Peri-Elastodynamic Simulations of Guided Ultrasonic Waves in Plate-Like Structure with Surface Mounted PZT
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Peri-Elastodynamic Formulation
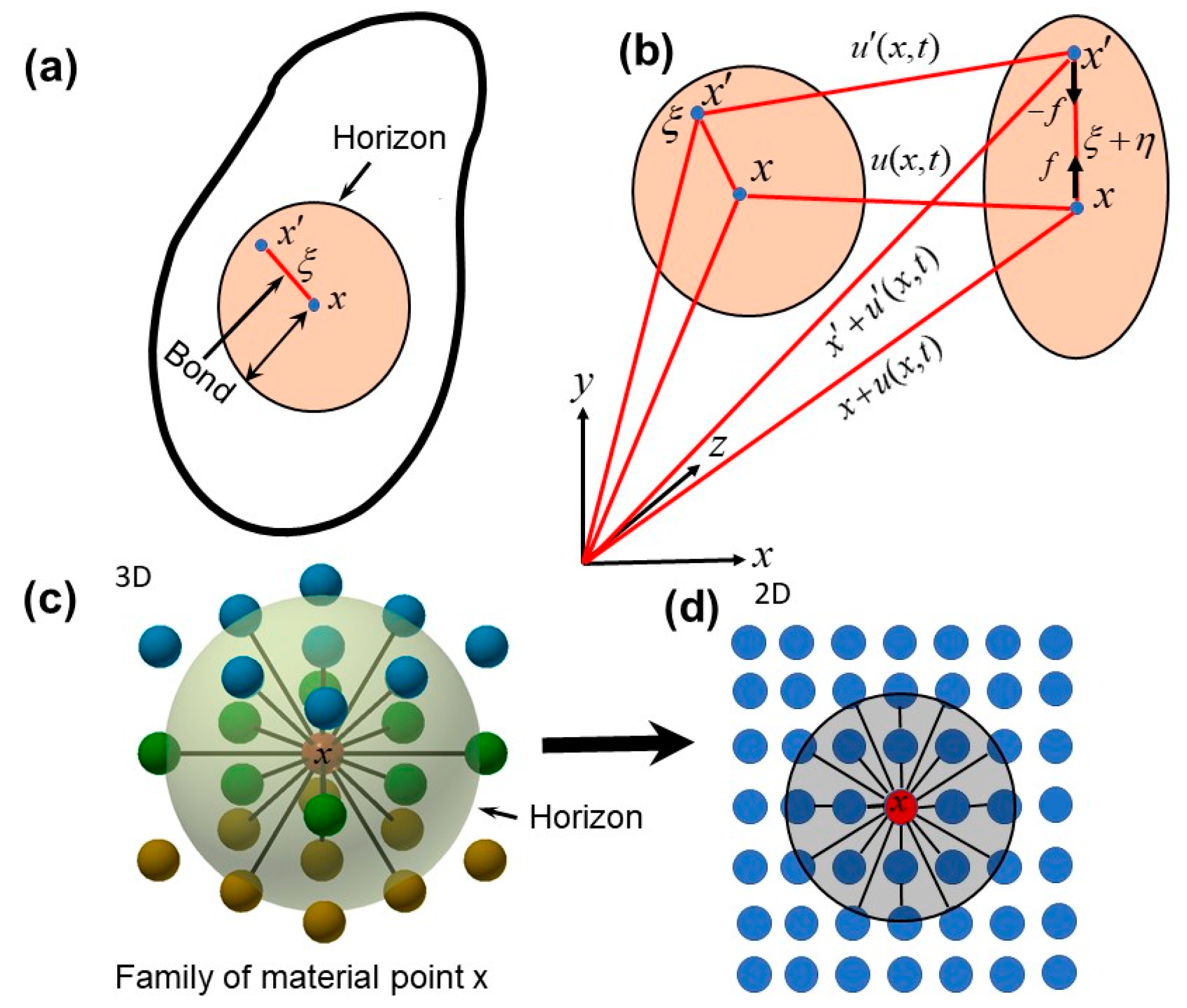
2.1. Basics of Bond-Based Peridynamic Formulation
2.2. Actuator Modelling with in Plane Excitation
2.3. Numerical Time Integration
2.4. Peri-Elastodynamic Spatial and Temporal Discretization
3. Lamb Wave Dispersion Relation
4. Numerical Computation and Results
4.1. Lamb Wave Propagation in the Pristine Plate
4.2. Vector Field Representation of the Lamb Wave Modes
5. Analysis of the Sensor Signals
Frequency-Wavenumber Analysis: Verification of the Simulation Results
6. Simulation of Wave Damage Interaction
7. Perspectives and Peri-Elastodynamic Application to the MEMS Devices
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kessler, S.S.; Spearing, S.M.; Soutis, C. Damage detection in composite materials using Lamb wave methods. Smart Mater. Struct. 2002, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Banerjee, S. Material State Awareness for Composites Part I: Precursor Damage Analysis Using Ultrasonic Guided Coda Wave Interferometry (CWI). Materials 2017, 10, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giurgiutiu, V. Structural Health Monitoring: With Piezoelectric Wafer Active Sensors; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Giurgiutiu, V. Lamb wave generation with piezoelectric wafer active sensors for structural health monitoring. Smart Struct. Mater. 2003, 5056, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Ha, S.; Chang, F. Time-domain spectral element method for built-in piezoelectric-actuator-induced lamb wave propagation analysis. AIAA J. 2008, 46, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Staszewski, W. Lamb wave propagation modelling for damage detection: I. Two-dimensional analysis. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paćko, P.; Bielak, T.; Spencer, A.B.; Staszewski, W.J.; Uhl, T.; Worden, K. Lamb wave propagation modelling and simulation using parallel processing architecture and graphical cards. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 075001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, A.; Cesnik, C.E. Finite-dimensional piezoelectric transducer modeling for guided wave based structural health monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 14, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, F. Accurate modeling of PZT-induced Lamb wave propagation in structures by using a novel spectral finite element method. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 095018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Chang, F.-K. Optimizing a spectral element for modeling PZT-induced Lamb wave propagation in thin plates. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 19, 015015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Aliabadi, M. On modelling three-dimensional piezoelectric smart structures with boundary spectral element method. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 055015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, F.; Jacobs, L.J.; Qu, J. Modeling elastic wave propagation in waveguides with the finite element method. NDT E Int. 1999, 32, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Rose, J.L. A boundary element solution for a mode conversion study on the edge reflection of Lamb waves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 99, 2097–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, H.; Sohn, Y. Numerical simulation and visualization of elastic waves using mass-spring lattice model. