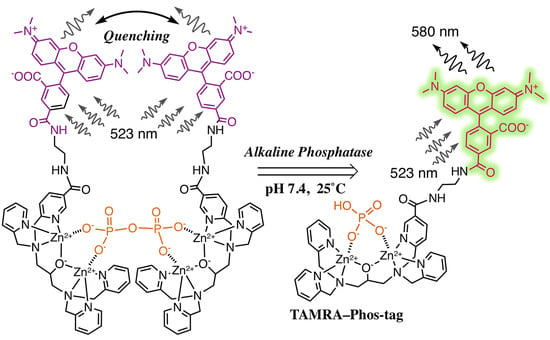
TAMRA/TAMRA Fluorescence Quenching Systems for the Activity Assay of Alkaline Phosphatase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Preparation of TAMRA-labeled Derivatives
2.4. Fluorescence Aanalysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of 5-TAMRA-Labeled Derivatives
3.2. Characteristics of the Phos-Tag-Based Fluorescence-quenching System
3.3. Real-Time Analysis of Dephosphorylation of TAMRA-PEA by Aalkaline Phosphatase
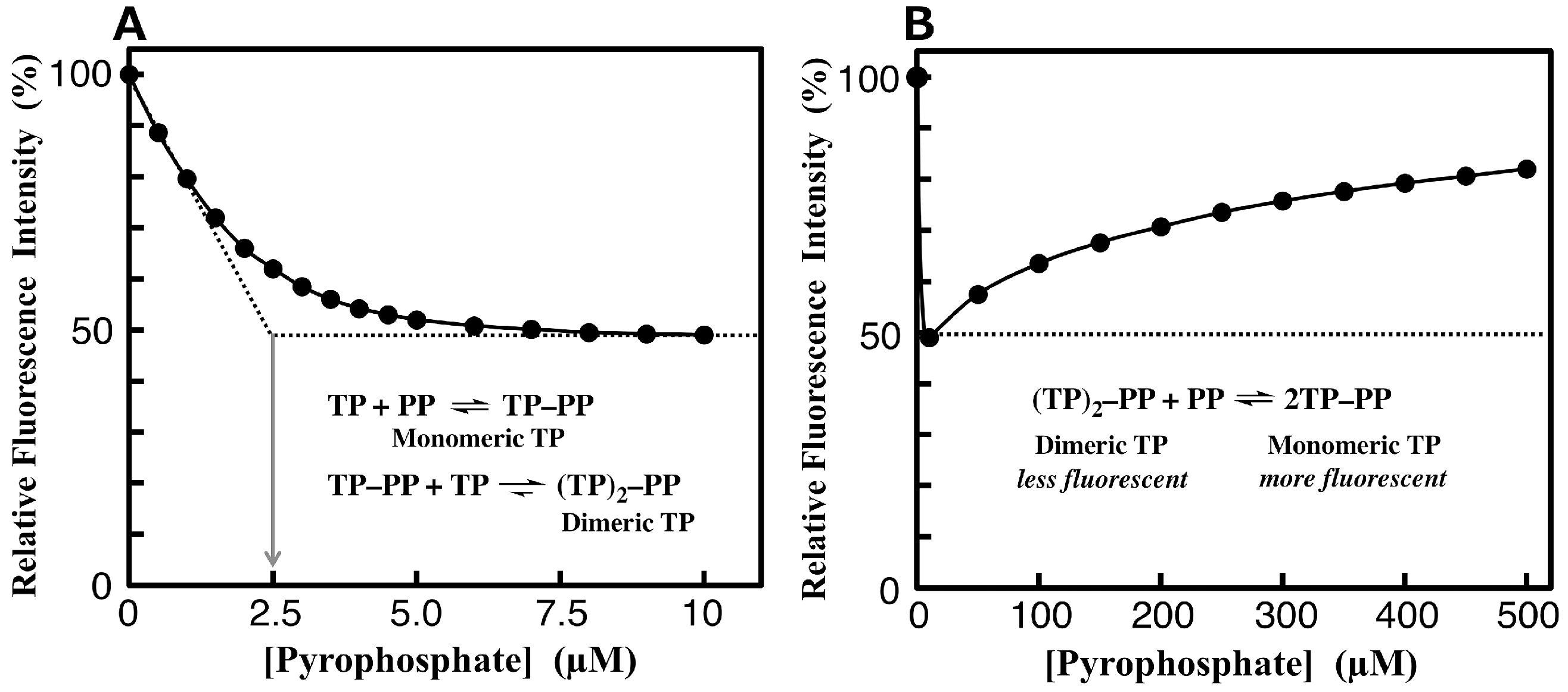
3.4. Fluorimetric Aanalysis of Pyrophosphate by Using TAMRA-Phos-tag
3.5. Phosphatase-Inhibitor Profiling by Using TAMRA-Phos-tag and Pyrophosphate
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Coleman, J.E. Structure and Mechanism of Alkaline Phosphatase. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1922, 21, 441–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millán, J.L. Alkaline Phosphatases: Structure, Substrate Specificity and Functional Relatedness to Other Members of a Large Superfamily of Enzymes. Purinergic Signal. 2006, 2, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, E.G.; Testa, R.; Savarino, V. Liver Enzyme Alteration: A Guide for Clinicians. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2005, 172, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinghen, S.T.; Moura, J.F.; Zancanella, P.; Rodrigues, G.A.; Pianovski, M.A.; Lalli, E.; Arnold, D.L.; Minozzo, J.C.; Callefe, L.G.; Ribeiro, R.C.; et al. Specific Immunoassays for Placental Alkaline Phosphatase as a Tumor Marker. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2006, 2006, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernley, H.N.; Walker, P.G. Kinetic Behaviour of Calf-intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase with 4-Methylumbelliferyl Phosphate. Biochem. J. 1965, 97, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, D. A New Fluorometric Turn-on Assay for Alkaline Phosphatase and Inhibitor Screening Based on Aggregation and Deaggregation of Tetraphenylethylene Molecules. Analyst 2013, 138, 2427–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.N.; Raines, R.T. Sensitive Fluorogenic Substrate for Alkaline Phosphatase. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 418, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbron, S.; Eggelte, H.J.; Fisher, M.; Rabin, B.R. Amplified Assay of Alkaline Phosphatase Using Flavin-Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate as Substrate. Anal. Biochem. 1992, 206, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Schanze, K.S. Conjugated Polyelectrolyte-based Real-time Fluorescence Assay for Alkaline Phosphatase with Pyrophosphate as Substrate. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8605–8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhou, H.; Yu, C. A Facile Method for Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Based on the Turn-on Fluorescence of Resorufin. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 6105–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, E.; Takahashi, M.; Takeda, H.; Shiro, M.; Koike, T. Recognition of Phosphate Monoester Dianion by an Alkoxide-bridged Dinuclear Zinc(II) Complex. Dalton Trans. 2004, 8, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, E.; Yamada, A.; Takeda, H.; Kinoshita-Kikuta, E.; Koike, T. Novel Immobilized Zinc(II) Affinity Chromatography for Phosphopeptides and Phosphorylated Proteins. J. Sep. Sci. 2005, 28, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, E.; Kinoshita-Kikuta, E.; Takiyama, K.; Koike, T. Phosphate-binding Tag, a New Tool to Visualize Phosphorylated Proteins. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2006, 5, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita-Kikuta, E.; Aoki, Y.; Kinoshita, E.; Koike, T. Label-free Kinase Profiling Using Phosphate Affinity Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunehiro, M.; Meki, Y.; Matsuoka, K.; Kinoshita-Kikuta, E.; Kinoshita, E.; Koike, T. A Phos-tag-based Magnetic-bead Mmethod for Rrapid and Selective Separation of Phosphorylated Biomolecules. