Location Information Quality: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Describing the Quality of Location Information: Related Work
3. A Model for Describing Location Information Quality
4. Factors Affecting the Quality of Location Information
4.1. Location Sensing Systems
4.1.1. Localization Technologies
4.1.2. Localization Measurements
4.1.3. Localization Methods
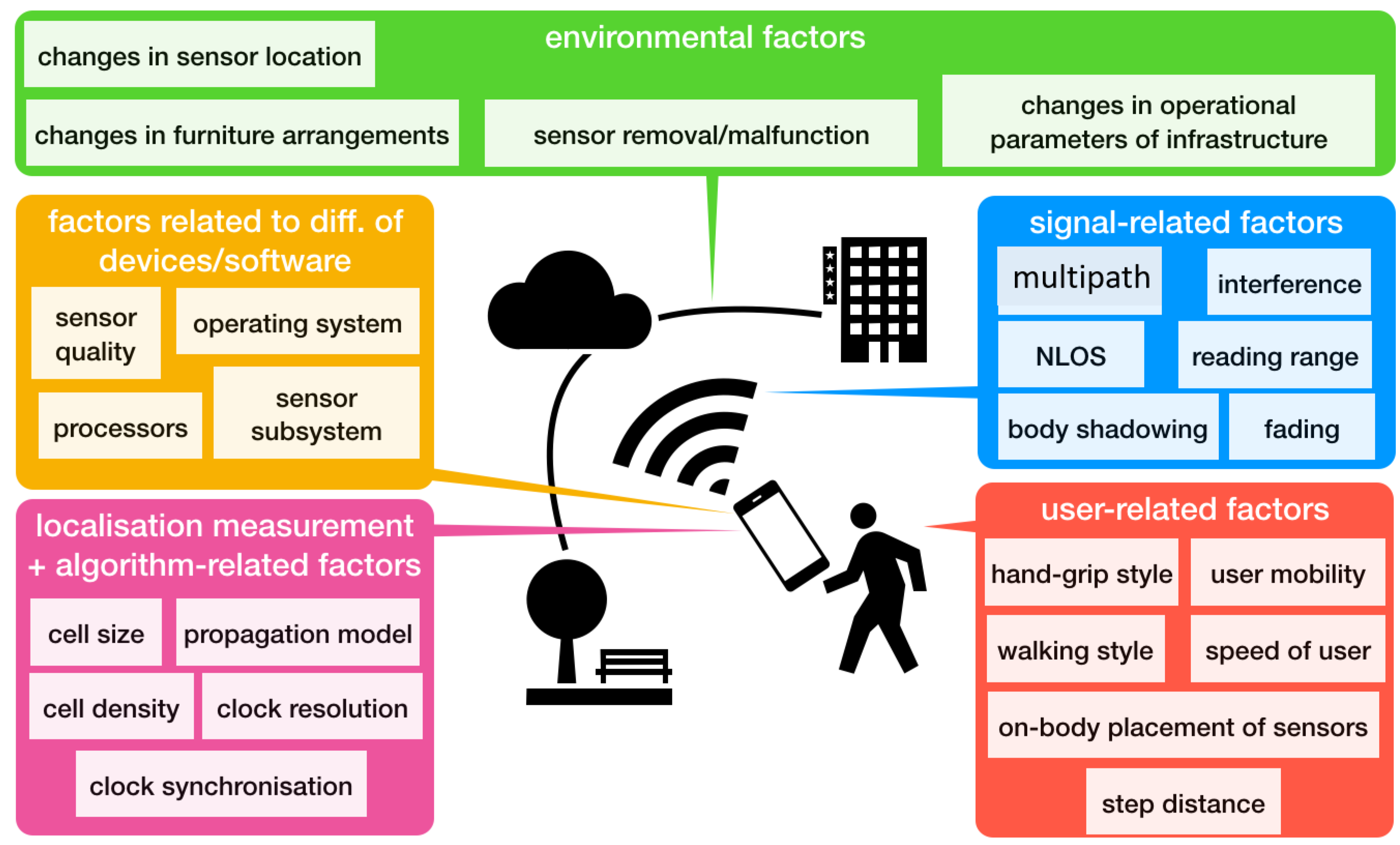
4.2. Factors Causing Quality Variations
4.2.1. Factors Related to the Nature of Signals
4.2.2. Factors Related to the Environment
4.2.3. Factors Related to Differences in Devices/Software
4.2.4. Factors Related to Localization Measurements/Algorithm
4.2.5. User Related Factors
4.2.6. Summary of the Factors Causing Quality Variations
4.3. Impact on Location Sensing Systems
5. Coping with Variations in the Quality of Location
6. Discussion
6.1. Benefits
6.2. Implications
6.3. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Youssef, M.; Agrawala, A. The Horus WLAN location determination system. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–8 June 2005; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Ranasinghe, C.; Krukar, J.; Kray, C. Visualizing Location Uncertainty on Mobile Devices: Cross-Cultural Differences in Perceptions and Preferences. In Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 2, p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Hightower, J.; Brumitt, B.; Borriello, G. The location stack: A layered model for location in ubiquitous computing. In Proceedings of the Fourth IEEE Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications, Washington, DC, USA, 20–21 June 2002; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Cheverst, K.; Davies, N.; Mitchell, K.; Friday, A.; Efstratiou, C. Developing a context-aware electronic tourist guide: some issues and experiences. In Proceedings of the 2000 SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, The Hague, The Netherlands, 1–6 April 2000; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Pospischil, G.; Umlauft, M.; Michlmayr, E. Designing LoL@, a mobile tourist guide for UMTS. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Conference on Mobile Human-Computer Interaction, Pisa, Italy, 18–20 September 2002; Springer: London, UK, 2002; pp. 140–154. [Google Scholar]
- Baus, J.; Kray, C. Frames of Reference, Positional Information and Navigational Assistance. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Society Conference, Pensacola Beach, FL, USA, 14–16 May 2002; pp. 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Aksenov, P.; Luyten, K.; Coninx, K. A unified scalable model of user localisation with uncertainty awareness for large-scale pervasive environments. In Proceedings of the 2011 Fifth International Conference on Next Generation Mobile Applications, Services and Technologies, Cardiff, UK, 14–16 September 2011; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 212–217. [Google Scholar]
- Dearman, D.; Varshavsky, A.; De Lara, E.; Truong, K.N. An exploration of location error estimation. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Innsbruck, Austria, 16–19 September 2007; Springer: London, UK, 2007; pp. 181–198. [Google Scholar]
- Lemelson, H.; King, T.; Effelsberg, W. A study on user acceptance of error visualization techniques. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking, and Services, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland, 21–25 July 2008; ICST (Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering): South Portland, ME, USA, 2008; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Kjærgaard, M.B.; Weckemann, K. Posq: Unsupervised fingerprinting and visualization of GPS positioning quality. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Mobile Computing, Applications, and Services, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 24–27 October 2010; Springer: London, UK, 2010; pp. 176–194. [Google Scholar]
