Time Modulated Arrays: From their Origin to Their Utilization in Wireless Communication Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
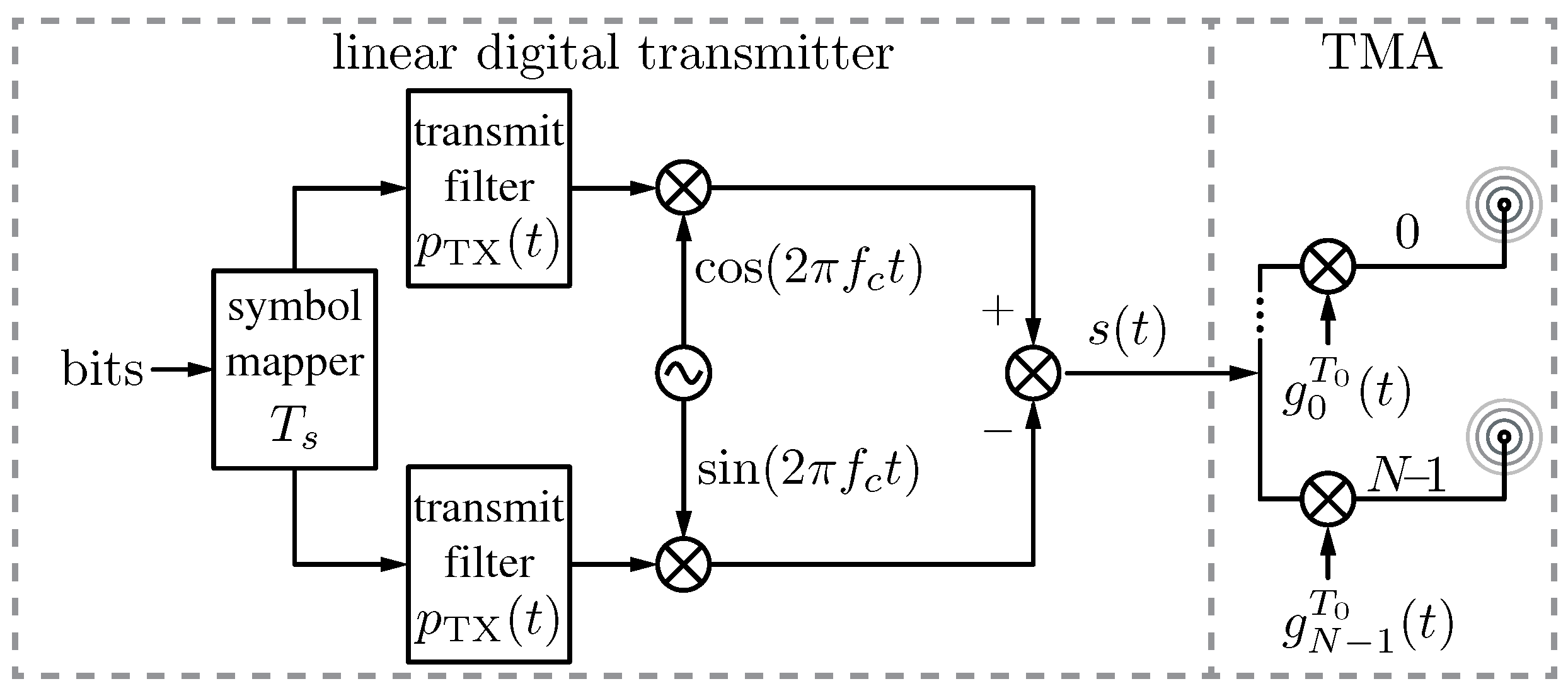
1.1. What is a TMA?
1.2. TMA Features
- exploit the fundamental pattern only —at the carrier frequency — with the aim of achieving ultra-low side-lobe level (SLL) while minimizing the SR, or
- profitably exploit the harmonic patterns, endowing the TMA with smart antenna capabilities.
- Hardware simplicity, with the subsequent impact on the size and the cost of the system.
- Power consumption, as it has been remarked and properly quantified in recent papers like (Table I, [2]) and (Tables I and II, [3]), which have also proposed hybrid analog–digital architectures for beamforming. Indeed, in a fully digital implementation of an linear beamforming network (LBFN), the number of required RF chains, L, must be equal to the number of antenna elements N. In practice, however, a relationship is often preferable due to a number of reasons, the power consumption per RF being the front-end one of the most important ones.
