A Survey of the Techniques for The Identification and Classification of Human Actions from Visual Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Object scope understanding where only the positions of persons and objects are detected.
- Tracking scope understanding where the trajectories and correspondence of objects are analyzed.
- Pose-level understanding that involves the analysis of the position of human body parts.
- Analysis of human activities and events.
2. Challenges
- Inter-class variations: Different people perform different actions in their own ways, which at times show very low resemblance to one another, e.g., walking methods may differ in stride length or speed.
- Intra-class similarities: Actions belonging to different classes may appear similar such as jogging and running.
- View point variations: The same action if observed from two independent viewpoints can appear to be different, and the data collected as a result may indicate separate classes.
- Environment: Cluttered or complex backgrounds can make the task of identification of clear human shapes much more difficult.
- Temporal variations: Temporal variations occur both in terms of action performance/completion and action observation.
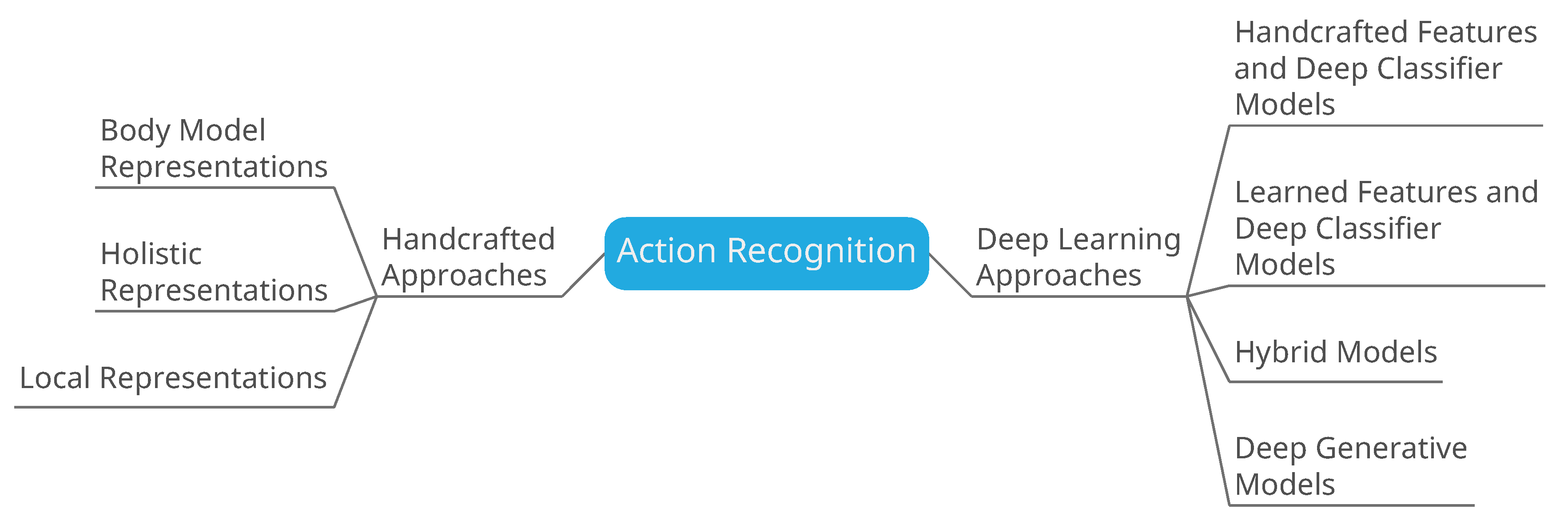
3. Handcrafted Approaches
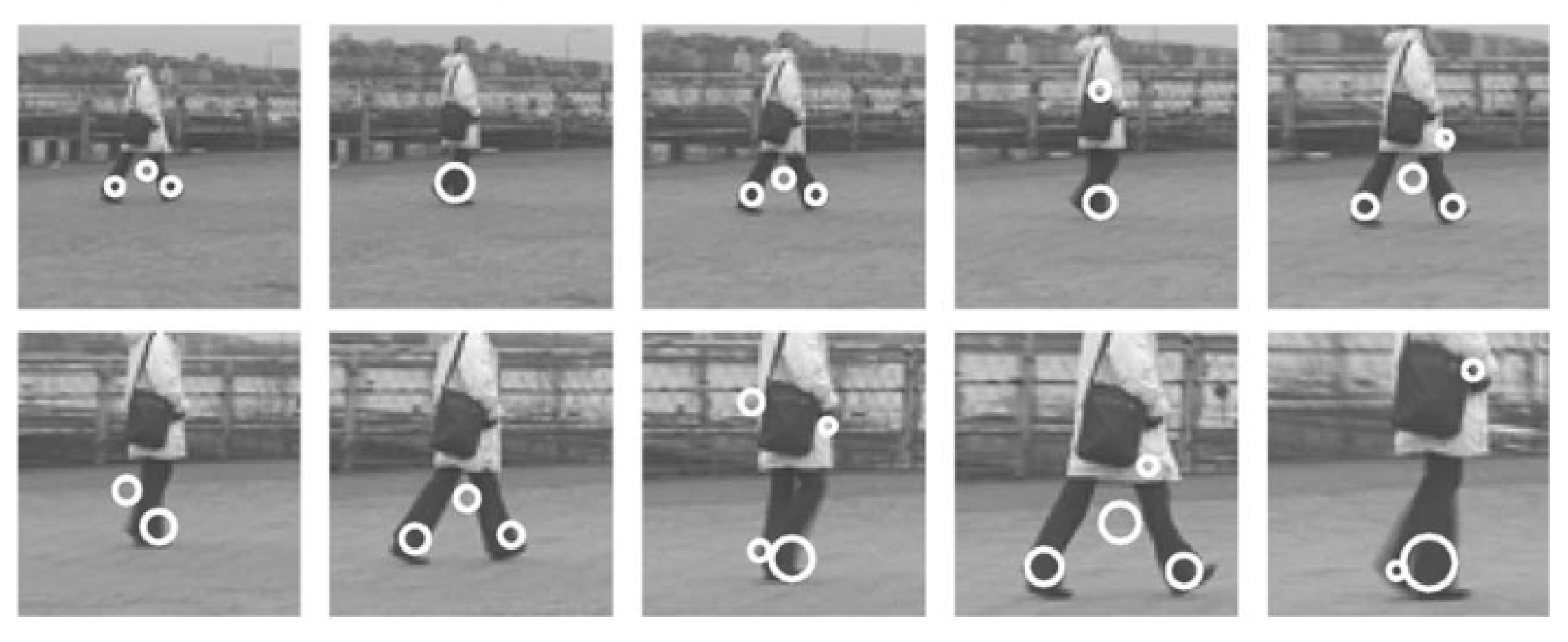
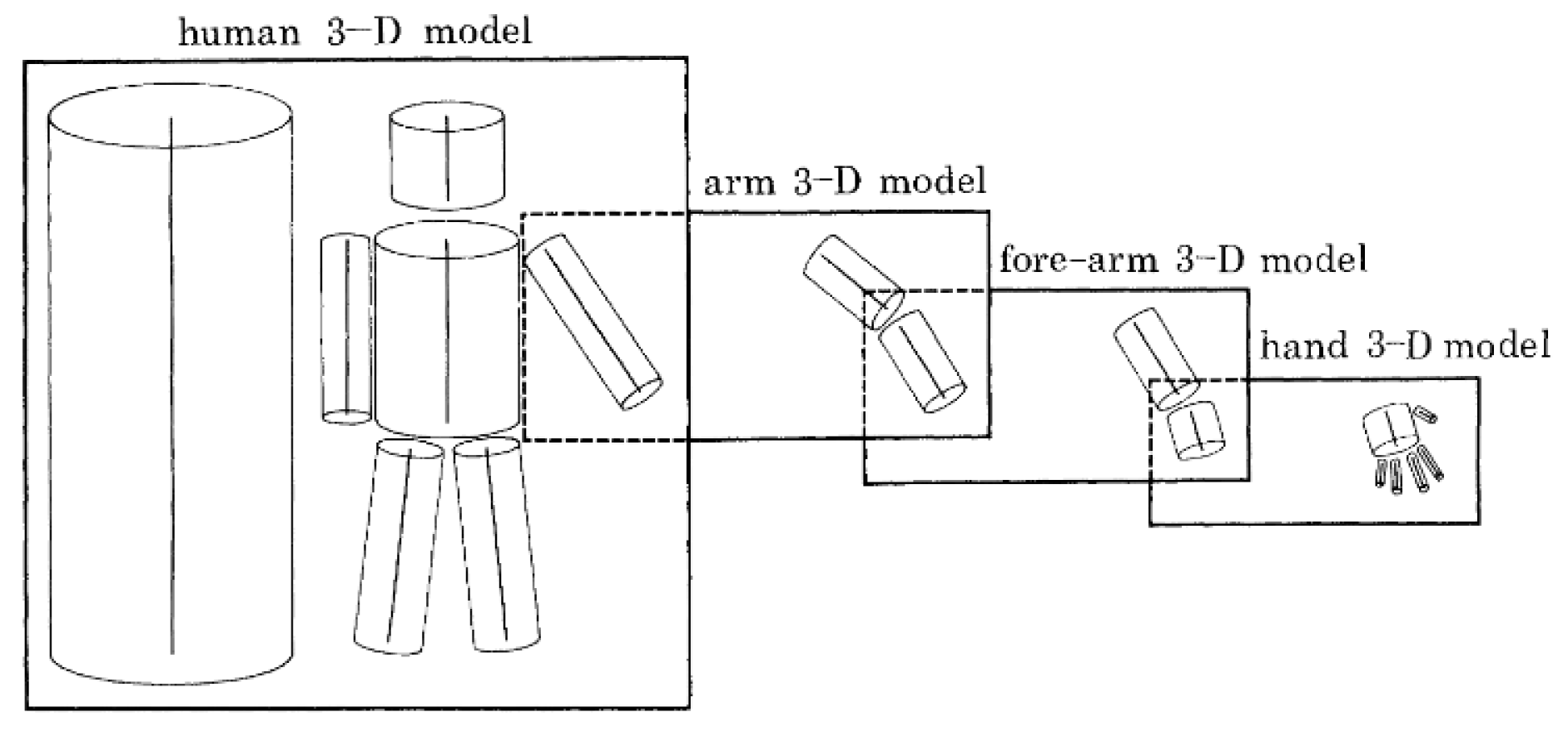
3.1. Body Models
3.2. Holistic Representations
3.3. Local Representations
3.3.1. Interest Point Detection
3.3.2. Local Descriptors
Edge and Motion Descriptors
3.3.3. Trajectory-Based Approaches
4. Deep Learning Approaches
4.1. Handcrafted Features and Deep Classifiers
4.2. Learned Representations and Deep Classifiers
4.3. Hybrid Models
4.4. Deep Generative Models
5. Datasets
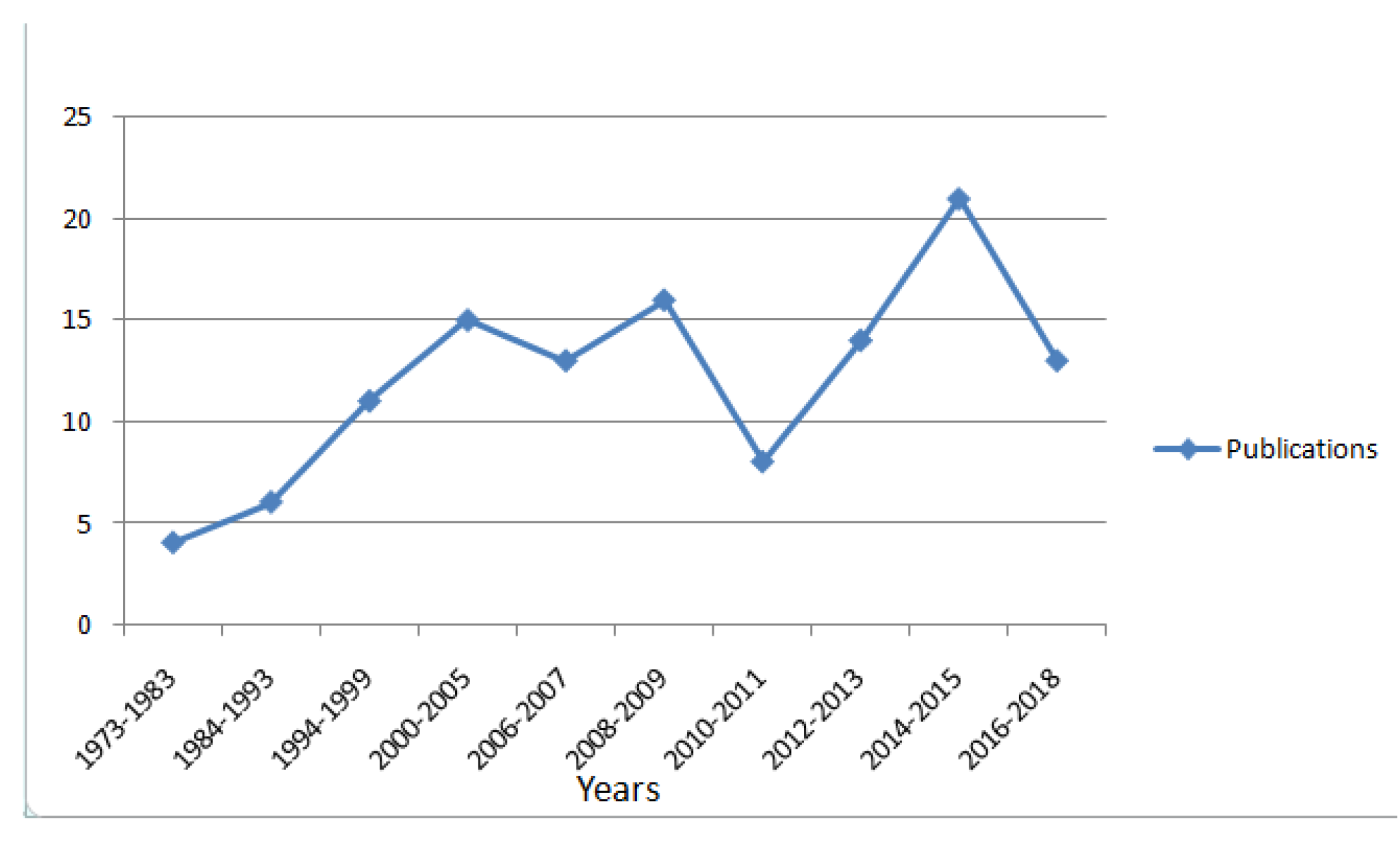
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turaga, P.; Chellappa, R.; Subrahmanian, V.; Udrea, O. Machine recognition of human activities: A survey. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Vid. Technol. 2008, 18, 1473–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeslund, T.; Hilton, A.; Krüger, V. A survey of advances in vision-based human motion capture and analysis. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2006, 104, 90–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, R. A survey on vision-based human action recognition. Image Vis. Comput. 2010, 28, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micucci, D.; Mobilio, M.; Napoletano, P. Unimib shar: A dataset for human activity recognition using acceleration data from smartphones. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtman, A.; Barshan, B.; Fidan, B. Activity recognition invariant to wearable sensor unit orientation using differential rotational transformations represented by quaternions. Sensors 2018, 18, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantoch, E. Recognition of sedentary behavior by machine learning analysis of wearable sensors during activities of daily living for telemedical assessment of cardiovascular risk. Sensors 2018, 18, 3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chieu, H.; Lee, W.; Kaelbling, L. Activity Recognition from Physiological Data Using Conditional Random Fields. Workshop at ICML. Available online: https://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/30197 (accessed on 14 November 2018).
