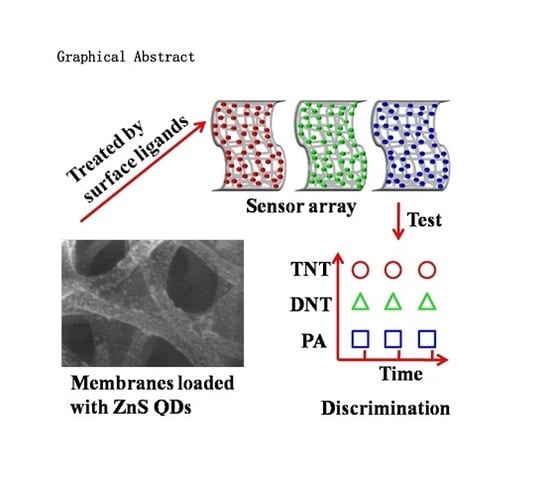
Multichannel Discriminative Detection of Explosive Vapors with an Array of Nanofibrous Membranes Loaded with Quantum Dots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Mn2+-Doped ZnS QDs
2.3. Preparation of Electrospun Nanofibrous Membrane
2.4. Preparation of Fluorescent Nanofibrous Membranes
2.5. Surface Modification of Fluorescent Nanofibrous Membranes
2.6. Quenching Tests of Fluorescent Nanofibrous Membranes towards Nitroaromatic Explosives
2.7. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Surface Modification of Fluorescent Nanofibrous Membranes
3.2. Fluorescent Nanofibrous Membrane Array for Explosive Sensing
3.3. Discriminative Detection Based on Fluorescent Nanofibrous Membrane Array
3.4. Homogeneity, Stability and Recoverability of Fluorescent Nanofibrous Membranes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rose, A.; Zhu, Z.; Madigan, C.F.; Swager, T.M.; Bulovi, V. Sensitivity gains in chemosensing by lasing action in organic polymers. Nature 2005, 434, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, A.; Havivi, E.; Shacham, R.; Hahamy, E.; Leibovich, R.; Pevzner, A.; Krivitsky, V.; Davivi, G.; Presman, I.; Elnathan, R. Supersensitive fingerprinting of explosives by chemically modified nanosensors arrays. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Ali, M.A.; Clulow, A.J.; Fan, S.; Burn, P.L.; Gentle, I.R.; Meredith, P.; Shaw, P.E. Unambiguous detection of nitrated explosive vapours by fluorescence quenching of dendrimer films. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Brückner, C.; Nieh, M.P.; Lei, Y. A fluorescent polymer film with self-assembled three-dimensionally ordered nanopores: preparation, characterization and its application for explosives detection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 14613–14621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; La, A.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Lei, Y. Novel Signal-Amplifying Fluorescent Nanofibers for Naked-Eye-Based Ultrasensitive Detection of Buried Explosives and Explosive Vapors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 3547–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, S.; Swager, T.M. Three-dimensional electronic delocalization in chiral conjugated polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2002, 41, 4225–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peveler, W.J.; Roldan, A.; Hollingsworth, N.; Porter, M.J.; Parkin, I.P. Multichannel Detection and Differentiation of Explosives with a Quantum Dot Array. ACS Nano. 2015, 10, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolesse, R.; Nardis, S.; Monti, D.; Stefanelli, M.; Natale, C.D. Porphyrinoids for Chemical Sensor Applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 10, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Dutta, S.; Chakrabarti, S.; Bairi, P.; Pal, T. Redox-switchable copper(I) metallogel: a metal-organic material for selective and naked-eye sensing of picric acid. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6308–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Zhao, L.; Bogale, R.F.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Qian, X.; Guo, S.; Zhao, J.; Ning, G. Highly Selective Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol and Cu2+ Ion Based on a Fluorescent Cadmium-Pamoate Metal-Organic Framework. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 21, 2029–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Deibert, B.J.; Li, J. Luminescent metal-organic frameworks for chemical sensing and explosive detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5815–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Su, K.; Long, Y.; Peng, Z.; Li, N.; Liu, F. A facile and sensitive fluorescent sensor using electrospun nanofibrous film for nitroaromatic explosive detection. J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21, 11895–11900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.C.; Nie, S. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 1998, 281, 2016–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enkin, N.; Sharon, E.; Golub, E.; Willner, I. Ag Nanocluster/DNA Hybrids: Functional Modules for the Detection of Nitroaromatic and RDX Explosives. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 4918–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, R.; Willner, I. NAD+/NADH-Sensitive Quantum Dots: Applications To Probe NAD+-Dependent Enzymes and To Sense the RDX Explosive. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, R.; Finder, T.; Bahshi, L.; Gill, R.; Willner, I. Functionalized CdSe/ZnS QDs for the Detection of Nitroaromatic or RDX Explosives. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 6416–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Tong, C.; Feng, L.; Wang, C.; He, Y.; Lü, C. Water-soluble polymer functionalized CdTe/ZnS quantum dots: a facile ratiometric fluorescent probe for sensitive and selective detection of nitroaromatic explosives. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 2132–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.; Huang, S.; Xu, S.; Hu, G.; Wang, L. Fluorescent nanosensors via photoinduced polymerization of hydrophobic inorganic quantum dots for the sensitive and selective detection of nitroaromatics. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2383–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, P.; Saikia, D.; Adhikary, N.C.; Sarma, N.S. Macromolecular Systems with MSA-Capped CdTe and CdTe/ZnS Core/Shell Quantum Dots as Superselective and Ultrasensitive Optical Sensors for Picric Acid Explosive. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhou, H.; Mei, Q.; Wang, S.; Guan, G.; Liu, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Instant visual detection of trinitrotoluene particulates on various surfaces by ratiometric fluorescence of dual-emission quantum dots hybrid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8424–8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zu, B.; Li, Y.; Dou, X. Contactless and Rapid Discrimination of Improvised Explosives Realized by Mn2+ Doping Tailored ZnS Nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 4578–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostmark, H.; Wallin, S.; Ang, H.G. Vapor Pressure of Explosives: A Critical Review. Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 2012, 37, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Yu, S.H. Nanoparticles meet electrospinning: recent advances and future prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4423–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Long, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.D.; Li, M.M.; Duvail, J.L.; Jiang, X.Y.; Yin, H.L. Advances in three-dimensional nanofibrous macrostructures via electrospinning. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 862–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.E.; Yong, T.; Ma, Z.; Ramaseshan, R. Electrospun nanofibers: Solving global issues. Mater. Today 2006, 9, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.Y.; Liu, B.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Gao, D.M.; Wang, F.; Fang, Q.L.; Zhang, Z.P. Amine-capped ZnS-Mn2+ nanocrystals for fluorescence detection of trace TNT explosive. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3458–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, J.; Mano, J.F. Molecular Interactions Driving the Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Multilayers. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8883–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.Y.; Xu, W.; Lin, F.W.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.K. Electrospun nanofibers of porphyrinated polyimide for the ultra-sensitive detection of trace TNT. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 184, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, M.; Voznyy, O.; Hu, L.; Fu, Q.Y.; Zhou, D.X.; Xia, Z.; Sargent, E.H.; Tang, J. Physically Flexible, Rapid-Response Gas Sensor Based on Colloidal Quantum Dot Solids. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, K. Quantum dots go large. Nature 2009, 459, 760–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.Y.; Chen, H.B.; Wang, H.M.; Peng, Z.; Yang, Y.F.; Zhang, G.Q.; Li, N.; Liu, F.; Pei, J. Highly sensitive detection of nitroaromatic explosives using an electrospun nanofibrous sensor based on a novel fluorescent conjugated polymer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 744, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.C.; Liu, Y.X.; Shaw, G.; Carrier, A.; Dey, S.; Zhao, J.; Lei, Y. Fundamental Study of Electrospun Pyrene-Polyethersulfone Nanofibers Using Mixed Solvents for Sensitive and Selective Explosives Detection in Aqueous Solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13189–13197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Duan, H.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhong, F.; Cao, Y.; Jia, D. Multichannel Discriminative Detection of Explosive Vapors with an Array of Nanofibrous Membranes Loaded with Quantum Dots. Sensors 2017, 17, 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112676
Wu Z, Duan H, Li Z, Guo J, Zhong F, Cao Y, Jia D. Multichannel Discriminative Detection of Explosive Vapors with an Array of Nanofibrous Membranes Loaded with Quantum Dots. Sensors. 2017; 17(11):2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112676
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zhaofeng, Haiming Duan, Zhijun Li, Jixi Guo, Furu Zhong, Yali Cao, and Dianzeng Jia. 2017. "Multichannel Discriminative Detection of Explosive Vapors with an Array of Nanofibrous Membranes Loaded with Quantum Dots" Sensors 17, no. 11: 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112676
APA StyleWu, Z., Duan, H., Li, Z., Guo, J., Zhong, F., Cao, Y., & Jia, D. (2017). Multichannel Discriminative Detection of Explosive Vapors with an Array of Nanofibrous Membranes Loaded with Quantum Dots. Sensors, 17(11), 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112676