- Damián-Reyes, P.; Favela, J.; Contreras-Castillo, J. Uncertainty management in context-aware applications: Increasing usability and user trust. Wirel. Person. Commun. 2011, 56, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, A.; Al-Muhtadi, J.; Chetan, S.; Campbell, R.; Mickunas, M.D. Middlewhere: A middleware for location awareness in ubiquitous computing applications. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM/IFIP/USENIX international conference on Middleware, Toronto, ON, Canada, 18–22 October 2004; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 397–416. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, G.T.; Ye, J.; Dobson, S.A.; Nixon, P. Loc8: A location model and extensible framework for programming with location. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2010, 9, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kray, C.; Kortuem, G. Adaptive Positioning for Ambient Systems. KI 2007, 21, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Marshall, A.; Yu, W. Path planning and following algorithms in an indoor navigation model for visually impaired. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Internet Monitoring and Protection, Silicon Valley, CA, USA, 1–6 July 2007; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- Alarifi, A.; Al-Salman, A.; Alsaleh, M.; Alnafessah, A.; Al-Hadhrami, S.; Al-Ammar, M.A.; Al-Khalifa, H.S. Ultra wideband indoor positioning technologies: Analysis and recent advances. Sensors 2016, 16, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, G.; Steenkiste, P. Providing contextual information to pervasive computing applications. In Proceedings of the First IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–26 March 2003; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Worboys, M. Imprecision in finite resolution spatial data. GeoInformatica 1998, 2, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; McKeever, S.; Coyle, L.; Neely, S.; Dobson, S. Resolving uncertainty in context integration and abstraction: context integration and abstraction. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Pervasive Services, Sorrento, Italy, 6–10 July 2008; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, P.; Salber, D. Modelling and using sensed context information in the design of interactive applications. In Engineering for Human-Computer Interaction; Springer: London, UK, 2001; pp. 317–335. [Google Scholar]
- Henricksen, K.; Indulska, J. Modelling and using imperfect context information. In Proceedings of the Second IEEE Annual Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops, Orlando, FL, USA, 14–17 March 2004; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Lo, A.; Niemegeers, I. A survey of indoor positioning systems for wireless personal networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2009, 11, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Darabi, H.; Banerjee, P.; Liu, J. Survey of wireless indoor positioning techniques and systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. C 2007, 37, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainetti, L.; Patrono, L.; Sergi, I. A survey on indoor positioning systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd International Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks (SoftCOM), Split, Croatia, 17–19 September 2014; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Brena, R.F.; García-Vázquez, J.P.; Galván-Tejada, C.E.; Muñoz-Rodriguez, D.; Vargas-Rosales, C.; Fangmeyer, J. Evolution of indoor positioning technologies: A survey. J. Sens. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-López, T.; Garrido, J.L.; Benghazi, K.; Chung, L. A survey on indoor positioning systems: Foreseeing a quality design. In Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence; Springer: London, UK, 2010; pp. 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Jiang, G.; Huang, C. A survey on indoor positioning technologies. In Theoretical and Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science; Springer: London, UK, 2011; pp. 198–206. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yi, Y.; Ni, L.M. A survey on wireless indoor localization from the device perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. 2016, 49, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deak, G.; Curran, K.; Condell, J. A survey of active and passive indoor localisation systems. Comput. Commun. 2012, 35, 1939–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Dobson, S.; McKeever, S. Situation identification techniques in pervasive computing: A review. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2012, 8, 36–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hightower, J.; Borriello, G. A survey and taxonomy of location systems for ubiquitous computing. IEEE Comput. 2001, 34, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Hu, X.; Gu, F.; Wang, D.; Yu, S. Improvement schemes for indoor mobile location estimation: A survey. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Chen, J.; Guo, W.; Liu, K.R. Signal processing techniques in network-aided positioning: A survey of state-of-the-art positioning designs. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2005, 22, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, H.A.; Roongpiboonsopit, D.; Kasemsuppakorn, P. Uncertainty in personal navigation services. J. Navig. 2011, 64, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greis, M.; Joshi, A.; Singer, K.; Schmidt, A.; Machulla, T. Uncertainty Visualization Influences how Humans Aggregate Discrepant Information. In Proceedings of the 2018 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–26 April 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; p. 505. [Google Scholar]
