Abstract
This paper presents a novel CNN-based architecture, referred to as Q-Net, to learn local feature descriptors that are useful for matching image patches from two different spectral bands. Given correctly matched and non-matching cross-spectral image pairs, a quadruplet network is trained to map input image patches to a common Euclidean space, regardless of the input spectral band. Our approach is inspired by the recent success of triplet networks in the visible spectrum, but adapted for cross-spectral scenarios, where, for each matching pair, there are always two possible non-matching patches: one for each spectrum. Experimental evaluations on a public cross-spectral VIS-NIR dataset shows that the proposed approach improves the state-of-the-art. Moreover, the proposed technique can also be used in mono-spectral settings, obtaining a similar performance to triplet network descriptors, but requiring less training data.
1. Introduction
Over the last few years, the number of consumer computer vision applications has increased dramatically. Today, computer vision solutions can be found in video game consoles [1], smartphone applications [2], and even in sports—just to name a few. Furthermore, safety-critical computer vision applications, such as autonomous driving systems, are no longer science fiction.
Ideally, we require the performance of those applications, particularly those that are safety-critical to remain constant under any external environment factors, such as changes in illumination or weather conditions. However, this is not always possible or very difficult to obtain solely using visible imagery, due to the inherent limitations of the images from that spectral band. For that reason, the use of images from different or multiple spectral bands is becoming more appealing. For example, the Microsoft Kinect 2 uses a near-infrared-camera to improve the detection performance in low light or no light conditions.
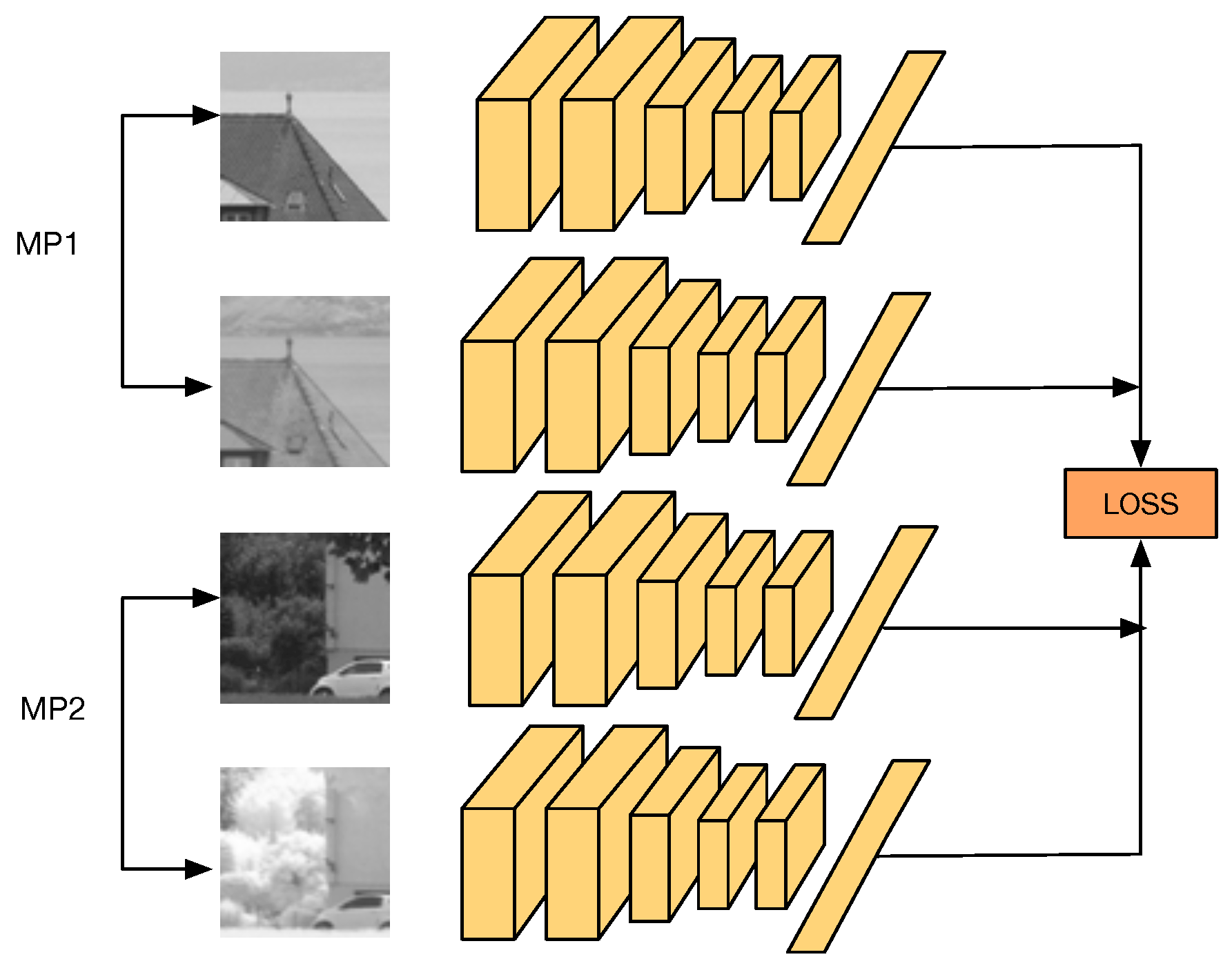
In this work, we are particularly interested in cross-spectral applications, i.e., computer-vision applications that make use of two different spectral bands to provide a richer representation of a scene, which otherwise could not be obtained from just one spectral band. We present a novel Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture, referred to as Q-Net, to learn local feature descriptors that are useful for matching image patches from two different spectral bands. Figure 1 shows an illustration of our proposal. The training network consists of four copies of the same CNN, i.e., weights are shared, which accepts as input two different cross-spectral image matching pairs (A matching pair consists of two image patches that show the same scene, regardless of the spectral band of the patches. On the contrary, a non-matching pair consists of two image patches that show two different scenes of the world). In the forward pass, the network computes several distances between the outputs of each CNN, obtaining the matching pair with the biggest distance and the non-matching pair with the smallest distance that will be later on used during the backpropagation step. This can be seen as always using the hardest cases of matching and non-matching pairs at each iteration. At testing, our network can be used as drop-in replacements for hand-made feature descriptors such as SIFT [3] in various cross-spectral tasks such as stereo-vision, object detection and image registration. It is important to notice that, during testing, it is just necessary for one of the four CNNs that were used during training. This CNN will act as a feature descriptor.
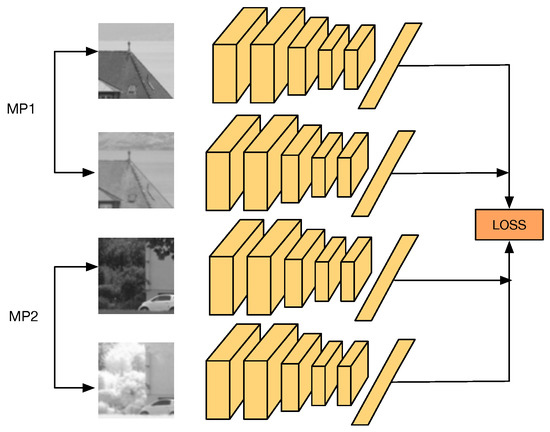
Figure 1.
