A Portable Phase-Domain Magnetic Induction Tomography Transceiver with Phase-Band Auto-Tracking and Frequency-Sweep Capabilities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
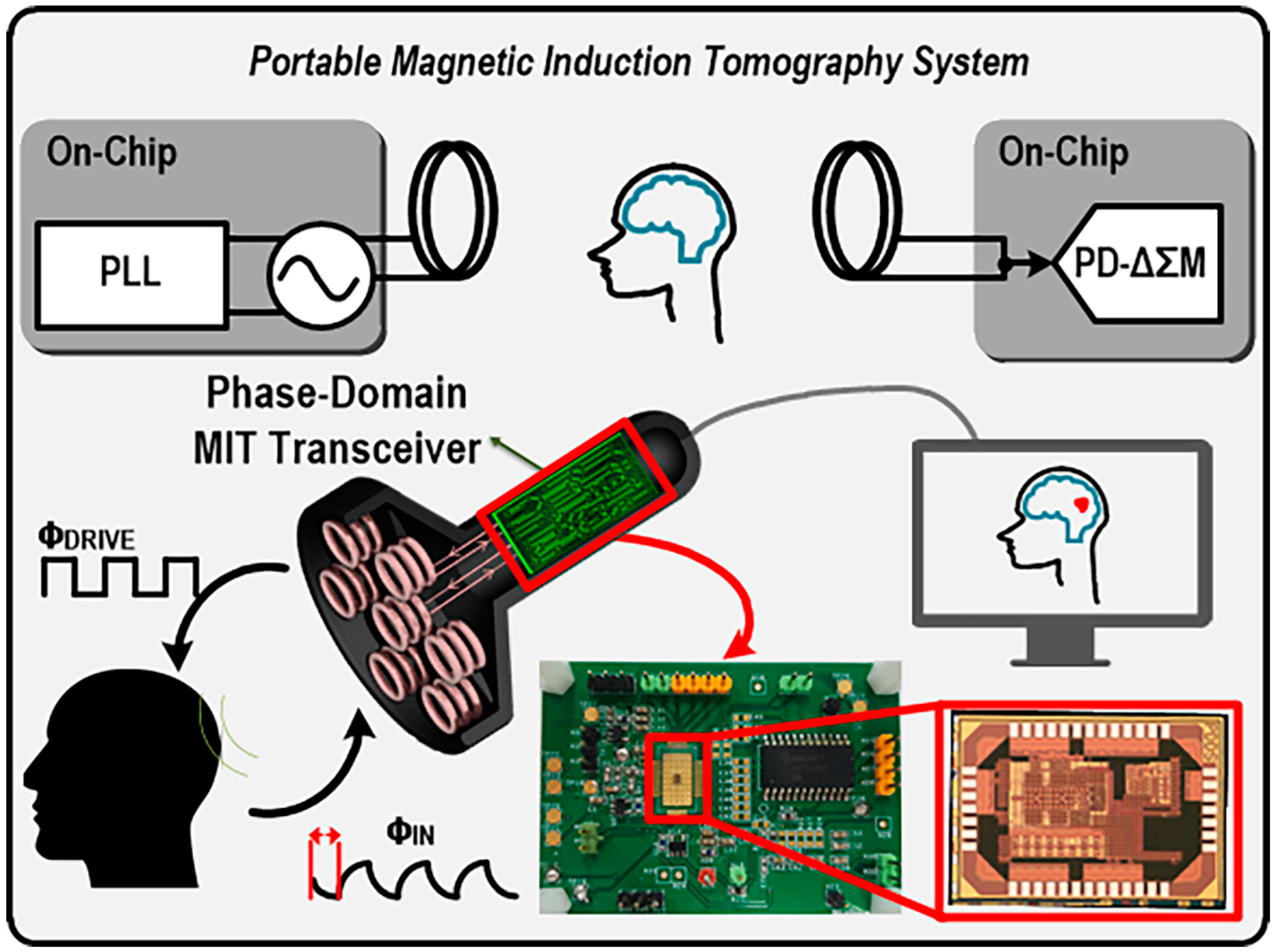
2. Portable Magnetic Induction Tomography System
3. Fully-Integrated Magnetic Induction Tomography Transceiver
3.1. Signal Generation with Phase-Locked Loop (PLL)
3.2. High-Resolution Phase-Information Detection with Phase-Band Auto-Tracking
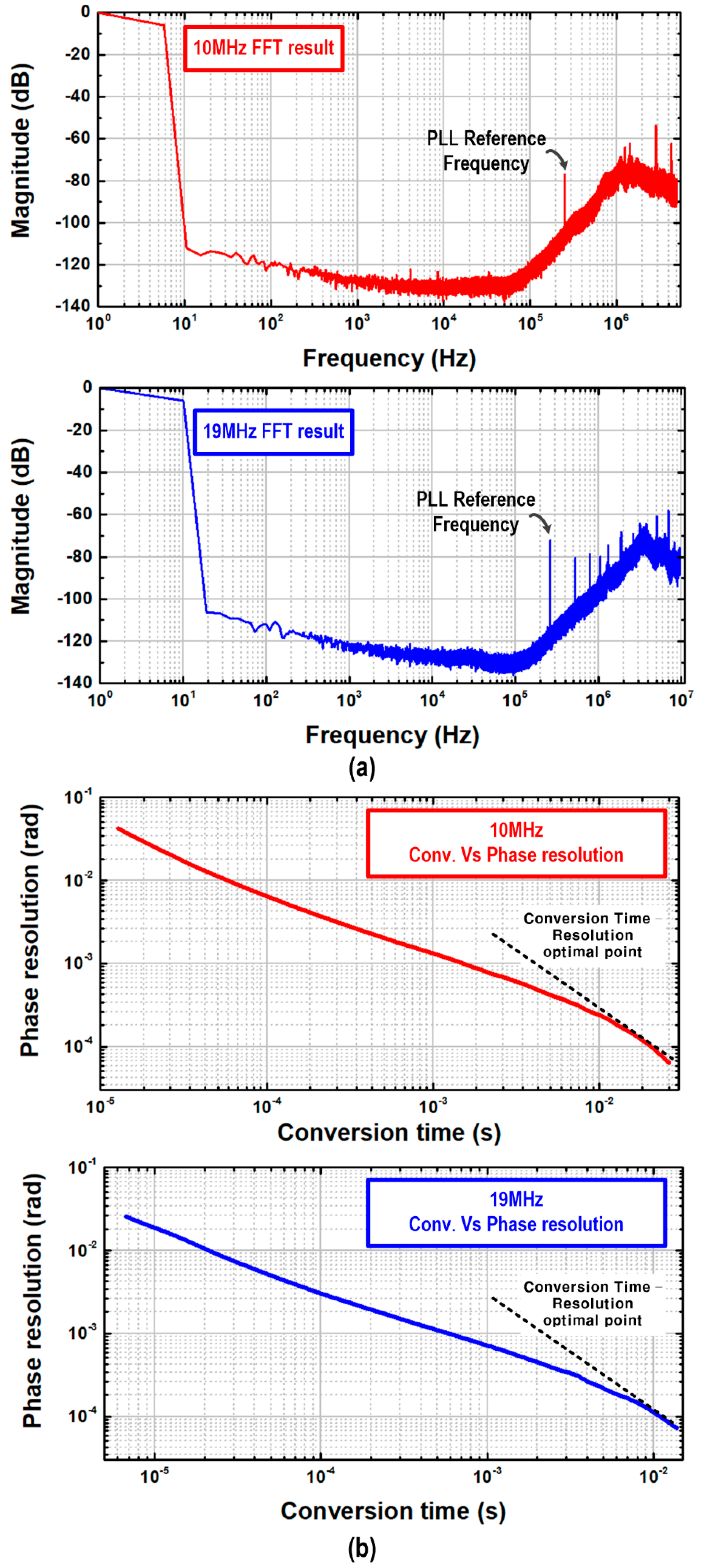
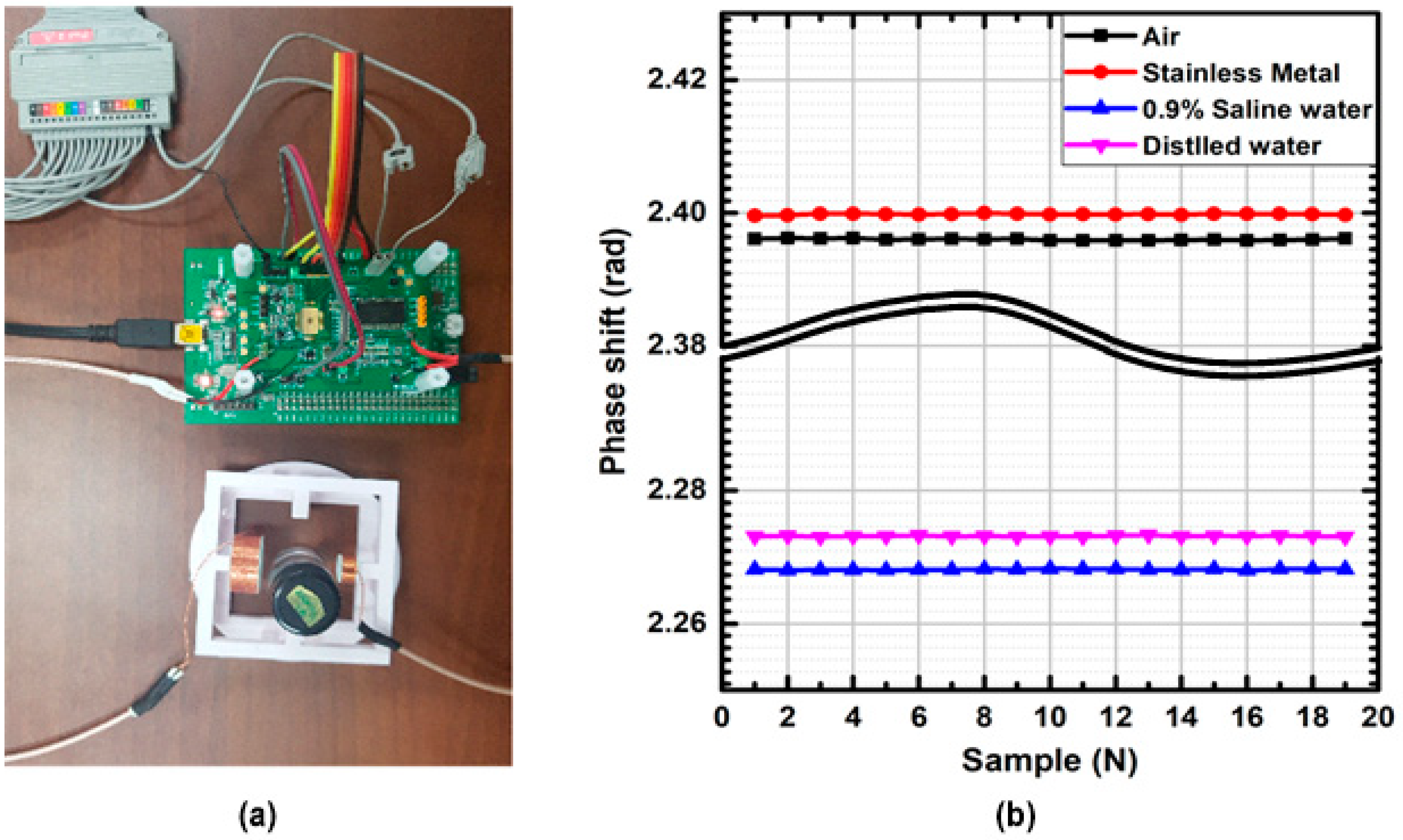
4. Measurement Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, G.; Ma, K.; Sun, J.; Jin, G.; Qin, M.; Feng, H. Twenty-Four-Hour Real-Time Continuous Monitoring of Cerebral Edema in Rabbits Based on a Noninvasive and Noncontact System of Magnetic Induction. Sensors 2017, 17, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Abascal, J.F.P.J.; Desco, M.; Soleimani, M. Total Variation Regularization with Split Bregman-Based Method in Magnetic Induction Tomography Using Experimental Data. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, G.; Xia, H. Magneto-Acousto-Electrical Tomography with Magnetic Induction for Conductivity Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2114–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariappan, L.; He, B. Magnetoacoustic Tomography with Magnetic Induction: Bioimepedance Reconstruction through Vector Source Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, D. Acoustic Source Analysis of Magnetoacoustic Tomography With Magnetic Induction for Conductivity Gradual-Varying Tissues. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Soleimani, M. Theoretical and Experimental Evaluation of Rotational Magnetic Induction Tomography. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 3324–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Wang, B. The Design of a Digital Magnetic Induction Tomography (MIT) System for Metallic Object Imaging Based on Half Cycle Demodulation. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, J.; Ward, R.; Lloyd, C.; Tatum, P.; Shenton-Taylor, C.; Taylor, S.; Bagley, G.; Joseph, M.; Watson, J.C. Effect of Shielding Conductivity on Magnetic Induction Tomographic Security Imagery. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patz, R.; Watson, S.; Ktistis, C.; Hamsch, M.; Peyton, A.J. Performance of a FPGA-based Direct Digitising Signal Measurement module for MIT. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 224, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.; Lau, R.W.; Gabriel, C. The dielectric properties of biological tissues: II. Measurements in the frequency range 10 Hz to 20 GHz. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2251–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Lee, Y.; Park, S.-B. Low-noise CMOS LC oscillator with dual-ring structure. Electron. Lett. 2004, 40, 1031–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; van Veldhoven, R.; Suy, H.; de Graaf, G.; Makinwa, K.A.A.; Pertijs, M. A phase-domain readout circuit for a CMOS-compatible thermal-conductivity-based carbon dioxide sensor. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2018; pp. 332–334. [Google Scholar]
- Shahmohammadi, M.; Souri, K.; Makinwa, K.A.A. A resistor-based temperature sensor for MEMS frequency references. In Proceedings of the 2013 ESSCIRC, Bucharest, Romania, 16–20 September 2013; pp. 225–228. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi, B. Design of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuits; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 324. ISBN 0-07-118815-0. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Rusu, A. A Power-Efficient Continuous-Time Incremental Sigma-Delta ADC for Neural Recording Systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2015, 62, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| This Work | [7] | [8] | [12] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| On-Chip Readout | Y | N | N | Y | |
| System | MIT | MIT | MIT | CO2 Sensor | |
| Method | PD-ΔΣM + PLL | Demodulation + A/D Conv. | Impedance analyzer + Sig gen. | PD-ΔΣM | |
| Technology | 0.18 μm | N/A | N/A | 0.18 μm | |
| Phase range [rad] | 2π | 2π | 2π | π/15 | |
| Power Consumption [W] | 15.084 m | N/A *** | N/A *** | 6.8 m | |