- Otsason, V.; Varshavsky, A.; LaMarca, A.; De Lara, E. Accurate GSM indoor localization. In UbiComp 2005: Ubiquitous Computing; Springer: London, UK, 2005; p. 903. [Google Scholar]
- Nuño-Maganda, M.; Herrera-Rivas, H.; Torres-Huitzil, C.; Marisol, H.M.C.; Coronado-Pérez, Y. On-Device Learning of Indoor Location for WiFi Fingerprint Approach. Sensors 2018, 18, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foxlin, E. Pedestrian tracking with shoe-mounted inertial sensors. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2005, 25, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harle, R. A survey of indoor inertial positioning systems for pedestrians. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhao, C.; Ding, G.; Gong, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, F. A reliable and accurate indoor localization method using phone inertial sensors. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–8 September 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Want, R.; Hopper, A.; Falcao, V.; Gibbons, J. The active badge location system. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 1992, 10, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Do, T.H.; Yoo, M. An in-depth survey of visible light communication based positioning systems. Sensors 2016, 16, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, N.U.; Naeem, A.; Pasha, M.A.; Jadoon, T.; Yuen, C. Indoor positioning using visible led lights: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2015, 48, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.; Jones, A.; Hopper, A. A new location technique for the active office. IEEE Person. Commun. 1997, 4, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Priyantha, N.B.; Chakraborty, A.; Balakrishnan, H. The cricket location-support system. In Proceedings of the 6th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Boston, MA, USA, 6–11 August 2000; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Azizyan, M.; Constandache, I.; Roy Choudhury, R. SurroundSense: Mobile phone localization via ambience fingerprinting. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Beijing, China, 20–25 September 2009; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Lau, Y.C.; Patil, A.P. LANDMARC: indoor location sensing using active RFID. In Proceedings of the First IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–26 March 2003; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 407–415. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.W.; Lin, C.Y. An Interactive Real-Time Locating System Based on Bluetooth Low-Energy Beacon Network. Sensors 2018, 18, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridolfi, M.; Van de Velde, S.; Steendam, H.; De Poorter, E. Analysis of the Scalability of UWB Indoor Localization Solutions for High User Densities. Sensors 2018, 18, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, S.N. Node positioning in zigbee network using trilateration method based on the received signal strength indicator (RSSI). Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2010, 46, 48–61. [Google Scholar]
- Steinhoff, U.; Omerčević, D.; Perko, R.; Schiele, B.; Leonardis, A. How computer vision can help in outdoor positioning. In Proceedings of the 2007 European Conference on Ambient Intelligence, Darmstadt, Germany, 7–10 November 2007; Springer: London, UK, 2007; pp. 124–141. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Afia, A.; Deambrogio, L.; Salós, D.; Escher, A.C.; Macabiau, C.; Soulier, L.; Gay-Bellile, V. Review and classification of vision-based localisation techniques in unknown environments. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2014, 8, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, M.; Kessel, M.; Marouane, C. Indoor positioning using smartphone camera. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Guimarães, Portugal, 21–23 September 2011; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, A.; Chen, R.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Wu, D. An Indoor Positioning System Based on Static Objects in Large Indoor Scenes by Using Smartphone Cameras. Sensors 2018, 18, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.; Lee, K.; Rhee, I. FM-based indoor localization via automatic fingerprint DB construction and matching. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Taipei, Taiwan, 25–28 June 2013; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 207–220. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Gan, Y.; Yang, J.; Sidhom, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ye, F. Push the limit of WiFi based localization for smartphones. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Istanbul, Turkey, 22–26 August 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 305–316. [Google Scholar]