- Nonexistence of issues related to synchronization, phase coherence or coupling between different RF chains.
2. State of the Art
2.1. The Origin of the TMA Concept
2.2. TMA Design under an (Exclusive) Antenna Perspective
2.2.1. Fundamental Mode Pattern
2.2.2. Harmonic Patterns
2.3. TMA Design under a Signal Processing Perspective
2.3.1. Interaction of TMAs with Information Signals: First Approaches
2.3.2. Towards Using TMAs in Wireless Communication Systems
- The referred restrictions are the following:
- The radiated power through the TMA is given by:where (expressed in watts) represents the power radiated by an isotropic antenna transmitting a linearly modulated equivalent baseband digital signal with a power density (it is possible to consider , with being the average transmit symbol energy and ρ the roll-off factor of the raised cosine filter), whereas represents the TMA power transfer function (dimensionless) accounting for both the array geometry and the time-modulated elements radiating a carrier signal. The expression coincides with the array total power in (Equation (30), [58]) and is employed to separate the useful power for () from the harmonic SR losses for ().
- A type of pulses that are more suitable for harmonic beamforming with TMA: the so-called sum-of-weighted-cosine (SWC) pulses [80].
- Based on the previous pulses, a new family of beamforming TMA, termed ETMA, is characterized and evaluated in terms of efficiency by properly comparing it to conventional beamforming TMA based on rectangular pulses.
3. Challenges and Future Research Lines
- The exploitation of TMA at transmission. Up to now, the applications of TMA in the area of digital communications mainly focus on receiving TMA. Hence, the performance of transmitting TMA from a signal processing outlook, and in different scenarios, is still an unexplored research field. We propose two areas which certainly deserve further exploration: (1) the performance analysis of transmitting TMA in multiuser scenarios; and (2) the feasibility of diversity transmission techniques with TMA.
- Performance with broadband signals. The TMA state of the art exclusively focuses on narrowband signals. However, communications nowadays must unavoidably deal with broadband signals. The higher the bandwidth, the higher the switching frequency in the TMA, the wider the bandwidth at the RF stage, and the higher the sampling rate at the ADC. On the other hand, an analysis of TMA behavior under frequency-selective fading still remains to be done.
- Beamforming design through the preprocessing of periodic pulses. More specifically, we propose a more accurate design of the periodic pulses in the frequency domain. The Fourier transform of a periodic pulse is a discrete spectrum with impulses at multiples of the time-modulation frequency and whose corresponding areas are times the associated exponential Fourier series coefficients. Therefore, a simpler design, by applying the Fourier series coefficients properties to preprocess conventional rectangular pulses before they are applied to the antenna elements, is possible.
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | analog-to-digital converter |
| AM | amplitude modulation |
| AWGN | additive white Gaussian noise |
| BER | bit error rate |
| BPSK | binary phase shift-keying |
| DAC | digital-to-analog converter |
| DOA | direction of arrival |
| ETMA | enhanced time-modulated array |
| FM | frequency modulation |
| LBFN | linear beamforming network |
| LFM | linearly frequency modulated |
| MRC | maximum ratio combining |
| RF | radio frequency |
| SLL | side-lobe level |
| SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
| SPDT | single-pole double-throw |
| SR | sideband radiation |
| SWC | sum-of-weighted-cosine |
| TMA | time-modulated array |
| TMRA | time-modulated reflector array |
References
- Renzo, M.D.; Haas, H.; Ghrayeb, A.; Sugiura, S.; Hanzo, L. Spatial Modulation for Generalized MIMO: Challenges, Opportunities, and Implementation. Proc. IEEE 2014, 102, 56–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heath, R.W.; González-Prelcic, N.; Rangan, S.; Roh, W.; Sayeed, A.M. An Overview of Signal Processing Techniques for Millimeter Wave MIMO Systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2016, 10, 436–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Rial, R.; Rusu, C.; González-Prelcic, N.; Alkhateeb, A.; Heath, R.W. Hybrid MIMO Architectures for Millimeter Wave Communications: Phase Shifters or Switches? IEEE Access 2016, 4, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, P.; Oliveri, G.; Mailloux, R.J.; Massa, A. Unconventional Phased Array Architectures and Design Methodologies—A Review. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 544–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummer, W.H.; Villeneuve, A.T.; Fong, T.; Terrio, F. Ultra-low sidelobes from time-modulated arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1963, 11, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, L.; Rocca, P.; Oliveri, G.; Massa, A. Harmonic Beamforming in Time-Modulated Linear Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 2538–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, A.; Chambers, B. Control of the harmonic radiation patterns of time-modulated antenna arrays. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 5–11 July 2008; pp. 1–4.