| SNDR [dB] | 101.7 | 95.73 | 59.3 * | 79.65 ** | N/A |
| Conv. time [s] | 15 m | 8 m | 10 m | 3 m | 1.8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, C.S.; Jeon, J.; Oh, B.; Chae, H.Y.; Park, K.; Son, H.; Kim, J.J. A Portable Phase-Domain Magnetic Induction Tomography Transceiver with Phase-Band Auto-Tracking and Frequency-Sweep Capabilities. Sensors 2018, 18, 3816. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113816
Park CS, Jeon J, Oh B, Chae HY, Park K, Son H, Kim JJ. A Portable Phase-Domain Magnetic Induction Tomography Transceiver with Phase-Band Auto-Tracking and Frequency-Sweep Capabilities. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):3816. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113816
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Chan Sam, Jiyun Jeon, Byungjoo Oh, Hee Young Chae, Kyeonghwan Park, Hungsun Son, and Jae Joon Kim. 2018. "A Portable Phase-Domain Magnetic Induction Tomography Transceiver with Phase-Band Auto-Tracking and Frequency-Sweep Capabilities" Sensors 18, no. 11: 3816. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113816
APA StylePark, C. S., Jeon, J., Oh, B., Chae, H. Y., Park, K., Son, H., & Kim, J. J. (2018). A Portable Phase-Domain Magnetic Induction Tomography Transceiver with Phase-Band Auto-Tracking and Frequency-Sweep Capabilities. Sensors, 18(11), 3816. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113816