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2013, 925, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takiyama, K.; Kinoshita, E.; Kinoshita-Kikuta, E.; Fujioka, Y.; Kubo, Y.; Koike, T. A Phos-tag-based Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer System for the Analysis of the Dephosphorylation of Phosphopeptides. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 388, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somura, M.; Takiyama, K.; Kinoshita-Kikuta, E.; Kinoshita, E.; Koike, T. A Phos-tag-based Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer System for the Analysis of the Kinase Reaction of a Substrate Peptide. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita-Kikuta, E.; Kurosaki, H.; Kunisada, N.; Kinoshita, E.; Koike, T. A Phos-tag-based Fluorescence Quenching System for Activity Assay and Inhibitor Screening for Alkaline Phosphatase. Am. J. Anal. Chem 2014, 5, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapsford, K.E.; Berti, L.; Medintz, I.L. Materials for Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Analysis: beyond Traditional Donor-acceptor Combinations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4562–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackman, M.J.; Corrie, J.E.T.; Croney, J.C.; Kelly, G.; Eccleston, J.F.; Jameson, D.M. Structural and Biochemical Characterization of a Fluorogenic Rhodamine-labeled Malarial Protease Substrate. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 12244–12252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, R.J.; Tadiello, C.J.; Chamberlain, L.M.; Grainger, D.W. Optical Properties and Application of a Reactive and Bioreducible Thiol-containing Tetramethylrhodamine Dimer. Bioconj. Chem. 2009, 20, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaasa, A.; Viil, I.; Enkvist, E.; Viht, K.; Raidaru, G.; Lavogina, D.; Uri, A. High-affinity Bisubstrate Probe for Fluorescence Anisotropy Binding/displacement Assays with Protein Kinases PKA and ROCK. Biochemistry 2009, 385, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, M.P.; Landt, M.; Ryan, L.M.; Mulivor, R.A.; Henthorn, P.S.; Fedde, K.N.; Mahuren, J.D.; Coburn, S.P. Alkaline Phosphatase: Placental and Tissue-nonspecific Isoenzymes Hydrolyze Phosphoethanolamine, Inorganic Pyrophosphate, and Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate. Substrate Accumulation in Carriers of Hypophosphatasia Corrects during Pregnancy. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 1440–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosset, M.; Chappelet-Tordo, D.; Lazdunski, M. Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase. Physical Properties and Qquaternary Sstructure. Biochemistry 1974, 13, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiba, A.; Kinoshita-Kikuta, E.; Kinoshita, E.; Koike, T. TAMRA/TAMRA Fluorescence Quenching Systems for the Activity Assay of Alkaline Phosphatase. Sensors 2017, 17, 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17081877
Shiba A, Kinoshita-Kikuta E, Kinoshita E, Koike T. TAMRA/TAMRA Fluorescence Quenching Systems for the Activity Assay of Alkaline Phosphatase. Sensors. 2017; 17(8):1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17081877
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiba, Akio, Emiko Kinoshita-Kikuta, Eiji Kinoshita, and Tohru Koike. 2017. "TAMRA/TAMRA Fluorescence Quenching Systems for the Activity Assay of Alkaline Phosphatase" Sensors 17, no. 8: 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17081877
APA StyleShiba, A., Kinoshita-Kikuta, E., Kinoshita, E., & Koike, T. (2017). TAMRA/TAMRA Fluorescence Quenching Systems for the Activity Assay of Alkaline Phosphatase. Sensors, 17(8), 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17081877