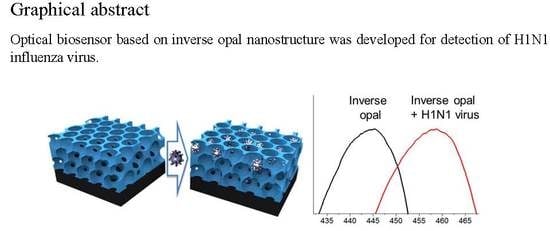
An Antibody-Immobilized Silica Inverse Opal Nanostructure for Label-Free Optical Biosensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of the SiO2-IO Nanostructures
2.3. Characterization of the SiO2-IO Nanostructures
2.4. Surface Functionalization of SiO2-IO for Antibody Immobilization
2.5. Detection of the Influenza Virus by the SiO2-IO Nanostructures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphologies of the SiO2-IO Nanostructures
3.2. Optical and Surface Properties of the SiO2-IO Nanostructures
3.3. Surface Functionalization of the SiO2-IO Nanostructures
3.4. Detection of the Influenza H1N1 Virus by SiO2-IO Nanostructures
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neumann, G.; Noda, T.; Kawaoka, Y. Emergence and pandemic potential of swine-origin H1N1 influenza virus. Nature 2009, 459, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Chiu, S.S.; Seto, W.H.; Peiris, M. Cost-effectiveness of rapid diagnosis of viral respiratory tract infections in pediatric patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1579–1581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karst, S.M. Pathogenesis of noroviruses, emerging RNA viruses. Viruses 2010, 2, 748–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.-S.; Park, N.-Y. Serodiagnostic comparison between two methods, ELISA and surface plasmon resonance for the detection of antibodies of classical swine fever. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2006, 68, 1327–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, H.; Hua, B.; Wang, H.; Cao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yu, A. Dual-probe assay for detection of lamivudine-resistance hepatitis B virus by real-time PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 132, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towner, J.S.; Sealy, T.K.; Khristova, M.L.; Albariño, C.G.; Conlan, S.; Reeder, S.A.; Quan, P.L.; Lipkin, W.I.; Downing, R.; Tappero, J.W.; et al. Newly discovered Ebola virus associated with hemorrhagic fever outbreak in Uganda. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevez, M.; Alvarez, M.; Lechuga, L.M. Integrated optical devices for lab-on-a-chip biosensing applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2012, 6, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gavela, A.F.; García, D.G.; Ramirez, J.C.; Lechuga, L.M. Last Advances in Silicon-Based Optical Biosensors. Sensors 2016, 16, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Olio, F.; Conteduca, D.; Ciminelli, C.; Armenise, M.N. New ultrasensitive resonant photonic platform for label-free biosensing. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 28593–28604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platform, M.L.B.; Olio, F.D. Design of a New Ultracompact Resonant Plasmonic. Sensors 2017, 17, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Gu, H.; Zhu, C.; Gu, Z. Bio-inspired variable structural color materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3297–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, W.; Megens, M.; Steinhardt, P.J.; Chaikin, P.M. Experimental measurement of the photonic properties of icosahedral quasicrystals. Nature 2005, 436, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schriemer, H.P.; van Driel, H.M.; Koenderink, A.F.; Vos, W.L. Modified spontaneous emission spectra of laser dye in inverse opal photonic crystals. Phys. Rev. A 2000, 63, 11801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncar, M.; Doll, T.; Vuckovic, J.; Scherer, A. Design and fabrication of silicon photonic crystal optical waveguides. J. Lightware Technol. 2000, 18, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S. Strong localization of photons in certain disordered dielectric superlattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 58, 2486–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yablonovitch, E. Inhibited Spontaneous Emission in Solid-State Physics and Electronics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 58, 1419–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Yin, Y. Responsive Photonic Crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1492–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsenault, A.C.; Puzzo, D.P.; Manners, I.; Ozin, G.A. Photonic-crystal full-colour displays. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H. Electrically Driven Single-Cell Photonic Crystal Laser. Science 2004, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.V.; Vijaya, R. Photonic crystal sensors: An overview. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2010, 34, 89–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanik, A.A.; Huang, M.; Kamohara, O.; Artar, A.; Geisbert, T.W.; Connor, J.H.; Altug, H. An optofluidic nanoplasmonic biosensor for direct detection of live viruses from biological media. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4962–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inci, F.; Tokel, O.; Wang, S.; Gurkan, U.A.; Tasoglu, S.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Demirci, U. Nanoplasmonic quantitative detection of intact viruses from unprocessed whole blood. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4733–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetin, A.E.; Etezadi, D.; Galarreta, B.C.; Busson, M.P.; Eksioglu, Y.; Altug, H. Plasmonic Nanohole Arrays on a Robust Hybrid Substrate for Highly Sensitive Label-Free Biosensing. ACS Photonics 2015, 2, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velev, O.D.; Jede, T.A.; Lobo, R.F.; Lenhoff, A.M. Porous silica via colloidal crystallization. Nature 1997, 389, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, B.T.; Blanford, C.F.; Stein, A. Synthesis of Macroporous Minerals with Highly Ordered Three-Dimensional Arrays of Spheroidal Voids. Science 1998, 281, 538–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenzl, C.; Hirsch, T.