The proposed network architecture. It consists of four copies of the same CNN that accepts as input two different cross-spectral correctly matched image pairs (MP1 and MP2). The network computes the loss based on multiples distance comparisons between the output of each CNN, looking for the matching pair with the biggest distance and the non-matching pair with the smallest distance. Both cases are then used for backpropagation of the network. This can be seen as positive and negative mining.
Our work is based on the recent success of the triplet network presented in [4], named PN-Net, but adapted to work with cross-spectral image pairs, where, for each matching pair, there are two possible non-matching patches—one for each spectrum. Results show that our technique is useful for learning cross-spectral feature descriptors that can be used as drop-in replacements of SIFT-like feature descriptors. Moreover, results also show that our network can be useful for learning local feature descriptors in the visible domain, with similar performance to PN-Net but requiring less training data.
In this article, we make the following contributions:
- We propose and evaluate three ways of using triplets for learning cross-spectral descriptors. Triplet networks were originally designed to work on visible imagery, so the performance on cross-spectral images is unknown.
- We propose a new training CNN-based architecture that outperforms the state-of-the-art in a public Visible and Near-Infrared (VIS-NIR) cross-spectral image pair dataset. Additionally, our experiments show that our network is also useful for learning local feature descriptors in the visible domain.
- Fully trained networks and source code are publicly available at [5].
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we give a short description of near-infrared images and the VIS-NIR cross-spectral dataset used to train and evaluate our work; differences between visible and infrared images are highlighted. Additionally, Section 2 also presents an overview of hand-made cross-spectral descriptors and CNN-based visible spectrum descriptors. The PN-Net triplet network is described in Section 3, introducing the motivations behind the proposed technique, which are presented in Section 4. Finally, in Section 5, we show the validity of our proposal through several experiments, ending with the conclusions in Section 6.
2. Background and Related Work
This section briefly introduces the near-infrared spectral band and highlights similarities and differences between images from this spectrum with respect to the visible spectrum. Additionally, the VIS-NIR cross-spectral image dataset used as a case study through the different sections of this manuscript is also presented. Finally, the most important methods proposed in the literature to describe images from two different spectral bands are reviewed, together with current CNN-based descriptor approaches used to describe images in the visible spectrum.
2.1. Near-Infrared Band
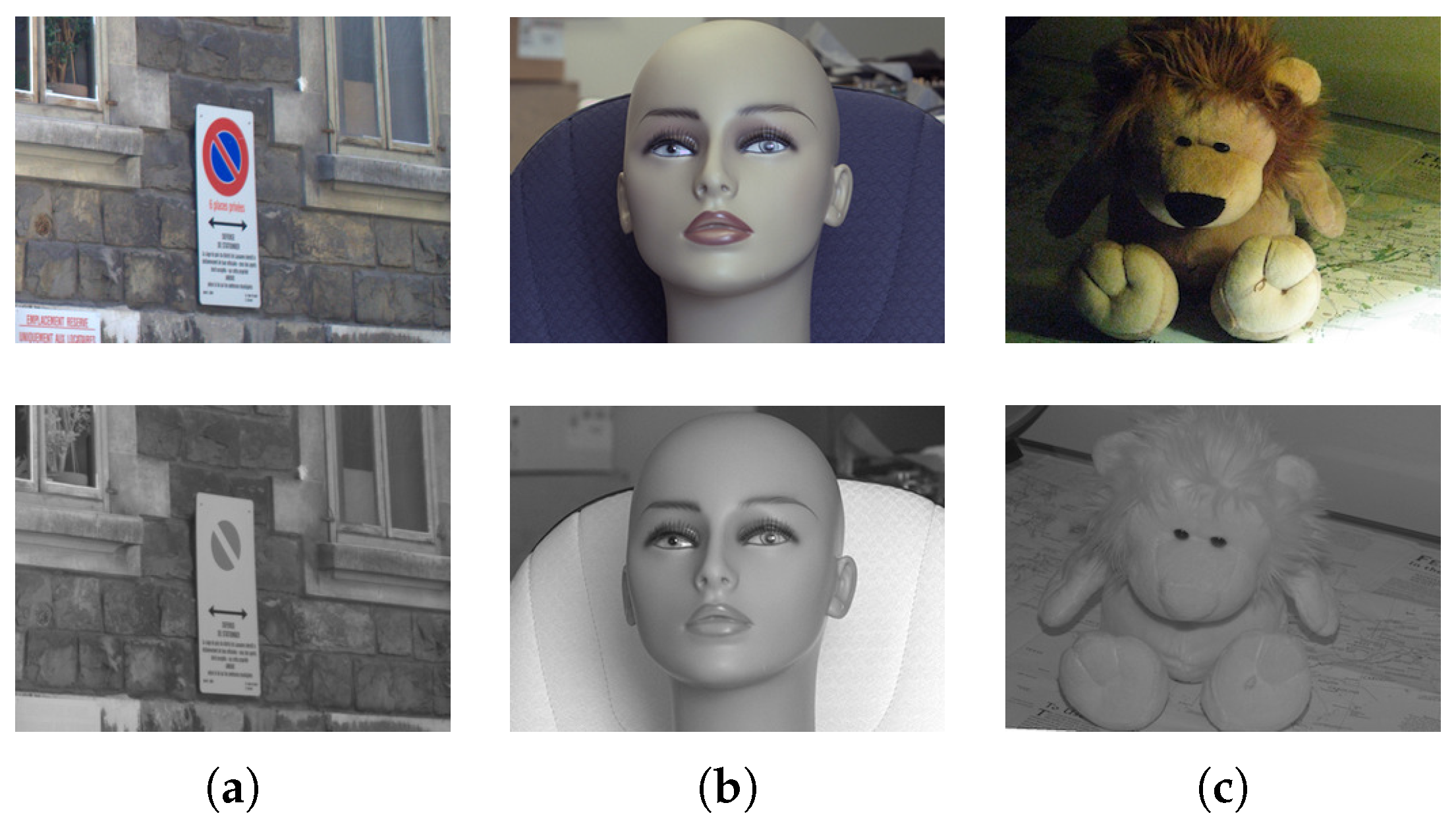
The near-infrared band (NIR: 0.7–1.4 m) is one of the five sub-bands of the infrared spectrum (0.7–1000 m). It is the closest infrared sub-band to the visible spectrum and images from both spectral bands share several visual similarities; in Figure 2, three pairs of VIS-NIR images are presented. It can be appreciated that images from both spectra are visually similar but with some notable differences. For example, red visible regions disappear in NIR images (see Figure 2a), the direction of the gradients can change (as in Figure 2b), and NIR images are more robust to different illumination settings (as in Figure 2c).

Figure 2.
VIS-NIR cross-spectral image pairs; top images are from the visible spectrum and bottom images from the near-infrared spectrum.
Recent advances in technology have made infrared imaging devices affordable for classical computer vision problems, from face recognition ([6]) to medical imaging ([7]). In some of these cases, infrared images are not used alone but in conjunction with images from other spectral bands (e.g., visible spectra). In these cases, infrared images need to be used in a framework that allows them to be handled in an efficient way in terms of the heterogeneity of the information ([8]), which is the main challenge to be solved and the motivation for current work.