- Yassin, A.; Nasser, Y.; Awad, M.; Al-Dubai, A.; Liu, R.; Yuen, C.; Raulefs, R.; Aboutanios, E. Recent advances in indoor localization: A survey on theoretical approaches and applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 19, 1327–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y. From RSSI to CSI: Indoor localization via channel response. ACM Comput. Surv. 2013, 46, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keunecke, K.; Scholl, G. Deriving 2D TOA/TDOA IEEE 802.11 g/n/ac location accuracy from an experimentally verified fading channel model. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Montbeliard-Belfort, France, 28–31 October 2013; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.; Klukas, R.; Messier, G.G. Using WLAN infrastructure for angle-of-arrival indoor user location. In Proceedings of the IEEE 68th Vehicular Technology Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 21–24 September 2008; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.H.; Congdon, P. Avoiding multipath to revive inbuilding WiFi localization. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Taipei, Taiwan, 25–28 June 2013; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 249–262. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, R.S. Evolution of positioning techniques in cellular networks, from 2G to 4G. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouet, M.; Dos Santos, A.L. RFID tags: Positioning principles and localization techniques. In Proceedings of the 2008 1st IFIP Wireless Days, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 24–27 November 2008; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gezici, S.; Tian, Z.; Giannakis, G.B.; Kobayashi, H.; Molisch, A.F.; Poor, H.V.; Sahinoglu, Z. Localization via ultra-wideband radios: A look at positioning aspects for future sensor networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2005, 22, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lymberopoulos, D.; Liu, J.; Priyantha, B. FM-based indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Ambleside, UK, 25–29 June 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 169–182. [Google Scholar]
- Faragher, R.; Harle, R. An analysis of the accuracy of bluetooth low energy for indoor positioning applications. In Proceedings of the 27th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2014), Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 September 2014; pp. 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cuthbert, L. Bluetooth positioning using RSSI and triangulation methods. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–14 January 2013; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 837–842. [Google Scholar]
- Ijaz, F.; Yang, H.K.; Ahmad, A.W.; Lee, C. Indoor positioning: A review of indoor ultrasonic positioning systems. In Proceedings of the 2013 15th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), PyeongChang, Korea, 27–30 January 2013; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 1146–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, C.; Segura, J.C.; Holm, S. Feasibility of ultrasound positioning based on signal strength. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sydney, Australia, 13–15 November 2012; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hightower, J.; Borriello, G. Location systems for ubiquitous computing. Computer 2001, 34, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mautz, R. Indoor Positioning Technologies. Habilitation Thesis, ETH Zurich, Department of Civil, Environmental and Geomatic Engineering, Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry, Zürich, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Roos, T.; Myllymaki, P.; Tirri, H. A statistical modeling approach to location estimation. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2002, 99, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, M.; Rachid, E. A survey of positioning techniques and location based services in wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Informatics, Communication and Energy Systems (SPICES), Calicut, India, 19–21 February 2015; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Beauregard, S.; Haas, H. Pedestrian dead reckoning: A basis for personal positioning. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Positioning, Navigation and Communication, Hannover, Germany, 16 March 2006; pp. 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Geier, J. Wireless LAN Implications, Problems, and Solutions. Available online: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2351131 (accessed on 15 June 2015).