- Aksoy, E.; Afacan, E. Calculation of Sideband Power Radiation in Time-Modulated Arrays With Asymmetrically Positioned Pulses. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, H.; Bickmore, R. Four-Dimensional Electromagnetic Radiators. Can. J. Phys. 1959, 37, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gan, Y.B.; Qing, A. Sideband suppression in time-modulated linear arrays by the differential evolution algorithm. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2002, 1, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gan, Y.B.; Qing, A.; Tan, P.K. Design of a uniform amplitude time modulated linear array with optimized time sequences. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2005, 53, 2337–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondevila, J.; Brégains, J.C.; Ares, F.; Moreno, E. Optimizing uniformly excited linear arrays through time modulation. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2004, 3, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondevila, J.; Brégains, J.C.; Ares, F.; Moreno, E. Application of time modulation in the synthesis of sum and difference patterns by using linear arrays. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2006, 48, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, L.; Rocca, P.; Manica, L.; Massa, A. Handling Sideband Radiations in Time-Modulated Arrays Through Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 1408–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.K.; Ghatak, R.; Mahanti, G.K. Minimization of side lobe level and side band radiation of a uniformly excited time modulated linear antenna array by using Artificial Bee Colony algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Symposium on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ISIEA), Langkawi, Malaysia, 25–28 September 2011; pp. 247–250.
- Mandal, S.K.; Mahanti, G.K.; Ghatak, R. Differential evolution algorithm for optimizing the conflicting parameters in time-modulated linear array antennas. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 2013, 51, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yu, H.; Liang, X.; Geng, J.; Jin, R. Sideband Radiation Level Suppression in Time-Modulated Array by Nonuniform Period Modulation. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y. Efficient Sideband Suppression in 4D Antenna Arrays with Multiple Time Modulation Frequencies. In Proceedings of the Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium (APSURSI), 2016 IEEE, Fajardo, Puerto Rico, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 699–700.
- Poli, L.; Rocca, P.; Manica, L.; Massa, A. Pattern synthesis in time-modulated linear arrays through pulse shifting. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2010, 4, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, S.; Zheng, L.; Nie, Z. Design of a Low Sidelobe Time Modulated Linear Array With Uniform Amplitude and Sub-Sectional Optimized Time Steps. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 4436–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Tennant, A. Reduced Sideband Levels in Time-Modulated Arrays Using Half-Power Sub-Arraying Techniques. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Tennant, A. Sideband level suppression in time-modulated linear arrays using modified switching sequences and fixed bandwidth elements. Electron. Lett. 2012, 48, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, E.T.; Poli, L.; Rocca, P.; D’Urso, M.; Massa, A. Pulse-Shaping Strategy for Time Modulated Arrays –Analysis and Design. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 3525–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Nie, Z.; Yang, F. Synthesis of low sidelobe planar antenna arrays with time modulation. In Proceedings of the 2005 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, Suzhou, China, 4–7 December 2005; Volume 3, pp. 1–3.
- Aksoy, E.; Afacan, E. An Inequality for the Calculation of Relative Maximum Sideband Level in Time-Modulated Linear and Planar Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 3392–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, A.; Chambers, B. Time-Switched Array Analysis of Phase-Switched Screens. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2009, 57, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gan, Y.; Tan, P. Evaluation of directivity and gain for time-modulated linear antenna arrays. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2004, 42, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, S.; Yao, R.; Nie, Z. Gain Improvement in Time-Modulated Linear Arrays Using SPDT Switches. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 994–997. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liang, X.; Jin, R.; Geng, J.; He, C.; Li, P. Efficiency Improvement For Time Modulated Antenna Arrays. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (2016 IEEE AP-S & USNC-URSI), Fajardo, Puerto Rico, 26 June–1 July 2016.