- Zhang, Y.; Peterson, B.; Dong, Z. A support-based reconstruction for sense mri. Sensors 2013, 13, 4029–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Tang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, Y. Exploring techniques for vision based human activity recognition: Methods, systems, and evaluation. Sensors 2013, 13, 1635–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, A.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D. Shape and motion features approach for activity tracking and recognition from kinect video camera. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 29th International Conference on IEEE, Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops (WAINA), Taipei, Taiwan, 27–29 March 2015; pp. 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, J. Learning actionlet ensemble for 3D human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 914–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z. Action recognition based on a bag of 3d points. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on IEEE, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.; Chen, C.-C.; Aggarwal, J. View invariant human action recognition using histograms of 3d joints. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Computer Society Conference on IEEE, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Gaglio, S.; Re, G.; Morana, M. Human activity recognition process using 3-d posture data. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2015, 45, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, J.; Ryoo, M. Human activity analysis: A review. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2011, 43, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wan, Y.; Saudagar, A.; Namuduri, K.; Buckles, B. Advances in human action recognition: A survey. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1501.05964. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, J.; Cai, Q. Human motion analysis: A review. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 1999, 73, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrila, D. The visual analysis of human movement: A survey. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 1999, 73, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Shao, L.; Xie, J.; Fan, Y.G. From handcrafted to learned representations for human action recognition: A survey. Image Vis. Comput. 2016, 55, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, S.; Harandi, M.; Porikli, F. Going deeper into action recognition: A Survey. Image Vis. Comput. 2017, 60, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on CVPR 2009 IEEE, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, A.; Javed, O.; Shah, M. Object tracking: A survey. Acm Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2006, 38, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, B.; Monekosso, D.; Remagnino, P.; Velastin, S.; Xu, L.-Q. Crowd analysis: A survey. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2008, 19, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinland, D.; Ronfard, R.; Boyer, E. A survey of vision-based methods for action representation, segmentation and recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2011, 115, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, J. Motion analysis: Past, present and future. In Distributed Video Sensor Networks; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Chaaraoui, A.; Climent-Pérez, P.; Flórez-Revuelta, F. A review on vision techniques applied to human behaviour analysis for ambient-assisted living. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 10873–10888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metaxas, D.; Zhang, S. A review of motion analysis methods for human nonverbal communication computing. Image Vis. Comput. 2013, 31, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, S.; Agrawal, A. A survey on activity recognition and behavior understanding in video surveillance. Vis. Comput. 2013, 29, 983–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedras, C.; Shah, M. Motion-based recognition a survey. Image Vis. Comput. 1995, 13, 129–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
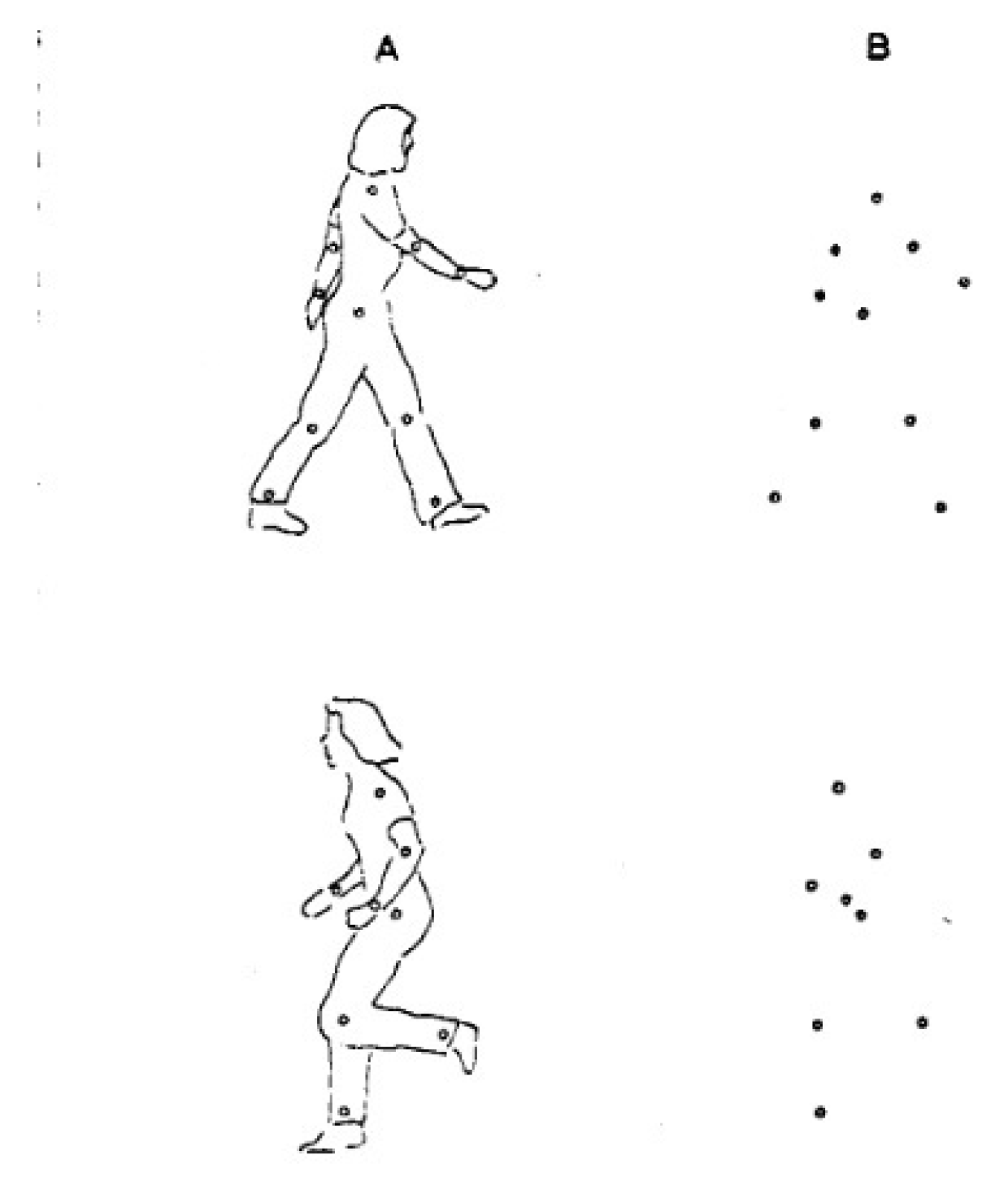
- Johansson, G. Visual perception of biological motion and a model for its Analysis. Percept. Psychophys. 1973, 14, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, D.; Nishihara, H. Representation and recognition of the spatial organization of three-dimensional shapes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1978, 200, 269–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hogg, D. Model-based vision: A program to see a walking person. Image Vis. Comput. 1983, 1, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, K. Towards model-based recognition of human movements in image sequences. CVGIP Image Underst. 1994, 59, 94–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrila, D.; Davis, L. Towards 3-d model-based tracking and recognition of human movement: A multi-view approach. In Proceedings of the International workshop on automatic face-and gesture-recognition, Zurich, Switzerland, 26–28 June 1995; pp. 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Green, R.; Guan, L. Quantifying and recognizing human movement patterns from monocular video images-part I: A new framework for modeling human motion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2004, 14, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, S.; Sullivan, J. Action recognition by shape matching to key frames. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Models Versus Exemplars in Computer Vision, Tokyo, Japan, 18–22 November 2001; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ogale, A.; Karapurkar, A.; Guerra-Filho, G.; Aloimonos, Y. View-Invariant Identification of Pose Sequences for Action Recognition. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&ved=2ahUKEwig37CPp9PeAhXO7GEKHfkGDQ4QFjABegQIBRAC&url=https%3A%2F%2Fpdfs.semanticscholar.org%2F98cb%2F29ae950ee4d3d9f23af0def90c9c3bfc771b.pdf&usg=AOvVaw1ste9TR_jRriyo-ytbTn_V (accessed on 14 November 2018).