- Ian Poole, A.C.L. Multipath Propagation Tutorial. Available online: https://zh.scribd.com/document/238396316/Multipath-Propagation-Tutorial (accessed on 16 November 2018).
- Chen, C.S. A non-line-of-sight error mitigation method for location estimation. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curran, K.; Norrby, S. RFID-enabled location determination within indoor environments. Int. J. Ambient Comput. Intell. 2009, 1, 63–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.N.; Truong, K.N.; Abowd, G.D. Powerline positioning: A practical sub-room-level indoor location system for domestic use. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Orange County, CA, USA, 17–21 September 2006; Springer: London, UK, 2006; pp. 441–458. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xi, W. WILL: Wireless indoor localization without site survey. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2013, 24, 839–848. [Google Scholar]
- Matic, A.; Papliatseyeu, A.; Osmani, V.; Mayora-Ibarra, O. Tuning to your position: FM radio based indoor localization with spontaneous recalibration. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), Mannheim, Germany, 29 March–2 April 2010; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.g.; Charrow, B.; Curtis, D.; Battat, J.; Minkov, E.; Hicks, J.; Teller, S.; Ledlie, J. Growing an organic indoor location system. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–18 June 2010; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 271–284. [Google Scholar]
- Blunck, H.; Kjærgaard, M.B.; Toftegaard, T.S. Sensing and classifying impairments of GPS reception on mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Pervasive Computing, Seattle, WA, USA, 21–25 March 2011; Springer: London, UK, 2011; pp. 350–367. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, S.; Radunovic, B.; Choudhury, R.R.; Minka, T. You are facing the Mona Lisa: Spot localization using PHY layer information. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Ambleside, UK, 25–29 June 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 183–196. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Pan, X.; Li, K.; Lv, Q.; Dick, R.P.; Hannigan, M.; Shang, L. Ariel: Automatic wi-fi based room fingerprinting for indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–8 September 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 441–450. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.B.; Juang, R.T.; Lin, H.P.; Ke, C.Y. Mobile location estimation based on differences of signal attenuations for GSM systems. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Columbus, OH, USA, 22–27 June 2003; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.L.; Li, C.H.; Ng, J.K.Y.; Leung, K.R. Location estimation via support vector regression. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2007, 6, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Kukkonen, J. A grid-based algorithm for on-device GSM positioning. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 26–29 September 2010; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg, J.; Nilsson, M.; Synnes, K. Positioning with bluetooth. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Telecommunications, Tahiti, French, 23 February–1 March 2003; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 2, pp. 954–958. [Google Scholar]
- Svalastog, M.S. Indoor Positioning-Technologies, Services and Architectures. Master’s Thesis, Department of Informatics, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Porcino, D.; Hirt, W. Ultra-wideband radio technology: Potential and challenges ahead. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2003, 41, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, R.; Batra, A. Ultra Wideband Systems: Technologies and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, S. Which RFID Frequency Is Right for Your Application? Available online: https://blog.atlasrfidstore.com/which-rfid-frequency-is-right-for-your-application (accessed on 1 June 2015).
