A Novel Microfluidic Point-of-Care Biosensor System on Printed Circuit Board for Cytokine Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TMB Detection
2.2. Assay-Incubated
2.3. Assay in Plasma
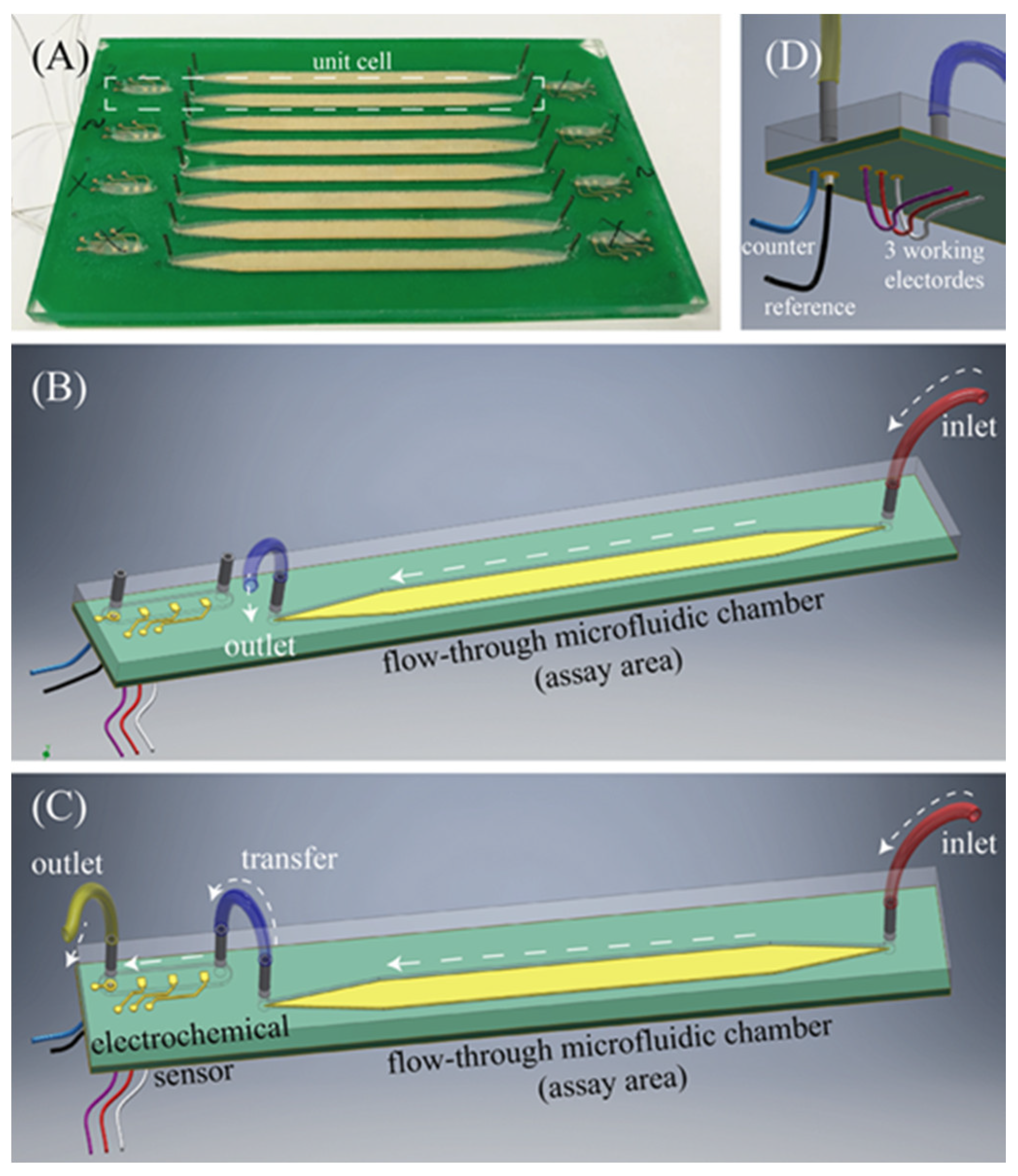
2.4. Assay Boards
2.5. The 16-Channel Bio-Instrumentation Board