2.2. Dataset
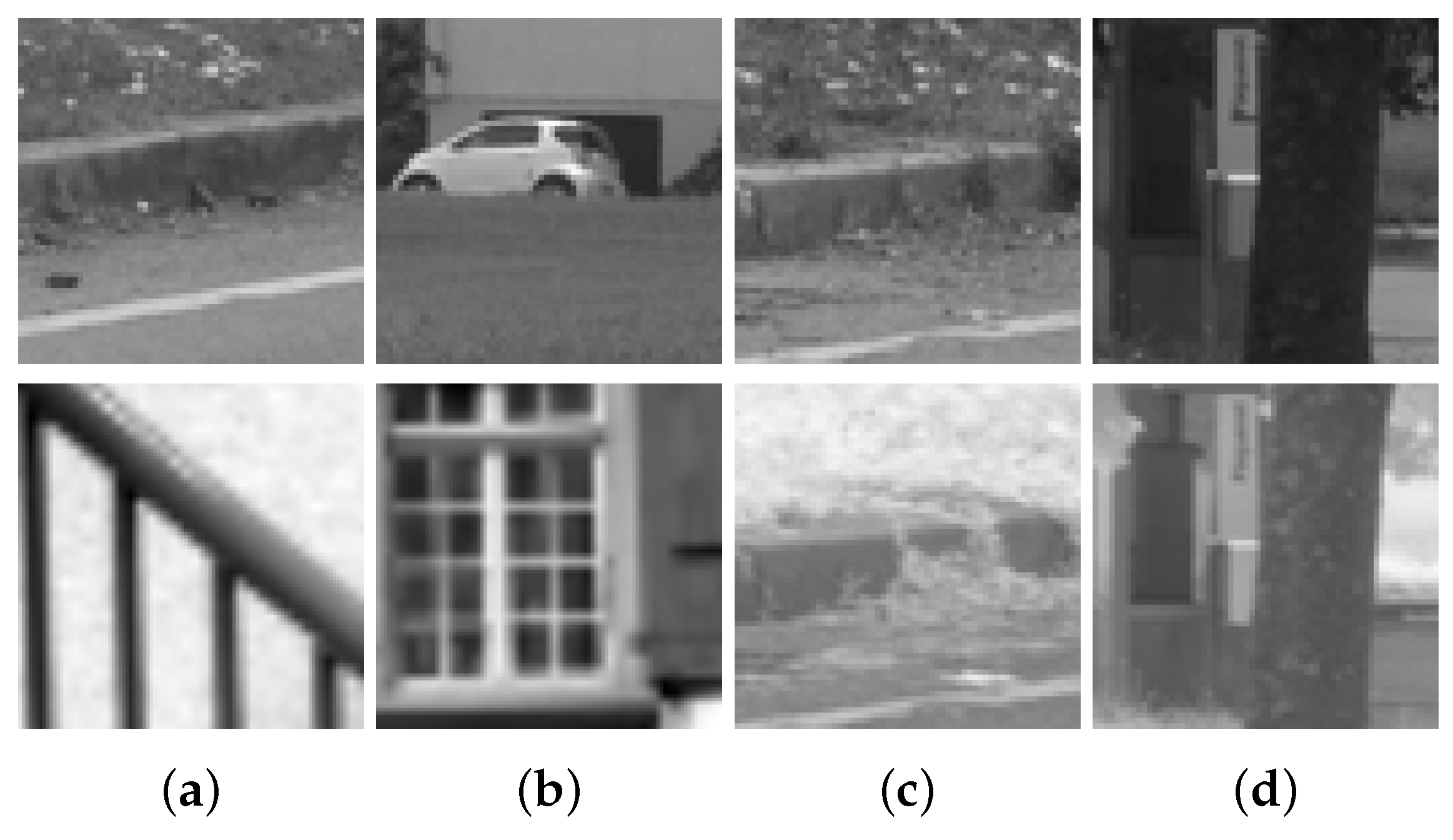
The dataset used in [9] has been considered in the current work to train and validate the proposed network. This dataset has been obtained from [10] and consists of more than 1 million VIS-NIR cross-spectral image pairs divided into nine different categories. Table 1 shows the distributions of patches for the different categories. Each image pair consists of two images of 64 × 64 pixels, one NIR and one visible in grayscale format. Finally, the number of matching and non-matching pairs is the same, so half of the samples correspond to correctly matched cross-spectral pairs and the other half to non-matching pairs (Matching and non-matching pairs belong to the same category. The dataset does not contain cross-category pairs). Figure 3 shows four samples of cross-spectral image pairs from the dataset.

Table 1.
Shows the number of cross-spectral image pairs per category on the VIS-NIR patch dataset used to train and evaluate our work.
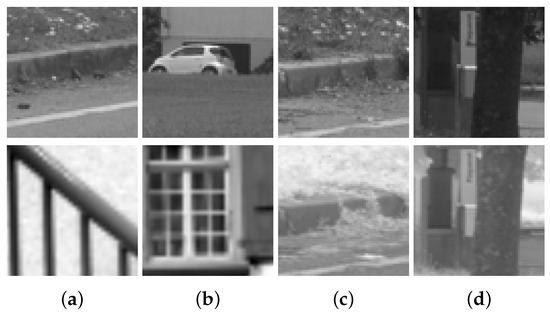
Figure 3.
Image patches from the VIS-NIR training set. The first row corresponds to grayscale images from the visible spectrum; and the second row to NIR images. (a,b): non-matching pairs; (c,d): correctly matched pairs.
2.3. Cross-Spectral Descriptors
The description of two images from two different spectral bands in the same way is a challenging task that cannot always be solved with classical feature descriptors such as SIFT ([3]) or SURF ([11]), due to the non-linear intensity variations that may exist between images from two different spectral bands. Early efforts focused on modifying gradient-based descriptors to work between instead of to reduce the effect of changes in the gradient direction between images from two different spectral bands. For example, Refs. [12,13] applied this strategy to SIFT and HOG, respectively, the first to match VIS-NIR local features and the second to compute the stereo disparity between a VIS and a thermal infrared camera. Although this strategy is simple, it improves the performance of those algorithms in cross-spectral scenarios.
Other works are based on the observations of [14]. In this study, concerning the joint statistics of visible and thermal images, the authors found a strong correlation between object boundaries of images from both spectra, i.e., texture information is lost and edge information remains similar between images from the different spectral bands. Ref. [15] describes cross-spectral image patches using a local version of the global EHD descriptors, focusing more on the information provided by the edges rather than in image texture. In a similar way, Refs. [16,17] compute cross-spectral features using the EHD algorithm over the image patch response to different Log-Gabor filters.
In a more recent work, Ref. [9] tested different CNN-based networks to measure the similarity between images from the VIS-NIR and the VIS-LWIR spectra. In their experiments, they showed that CNN-based networks can outperform the state-of-the-art in terms of matching performance. However, with regard to speed, their networks are much slower than classical solutions, a problem that we address in the current work, training a cross-spectral descriptor that can be used as a replacement of SIFT and many other -based descriptors.