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2000, 47, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanyam, R.; Quinney, D.; Challis, R.E.; Todd, C.P.D. A finite-difference simulation of ultrasonic Lamb waves in metal sheets with experimental verification. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1996, 29, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamini, A.; Biondini, F. Finite strip modeling for optimal design of prestressed folded plate structures. Eng. Struct. 2004, 26, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, P.; Schweitzer, M.A. Simulation of wave propagation and impact damage in brittle materials using peridynamics. In Recent Trends in Computational Engineering-CE2014; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 251–265. [Google Scholar]
- Nishawala, V.V.; Ostoja-Starzewski, M.; Leamy, M.J.; Demmie, P.N. Simulation of elastic wave propagation using cellular automata and peridynamics and comparison with experiments. Wave Motion 2016, 60, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluska, P.; Staszewski, W.J.; Leamy, M.J.; Uhl, T. Cellular automata for Lamb wave propagation modelling in smart structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 085022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leckey, C.A.; Rogge, M.D.; Miller, C.A.; Hinders, M.K. Multiple-mode Lamb wave scattering simulations using 3D elastodynamic finite integration technique. Ultrasonics 2012, 52, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Kundu, T.; Alnuaimi, N.A. DPSM technique for ultrasonic field modelling near fluid-solid interface. Ultrasonics 2007, 46, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijanka, P.; Radecki, R.; Packo, P.; Staszewski, W.J.; Uhl, T. GPU-based local interaction simulation approach for simplified temperature effect modelling in Lamb wave propagation used for damage detection. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 035014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Cesnik, C.E. Local Interaction Simulation Approach for Efficient Modeling of Linear and Nonlinear Ultrasonic Guided Wave Active Sensing of Complex Structures. J. Nondestruct. Eval. Diagn. Progn. Eng. Syst. 2018, 1, 011008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzani, A.; Viola, E.; Bartoli, I.; Di Scalea, F.L.; Rizzo, P. A semi-analytical finite element formulation for modeling stress wave propagation in axisymmetric damped waveguides. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 318, 488–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balikin, A. Numerical Simulation of Guided Waves for SHM-a Literature Survey; UPSSP Platform Grant Report; Dynamics Research Group, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Sheffield: Sheffield, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Silling, S.A. Reformulation of elasticity theory for discontinuities and long-range forces. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2000, 48, 175–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silling, S.A.; Askari, E. A meshfree method based on the peridynamic model of solid mechanics. Comput. Struct. 2005, 83, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi, M.H.; Alebrahim, R.; Kundu, T. Peri-ultrasound for modeling linear and nonlinear ultrasonic response. Ultrasonics 2017, 80, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martowicz, A.; Ruzzene, M.; Staszewski, W.J.; Uhl, T. Non-local modeling and simulation of wave propagation and crack growth. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1581, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobaru, F.; Foster, J.T.; Geubelle, P.H.; Silling, S.A. Handbook of Peridynamic Modeling; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, Y.D.; Bobaru, F. Studies of dynamic crack propagation and crack branching with peridynamics. Int. J. Fract. 