- Manica, L.; Rocca, P.; Poli, L.; Massa, A. Almost Time-Independent Performance in Time-Modulated Linear Arrays. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2009, 8, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, P.; Poli, L.; Massa, A. Instantaneous directivity optimisation in time-modulated array receivers. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2012, 6, 1590–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, L.; Rocca, P.; Oliveri, G.; Massa, A. Adaptive nulling in time-modulated linear arrays with minimum power losses. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2011, 5, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, P.; Poli, L.; Oliveri, G.; Massa, A. Adaptive Nulling in Time-Varying Scenarios Through Time-Modulated Linear Arrays. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gan, Y.B.; Khiang, T.P. A new technique for power-pattern synthesis in time-modulated linear arrays. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2003, 2, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balderas, L.I.; Reyna, A.; Panduro, M.A. Time-Modulated Concentric Ring Antenna Array for a Wide Coverage Pattern. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium (APSURSI), Fajardo, Puerto Rico, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 709–710.
- Li, G.; Yang, S.; Nie, Z. A Study on the Application of Time Modulated Antenna Arrays to Airborne Pulsed Doppler Radar. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2009, 57, 1579–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euzière, J.; Guinvarc’h, R.; Uguen, B.; Gillard, R. Optimization of Sparse Time-Modulated Array by Genetic Algorithm for Radar Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masotti, D.; Francia, P.; Costanzo, A.; Rizzoli, V. Rigorous Electromagnetic/Circuit-Level Analysis of Time-Modulated Linear Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 5465–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.M.; Wu, W.; Fang, D.G. Efficient and Effective Full-Wave Analysis of the Instantaneous and Average Behaviors of Time-Modulated Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 2902–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, H. A new technique for electronic scanning. IRE Trans Antennas Propag. 1961, 9, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, G.; Yashchyshyn, Y.; Jarzynka, M. Time-Modulated Antenna Array with Lossless Switching Network. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 1827–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; Nie, Z. A Hybrid Analog-Digital Adaptive Beamforming in Time-Modulated Linear Arrays. Electromagnetics 2010, 30, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Tennant, A. A Two-Channel Time Modulated Linear Array With Adaptive Beamforming. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, L.; Moriyama, T.; Rocca, P. Pulse splitting for harmonic beamforming in time- modulated linear arrays. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barott, W.C.; Himed, B. Time-Modulated Array Pattern for Sidelobe Blanking in Spectrometry and Radar. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; Nie, Z.P. A novel electronic beam steering technique in time modulated antenna array. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2009, 97, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Tennant, A. Simultaneous control of sidelobe level and harmonic beam steering in time-modulated linear arrays. Electron. Lett. 2010, 46, 201–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, S.; Nie, Z. Direction of Arrival Estimation in Time Modulated Linear Arrays With Unidirectional Phase Center Motion. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Tennant, A. Experimental Two-Element Time-Modulated Direction Finding Array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 986–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liang, X.; Li, Z.; Geng, J.; Jin, R. Direction Finding by Time-Modulated Array With Harmonic Characteristic Analysis. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tennant, A. Time-modulated reflector array. Electron. Lett. 2012, 48, 972–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tennant, A. Experimental Time-Modulated Reflector Array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 6533–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, F.; Tennant, A. Increasing the energy efficiency of time-modulated reflector-arrays using double layer designs. In Proceedings of the 2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Davos, Switzerland, 10–15 April 2016; pp. 1–5.
- Masotti, D.; Costanzo, A.; Prete, M.D.; Rizzoli, V. Time-Modulation of Linear Arrays for Real-Time Reconfigurable Wireless Power Transmission. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.M.; Wu, W.; Fang, D.G. Single-Sideband Time-Modulated Phased Array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.M.; Wu, W.; Fang, D.G. Study on Reconfigurable Coaperture Antenna Arrays Based on Time-Modulation and Retrodirective Techniques. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 1713–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.M.; Wu, W.; Fang, D.G. Frequency Diverse Array Antenna Using Time-Modulated Optimized Frequency Offset to Obtain Time-Invariant Spatial Fine Focusing Beampattern. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 4434–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brégains, J.C.; Fondevila-Gómez, J.; Franceschetti, G.; Ares, F. Signal Radiation and Power Losses of Time-Modulated Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2008, 56, 1799–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Nie, Z.P. A study of AM and FM signal reception of time modulated linear antenna arrays. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 2009, 7, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, S.; Yao, R.; Huang, M.; Nie, Z.P. Unified Time- and Frequency-Domain Study on Time-Modulated Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 3069–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, Y.; Karahan, M.; Aksoy, E. A dual channel AM receiver structure in 4D arrays. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–25 July 2015; pp. 804–805.