It is important to note that many methods that are not based on the use of feature descriptors have been proposed in the literature to match images from different spectral bands. For example, Ref. [18] proposes a non-rigid visible and infrared face registration technique based on the Gaussian field criterion, and Ref. [19] uses a dense matching strategy based on variational approaches to match different multi-modal images.
2.4. CNN-Based Feature Descriptor Approaches
During the last decades, carefully hand-made feature descriptors, such as SIFT or SURF, have been popular in the computer vision community. However, in the last few years, such approaches have started to be outperformed by CNN-based solutions in different feature descriptors benchmarks (e.g., [4,20,21]). Ref. [20] proposes a max–margin criterion over a siamese network to compute the similarity between two different image patches. Ref. [21] follows a similar approach, but instead of using a metric network, it directly minimizes the distance between the descriptor of two images in the loss function, making their trained descriptor a drop-in replacement to SIFT-like descriptors. More importantly, it notices that after a few training epochs, most of the non-matching samples used to train the network were not giving new information, making it necessary to use mining strategies to improve the performance of the networks. In the same way, Ref. [4] proposes a triplet network to mine negative samples with each input triplet, improving the performance of siamese networks.
The current works are strongly based on the triplet network proposed by [4], but adapted to be used in cross-spectral image pairs. We use quadruplets instead of triplets, and we do not only mine non-matching samples but also correctly matched samples. In Section 3 and Section 4, both architectures are detailed.
Notice that, in this review, we only include CNN-based feature descriptors that can be used as a replacement for common hand-made descriptors, since they are useful for real-time applications. Other solutions have been proposed skipping the process of description and matching, doing everything with a CNN and trading matching performance for speed—for example, the 2ch network from [20], MatchNet from [22] and the siamese network from [23].
3. PN-Net (Triplet Network)
In this section, we describe the architecture of PN-Net ([4]), a state-of-the-art triplet network for learning local features descriptors. Although PN-Net was not intended to be used as a network for learning cross-spectral descriptors, we propose three ways to use PN-Net in such settings. In summary, this section objective is twofold:
- As previously stated, our network is similar to the triplet network but specifically designed to learn cross-spectral local feature descriptors. A brief description of this network will help to set the basis of our proposal in Section 4.
- We explain the motivation behind our proposal through several experiments. After training PN-Net to learn cross-spectral feature descriptors, we discovered that the network performance improved when we randomly alternated between non-matching patches from both spectra.
3.1. PN-Net Architecture
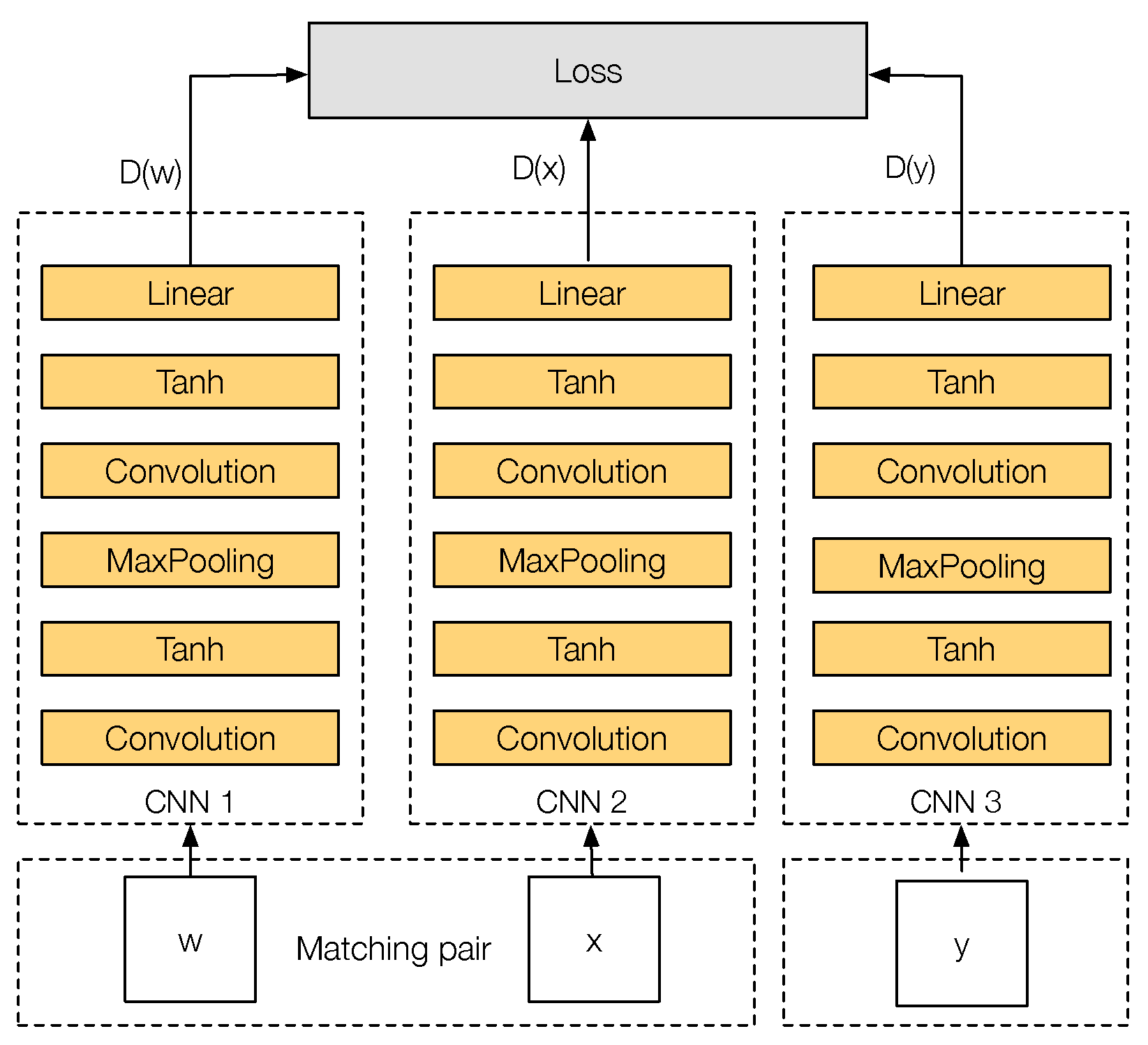
Figure 4 shows the training architecture of PN-Net. The network has three inputs, where each input corresponds to a different image patch. Formally, the input is a tuple , where w and x are two matching image patches and y is a non-matching image patch to w and x. Each one of these patches will feed one of the three CNN towers that the network has: CNN 1, CNN 2 and CNN 3. The three CNN towers of the network share the same parameters during the entire training stage. Finally, the output of each tower will be a descriptor D of configurable size that describes each input patch.