2010, 162, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madenci, E.; Oterkus, E. Peridynamic Theory and Its Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Hafezi, M.H.; Kundu, T. Peri-ultrasound modeling for surface wave propagation. Ultrasonics 2018, 84, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafezi, M.H.; Kundu, T. Peri-Ultrasound Modeling of Dynamic Response of an Interface Crack Showing Wave Scattering and Crack Propagation. J. Nondestruct. Eval. Diagn. Progn. Eng. Syst. 2018, 1, 011003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, D.; Liu, N. Analyzing dynamic fracture process in fiber-reinforced composite materials with a peridynamic model. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2017, 178, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Askari, A.; Weckner, O.; Silling, S. Peridynamic Analysis of Impact Damage in Composite Laminates. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2008, 21, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurgiutiu, V. Tuned Lamb Wave Excitation and Detection with Piezoelectric Wafer Active Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2005, 16, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Giurgiutiu, V. WFR-2D: An analytical model for PWAS-generated 2D ultrasonic guided wave propagation. In Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures and Materials + Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–13 March 2014; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, M.L.; Seleson, P.; Plimpton, S.J.; Silling, S.A.; Lehoucq, R.B. Peridynamics with LAMMPS: A User Guide, v0. 3 Beta; Sandia Report (2011–8253); Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2011.
- Leckey, C.A.C.; Rogge, M.D.; Raymond Parker, F. Guided waves in anisotropic and quasi-isotropic aerospace composites: Three-dimensional simulation and experiment. Ultrasonics 2014, 54, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlakovic, B.; Lowe, M.; Alleyne, D.; Cawley, P. Disperse: A General Purpose Program for Creating Dispersion Curves. In Review of Progress in Quantitative Nondestructive Evaluation; Thompson, D.O., Chimenti, D.E., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; Volume 16A, pp. 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Michaels, T.E.; Michaels, J.E.; Ruzzene, M. Frequency-wavenumber domain analysis of guided wavefields. Ultrasonics 2011, 51, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Aluminum 6061-T6 Material Properties | |
|---|---|
| Density, ρ | 2700 kg/m3 |
| Young’s Modulus, E | 69 GPa |
| Poisson ratio, ν | 0.33 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patra, S.; Ahmed, H.; Banerjee, S. Peri-Elastodynamic Simulations of Guided Ultrasonic Waves in Plate-Like Structure with Surface Mounted PZT. Sensors 2018, 18, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010274
Patra S, Ahmed H, Banerjee S. Peri-Elastodynamic Simulations of Guided Ultrasonic Waves in Plate-Like Structure with Surface Mounted PZT. Sensors. 2018; 18(1):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010274
Chicago/Turabian StylePatra, Subir, Hossain Ahmed, and Sourav Banerjee. 2018. "Peri-Elastodynamic Simulations of Guided Ultrasonic Waves in Plate-Like Structure with Surface Mounted PZT" Sensors 18, no. 1: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010274
APA StylePatra, S., Ahmed, H., & Banerjee, S. (2018). Peri-Elastodynamic Simulations of Guided Ultrasonic Waves in Plate-Like Structure with Surface Mounted PZT. Sensors, 18(1), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010274





