Pulse Oximetry with Two Infrared Wavelengths without Calibration in Extracted Arterial Blood
Abstract
:1. Introduction
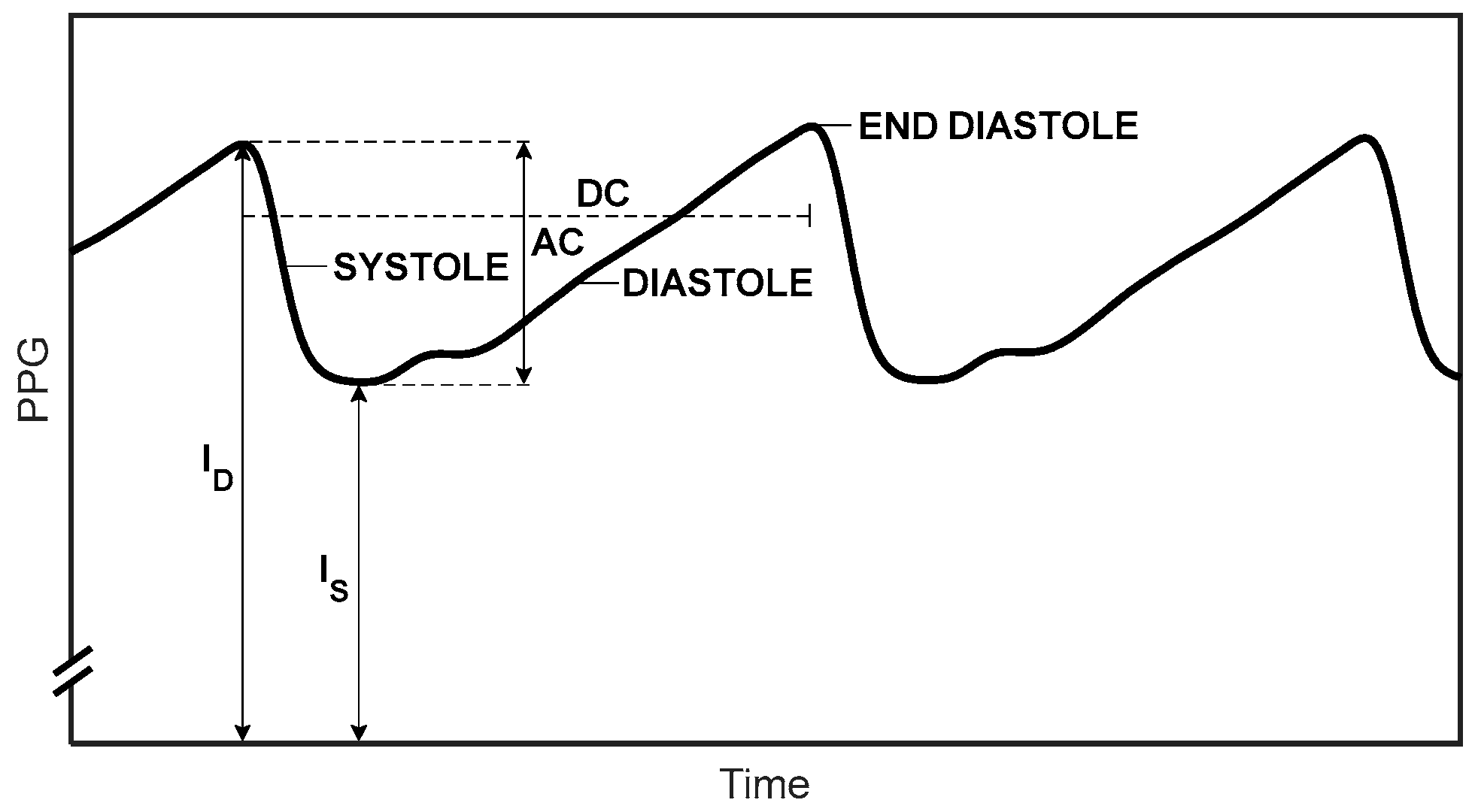
Measurement of Oxygen Saturation in Arterial Blood
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Pulse Oximeter
2.2. Determination of SpO2
2.3. Subjects and Methods
3. Results
3.1. SpO2 Measurement in Breath Holding
3.2. Comparison of SpO2 with Invasive Measurement of SaO2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seguin, P.; Le Rouzo, A.; Tanguy, M.; Guillou, Y.M.; Feuillu, A.; Mallédant, Y. Evidence for the need of bedside accuracy of pulse oximetry in an intensive care unit. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Louw, A.; Cracco, C.; Cerf, C.; Harf, A.; Duvaldestin, P.; Lemaire, F.; Brochard, L. Accuracy of pulse oximetry in the intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med. 2001, 27, 1606–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosychuk, R.J.; Hudson-Mason, A.; Eklund, D.; Lacaze-Masmonteil, T. Discrepancies between arterial oxygen saturation and functional oxygen saturation measured with pulse oximetry in very preterm infants. Neonatology 2012, 101, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, P.A.; Newth, C.J.; Khemani, R.G. Accuracy of pulse oximetry in children. Pediatrics 2014, 133, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshminrusimha, S.; Manja, V.; Mathew, B.; Suresh, G.K. Oxygen targeting in preterm infants: A physiological interpretation. J. Perinatol. 2015, 35, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.J.; Polin, R.A. Committee on fetus and newborn. Oxygen targeting in extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20161576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieben, O. Light absorbance in pulse oximetry. In Design of Pulse Oximeters; Webster, J.G., Ed.; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, UK, 1997; pp. 40–55. ISBN 9780750304672. [Google Scholar]
- Mannheimer, P.D.; Casciani, J.R.; Fein, M.E.; Nierlich, S.L. Wavelength selection for low-saturation pulse oximetry. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1997, 44, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitzan, M.; Babchenko, A.; Khanokh, B.; Taitelbaum, H. The measurement of oxygen saturation in venous blood by dynamic near IR spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2000, 5, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriacou, P.A. Pulse oximetry in the esophagus. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, R1–R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.G.; Liu, H. Variation of haemoglobin extinction coefficients can cause errors in the determination of haemoglobin concentration measured by near-infrared spectroscopy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 6295–6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannheimer, P.D. The light–tissue interaction of pulse oximetry. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 105, S10–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyle, J.T.B. Pulse Oximetry; BMJ Books: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, J.P.; Langford, R.M.; Chang, S.H.; Kyriacou, P.A.; Jones, D.P. Photoplethysmographic measurements from the esophagus using a new fiber-optic reflectance sensor. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 077005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friebel, M.; Helfmann, J.; Netz, U.; Meinke, M. Influence of oxygen saturation on the optical scattering properties of human red blood cells in the spectral range 250 to 2000 nm. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitzan, M.; Noach, S.; Tobal, E.; Adar, Y.; Miller, Y.; Shalom, E.; Engelberg, S. Calibration-free pulse oximetry based on two wavelengths in the infrared—A preliminary study. Sensors (Basel) 2014, 14, 7420–7434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.G.; (Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, Gwangju, South Korea); Liu, H.; (Joint Graduate Program in Biomedical Engineering, University of Texas at Arlington/University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas). Personal Communication.
- Hamber, E.A.; Bailey, P.L.; James, S.W.; Wells, D.T.; Lu, J.K.; Pace, N.L. Delays in the detection of hypoxemia due to site of pulse oximetry probe placement. J. Clin. Anesth. 1999, 11, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, P.; Blogg, S.L.; Gennser, M. Pulse oximetry to detect hypoxemia during apnea: Comparison of finger and ear probes. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2007, 78, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fouzas, S.; Priftis, K.N.; Anthrcopoulos, M.B. Pulse oximetry in pediatric practice. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, G.D.; McAuley, D.F.; Giles, S.; Routledge, H.; Gao, F. Do changes in pulse oximeter oxygen saturation predict equivalent changes in arterial oxygen saturation? Crit. Care 2003, 7, R67–R71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleen, M.; Messmer, K. Toxicity of high PaO2. Minerva Anestesiol. 1999, 65, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomson, L.; Paton, J. Oxygen toxicity. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2014, 15, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijlstra, W.G.; Buursma, A.; Meeuwsen-van der Roest, W.P. Absorption spectra of human fetal and adult oxyhemoglobin, de-oxyhemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin, and methemoglobin. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]








| Number | SaO2 | SpO2 | SaO2/SpO2 JCT | SpO2 JCT × CF | ΔSpO2 JCT | ΔSpO2 Nellcor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nellcor | JCT | ||||||