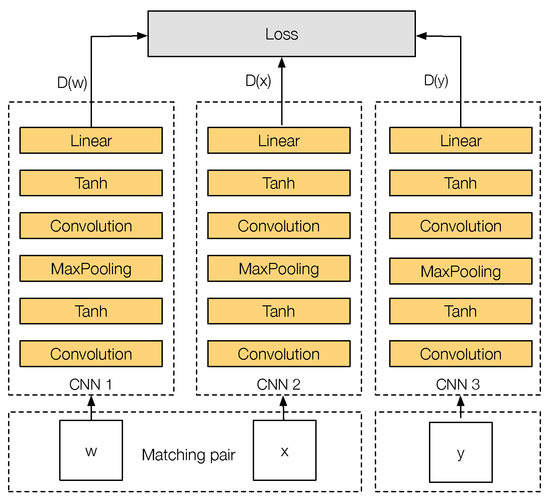
Figure 4.
PN-Net training triplet architecture.
3.2. PN-Net Loss
The loss function is described as follows:
where corresponds to the distance between the descriptors of the matching pair w and x, ; corresponds to the distance between the descriptors of the non-matching pair w and y, ; and corresponds to the distance between the descriptors of the second non-matching pair x and y, .
In essence, the objective of the loss function is to penalize small distances between non-matching pairs, and large distances between matching pairs. Ideally, we want to be equal to zero and to be equal to one, i.e, . Computing the minimum distances between the non-matching pairs is a type of mining strategy, were the network always performs backpropagation using the hardest non-matching sample of each triplet T, i.e, the non-matching sample with the smallest distance. The mining strategy is used to avoid the problems described in [21] and mentioned in Section 2. Finally, the MSE is used to penalize values of different than zero and values of different than one.
3.3. Cross-Spectral PN-Net
One key difference between mono-spectral and cross-spectral image pairs is that, for each cross-spectral matching pair, we have two non-matching possible image patches—one for each spectrum. Thus, the question is, which image patch do we use as y? We propose three simple and naive solutions: (i) y is an RGB non-matching image; (ii) y is an NIR non-matching image and (iii) y is randomly chosen between RGB and NIR.
We test each one of the aforementioned solutions in the dataset used in [9] and presented in Section 2 . We train each network nine times, once per category and tested on the other eight categories. In Table 2, we present our results in terms of the false positive rate at Recall (FPR95). In essence, we evaluate how well the descriptors can distinguish between correct and incorrect matches. Results show that randomly using y between an NIR and RGB patch was better than the other two solutions. This gives us a hint that using images from both spectra to mine the network is better than using images just from one, which we expected, assuming that a balanced number of non-matching images from both spectra will help to produce better results.

Table 2.
Average FPR95 for each category.
The motivations behind our quadruplet network are straightforward. As stated before, for each cross-spectral matching pair, we have at least two non-matching patches from another spatial location, each one from one of the spectra to be trained. Similar to triplets, we propose Q-Net, a quadruplet network for learning cross-spectral feature descriptors.
3.4. Q-Net Architecture
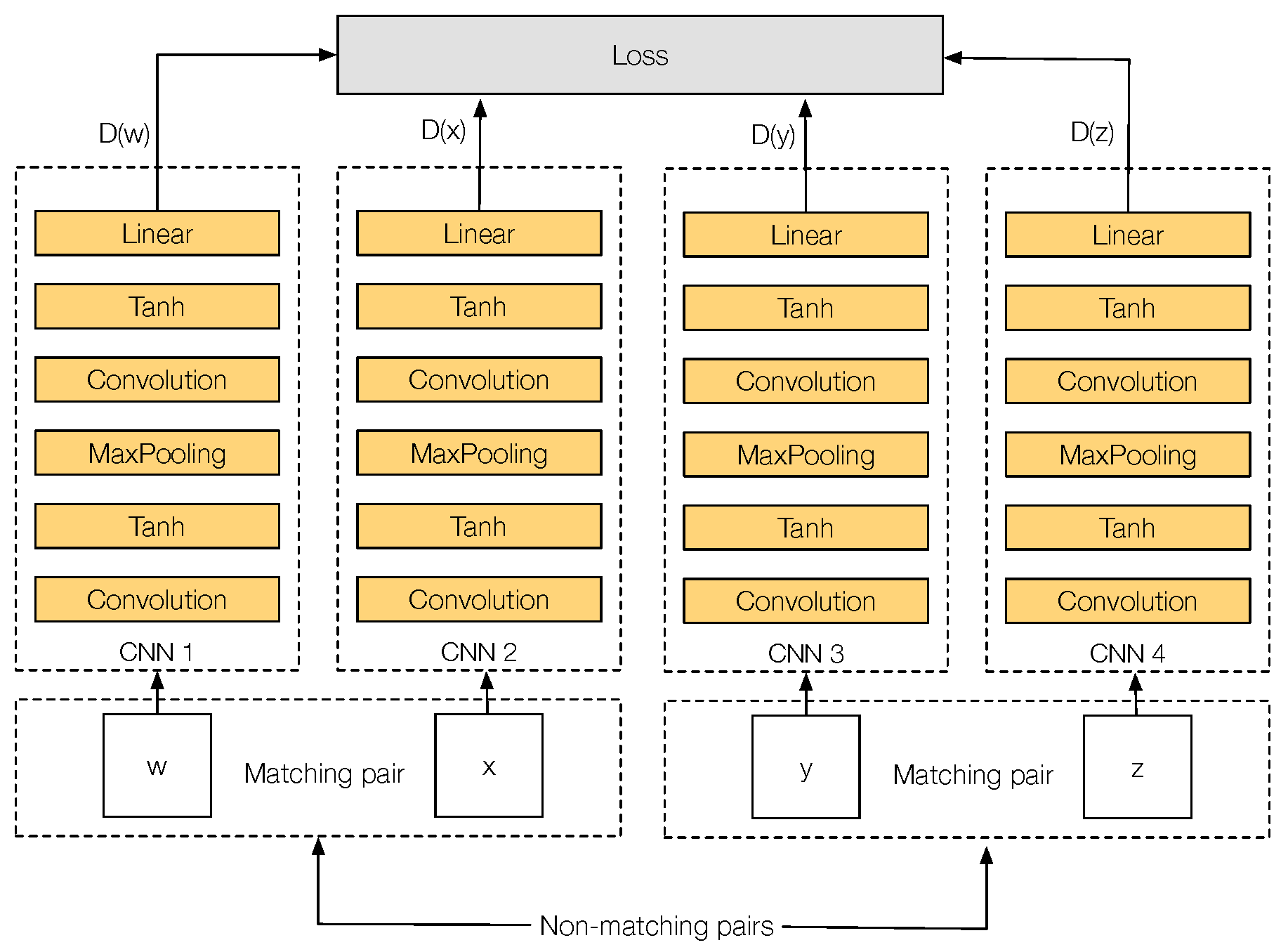
The architecture of Q-Net is similar to PN-Net, but using four copies of the same network instead of three (see Figure 5). The input is a tuple Q, with four different input patches , which is formed by two different cross-spectral matching pairs: (w, x), and (y, z), allowing the network to mine not just non-matching cross-spectral image pairs at each iteration, but also cross-spectral correctly matched pairs.
