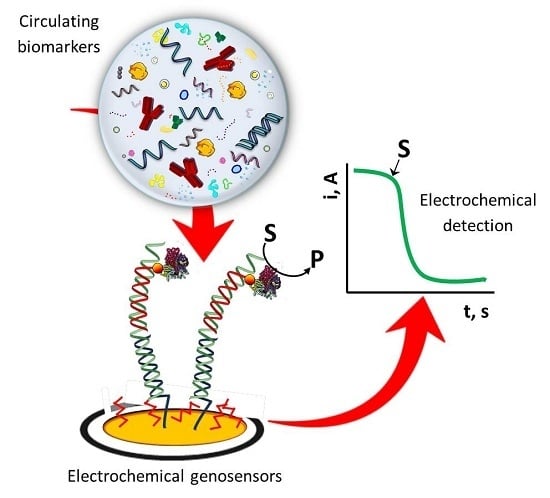
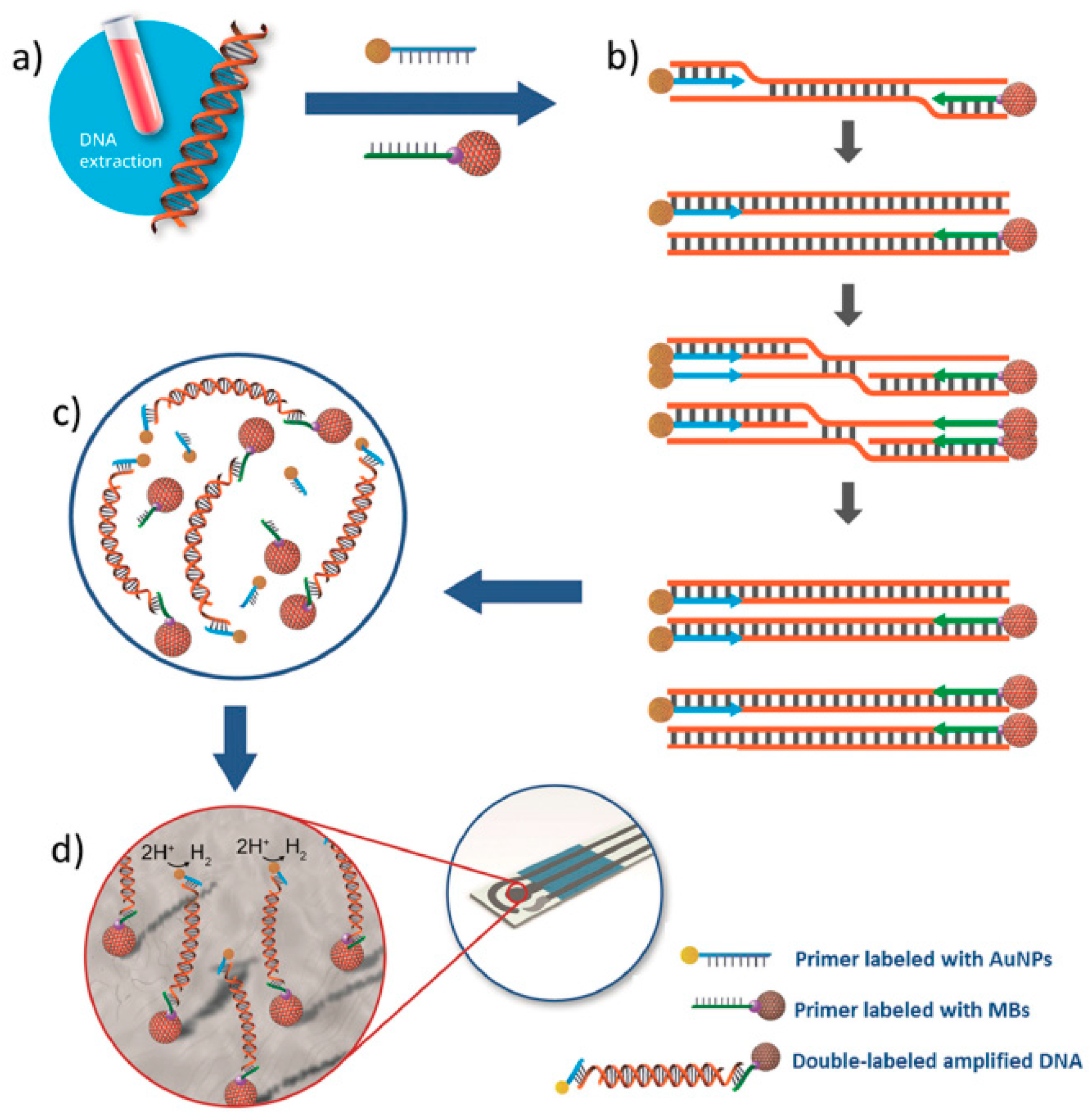
Electrochemical Genosensing of Circulating Biomarkers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Circulating Biomarkers
- -
- Risk screening biomarkers, used to determine disease susceptibility of an individual,
- -
- Prognostic biomarkers which provides information on the probability of the disease in an untreated individual,
- -
- Predictive biomarkers, particular proteins or genes indicating sensitivity or resistance to a specific therapy, and
- -
- Diagnostic and disease monitoring biomarkers, used to aid the diagnosis and monitoring the progression of disease.