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Photonic crystals for chemical sensing and biosensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 3318–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Wei, H.; Gu, Z.Z.; Lu, Z. Macroporous ordered titanium dioxide (TiO2) inverse opal as a new label-free immunosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 625, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Cui, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, J. Enzyme-based inverse opals: a facile and promising platform for fabrication of biocatalysts. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 5490–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couturier, J.-P.; Sütterlin, M.; Laschewsky, A.; Hettrich, C.; Wischerhoff, E. Responsive inverse opal hydrogels for the sensing of macromolecules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 6641–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeng, B.; Park, Y.; Park, J. Direct label-free detection of Rotavirus using a hydrogel based nanoporous photonic crystal. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 7384–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, B.; Mishchenko, L.; Davis, S.; Sandhage, K.H.; Aizenberg, J. Assembly of large-area, highly ordered, crack-free inverse opal films. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10354–10359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakša, G.; Štefane, B.; Kovač, J. XPS and AFM characterization of aminosilanes with different numbers of bonding sites on a silicon wafer. Surf. Interface Anal. 2013, 45, 1709–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, D.; Wan, G.; Xu, J.; Hou, W. Facile synthesis of concentrated gold nanoparticles with low size-distribution in water: Temperature and pH controls. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijnhoven, J.E.G.J.; Vos, W.L. Preparation of Photonic Crystals Made of Air Spheres in Titania. Science 1998, 281, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.S.; Heineman, D.; Graugnard, E.; Summers, C.J. Atomic layer deposition in porous structures: 3D photonic crystals. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 244, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Santamaría, F.; Ibisate, M.; Rodríguez, I.; Meseguer, F.; López, C. Photonic band engineering in opals by growth of Si/Ge multilayer shells. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.; Chomski, E.; Grabtchak, S.; Ibisate, M.; John, S.; Leonard, S.; Lopez, C.; Meseguer, F.; Miguez, H.; Mondia, J.; et al. Large-scale synthesis of a silicon photonic crystal with a complete three-dimensional bandgap near 1.5 micrometres. Nature 2000, 405, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirumkudulu, M.S.; Russel, W.B. Cracking in drying latex films. Langmuir 2005, 21, 4938–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatton, B.; Mishchenko, L.; Norwood, R.; Davis, S.; Sandhage, K.; Aizenberg, J. An evaporative co-assembly method for highly ordered inverse opal films. In Proceedings of the SPIE Advanced Fabrication Technologies for Micro/Nano Optics and Photonics II, San Jose, CA, USA, 24–29 January 2009; Volume 7205, p. 72050F-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtz, J.H.; Asher, S.A. Polymerized colloidal crystal hydrogel films as intelligent chemical sensing materials. Nature 1997, 389, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Waterland, M.R. Opal and inverse opal photonic crystals: Fabrication and characterization. Polyhedron 2007, 26, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, L.F. New Table of the Refractive Index of Pure Glycerol at 20 °C. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1934, 26, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkles, B. Hydrophobicity, Hydrophilicity and Silanes. Paint Coat. Ind. 2006, 22, 114. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.; Jeong, J.Y.; Chung, B.H. Recent advances in immobilization methods of antibodies on solid supports. Analyst 2008, 133, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6060–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E. Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as peroxidase mimetics and their applications in H2O2 and glucose detection. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2250–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlbold, T.J.; Krammer, F. In the shadow of hemagglutinin: A growing interest in influenza viral neuraminidase and its role as a vaccine antigen. Viruses 2014, 6, 2465–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.Y.; Lee, U.; Chung, B.H.; Jung, J. A scanometric antibody probe for facile and sensitive immunoassays. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8865–8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, W.S.; Kang, T.; Kim, S.-H.; Jeong, J. An Antibody-Immobilized Silica Inverse Opal Nanostructure for Label-Free Optical Biosensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010307
Lee WS, Kang T, Kim S-H, Jeong J. An Antibody-Immobilized Silica Inverse Opal Nanostructure for Label-Free Optical Biosensors. Sensors. 2018; 18(1):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010307
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Wang Sik, Taejoon Kang, Shin-Hyun Kim, and Jinyoung Jeong. 2018. "An Antibody-Immobilized Silica Inverse Opal Nanostructure for Label-Free Optical Biosensors" Sensors 18, no. 1: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010307
APA StyleLee, W. S., Kang, T., Kim, S.-H., & Jeong, J. (2018). An Antibody-Immobilized Silica Inverse Opal Nanostructure for Label-Free Optical Biosensors. Sensors, 18(1), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010307