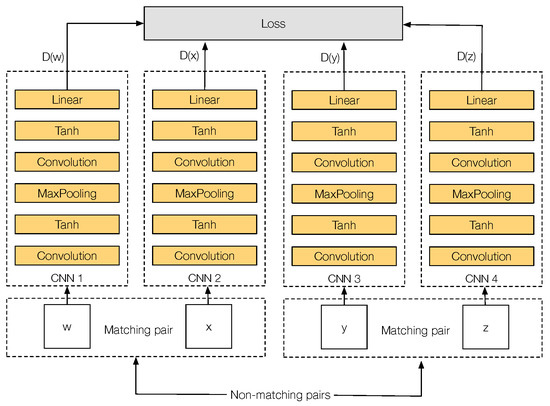
Figure 5.
Q-Net training quadruplet architecture.
4. Q-Net
4.1. Q-Net Loss
Q-Net loss function extends the mining strategy from PN-Net presented in Section 3.2. Specifically, we add two more distance comparisons to , making the loss suitable for cross-spectral scenarios, and we extend the mining strategy from the non-matching pairs to the correctly matched pairs. At each training step, the network uses the matching pair with larger distance and the non-matching pair with the smallest distance. The loss function is described as follows:
where corresponds to the distance between the descriptors of the matching pair w and x, ; corresponds to the distance between the descriptors of the matching pair y and z, ; corresponds to the distance between the descriptors of the non-matching pair w and y, ; corresponds to the distance between the descriptors of the non-matching pair x and y, ; corresponds to the distance between the descriptors of the non-matching pair w and z, ; and corresponds to the distance between the descriptors of the non-matching pair x and z, .
The proposed loss function takes into account all the possible non-matching combinations. For example, if we want to train a network to learn similarities between the VIS and the NIR spectral bands, will compare two VIS-NIR non-matching pairs: one VIS-VIS non-matching pair and one NIR-NIR non-matching pair, instead of using a random function as we did with PN-Net. Moreover, since we are trying to learn a common representation between the NIR and the VIS, comparing VIS-VIS and NIR-NIR cases helps the network to have more training examples. Since it is necessary to have two cross-spectral matching pairs to compute , it was natural to extend the mining strategy to , obtaining at each step the cross-spectral matching pair with the larger distance.
Our method allows for learning cross-spectral distances, mining positives and negatives samples at the same time. This approach can also be used in monospectral scenarios, providing a more efficient mining strategy than previous works. Results that support our claim are presented in the next section. More importantly, our method can be extended to other cross-spectral or cross-modality scenarios. Even more, it can be extended to other applications such as heterogeneous face recognition, where it is necessary to learn distance metrics between faces from different spectral bands.
5. Experimental Evaluation
In this section, we evaluate the performance of the proposed Q-Net on (1) the VIS-NIR dataset introduced in Section 2.2; and (2) the VIS standard benchmark for feature descriptors from [24]. The performance, in both cases, is measured using the FPR95 as in Section 3.
5.1. VIS-NIR Scene Dataset
In this section, we evaluate the performance of our network on the VIS-NIR dataset presented in Section 2. As in [9], we train on the country sequence and test in the remaining eight categories.
Training: Q-Net and PN-Net networks were trained using Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) with a learning rate of 1.1, weight decay of 0.0001, batch size of 128, momentum of 0.9 and learning rate decay of 0.000001. Trained data was shuffled at the beginning of each epoch and each input patch was normalized to its mean intensity. The trained data was split into two, where 95% of the data was used as training data and 5% as validation. Training was performed with and without data augmentation (DA), where the augmented data was obtained by flipping the images vertically and horizontally, and rotating the images by 90, 180 and 270 degrees. Each network was trained ten times to account for randomization effects in the initialization. Lastly, we used a grid search strategy to find the best parameters.
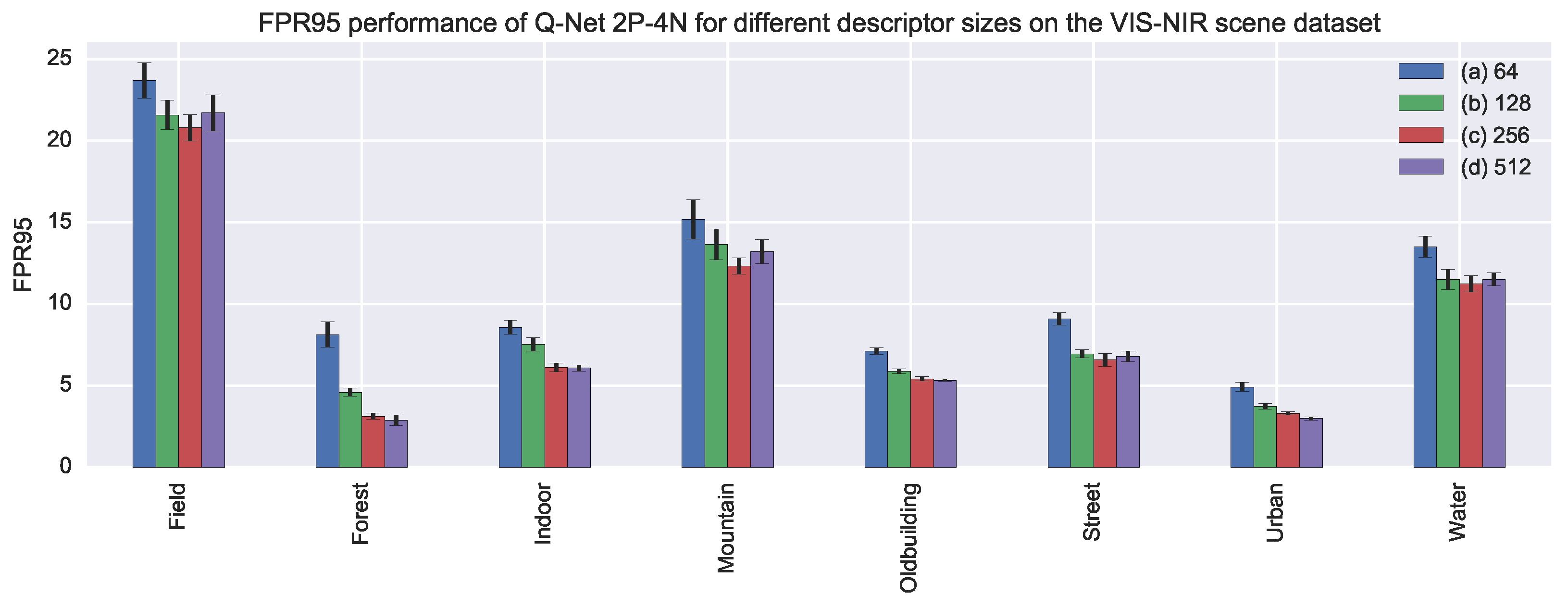
Model details: Model details are described in Table 3. The layers and parameters are the same from [4], which, after several experimental results, proved to be suitable for describing cross-spectral patches. Notice that, for feature description, shallow models are suitable, since lower layers are more general than the upper ones. The descriptor size was obtained through experimentation. We tested the performance when different descriptor sizes were used. Figure 6 shows the results of our experiment. From the figure we can see that there is a gain in increasing the descriptor size until 256. Descriptor sizes bigger than 256 did not perform better.

Table 3.
Q-Net layer descriptions.