- Rittscher, J.; Blake, A. Classification of human body motion. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; Volume 1, pp. 634–639. [Google Scholar]
- Darrell, T.; Pentland, A. Space-time gestures. In Proceedings of the 1993 CVPR’93 IEEE Computer Society Conference on IEEE, Computer Vision and PatternRecognition, New York, NY, USA, 15–17 June 1993; pp. 335–340. [Google Scholar]
- Yamato, J.; Ohya, J.; Ishii, K. Recognizing human action in time-sequential images using hidden markov model. In Proceedings of the 1992 IEEE CVPR’92 Computer Society Conference on IEEE, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Champaign, IL, USA, 15–18 June 1992; pp. 379–385. [Google Scholar]
- Bobick, A.; Davis, J. The recognition of human movement using temporal templates. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorelick, L.; Blank, M.; Shechtman, E.; Irani, M.; Basri, R. Actions as space-time Shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 2247–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, A.; Shah, M. Actions sketch: A novel action representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE CVPR 2005 Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 984–989. [Google Scholar]
- Elgammal, A.; Shet, V.; Yacoob, Y.; Davis, L. Learning dynamics for exemplar-based gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Madison, WI, USA, 18–20 June 2003; Volume 1, p. I-I. [Google Scholar]
- Weinland, D.; Boyer, E. Action recognition using exemplar-based embedding. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2008 IEEE Conference on IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, F.; Nevatia, R. Single view human action recognition using key pose matching and viterbi path searching. In Proceedings of the CVPR’07 IEEE Conference on IEEE, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sminchisescu, C.; Kanaujia, A.; Metaxas, D. Conditional models for contextual human motion recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2006, 104, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Chan, S.; Chia, L.-T. Motion context: A new representation for human action recognition. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 817–829. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, R.; Polana, R. Qualitative recognition of motion using temporal texture. CVGIP Image Underst. 1992, 56, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polana, R.; Nelson, R. Low level recognition of human motion (or how to get your man without finding his body parts). In Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE Workshop on IEEE, Motion of Non-Rigid and Articulated Objects, Austin, TX, USA, 11–12 November 1994; pp. 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, R.; Turk, M. View-based interpretation of real-time optical flow for gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the Third IEEE International Conference on IEEE, Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Nara, Japan, 14–16 April1998; pp. 416–421. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Efros, A.; Berg, A.; Mori, G.; Malik, J. Recognizing Action at a Distance Null; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; p. 726. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, N.; Reid, I. Behaviour understanding in video: A combined method. In Proceedings of the ICCV 2005 Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Beijing, China, 17–21 October 2005; Volume 1, pp. 808–815. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sabzmeydani, P.; Mori, G. Semi-latent dirichlet allocation: A hierarchical model for human action recognition. In Human Motion–Understanding, Modeling, Capture and Animation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 240–254. [Google Scholar]
- Zelnik-Manor, L.; Irani, M. Event-based analysis of video. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001; Volume 2, p. II. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–26 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Thurau, C.; Hlavác, V. Pose primitive based human action recognition in videos or still images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on CVPR Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Laptev, I.; Marszalek, M.; Schmid, C.; Rozenfeld, B. Learning realistic human actions from movies. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Laptev, I.; Pérez, P. Retrieving actions in movies. In Proceedings of the ICCV 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Sorokin, A. Human activity recognition with metric learning. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 548–561. [Google Scholar]
- Morguet, P.; Lang, M. Spotting dynamic hand gestures in video image sequences using hidden markov models. In Proceedings of the ICIP 98, 1998 International Conference on IEEE Image Processing, Chicago, IL, USA, 4–7 October 1998; pp. 193–197. [Google Scholar]
- Laptev, I. On space-time interest points. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2005, 64, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.; Stephens, M. A combined corner and edge detector. In Alvey Vision Conference; Citesee: Manchester, UK, 1988; Volume 15, p. 10-5244. [Google Scholar]
- Willems, G.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. An efficient dense and scale-invariant spatio-temporal interest point detector. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 650–663. [Google Scholar]
