diagnose Chagas Disease: A Brief Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2629. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112629
Rocha-Gaso M-I, Villarreal-Gómez L-J, Beyssen D, Sarry F, Reyna M-A, Ibarra-Cerdeña C-N. Biosensors to Diagnose Chagas Disease: A Brief Review. Sensors. 2017; 17(11):2629. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112629
Chicago/Turabian StyleRocha-Gaso, María-Isabel, Luis-Jesús Villarreal-Gómez, Denis Beyssen, Frédéric Sarry, Marco-Antonio Reyna, and Carlos-Napoleón Ibarra-Cerdeña. 2017. "Biosensors to Diagnose Chagas Disease: A Brief Review" Sensors 17, no. 11: 2629. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112629
APA StyleRocha-Gaso, M.-I., Villarreal-Gómez, L.-J., Beyssen, D., Sarry, F., Reyna, M.-A., & Ibarra-Cerdeña, C.-N. (2017). Biosensors to Diagnose Chagas Disease: A Brief Review. Sensors, 17(11), 2629. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112629