- Gu, W.; Aminikashani, M.; Kavehrad, M. Indoor visible light positioning system with multipath reflection analysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 7–11 January 2016; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 89–92. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Steinhoff, U.; Schiele, B. Dead reckoning from the pocket-an experimental study. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), Mannheim, Germany, 29 March–2 April 2010; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 162–170. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y. Locating in fingerprint space: wireless indoor localization with little human intervention. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Istanbul, Turkey, 22–26 August 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Sen, S.; Elgohary, A.; Farid, M.; Youssef, M.; Choudhury, R.R. No need to war-drive: Unsupervised indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Ambleside, UK, 25–29 June 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Chan, S.H.G.; Yu, L.; Liu, N. Calibration-free fusion of step counter and wireless fingerprints for indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Osaka, Japan, 7–11 September 2015; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 897–908. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Yuen, C.; Do, T.N.; Tan, U.X. Fusing similarity-based sequence and dead reckoning for indoor positioning without training. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 4197–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Shangguan, L.; Yi, K.; Liu, Y. Enhancing wifi-based localization with visual clues. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Osaka, Japan, 7–11 September 2015; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 963–974. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Shangguan, L.; Yi, K.; Liu, Y. Indoor localization via multi-modal sensing on smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Heidelberg, Germany, 12–16 September 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 208–219. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, A.; Chintalapudi, K.K.; Padmanabhan, V.N.; Sen, R. Zee: Zero-effort crowdsourcing for indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Istanbul, Turkey, 22–26 August 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 293–304. [Google Scholar]
- Mariakakis, A.T.; Sen, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.H. Sail: Single access point-based indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Bretton Woods, NH, USA, 16–19 June 2014; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 315–328. [Google Scholar]
- Aksenov, P.; Luyten, K.; Coninx, K. O brother, where art thou located? Raising awareness of variability in location tracking for users of location-based pervasive applications. J. Locat. Based Serv. 2012, 6, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baus, J.; Krüger, A.; Wahlster, W. A resource-adaptive mobile navigation system. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–16 January 2002; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kray, C.; Kortuem, G. Interactive positioning based on object visibility. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Conference on Mobile Human-Computer Interaction, Glasgow, UK, 13–16 September 2004; Springer: London, UK, 2004; pp. 276–287. [Google Scholar]
- Benford, S.; Crabtree, A.; Flintham, M.; Drozd, A.; Anastasi, R.; Paxton, M.; Tandavanitj, N.; Adams, M.; Row-Farr, J. Can you see me now? ACM Trans. Comput.-Hum. Interact. 2006, 13, 100–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Quality of Location Information | Quality of Location System | |
|---|---|---|---|
| [4] | level of reception of location information, last known location, time elapsed since the last reading | ✓ | |
| [6] | precise information, unprecise information, no information, false information | ✓ | |
| [7] | error, age, update rate, precision | ✓ | |
| [11] | accuracy, precision, lack of information, lapsed information, ambiguous information (contradictory readings from different sensors) | ✓ | |
| [12] | resolution, freshness | ✓ | |
| [13] | granularity, sampling frequency of a sensor, coverage, accuracy, precision | ✓ | ✓ |
| [14] | recency (time), maximum deviation (expressed as distance in meters), confidence | ✓ | |
| [30] | incompleteness, accuracy, timeliness, reliability | ✓ | |
| [15] | accuracy and precision, coverage and its resolution, latency in making location updates, building’s infrastructure impact, effect of random errors on the system such as errors caused by signal interference and reflection | ✓ | |