- Dollár, P.; Rabaud, V.; Cottrell, G.; Belongie, S. Behavior recognition via sparse spatio-temporal features. In Proceedings of the 2005 2nd Joint IEEE International Workshop on IEEE, Visual Surveillance and Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance, Beijing, China, 15–16 October 2005; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Messing, R.; Pal, C.; Kautz, H. Activity recognition using the velocity histories of tracked keypoints. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009; pp. 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Matikainen, P.; Hebert, M.; Sukthankar, R. Trajectons: Action recognition through the motion analysis of tracked features. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009; pp. 514–521. [Google Scholar]
- Klaser, A.; Marszałek, M.; Schmid, C. A spatio-temporal descriptor based on 3d-gradients. In Proceedings of the BMVC 2008-19th British Machine Vision Conference, British Machine Vision Association, Leeds, UK, 28–29 September 2008; p. 275. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B.; Schmid, C. Human detection using oriented histograms of flow and appearance. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springe: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 428–441. [Google Scholar]
- Kantorov, V.; Laptev, I. Efficient feature extraction, encoding and classification for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2593–2600. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Kläser, A.; Schmid, C.; Liu, C.-L. Action recognition by dense trajectories. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 3169–3176. [Google Scholar]
- Vig, E.; Dorr, M.; Cox, D. Space-variant descriptor sampling for action recognition based on saliency and eye movements. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 84–97. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.-G.; Dai, Q.; Xue, X.; Liu, W.; Ngo, C.-W. Trajectory-based modeling of human actions with motion reference points. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 425–438. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Schmid, C. Action recognition with improved trajectories. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on IEEE, Computer Vision (ICCV), Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 3551–3558. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Zou, C.; Qiao, Y.; Peng, Q. Action recognition with stacked fisher vectors. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 581–595. [Google Scholar]
- Perronnin, F.; Sánchez, J.; Mensink, T. Improving the fisher kernel for large-scale image classification. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield, K.; Simonyan, K.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Return of the devil in the details: Delving deep into convolutional nets. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1405.3531. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Z.; Lin, M.; Li, X.; Hauptmann, A.; Raj, B. Beyond gaussian pyramid: Multi-skip feature stacking for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 204–212. [Google Scholar]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 3104–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Lu, H. Deep visual tracking: Review and experimental comparison. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 76, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, S.; Sarvadevabhatla, R.; Mopuri, K.; Prabhu, N.; Kruthiventi, S.; Babu, R. A taxonomy of deep convolutional neural nets for computer vision. Front. Robot. AI 2016, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciresan, D.; Meier, U.; Gambardella, L.; Schmidhuber, J. Convolutional neural network committees for handwritten character classification. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on IEEE, Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR), Beijing, China, 18–21 September 2011; pp. 1135–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Cireşan, D.; Meier, U. Multi-column deep neural networks for offline handwritten chinese character classification. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Killarney, Ireland, 12–17 July 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Hori, T.; Watanabe, S. Joint ctc-attention based end-to-end speech recognition using multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on IEEE, Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 4835–4839. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Valentini-Botinhao, C.; Watts, O.; King, S. Deep neural networks employing multi-task learning and stacked bottleneck features for speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on IEEE, Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), South Brisbane, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; pp. 4460–4464. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Ho.; Lee, J.S.; Yang, H.-S. Human action recognition using a modified convolutional neural network. In International Symposium on Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.P.; Palmer, L.A. An evaluation of the two-dimensional Gabor filter model of simple receptive fields in cat striate cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 1987, 58, 1233–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhuang, H.; Serre, T.; Wolf, L.; Poggio, T. A biologically inspired system for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th International Conference on ICCV 2007 Computer Vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima, K.; Miyake, S.; Ito, T. Neocognitron: A neural network model for a mechanism of visual pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1983, 5, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutch, J.; Lowe, D.G. Multiclass object recognition with sparse, localized features. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; Volume 1, pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Serre, T.; Wolf, L.; Poggio, T. Object Recognition with Features Inspired by Visual Cortex; Massachusetts Inst of Tech Cambridge Dept of Brain and Cognitive Sciences: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Yu, K. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varol, G.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Long-term temporal convolutions for action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.Y.-H.; Hausknecht, M.; Vijayanarasimhan, S.; Vinyals, O.; Monga, R.; Toderici, G. Beyond short snippets: Deep networks for video classification. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4694–4702. [Google Scholar]
- Karpathy, A.; Toderici, G.; Shetty, S.; Leung, T.; Sukthankar, R.; Fei, L. Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1725–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4489–4497. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Jia, K.; Yeung, D.-Y.; Shi, B. Human action recognition using factorized spatio-temporal convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4597–4605. [Google Scholar]
- Baccouche, M.; Mamalet, F.; Wolf, C.; Garcia, C.; Baskurt, A. Sequential deep learning for human action recognition. In International Workshop on Human Behavior Understanding; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Donahue, J.; Anne Hendricks, L.; Guadarrama, S.; Rohrbach, M.; Venugopalan, S.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 2625–2634. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, A.; Fallside, F. Static and dynamic error propagation networks with application to speech coding. In Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1988; pp. 632–641. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 568–576. [Google Scholar]
- Brox, T.; Bruhn, A.; Papenberg, N.; Weickert, J. High accuracy optical flow estimation based on a theory for warping. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004; pp. 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Collobert, R.; Weston, J. A unified architecture for natural language processing: Deep neural networks with multitask learning. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning, Helsinki, Finland, 5–9 July 2008; pp. 160–167. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Feichtenhofer, C.; Pinz, A.; Zisserman, A. Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1933–1941. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Qiao, Y.; Tang, X. Action recognition with trajectory-pooled deep-convolutional descriptors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4305–4314. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, J.; Perronnin, F.; Mensink, T.; Verbeek, J. Image classification with the fisher vector: Theory and practice. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2013, 105, 222–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Mansimov, E.; Salakhudinov, R. Unsupervised learning of video representations using lstms. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–1 July 2015; pp. 843–852. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, P.; Larochelle, H.; Bengio, Y.; Manzagol, P.-A. Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning, ACM, Helsinki, Finland, 5–9 July 2008; pp. 1096–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Recognition of human activities using continuous autoencoders with wearable sensors. Sensors 2016, 16, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, C.-Y.; Cheng, W.-C.; Liou, J.-W.; Liou, D.-R. Autoencoder for words. Neurocomputing 2014, 139, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-C.; Orton, M.; Collins, D.; Doran, S.; Leach, M. Stacked autoencoders for unsupervised feature learning and multiple organ detection in a pilot study using 4D patient data. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 1930–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Chang, H.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Modeling video dynamics with deep dynencoder. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, M.; Couprie, C.; LeCun, Y. Deep multi-scale video prediction beyond mean square error. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1511.05440. [Google Scholar]
- Chaquet, J.; Carmona, E.; Fernández-Caballero, A. A survey of video datasets for human action and activity recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2013, 117, 633–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuldt, C.; Laptev, I.; Caputo, B. Recognizing human actions: A local svm approach. In Proceedings of the 17th ICPR 2004 International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cambridge, UK, 26–26 August 2004; Volume 3, pp. 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.; Santos-Victor, J.; Crowley, J. Caviar: Context Aware Vision Using Image-Based Active Recognition. 2005. Available online: https://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/CAVIAR/ (accessed on 14 November 2018).
- Rodriguez, M.; Ahmed, J.; Shah, M. Action mach a spatio-temporal maximum average correlation height filter for action recognition. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.; Shah, M. Recognizing 50 human action categories of web videos. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2013, 24, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, K.; Zamir, A.; Shah, M. Ucf101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1212.0402. [Google Scholar]