| 1 | 98 | 100 | 92.3 | 1.06 | 97.4 | −0.63 | 2.00 |
| 2 | 98 | 99 | 92.1 | 1.06 | 97.2 | −0.83 | 1.00 |
| 3 | 96 | 94 | 86.8 | 1.11 | 91.5 | −4.45 | −2.00 |
| 4 | 95 | 98 | 93.2 | 1.02 | 98.4 | 3.36 | 3.00 |
| 5 | 97 | 98 | 89.7 | 1.08 | 94.7 | −2.32 | 1.00 |
| 6 | 96 | 99 | 94.6 | 1.01 | 99.8 | 3.85 | 3.00 |
| 7 | 96 | 100 | 93.3 | 1.03 | 98.5 | 2.45 | 4.00 |
| 8 | 97 | 95 | 92.8 | 1.04 | 98.0 | 0.95 | −2.00 |
| 9 | 98 | 100 | 96.0 | 1.02 | 101.3 | 3.34 | 2.00 |
| 10 | 93 | 96 | 87.7 | 1.06 | 92.5 | −0.52 | 3.00 |
| 11 | 93 | 93 | 89.5 | 1.04 | 94.4 | 1.40 | 0.00 |
| 12 | 99 | 100 | 89.0 | 1.11 | 93.9 | −5.10 | 1.00 |
| 13 | 96 | 99 | 90.9 | 1.06 | 95.9 | −0.13 | 3.00 |
| 1 | 89 | 90 | 80.4 | 1.11 | 84.8 | −4.16 | 1.00 |
| 2 | 96 | 93 | 92.0 | 1.04 | 97.1 | 1.12 | −3.00 |
| 3 | 95 | 94 | 92.3 | 1.03 | 97.4 | 2.39 | −1.00 |
| 4 | 82 | 87 | 84.7 | 0.97 | 89.3 | 7.35 | 5.00 |
| 5 | 89 | 90 | 81.7 | 1.09 | 86.2 | −2.76 | 1.00 |
| 6 | 99 | 100 | 96.6 | 1.02 | 101.9 | 2.94 | 1.00 |
| 7 | 91 | 91 | 80.9 | 1.13 | 85.3 | −5.68 | 0.00 |
| 8 | 93 | 87 | 82.7 | 1.12 | 87.2 | −5.78 | −6.00 |
| 9 | 96 | 91.7 | 1.05 | 96.8 | 0.76 | ||
| 10 | 70 | 87 | 71.5 | 0.98 | 75.5 | 5.46 | 17.00 |
| 11 | 94 | 93 | 91.4 | 1.03 | 96.5 | 2.47 | −1.00 |
| 12 | 92 | 93 | 86.6 | 1.06 | 91.4 | −0.62 | 1.00 |
| 13 | 89 | 90 | 84.6 | 1.05 | 89.2 | 0.22 | 1.00 |
| 14 | 89 | 89 | 85.6 | 1.04 | 90.3 | 1.30 | 0.00 |
| 15 | 95 | 94 | 86.8 | 1.09 | 91.6 | −3.36 | −1.00 |
| 16 | 87 | 88 | 80.9 | 1.08 | 85.4 | −1.64 | 1.00 |
| Mean | 93.0 | 94.2 | 88.2 | 1.055 | 93.1 | 0.05 | 1.25 |
| Std | 6.0 | 4.6 | 5.7 | 0.04 | 6.0 | 3.34 | 3.83 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yossef Hay, O.; Cohen, M.; Nitzan, I.; Kasirer, Y.; Shahroor-karni, S.; Yitzhaky, Y.; Engelberg, S.; Nitzan, M. Pulse Oximetry with Two Infrared Wavelengths without Calibration in Extracted Arterial Blood. Sensors 2018, 18, 3457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103457
Yossef Hay O, Cohen M, Nitzan I, Kasirer Y, Shahroor-karni S, Yitzhaky Y, Engelberg S, Nitzan M. Pulse Oximetry with Two Infrared Wavelengths without Calibration in Extracted Arterial Blood. Sensors. 2018; 18(10):3457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103457
Chicago/Turabian StyleYossef Hay, Ohad, Meir Cohen, Itamar Nitzan, Yair Kasirer, Sarit Shahroor-karni, Yitzhak Yitzhaky, Shlomo Engelberg, and Meir Nitzan. 2018. "Pulse Oximetry with Two Infrared Wavelengths without Calibration in Extracted Arterial Blood" Sensors 18, no. 10: 3457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103457
APA StyleYossef Hay, O., Cohen, M., Nitzan, I., Kasirer, Y., Shahroor-karni, S., Yitzhaky, Y., Engelberg, S., & Nitzan, M. (2018). Pulse Oximetry with Two Infrared Wavelengths without Calibration in Extracted Arterial Blood. Sensors, 18(10), 3457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103457