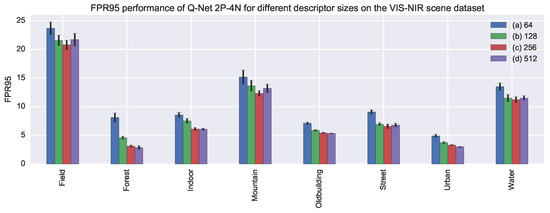
Figure 6.
FPR95 performance on the VIS-NIR scene dataset for Q-Net 2P-4N using different descriptor sizes ((a) 64; (b) 128; (c) 256 and (d) 512). Shorter bars indicate better performances. On top of the bars, standard deviation values are represented with segments.
Software and hardware: All the code was implemented using the Torch framework ([25]). The GPU consisted of an NVIDIA Titan X and the network was trained in between five and ten hours when we used data augmentation.
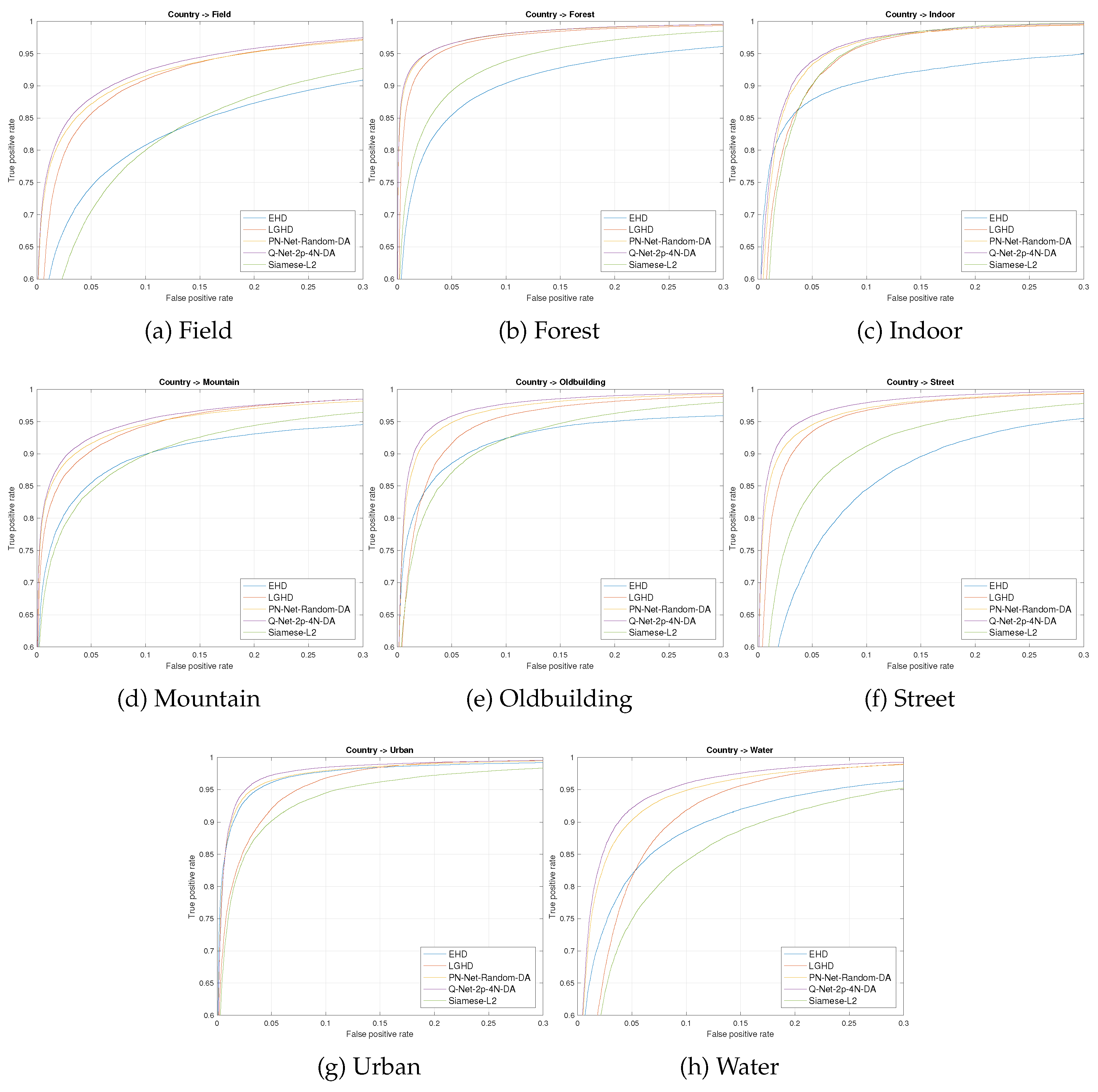
Results are shown in Table 4. Firstly, we evaluated EHD ([15]) and LGHD ([17]), two hand-made descriptors that were used as a baseline in terms of matching performance. The performance of LGHD is under 10% and can be considered as state-of-the-art results before the current work. Secondly, we test a siamese network based on the work of [20] that performs better than EHD, but worse than the state-of-the-art. Thirdly, PN-Net and its variant were tested, not being able to surpass the performance of LGHD without using data augmentation. In the other case, Q-Net proved to be better than the state-of-the-art even without data augmentation, showing the importance of mining on the non-matching and matching samples in cross-spectral scenarios. Additionally, we tested our model increasing the training data using the previously detailed data augmentation technique, improving the state-of-the-art by 2.91%. For a more detailed comparison of the different feature descriptors evaluated in the current work, we provide the corresponding Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves in Figure 7.

Table 4.
FPR95 performance on the VIS-NIR scene dataset. Each network, i.e., siamese-L2, PN-Net and Q-Net, were trained in the country sequence and tested in the other eight sequences as in [9]. Smaller results indicate better performance. In brackets, the standard deviation is provided.
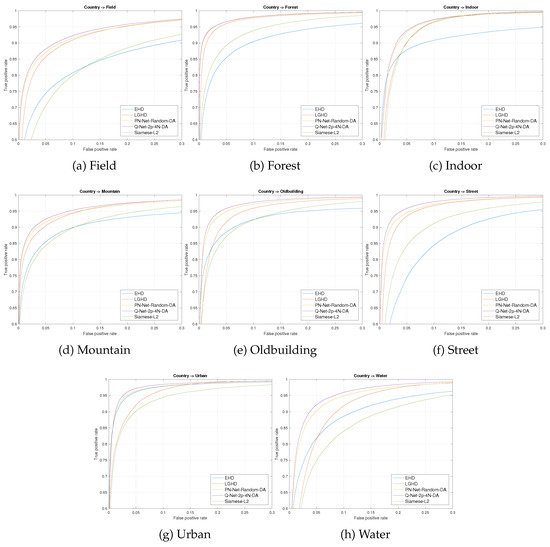
Figure 7.
ROC curves for the different descriptors evaluated on the VIS-NIR dataset. For Q-Net and PN-Net, we selected the network with the best performance. Each subfigure shows the result in one of eight tested categories of the dataset.