3. Electrochemical Genosensing of Circulating Biomarkers
3.1. Electrochemical Genosensing of Cancer Biomarkers
3.2. Electrochemical Genosensing of Neurodegenerative Diseases Biomarkers
3.3. Electrochemical Genosensing of Viral Infections Biomarkers
3.4. Electrochemical Genosensing of Bacterial Infections Biomarkers
4. General Considerations
5. Challenges to Address and Future Prospects
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACV | alternating current voltammetry |
| AP | alkaline phosphatase |
| AP1, AP2 | auxiliary probes |
| aPCR | asymmetric PCR |
| APTMS | (3-aminopropyl)trimethoxysilane |
| AuNPs | gold nanoparticles |
| AuNRs | gold nanorods |
| CFU | colony forming unit |
| CPEG | O-(3-carboxypropyl)-O′-[2-(3-mercaptopropionyl-amino)ethyl]-polyethylene glycol |
| CPs | conducting polymers |
| CV | cyclic voltammetry |
| daPCR | direct asymmetric PCR |
| DENV-3 | dengue virus serotype 3 |
| DNS | duplex specific nuclease |
| DPV | differential pulse voltammetry |
| ds | double-stranded |
| DSNATR | duplex-specific nuclease assisted target recycling |
| EDC | 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EIS | electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| ELISAs | enzyme linked immunosorbent assays |
| Fc | ferrocene |
| FITC | fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| GCE | glassy carbon electrode |
| GO | graphene oxide |
| GSHs | graphene and mesoporous hybrid nanomaterials |
| HDA | helicase-dependent DNA amplification |
| HER | hydrogen evolution reaction |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| HPV | human papillomavirus |
| HQ | hydroquinone |
| ITO | indium-tin oxide |
| LODs | detection limits |
| LSV | linear sweep voltammetry |
| MB | methylene blue |
| MBs | magnetic beads |
| MCH | 6-mercaptohexanol |
| MSGNs | graphene and mesoporous multifunctional hybrids materials |
| MWCNTs | multi-walled carbon nanotubes |
| NHS | N-hydroxysuccinimide |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung carcinoma |
| PAMAM | polyamidoamine |
| PANI | polyaniline |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| Pg | Porphyromonas gingivalis |
| PGE | pencil graphite electrode |
| POC | point-of-care |
| POCT | POC tests |
| PrPC | human cellular prions |
| Py | pyrrole |
| RPA | isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification |
| SAM | self-assembled monolayer |
| SDA | strand displacement amplification |
| Sp | signaling probe |
| SPEs | screen-printed electrodes |
| SPCEs | screen-printed carbon electrodes |
| ss | single-stranded |
| Strep-HRP | streptavidin-peroxidase |
| SWV | square wave voltammetry |
| TMB | 3,3′,5,5′ tetramethylbenzidine |
| TSEs | transmissible spongiform encephalopathies |
| TTF | tetrathiafulvalene |
References
- Silveira, C.M.; Monteiro, T.; Almeida, M.G. Biosensing with Paper-Based Miniaturized Printed Electrodes–A Modern Trend. Biosensors 2016, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Li, X.-B.; Lopa, N.S.; Ahn, S.J.; Lee, J.-J. Electrochemical DNA Hybridization Sensors Based on Conducting Polymers. Sensors 2015, 15, 3801–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Lillehoj, P.B.; Ho, C.-M. DNA diagnostics: Nanotechnology-enhanced electrochemical detection of nucleic acids. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 67, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa Rama, E.; Costa-García, A. Screen-Printed Electrochemical Immunosensors for the Detection of Cancer and Cardiovascular Biomarkers. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1700–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, C.K.; Kadimisetty, K.; Otieno, B.A.; Tang, C.; Malla, S.; Krause, C.E.; Rusling, J.F. Electrochemistry-based Approaches to Low Cost, High Sensitivity, Automated, Multiplexed Protein Immunoassays for Cancer Diagnostics. Analyst 2016, 141, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawiwan, L. Development of Electrochemical Immunosensors towards Point-of-care Cancer Diagnostics: Clinically Relevant Studies. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1716–1729. [Google Scholar]
- Bahadır, E.B.; Gintürk, M.K. Applications of electrochemical immunosensors for early clinical diagnostics. Talanta 2015, 132, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusling, J.F.; Kumar, C.V.; Gutkind, J.S.; Patel, V. Measurement of biomarker proteins for point-of-care early detection and monitoring of cancer. Analyst 2010, 135, 2496–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Bhirde, A.A.; Morgan, N.Y.; Eden, H.S.; Chen, X. Electrochemical Immunosensors for Detection of Cancer Protein Biomarkers. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6546–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda, M.T.; Merkoçi, A.; Pumera, M.; Alegret, S. Electrochemical genosensors for biomedical applications based on gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1961–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Xiong, E.H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.H.; Chen, J.H. Nanomaterials as signal amplification elements in DNA-based electrochemical sensing. Nano Today 2014, 9, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, P.A.; Sandhyarani, N. Graphene-DNA electrochemical sensor for the sensitive detection of BRCA1 gene. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.-F.; Rijiravanich, P.; Singh, K.K.B.; Surareungchai, W.; Yean, C.Y. An Electrochemical Genosensing Assay Based on Magnetic Beads and Gold Nanoparticle-Loaded Latex Microspheres for Vibrio cholerae Detection. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, X.; Yan, S.; Wang, M.; Liu, P.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, C. Single-walled carbon nanotubes-carboxylfunctionalized graphene oxide-based electrochemical DNA biosensor for thermolabile hemolysin gene detection. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 5303–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Electrochemical DNA Sensors: From nanoconstruction to biosensing. Curr. Org. Chem. 2011, 15, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandtke, T.; Woźniak, J.; Kopiński, P. Aptamers in diagnostics and treatment of viral infections. Viruses 2015, 7, 751–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.K.R. Monitoring Intact Viruses Using Aptamers. Biosensors 2016, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hianik, T. Affinity Biosensors for Detection Immunoglobulin E and Cellular Prions Antibodies vs. DNA Aptamers. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1764–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.M.; Gonçalves, I.C.; Magalhães, F.D. Graphene-based materials biocompatibility: A review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerface 2013, 111, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Okon, S.L. Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Immunosensors for Clinically Significant Biomarkers. Materials 2014, 7, 4669–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, F.; Yang, H.-H.; Chen, G. An ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor for detection of DNA species related to oral cancer based on nuclease-assisted target recycling and amplification of DNAzyme. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8004–8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhao, M.; Qiu, B.; Guo, L.; Lin, Z.; Yang, H.-H. Ultraselective homogeneous electrochemical biosensor for DNA species related to oral cancer based on nicking endonuclease assisted target recycling amplification. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9204–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Lin, C.-C.; Joon, A.; Feng, Z.; Troche, G.; Lira, M.E.; Chia, D.; Mao, M.; Ho, C.-L.; Su, W.-C.; et al. Noninvasive saliva-based EGFR gene mutation detection in patients with lung cancer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban-Fernández de Ávila, B.; Araque, E.; Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; Dalkiran, B.; Barderas, R.; Villalonga, R.; Kiliç, E.; Pingarrón, J.M. Dual Functional Graphene Derivative-Based Electrochemical Platforms for Detection of the TP53 Gene with Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Selectivity in Biological Samples. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Campuzano, S.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Gamella, M.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical bioplatforms for the simultaneous determination of interleukin (IL)-8 mRNA and IL-8 protein oral cancerbiomarkers in raw saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Bai, W.; Dong, C.; Guo, R.; Liu, Z. An ultrasensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor based on graphene/Au nanorod/polythionine for human papillomavirus DNA detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zari, N.; Amine, A.; Ennaji, M.M. Label-free DNA biosensor for electrochemical detection of short DNA sequences related to human papilloma virus. Anal. Lett. 2009, 42, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piro, B.; Kapella, A.; Le, V.H.; Anquetin, G.; Zhang, Q.D.; Reisberg, S.; Noel, V.; Tran, L.D.; Duc, H.T.; Pham, M.C. Towards the development of human papillomavirus infection by a reagentless electrochemical peptide biosensor. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 10688–10693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.R.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Fernandes, R.; Sales, M.G. Novel and simple electrochemical biosensor monitoring attomolar levels of miRNA-155 in breast cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimzadeh, M.; Rahaiea, M.; Nasirizadeh, N.; Ashtari, K.; Naderi-Manesh, H. An electrochemical nanobiosensor for plasma miRNA-155, based on graphene oxide and gold nanorod, for early detection of breast cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yi, X.; Tang, H.; Han, H.; Wu, M.; Zhou, F. Direct quantification of MicroRNA at low picomolar level in sera of glioma patients using a competitive hybridization followed by amplified voltammetric detection. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6400–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouari, M.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Raouafi, N. Competitive RNA-RNA hybridization-based integrated nanostructured-disposable electrode for highly sensitive determination of miRNAs in cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labib, M.; Khan, N.; Ghobadloo, S.M.; Cheng, J.; Pezacki, J.P.; Berezovski, M.V. Three-mode electrochemical sensing of ultralow microRNA levels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 3027–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Campuzano, S.; López-Hernández, E.; Conzuelo, F.; Granados, R.; Sánchez-Puelles, J.M.; Pingarrón, J.M. Magnetobiosensors based on viral protein p19 for microRNA determination in cancer cells and tissues. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 24, 6168–6171. [Google Scholar]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Campuzano, S.; López-Hernández, E.; Granados, R.; Sánchez-Puelles, J.M.; Pingarrón, J.M. Direct Determination of miR-21 in Total RNA Extracted from Breast Cancer Samples Using Magnetosensing Platforms and the p19 Viral Protein as Detector Bioreceptor. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 2080–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Campuzano, S.; López-Hernández, E.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Barderas, R.; Granados, R.; Sánchez-Puelles, J.M.; Pingarrón, J.M. Simultaneous detection of two breast cancer-related miRNAs in tumor tissues using p19-based disposable amperometric magnetobiosensing platforms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Campuzano, S.; Farchado-Dinia, M.; Barderas, R.; San Segundo-Acosta, P.; Montoya, J.J.; Pingarrón, J.M. Fast Electrochemical miRNAs Determination in Cancer Cells and Tumor Tissues with Antibody-Functionalized Magnetic Microcarriers. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Campuzano, S.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Sagrera, A.; Domínguez-Cañete, J.J.; Granados, R.; Sánchez-Puelles, J.M.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical miRNAs Determination in Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Breast Tumor Tissues Association with HER2 Expression. JSM Biotechnol. Biomed. Bioeng. 2016, 3, 1064. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, W.; Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Fu, F. A novel electrically magnetic-controllable electrochemical biosensor for the ultrasensitive and specific detection of attomolar level oral cancer-related micro-RNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.Q.; Deng, H.M.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z.Q. A highly sensitive and selective electrochemical biosensor for direct detection of microRNAs in serum. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4784–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, B.; Liu, Y.; Tabata, M.; Zhu, H.; Miyahara, Y. Sensitive detection of microRNA by chronocoulometry and rolling circle amplification on a gold electrode. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9704–9706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Shen, B.; Yuan, R.; Cheng, W.; Xu, H.; Ding, S. An electrochemical biosensor for highly sensitive determination of microRNA based on enzymatic and molecular beacon mediated strand displacement amplification. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 756, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, D.-Z.; Cai, S.-X.; Chen, M.; Xia, Y.-K.; Wu, F.; Chen, J.-H. An immobilization-free electrochemical impedance biosensor based on duplex-specific nuclease assisted target recycling for amplified detection of microRNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.-F.; Jiang, N.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, L.; Chen, X.; Jiang, L.-P.; Abdel-Halim, E.S.; Zhu, J.-J. Target-triggered triple isothermal cascade amplification strategy for ultrasensitive microRNA-21 detection at sub-attomole level. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Campuzano, S.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Montoya, J.J.; Pingarrón, J.M. Sensitive electrochemical determination of miRNAs based on a sandwich assay onto magnetic microcarriers and hybridization chain reaction amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miodek, A.; Castillo, G.; Hianik, T.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. Electrochemical aptasensor of human cellular prion based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified with dendrimers: A platform for connecting redox markers and aptamers. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7704–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collinge, J. Prion diseases of humans and animals: Their causes and molecular basis. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 24, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Target-responsive DNA-capped nanocontainer used for fabricating universal detector and performing logic operations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Ji, H.; Sun, H.; Ding, C.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Label-free ratiometric electrochemical detection of the mutated apolipoprotein E. gene associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12080–12083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQuistan, A.; Zaitouna, A.J.; Echeverria, E.; Lai, R.Y. Use of thiolated oligonucleotides as anti-fouling diluents in electrochemical peptide-based sensors. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 4690–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, N.; Souza, E.; Ferreira, D.; Zanforlin, D.; Bezerra, W.; Borba, M.A.; Arruda, M.; Lopes, K.; Nascimento, G.; Martins, D.; et al. A Sensitive and Selective Label-Free Electrochemical DNA Biosensor for the Detection of Specific Dengue Virus Serotype 3 Sequences. Sensors 2015, 15, 15562–15577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.; Ryu, M.; Park, C.Y.; Ahn, J.; Park, H.G.; Choi, C.; Ha, S.-D.; Park, T.J.; Park, J.P. High sensitive and selective electrochemical biosensor: Label-free detection of human norovirus using affinity peptide as molecular binder. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Campuzano, S.; Halford, C.; Haake, D.A.; Wang, J. Ternary Surface Monolayers for Ultrasensitive (Zeptomole) Amperometric Detection of Nucleic Acid Hybridization without Signal Amplification. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8830–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; García, J.L.; García, E.; García, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Development of amperometricmagnetogenosensors coupled to asymmetric PCR for the specific detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 2413–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotillo, A.; Pedrero, M.; de Pablos, M.; García, J.L.; García, E.; García, P.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Mingorance, J.; Campuzano, S. Clinical evaluation of a disposable amperometric magneto-genosensor for the detection and identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 103, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, K.; Sekine, S.; Uenoyama, T.; Wada, M.; Ikeuchi, T.; Saito, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Tamiya, E. Quantitative detection for Porphyromonas gingivalis in tooth pocket and saliva by portable electrochemical DNA sensor linked with PCR. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 2686–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, K.E.; Mohan, R.; Patel, S.; Wong, P.K.; Hsieh, M.; Liao, J.C. Development of a Biosensor-Based Rapid Urine Test for Detection of Urogenital Schistosomiasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiruppathiraja, C.; Kamatchiammal, S.; Adaikkappan, P.; Santhosh, D.J.; Alagar, M. Specific detection of Mycobacterium sp. genomic DNA using dual labeled gold nanoparticle based electrochemical biosensor. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 417, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miodek, A.; Mejri, N.; Gomgnimbou, M.; Sola, C.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. E-DNA Sensor of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Based on Electrochemical Assembly of Nanomaterials (MWCNTs/PPy/PAMAM). Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9257–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heifets, L.B.; Cangelosi, G.A. Drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A neglected problem at the turn of the century [State of the Art]. Int. J. Tuber. Lung Dis. 1999, 3, 564–581. [Google Scholar]
- Matsishin, M.; Rachkov, A.; Errachid, A.; Dzyadevych, S.; Soldatkin, A. Development of impedimetric DNA biosensor for selective detection and discrimination of oligonucleotide sequences of the rpoB gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreda-García, S.; González-Álvarez, M.J.; de los Santos-Álvarez, N.; Palacios-Gutiérrez, J.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J. Attomolar quantitation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by asymmetric helicase-dependent isothermal DNA-amplification and electrochemical detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreda-García, S.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de los Santos Álvarez, N.