- Marszalek, M.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Actions in context. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2009 IEEE Conference on IEEE, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 2929–2936. [Google Scholar]
- Nagel, W.; Kröner, D.; Resch, M. High Performance Computing in Science and Engineering’17; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Mahadevan, V.; Vasconcelos, N. Vlad3: Encoding dynamics of deep features for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1951–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Lev, G.; Sadeh, G.; Klein, B.; Wolf, L. Rnn fisher vectors for action recognition and image annotation. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 833–850. [Google Scholar]
- Bilen, H.; Fernando, B.; Gavves, E.; Vedaldi, A.; Gould, S. Dynamic image networks for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Jiang, Y.-G.; Wang, X.; Ye, H.; Xue, X.; Wang, J. Fusing multi-stream deep networks for video classification. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1509.06086. [Google Scholar]



| Survey | Scope |
|---|---|
| Poppe [4] | Handcrafted action features and classification models |
| Aggarwal and Ryoo [15] | Individual and group activity analysis |
| Turaga et al. [1] | Human actions, complex activities |
| Moeslund et al. [2] | Human action analysis |
| Poppe [3] | Human action recognition |
| Cheng et al. [16] | Handcrafted models |
| Aggarwal and Cai [17] | Human action analysis |
| Gavrila [18] | Human body and hands tracking-based motion analysis |
| Yilmaz et al. [22] | Object detection and tracking |
| Zhan et al. [23] | Surveillance and crowd analysis |
| Weinland et al. [24] | Action recognition |
| Aggarwal [25] | Motion analysis fundamentals |
| Chaaraoui et al. [26] | Human behavior analysis and understanding |
| Metaxas and Zhang [27] | Human gestures to group activities |
| Vishwakarma and Agrawal [28] | Activity recognition and monitoring |
| Cedras and Shah [29] | Motion-based recognition approaches |
| Dataset | Type | No. of Videos | No. of Classes | No. of Subjects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KTH [119] | Indoor/Outdoor | 600 | 6 | 25 |
| Weizmann [42] | Outdoor | 90 | 10 | 9 |
| CAVIAR [120] | Indoor/Outdoor | 80 | 9 | numerous |
| UCFSports [121] | Television sports | 150 | 10 | numerous |
| UCF-50 [122] | YouTube videos | - | 50 | numerous |
| UCF-101 [123] | YouTube videos | 13,320 | 101 | numerous |
| Sports-1 M [96] | YouTube sports | 1,133,158 | 487 | numerous |
| Hollywood2 [124] | Clips from Hollywood movies | 1707 | 12 | numerous |
| HMDB-51 [125] | YouTube, movies | 7000 | 51 | numerous |
| Paper | Year | Technique | UCF-101 | HMDB-51 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Handcrafted Features | |||||
| Wang et al. [71] | 2011 | Dense Trajectory | UCF Sports 88.2 | ||
| Wang et al. [74] | 2013 | Dense Trajectory | UCF-50 91.2 | ||
| Learned Models | |||||
| Ji et al. [93] | 2013 | 3D Convolution | KTH 90.2 | ||
| Tran et al. [97] | 2015 | C3D generic descriptor | 90.4 | ||
| Karpathy et al. [96] | 2014 | Slow fusion | Sports-1 80.2 | ||
| Sun et al. [98] | 2015 | Factorized spatiotemporal CovNets | 88.1 | 59.1 | |
| Wang et al. [107] | 2015 | Two-stream | 89.3 | ||
| Ng et al. [95] | 2015 | Conv Pooling | 88.2 | Sports-1 73.1 | |
| Ng et al. [95] | 2015 | LSTM | 88.6 | ||
| Donahue et al. [100] | 2015 | LRCN | 82 | ||
| Jiang et al. [73] | 2012 | Trajectories | 78.5 | 48.4 | |
| Varol et al. [94] | 2017 | Long-term temporal convolutions | 91.7 | 64.8 | |
| Li et al. [126] | 2016 | VLAD | 92.2 | ||
| Hybrid Models | |||||
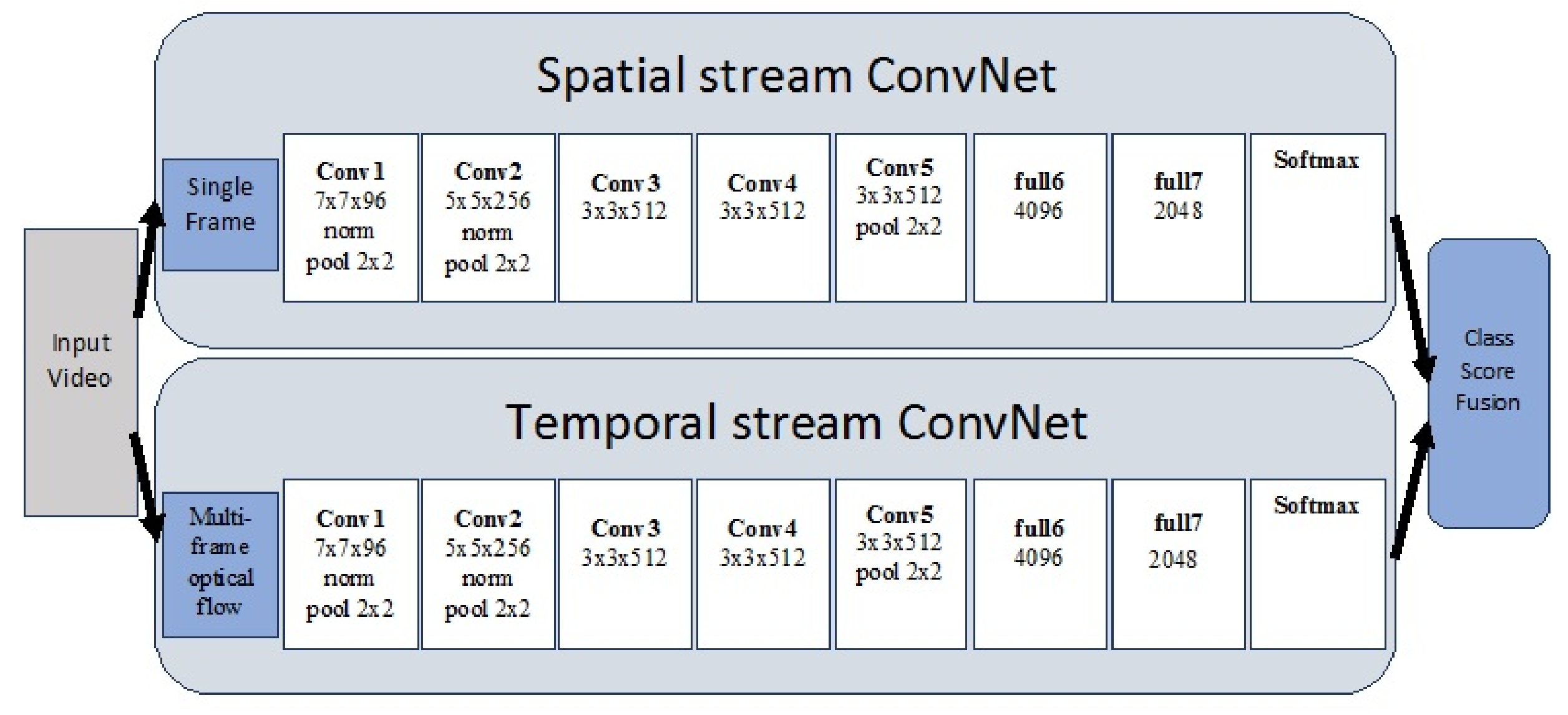
| Simonyan and Zisserman [102] | 2014 | Two-stream CNN | 88.0 | 59.4 | |
| Feichtenhofer et al. [106] | 2016 | ResNet | 93.5 | 69.2 | |
| Wang et al. [107] | 2015 | Trajectory pooling + Fisher vector | 91.5 | 65.9 | |
| Lev et al. [127] | 2016 | RNN Fisher vector | 94.08 | 67.71 | |
| Bilen et al. [128] | 2016 | Dynamic Image network | 89.1 | 65.2 | |
| Wu et al. [129] | 2015 | Adaptive multi-stream fusion | 92.6 | ||
| Deep Generative Models | |||||
| Srivastava et al. [109] | 2015 | LSTM autoencoder | 75.8 | 44.1 | |
| Mathieu [117] | 2015 | Adversarial network | ≈90 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saif, S.; Tehseen, S.; Kausar, S. A Survey of the Techniques for The Identification and Classification of Human Actions from Visual Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 3979. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113979
Saif S, Tehseen S, Kausar S. A Survey of the Techniques for The Identification and Classification of Human Actions from Visual Data. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):3979. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113979
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaif, Shahela, Samabia Tehseen, and Sumaira Kausar. 2018. "A Survey of the Techniques for The Identification and Classification of Human Actions from Visual Data" Sensors 18, no. 11: 3979. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113979
APA StyleSaif, S., Tehseen, S., & Kausar, S. (2018). A Survey of the Techniques for The Identification and Classification of Human Actions from Visual Data. Sensors, 18(11), 3979. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113979