- Guo, J.; Yang, S.; Zhu, Q.; Nie, Z.P. 4D antenna arrays for LFM signal transmission. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–25 July 2015; pp. 820–821.
- Euzière, J.; Guinvar’h, R.; Hinostroza, I.; Uguen, B.; Gillard, R. Time Modulated Array for dual function radar and communication. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–25 July 2015; pp. 806–807.
- Euzière, J.; Guinvar’h, R.; Hinostroza, I.; Uguen, B.; Gillard, R. Optimizing communication in TMA for radar. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Fajardo, Puerto Rico, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 705–706.
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, S.; Yao, R.; Nie, Z. Directional Modulation Based on 4-D Antenna Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, P.; Zhu, Q.; Bekele, E.T.; Yang, S.; Massa, A. 4-D Arrays as Enabling Technology for Cognitive Radio Systems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 1102–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Poli, L.; Rocca, P.; Massa, A. Pulse Sequence Optimization in Time-Modulated Arrays for Secure Communications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium (APSURSI), Fajardo, Puerto Rico, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 695–696.
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, S.; Rocca, P.; Nie, Z. Signal-to-noise ratio and time-modulated signal spectrum in four-dimensional antenna arrays. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2015, 9, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liang, X.; Zhou, B.; Geng, J.; Jin, R. Space-Division Multiple Access Based on Time-Modulated Array. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, G.; Jarzynka, M.; Yashchyshyn, Y. Experimental study of signal reception by means of time-modulated antenna array. In Proceedings of the 2016 21st International Conference on Microwave, Radar and Wireless Communications (MIKON), Krakow, Poland, 9–11 May 2016; pp. 1–4.
- Yashchyshyn, Y.; Derzakowski, K.; Bajurko, P.R.; Marczewski, J.; Kozłowski, S. Time-Modulated Reconfigurable Antenna Based on Integrated S-PIN Diodes for mm-Wave Communication Systems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 4121–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneiro-Catoira, R.; Brégains, J.; García-Naya, J.A.; Castedo, L. On the Feasibility of Time-Modulated Arrays for Digital Linear Modulations: A Theoretical Analysis. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 6114–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, A. Wireless Communications; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Proakis, J.G. Digital Communications, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Maneiro-Catoira, R.; Brégains, J.; García-Naya, J.A.; Castedo, L. Impact of Time-Modulated Arrays on the BER of Linear Digital Modulations. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2015, 29, 2147–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklar, B. Digital Communications, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Maneiro-Catoira, R.; Brégains, J.; García-Naya, J.A.; Castedo, L.; Rocca, P.; Poli, L. Performance Analysis of Time-Modulated Arrays for the Angle Diversity Reception of Digital Linear Modulated Signals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2017, 11, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, K.M.M. Window Functions and their Applications in Signal Processing, 1st ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Maneiro-Catoira, R.; Brégains, J.; García-Naya, J.A.; Castedo, L. Enhanced Time-Modulated Arrays for Harmonic Beamforming. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2017, 11, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttall, A. Some windows with very good sidelobe behavior. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1981, 29, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maneiro-Catoira, R.; Brégains, J.; García-Naya, J.A.; Castedo, L. Time Modulated Arrays: From their Origin to Their Utilization in Wireless Communication Systems. Sensors 2017, 17, 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030590
Maneiro-Catoira R, Brégains J, García-Naya JA, Castedo L. Time Modulated Arrays: From their Origin to Their Utilization in Wireless Communication Systems. Sensors. 2017; 17(3):590. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030590
Chicago/Turabian StyleManeiro-Catoira, Roberto, Julio Brégains, José A. García-Naya, and Luis Castedo. 2017. "Time Modulated Arrays: From their Origin to Their Utilization in Wireless Communication Systems" Sensors 17, no. 3: 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030590
APA StyleManeiro-Catoira, R., Brégains, J., García-Naya, J. A., & Castedo, L. (2017). Time Modulated Arrays: From their Origin to Their Utilization in Wireless Communication Systems. Sensors, 17(3), 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030590