| [22] | security and privacy, cost, performance, robustness and fault tolerance, complexity, user preference, commercial availability, limitation | ✓ | |
| [23] | accuracy, precision, complexity, scalability, robustness, cost | ✓ | |
| [16] | accuracy, availability, coverage area, scalability, cost, privacy | ✓ | |
| [24] | accuracy, coverage, cost, complexity, applicative environment | ✓ | |
| [25] | accuracy, coverage, cost | ✓ | |
| [26] | accuracy, precision, robustness, complexity, scalability, cost | ✓ | |
| [27] | range, accuracy, localization algorithm used, cost | ✓ | |
| [28] | accuracy, reliability, robustness | ✓ | |
| [31] | accuracy, precision, scale, cost | ✓ | |
| [32] | accuracy, complexity, cost, power consumption, usability | ✓ |
| Localization Technology | Localization Measurement/Method | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNSS | WiFi | Mobile Network | BT | UWB | RFID | Zigbee | Vision/Image | IR | VLC | Inertial | Ultrasound | Cell-ID | TOA | TDOA | AOA | RSS | Fingerprinting | Prop. Modelling | DR | ||
| Signal-related | Multipath | ✓[83] | ✓[65,85] | ✓[48,66] | ✓[50] | ✓[22,90] | ✓[94] | ✓[58] | ✓[58] | ||||||||||||
| Interference | ✓[86] | ✓[48,66] | ✓[16,23,92] | ✓[16,50,71] | ✓[22,90] | ✓[42] | ✓[40,95] | ✓[68] | ✓[40,95] | ||||||||||||
| NLOS | ✓[83] | ✓[48,66] | ✓[24,47,78,93] | ✓[16,27] | ✓[88] | ✓[88] | ✓[88] | ||||||||||||||
| Body shadowing | ✓[65,85] | ✓[48,66] | ✓[58] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Fading | ✓[83] | ✓[65,85] | ✓[48,66] | ✓[24,47,78,93] | ✓[58] | ✓[58] | |||||||||||||||
| Reading range of sensors | ✓[24,47,78,93] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Environmental | Nature of the environment | ✓[58] | ✓[16,90] | ✓[22] | ✓[58,79] | ✓[58,79] | ✓[42] | ||||||||||||||
| Environmental dynamics | ✓[65,85] | ✓[86] | ✓[71] | ✓[24,47,78,93] | ✓[24,68] | ✓[88] | ✓[58,79] | ✓[58,79] | |||||||||||||
| changes to operational parameters | ✓[79] | ✓[86] | ✓[58,79] | ✓[58,79] | |||||||||||||||||
| Different locations-same signal signature | ✓[56] | ✓[56] | |||||||||||||||||||
| Device/software differences | Differences in devices used | ✓[10,83] | ✓[65,84,85] | ✓[16,23,92] | ✓[42,51] | ✓[42] | |||||||||||||||
| Quality of sensors | ✓[83] | ✓[84] | ✓[16,23,92] | ✓[24,47] | ✓[42,51] | ✓[42] | |||||||||||||||
| Quality of processors | ✓[83] | ✓[84] | ✓[16,23,92] | ✓[47] | ✓[51] | ✓[42] | |||||||||||||||
| Sensor-subsystem | ✓[47] | ✓[51] | |||||||||||||||||||
| OS/other software | ✓[51] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (Localization measurement/Algorithm)-related | Cell-size | ✓[16,88] | |||||||||||||||||||
| Cell-density | ✓[16,88] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Interference from near-by cells | ✓[86] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Clock synchronization | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Resolutions of clocks | ✓[42] | ✓[42] | |||||||||||||||||||
| Antenna resolution | ✓[84] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Antenna array size | ✓[84] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Outdated fingerprint databases | ✓[82] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Prop. model used | ✓[57] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| User-related | Hand grip styles | ✓[40,83,84] | |||||||||||||||||||
| Body placement of the receiver/tags | ✓[83] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | |||||||||||||
| Walking style | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | |||||||||||||||
| Walking speed | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | ✓[40] | |||||||||||||||
| mobility of the user | ✓[47] | ✓[42] | ✓[40,95] | ✓[40,95] | |||||||||||||||||
| Orientation of the device | ✓[83] | ✓[65,85] | ✓[40] | ||||||||||||||||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ranasinghe, C.; Kray, C. Location Information Quality: A Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 3999. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113999
Ranasinghe C, Kray C. Location Information Quality: A Review. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):3999. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113999
Chicago/Turabian StyleRanasinghe, Champika, and Christian Kray. 2018. "Location Information Quality: A Review" Sensors 18, no. 11: 3999. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113999
APA StyleRanasinghe, C., & Kray, C. (2018). Location Information Quality: A Review. Sensors, 18(11), 3999. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113999






