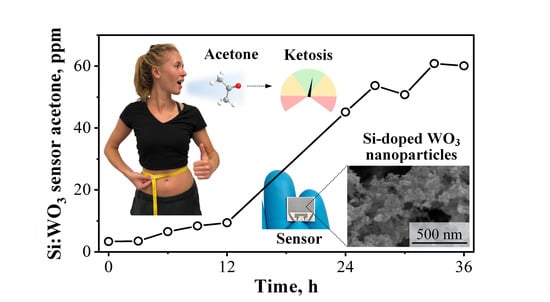
Guiding Ketogenic Diet with Breath Acetone Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acetone Sensor Fabrication and Film Characterization
2.2. Breath and Blood Analysis
2.3. Study Protocol
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Study Cohort
3.2. Breath Acetone Sensor Design
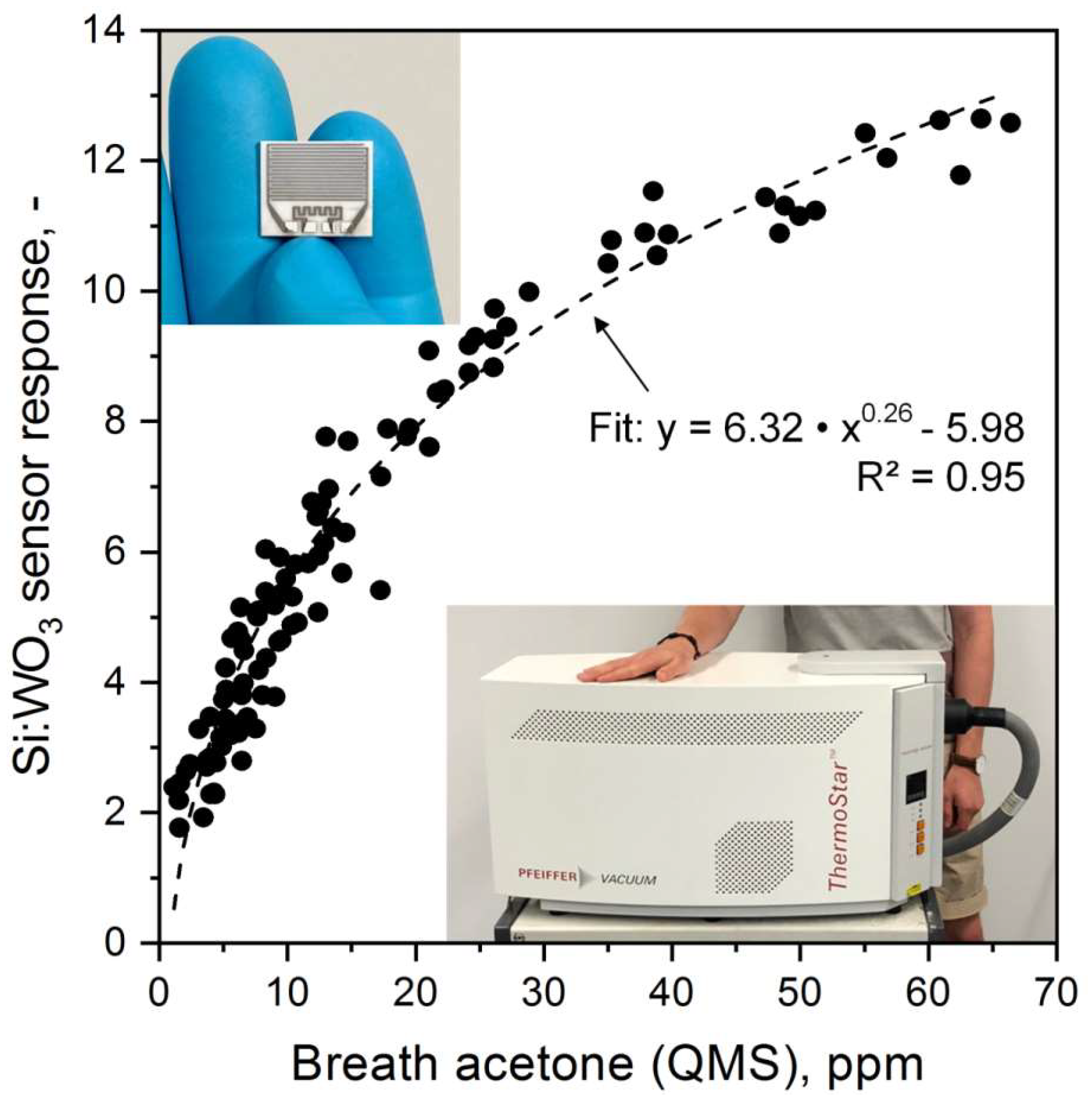
3.3. Sensor Performance and Calibration at Elevated Breath Acetone Concentrations
3.4. Monitoring Individual Ketosis through Breath and Blood
3.5. Correlations between Breath and Blood Parameters
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wheless, J.W. History of the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laxer, K.D.; Trinka, E.; Hirsch, L.J.; Cendes, F.; Langfitt, J.; Delanty, N.; Resnick, T.; Benbadis, S.R. The consequences of refractory epilepsy and its treatment. Epilepsy Behav. 2014, 37, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yancy, W.S.; Olsen, M.K.; Guyton, J.R.; Bakst, R.P.; Westman, E.C. A low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-fat diet to treat obesity and hyperlipidemia: A randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, J. Interest in the Ketogenic Diet Grows for Weight Loss and Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA 2018, 319, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westman, E.C.; Yancy, W.S., Jr.; Mavropoulos, J.C.; Marquart, M.; McDuffie, J.R. The effect of a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-glycemic index diet on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mardinoglu, A.; Wu, H.; Bjornson, E.; Zhang, C.; Hakkarainen, A.; Rasanen, S.M.; Lee, S.; Mancina, R.M.; Bergentall, M.; Pietilainen, K.H.; et al. An Integrated Understanding of the Rapid Metabolic Benefits of a Carbohydrate-Restricted Diet on Hepatic Steatosis in Humans. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youm, Y.-H.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Grant, R.W.; Goldberg, E.L.; Bodogai, M.; Kim, D.; D’agostino, D.; Planavsky, N.; Lupfer, C.; Kanneganti, T.D. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome–mediated inflammatory disease. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cox, P.J.; Kirk, T.; Ashmore, T.; Willerton, K.; Evans, R.; Smith, A.; Murray, A.J.; Stubbs, B.; West, J.; McLure, S.W.; et al. Nutritional Ketosis Alters Fuel Preference and Thereby Endurance Performance in Athletes. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Multi-dimensional roles of ketone bodies in fuel metabolism, signaling, and therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 262–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, G.F., Jr. Fuel metabolism in starvation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2006, 26, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegardt, F.G. Transcriptional regulation of mitochondrial HMG-CoA synthase in the control of ketogenesis. Biochimie 1998, 80, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa-Veloso, K.; Likhodii, S.S.; Cunnane, S.C. Breath acetone is a reliable indicator of ketosis in adults consuming ketogenic meals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, G. The calorie deficiency hypothesis of ketogenesis tested in man. Metabolism 1965, 14, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.C. Measuring breath acetone for monitoring fat loss: Review. Obesity 2015, 23, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spanel, P.; Dryahina, K.; Rejskova, A.; Chippendale, T.W.E.; Smith, D. Breath acetone concentration; biological variability and the influence of diet. Physiol. Meas. 2011, 32, N23–N31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa-Veloso, K.; Likhodii, S.S.; Rarama, E.; Benoit, S.; Liu, Y.-M.C.; Chartrand, D.; Curtis, R.; Carmant, L.; Lortie, A.; Comeau, F.J. Breath acetone predicts plasma ketone bodies in children with epilepsy on a ketogenic diet. Nutrition 2006, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergenstal, R.M.; Garg, S.; Weinzimer, S.A.; Buckingham, B.A.; Bode, B.W.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Kaufman, F.R. Safety of a hybrid closed-loop insulin delivery system in patients with type 1 diabetes. JAMA 2016, 316, 1407–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzsányi, V.; Kalapos, M.P.; Schmidl, C.; Karall, D.; Scholl-Bürgi, S.; Baumann, M. Breath profiles of children on ketogenic therapy. J. Breath Res. 2018, 12, 036021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Figaro TGS 813: Technical Datasheet. Available online: http://www.figarosensor.com/products/813pdf.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2018).