In addition, we tested the performance when different descriptor sizes were used. Figure 6 shows the results of our experiment. From the figure, we can see that there is a gain in increasing the descriptor size until 256. Descriptor sizes bigger than 256 did not perform better.
5.2. Multi-View Stereo Correspondence Dataset
Although the proposed approach has been motivated to tackle the cross-spectral problem, in this section, we evaluate the proposed architecture when a visible spectrum dataset is considered. This is intended to evaluate the validity of the proposed approach in classical scenarios.
For the evaluation, we used the multi-view stereo correspondence dataset from [24], which is considered a standard benchmark for testing local feature descriptors in the visible domain (e.g., [4,20,21,22]). The dataset contains more than 1.2 million patches of size 64 × 64 divided into three different sets: Liberty, Notredame and Yosemite, where each image patch was computed from Difference of Gaussian (DOG) maxima. We followed the standard protocol of evaluation, training our network three times, one at each sequence, and testing the FPR95 in the remaining two sequences. In our evaluation, we compared our model against two other learned descriptors, the first from [20] and the second from [4]; which can be considered state-of-the-art.
Training. Quadruplet networks were trained using Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) with a learning rate of 0.1, weight decay of 0.0001, batch size of 128, momentum of 0.9 and learning rate decay of 0.000001. Trained data was shuffled at the beginning of each epoch and each input patch was normalized using zero-mean and unit variance. We split up each training sequence into two sets, where 80% of the data was used as training data and the 20% left as validation data. We used the same software and hardware from the previous experiment. As in the previous experiment, Q-Net and PN-Net networks were trained ten times to account for randomization effects in the initialization.
Table 5 shows the results of our experiments. Q-Net and PN-Net performed better than the siamese-L2 network proposed by [20], which is an expected result, since the siamese-L2 network was not optimized for comparison during training as the other two networks were. Q-Net performed better than PN-Net by a small margin but using much less training data. When comparing both techniques with the same amount of data, the difference becomes bigger—meaning that our network needs less data to train than PN-Net, i.e., Q-Net needs less training data than PN-Net and it converges more quickly.

Table 5.
Matching results in the multi-view stereo correspondence dataset. Evaluations were made on the 100 K image pairs’ ground truth recommended from the authors. Results correspond to FPR95. The smallest results indicate better performance. The standard deviation is provided in brackets.
Regarding training time, both networks perform similarly. In our experiments, PN-Net was about 9% faster than Q-Net when both networks where trained with the same amount of patches. In essence, the improved accuracy performance of Q-Net is related to a small loss in training speed.
6. Conclusions
This paper presents a novel CNN-based architecture to learn cross-spectral local feature descriptors. Experimental results with a VIS-NIR dataset showed the validity of the proposed approach, improving the state-of-the-art by almost 3%. The experimental results showed that the proposed approach is also valid for training local feature descriptors in the visible spectrum, providing a network with similar performance to the state-of-the-art, but requiring less training data.
Future work might consider using the same architecture for different cross-spectral applications such as heterogeneous face recognition.
Acknowledgments
This work has been partially supported by the Spanish Government under Project TIN2014-56919-C3-2-R and the Chilean Government under project Fondef ID14I10364. Cristhian A. Aguilera has been supported by Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona.
Author Contributions
The work presented here was carried out in collaboration between all authors. Cristhian A. Aguilera and Angel D. Sappa defined the research topic and implementation. Cristhian Aguilera provided resources to carry out the experiments and helped to edit the manuscript with Ricardo Toledo.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, Z. Microsoft Kinect Sensor and Its Effect. IEEE MultiMedia 2012, 19, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.W.; Lane, N.D.; Chen, F.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Bao, T.J.; Montes-de Oca, M.; Cheng, Y.; Lin, M.; Torresani, L.; et al. CarSafe app: Alerting drowsy and distracted drivers using dual cameras on smartphones. Proceeding of the 11th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services (ACM 2013), Taipei, Taiwan, 25–28 June 2013; pp. 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balntas, V.; Johns, E.; Tang, L.; Mikolajczyk, K. PN-Net: Conjoined Triple Deep Network for Learning Local Image Descriptors. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1601.05030. [Google Scholar]
- Github. Qnet. Available online: http://github.com/ngunsu/qnet (accessed on 15 April 2017).
- Yi, D.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Shared representation learning for heterogenous face recognition. Proceeding of the 2015 11th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 4–8 May 2015; Volume 1, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ring, E.; Ammer, K. The technique of infrared imaging in medicine. In Infrared Imaging; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Klare, B.F.; Jain, A.K. Heterogeneous face recognition using kernel prototype similarities. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, C.A.; Aguilera, F.J.; Sappa, A.D.; Aguilera, C.; Toledo, R. Learning cross-spectral similarity measures with deep convolutional neural networks. Proceeding of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.; Susstrunk, S. Multi-spectral SIFT for scene category recognition. Proceeding of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, H.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Surf: Speeded up robust features. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 404–417. [Google Scholar]
- Firmenichy, D.; Brown, M.; Süsstrunk, S. Multispectral interest points for RGB-NIR image registration. Proceeding of the 2011 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Brussels, Belgium, 11–14 September 2011; pp. 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Pinggera, P.; Breckon, T.; Bischof, H. On Cross-Spectral Stereo Matching using Dense Gradient Features. Proceeding of the British Machine Vision Conference, Surrey, UK, 3–7 September 2012; pp. 526.1–526.12. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, N.J.W.; Avidan, S.; Matusik, W.; Pfister, H. Statistics of Infrared Images. Proceeding of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 18–23 June 2007; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, C.; Barrera, F.; Lumbreras, F.; Sappa, A.; Toledo, R. Multispectral image feature points. Sensors 2012, 12, 12661–12672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouats, T.; Aouf, N.; Sappa, A.D.; Aguilera, C.; Toledo, R. Multispectral Stereo Odometry. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 16, 1210–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, C.A.; Sappa, A.D.; Toledo, R. LGHD: A feature descriptor for matching across non-linear intensity variations. Proceeding of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Ma, Y.; Tian, J. Non-rigid visible and infrared face registration via regularized Gaussian fields criterion. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jia, J. Multi-modal and Multi-spectral Registration for Natural Images. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 309–324. [Google Scholar]
- Zagoruyko, S.; Komodakis, N. Learning to compare image patches via convolutional neural networks. Proceeding of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4353–4361. [Google Scholar]
- Simo-Serra, E.; Trulls, E.; Ferraz, L.; Kokkinos, I.; Fua, P.; Moreno-Noguer, F. Discriminative Learning of Deep Convolutional Feature Point Descriptors. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 13–16 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Leung, T.; Jia, Y.; Sukthankar, R.; Berg, A.C. MatchNet: Unifying Feature and Metric Learning for Patch-Based Matching. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zbontar, J.; LeCun, Y. Stereo matching by training a convolutional neural network to compare image patches. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2016, 17, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Winder, S.; Hua, G.; Brown, M. Picking the best DAISY. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2009), Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 178–185. [Google Scholar]
- Collobert, R.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Farabet, C. Torch7: A matlab-like environment for machine learning. In Proceedings of the BigLearn, NIPS Workshop, Granada, Spain, 12–17 December 2011. Number EPFL-CONF-192376. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).