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Comparison of isothermal helicase-dependent amplification and PCR for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by an electrochemical genomagnetic assay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 8603–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zribi, B.; Roy, E.; Pallandre, A.; Chebil, S.; Koubaa, M.; Mejri, N.; Magdinier Gomez, H.; Sola, C.; Korri-Youssoufi, H.; Haghiri-Gosnet, A.-M. A microfluidic electrochemical biosensor based on multiwall carbon nanotube/ferrocene for genomic DNA detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in clinical isolates. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 014115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.F.K.; Andrade, C.A.S.; de Melo, C.P.; Gomes, D.S.; Silva, L.G.; Dias, R.V.; Balbino, V.Q.; Oliveira, M.D.L. Impedimetric sensor for Leishmaniainfantum genome based on gold nanoparticles dispersed in polyaniline matrix. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 2810–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Baptista-Pires, L.; Serrano, L.; Altet, L.; Francino, O.; Sánchez, A.; Merkoçi, A. Magnetic Bead/Gold Nanoparticle Double-Labeled Primers for Electrochemical Detection of Isothermal Amplified Leishmania DNA. Small 2016, 12, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Electrode | Approach/Type of Hybridization Assay | Target miRNA/Disease | Electrochemical Technique/Redox Probe | L.R. | LOD | Applicability | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold disk electrode | Immobilization of a thiolated DNA probe/Direct competitive and complexation of the biotin-miRNA with Fc-capped AuNPs/streptavidin (Strep) conjugates | miRNA-182 | CV/Fc | 10 fM–2.0 pM | 10 fM | Sera of glioma patients | [31] |
| Magnetic-controllable gold electrode | Sandwich hybridization, ‘‘junction-probe’’ isothermal amplification strategy and MBs-based enzymatic amplification | hsa-miR-200a | Chronoamperometry/TMB + H2O2 | 1 aM–10 fM | 0.22 aM | Spiked saliva samples | [39] |
| AuNPs-modified SPCE | Immobilization of a thiolated RNA probe/Direct hybridization (1), p. 19 binding onto the RNA-RNA duplex formed on the electrode surface (2) and displacement of the p19 attached to the electrode by incubation in a mixture of a target miRNA and a nonthiolated RNA probe at high concentration | miRNA-21, miRNA-32, and miRNA-122 | SWV/K3[Fe(CN)6] and [Ru(NH3)6]Cl3 | 10 aM–1 μM | 5 aM | Human serum samples | [33] |
| Gold disk electrode | Immobilization of a thiolated DNA probe together with thioglycolic acid, direct hybridization and isothermal amplification by a DSN | miRNA let-7b | EIS/[Fe(CN)6]4−/3− | 2.0 fM–2.0 pM | 1.0 fM | Human serum samples | [40] |
| Three-electrode biosensor fabricated on a polystyrene substrate | Immobilization of a thiolated DNA probe (probe 1), MCH and BSA/Direct hybridization and RCA amplification using a mixture of the target miRNA, probe 2 (DNA added for initiation of RCA amplification), a cyclized padlock probe and phi29 DNA polymerase | miRNA-143/Cancer | Chronocoulometry/Ruhex | 100 fM–1 nM | 100 fM | Spiked human blood samples | [41] |
| Gold disk electrode | Immobilization of a molecular beacon, sandwich hybridization and mediated SDA (using Klenow fragment (3′–5′exo) and Nb.BbvCI nicking exonuclease) and enzymatic amplifications (Strep-AP) | miRNA-222 | DPV/α-NP | 50 pM–10 nM | 40 pM | Spiked human serum samples | [42] |
| Au-SPEs | Immobilization of a thiolated RNA probe/Direct | miRNA-155/ | SWV/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | 10 aM–1.0 nM | 5.7 aM | Human serum samples | [29] |
| GCE functionalized with AuNRs decorated on GO sheets | Immobilization of a thiolated RNA probe/Direct | miRNA-155 | DPV/Oracet Blue (OB) | 2.0 fM–8.0 pM | 0.6 fM | Spiked human plasma samples | [30] |
| Magnetic-GCE | DSNATR and biotinylated capture probes enriched from the solution to the electrode surface using MBs | miRNA-21 | EIS/[Fe(CN)6]4−/3− | — | 60 aM | Human serum samples | [43] |
| GCE | target recycling, nicking-replication reaction and DNAzyme catalysis coupling | miRNA-21 | Amperometry/TMB + H2O2 | 1 aM–100 pM | 0.5 aM | Spiked human serum samples | [44] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campuzano, S.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical Genosensing of Circulating Biomarkers. Sensors 2017, 17, 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040866
Campuzano S, Yáñez-Sedeño P, Pingarrón JM. Electrochemical Genosensing of Circulating Biomarkers. Sensors. 2017; 17(4):866. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040866
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampuzano, Susana, Paloma Yáñez-Sedeño, and José Manuel Pingarrón. 2017. "Electrochemical Genosensing of Circulating Biomarkers" Sensors 17, no. 4: 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040866
APA StyleCampuzano, S., Yáñez-Sedeño, P., & Pingarrón, J. M. (2017). Electrochemical Genosensing of Circulating Biomarkers. Sensors, 17(4), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040866