- Steinhauer, S.; Chapelle, A.; Menini, P.; Sowwan, M. Local CuO Nanowire Growth on Microhotplates: In Situ Electrical Measurements and Gas Sensing Application. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güntner, A.T.; Koren, V.; Chikkadi, K.; Righettoni, M.; Pratsinis, S.E. E-Nose sensing of low-ppb formaldehyde in gas mixtures at high relative humidity for breath screening of lung cancer? ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruta, A.; Itoh, T.; Mikami, M.; Kinemuchi, Y.; Terasaki, I.; Murayama, N.; Shin, W. Trial of an All-Ceramic SnO2 Gas Sensor Equipped with CaCu3Ru4O12 Heater and Electrode. Materials 2018, 11, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righettoni, M.; Ragnoni, A.; Güntner, A.T.; Loccioni, C.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Risby, T.H. Monitoring breath markers under controlled conditions. J. Breath Res. 2015, 9, 047101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blattmann, C.O.; Güntner, A.T.; Pratsinis, S.E. In Situ Monitoring of the Deposition of Flame-Made Chemoresistive Gas-Sensing Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 23926–23933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Teleki, A.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Gouma, P.I. Ferroelectric WO3 Nanoparticles for Acetone Selective Detection. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4794–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righettoni, M.; Tricoli, A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Si:WO3 Sensors for Highly Selective Detection of Acetone for Easy Diagnosis of Diabetes by Breath Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3581–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righettoni, M.; Tricoli, A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Thermally Stable, Silica-Doped ε-WO3 for Sensing of Acetone in the Human Breath. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 3152–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schon, S.; Theodore, S.J.; Güntner, A.T. Versatile breath sampler for online gas sensor analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 1780–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güntner, A.T.; Sievi, N.A.; Theodore, S.J.; Gulich, T.; Kohler, M.; Pratsinis, S.E. Noninvasive Body Fat Burn Monitoring from Exhaled Acetone with Si-doped WO3-sensing Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10578–10584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güntner, A.T.; Pineau, N.J.; Mochalski, P.; Wiesenhofer, H.; Agapiou, A.; Mayhew, C.A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Sniffing Entrapped Humans with Sensor Arrays. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4940–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Güntner, A.T.; Pineau, N.J.; Chie, D.; Krumeich, F.; Pratsinis, S.E. Selective sensing of isoprene by Ti-doped ZnO for breath diagnostics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 5358–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güntner, A.T.; Righettoni, M.; Pratsinis, S.E. Selective sensing of NH3 by Si-doped α-MoO3 for breath analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 223, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.; Kupferthaler, A.; Unterkofler, K.; Koc, H.; Teschl, S.; Teschl, G.; Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.; Hinterhuber, H.; Amann, A. Isoprene and acetone concentration profiles during exercise on an ergometer. J. Breath Res. 2009, 3, 027006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karl, T.; Prazeller, P.; Mayr, D.; Jordan, A.; Rieder, J.; Fall, R.; Lindinger, W. Human breath isoprene and its relation to blood cholesterol levels: New measurements and modeling. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 91, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, S.; Spanel, P.; Smith, D. Quantitative analysis of ammonia on the breath of patients in end-stage renal failure. Kidney Int. 1997, 52, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, J.M.; Kelly, M.T.; Freeman, J.B. The Epilepsy Diet Treatment: An Introduction to the Ketogenic Diet; Demos Vermande: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mädler, L.; Roessler, A.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Sahm, T.; Gurlo, A.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Direct formation of highly porous gas-sensing films by in situ thermophoretic deposition of flame-made Pt/SnO2 nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society European Respiratory Society. Recommendations for Standardized Procedures for the Online and Offline Measurement of Exhaled Lower Respiratory Nitric Oxide and Nasal Nitric Oxide. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 912–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Francesco, F.; Loccioni, C.; Fioravanti, M.; Russo, A.; Pioggia, G.; Ferro, M.; Roehrer, I.; Tabucchi, S.; Onor, M. Implementation of Fowler’s method for end-tidal air sampling. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2, 037009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righettoni, M.; Tricoli, A.; Gass, S.; Schmid, A.; Amann, A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Breath acetone monitoring by portable Si:WO3 gas sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 738, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mifflin, M.D.; St Jeor, S.T.; Hill, L.A.; Scott, B.J.; Daugherty, S.A.; Koh, Y.O. A new predictive equation for resting energy expenditure in healthy individuals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankenfield, D.C. Bias and accuracy of resting metabolic rate equations in non-obese and obese adults. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, P.M. Checkliste Ernährung; Georg Thieme Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- De Lacy Costello, B.; Amann, A.; Al-Kateb, H.; Flynn, C.; Filipiak, W.; Khalid, T.; Osborne, D.; Ratcliffe, N.M. A review of the volatiles from the healthy human body. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, P.M.; Sleight, A.W.; Vogt, T. Ferroelectric Tungsten Trioxide. J. Solid State Chem. 1997, 131, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.-Q.; Ji, H.-M.; Wang, D.-H.; Bai, X.; Sun, X.-H.; Jin, Z.-G. Exposed facets induced enhanced acetone selective sensing property of nanostructured tungsten oxide. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 13602–13611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.W. A non-linear diffusion-reaction model of electrical conduction in semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1990, 1, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Understanding the fundamental principles of metal oxide based gas sensors; the example of CO sensing with SnO2 sensors in the presence of humidity. J. Phys.-Condes. Matter 2003, 15, R813–R839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.; Španěl, P.; Smith, D. A longitudinal study of ethanol and acetaldehyde in the exhaled breath of healthy volunteers using selected-ion flow-tube mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushch, I.; Arendacka, B.; Stolc, S.; Mochalski, P.; Filipiak, W.; Schwarz, K.; Schwentner, L.; Schmid, A.; Dzien, A.; Lechleitner, M. Breath isoprene—Aspects of normal physiology related to age, gender and cholesterol profile as determined in a proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry study. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2008, 46, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güntner, A.T.; Abegg, S.; Wegner, K.; Pratsinis, S.E. Zeolite membranes for highly selective formaldehyde sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Broek, J.; Güntner, A.T.; Pratsinis, S.E. Highly Selective and Rapid Breath Isoprene Sensing Enabled by Activated Alumina Filter. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, T.; Miwa, T.; Tsuruta, A.; Akamatsu, T.; Izu, N.; Shin, W.; Park, J.; Hida, T.; Eda, T.; Setoguchi, Y. Development of an Exhaled Breath Monitoring System with Semiconductive Gas Sensors, a Gas Condenser Unit, and Gas Chromatograph Columns. Sensors 2016, 16, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saslow, L.R.; Kim, S.; Daubenmier, J.J.; Moskowitz, J.T.; Phinney, S.D.; Goldman, V.; Murphy, E.J.; Cox, R.M.; Moran, P.; Hecht, F.M. A randomized pilot trial of a moderate carbohydrate diet compared to a very low carbohydrate diet in overweight or obese individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus or prediabetes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veech, R.L.; Chance, B.; Kashiwaya, Y.; Lardy, H.A.; Cahill, G.F. Ketone bodies, potential therapeutic uses. IUBMB Life 2001, 51, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- VanItallie, T.B.; Nufert, T.H. Ketones: Metabolism’s ugly duckling. Nutr. Rev. 2003, 61, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canziani, B.C.; Uestuener, P.; Fossali, E.F.; Lava, S.A.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Agostoni, C.; Milani, G.P. Clinical Practice: Nausea and vomiting in acute gastroenteritis: Physiopathology and management. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018, 177, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, P.A.C.; McEneny, J. The biochemistry of ketogenesis and its role in weight management, neurological disease and oxidative stress. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 68, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Macronutrient | Whipping Cream [wt%] | Protein Supplement Powder [wt%] |
|---|---|---|
| Fat | 35 | 2 |
| Carbohydrates | 3 | 3.8 |
| Protein | 3 | 80 |
| Calories [kcal/g] | 3.37 | 3.65 |
| Volunteer [-] | Gender [-] | Age [y] | Weight [kg] | Height [m] | BMI [kg/m²] | Physical Activity Factors [-] | 24-h Energy Expenditure [kcal/d] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | f | 21 | 58.0 | 1.59 | 22.94 | 1.4 | 1831 |
| 2 | m | 23 | 69.4 | 1.77 | 22.15 | 1.4 | 2352 |
| 3 | m | 22 | 72.0 | 1.80 | 22.22 | 1.4 | 2610 |
| 4 | f | 22 | 51.4 | 1.63 | 19.35 | 1.4 | 1753 |
| 5 | m | 22 | 51.8 | 1.78 | 16.35 | 1.4 | 1598 |
| 6 | f | 28 | 78.8 | 1.63 | 29.66 | 1.4 | 2234 |
| 7 | f | 25 | 74.1 | 1.71 | 25.34 | 1.4 | 2142 |
| 8 | m | 22 | 73.2 | 1.73 | 24.46 | 1.4 | 1807 |
| 9 | m | 22 | 74.5 | 1.80 | 22.99 | 1.4 | 2471 |
| 10 | m | 22 | 70.8 | 1.82 | 21.37 | 1.6 | 2786 |
| 11 | f | 21 | 59.4 | 1.72 | 20.08 | 1.5 | 2100 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Güntner, A.T.; Kompalla, J.F.; Landis, H.; Theodore, S.J.; Geidl, B.; Sievi, N.A.; Kohler, M.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Gerber, P.A. Guiding Ketogenic Diet with Breath Acetone Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 3655. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113655
Güntner AT, Kompalla JF, Landis H, Theodore SJ, Geidl B, Sievi NA, Kohler M, Pratsinis SE, Gerber PA. Guiding Ketogenic Diet with Breath Acetone Sensors. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):3655. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113655
Chicago/Turabian StyleGüntner, Andreas T., Julia F. Kompalla, Henning Landis, S. Jonathan Theodore, Bettina Geidl, Noriane A. Sievi, Malcolm Kohler, Sotiris E. Pratsinis, and Philipp A. Gerber. 2018. "Guiding Ketogenic Diet with Breath Acetone Sensors" Sensors 18, no. 11: 3655. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113655
APA StyleGüntner, A. T., Kompalla, J. F., Landis, H., Theodore, S. J., Geidl, B., Sievi, N. A., Kohler, M., Pratsinis, S. E., & Gerber, P. A. (2018). Guiding Ketogenic Diet with Breath Acetone Sensors. Sensors, 18(11), 3655. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113655