3. Results and Discussion
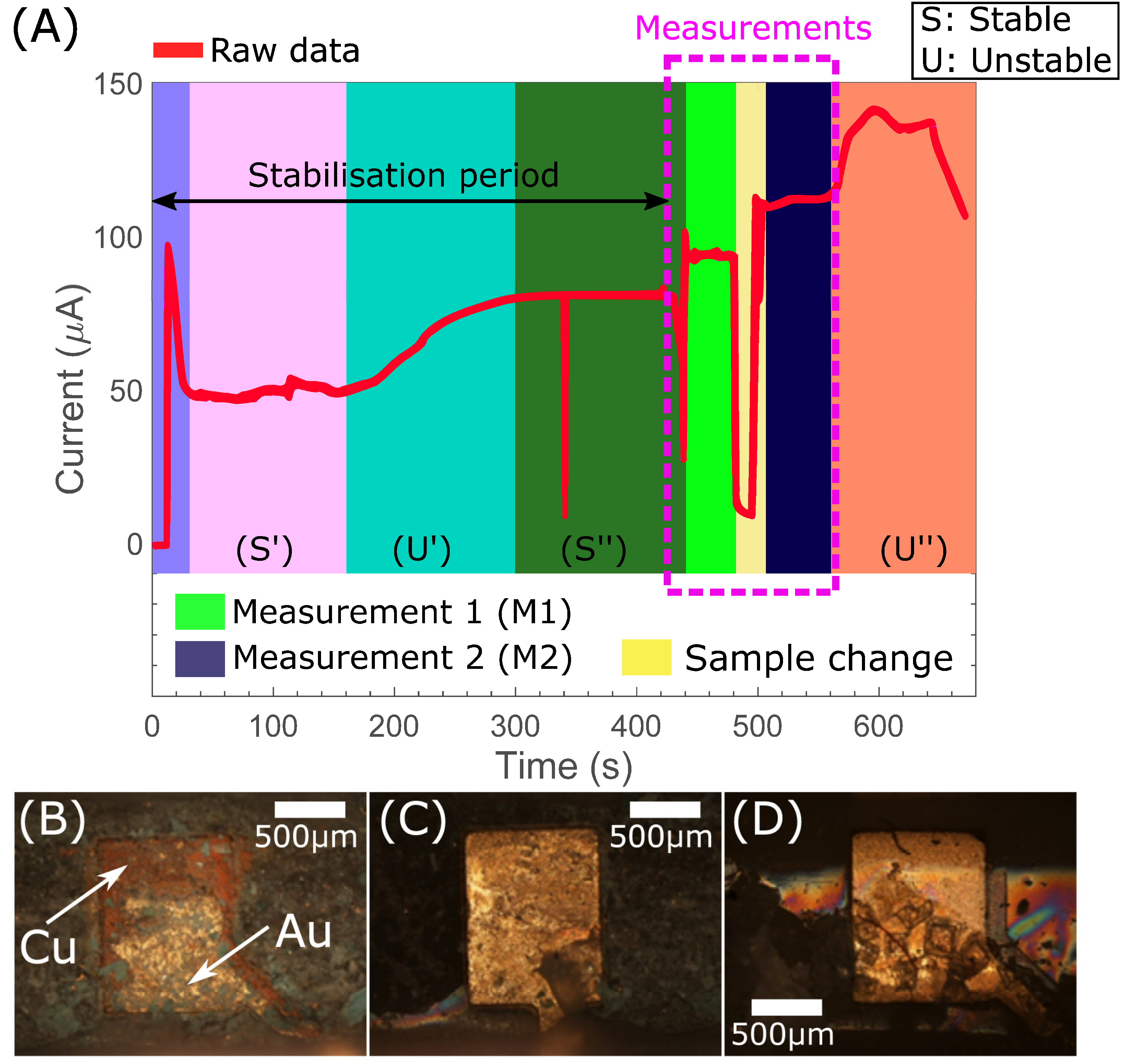
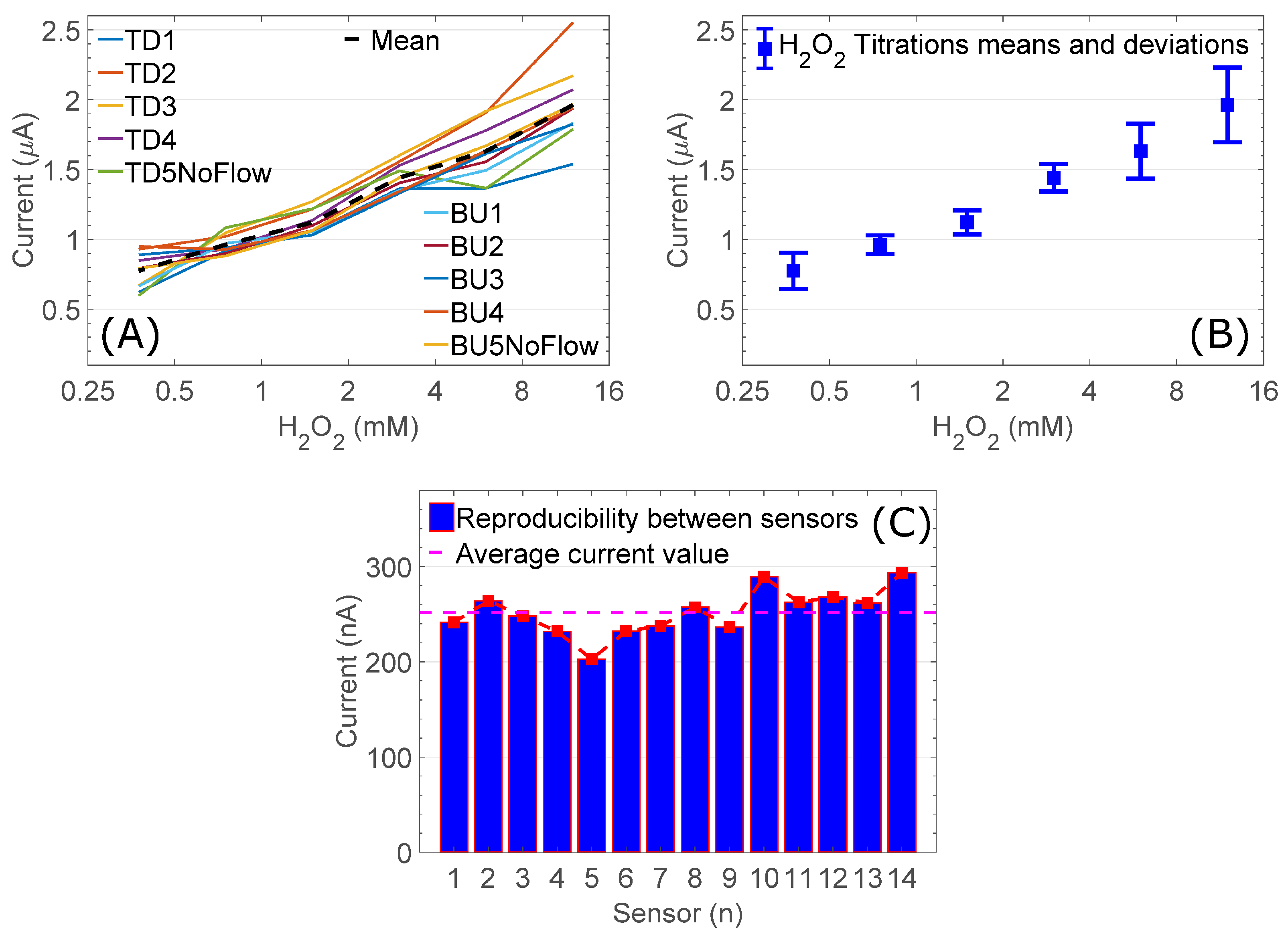
3.1. Demonstration of Electrochemical H2O2 Measurement
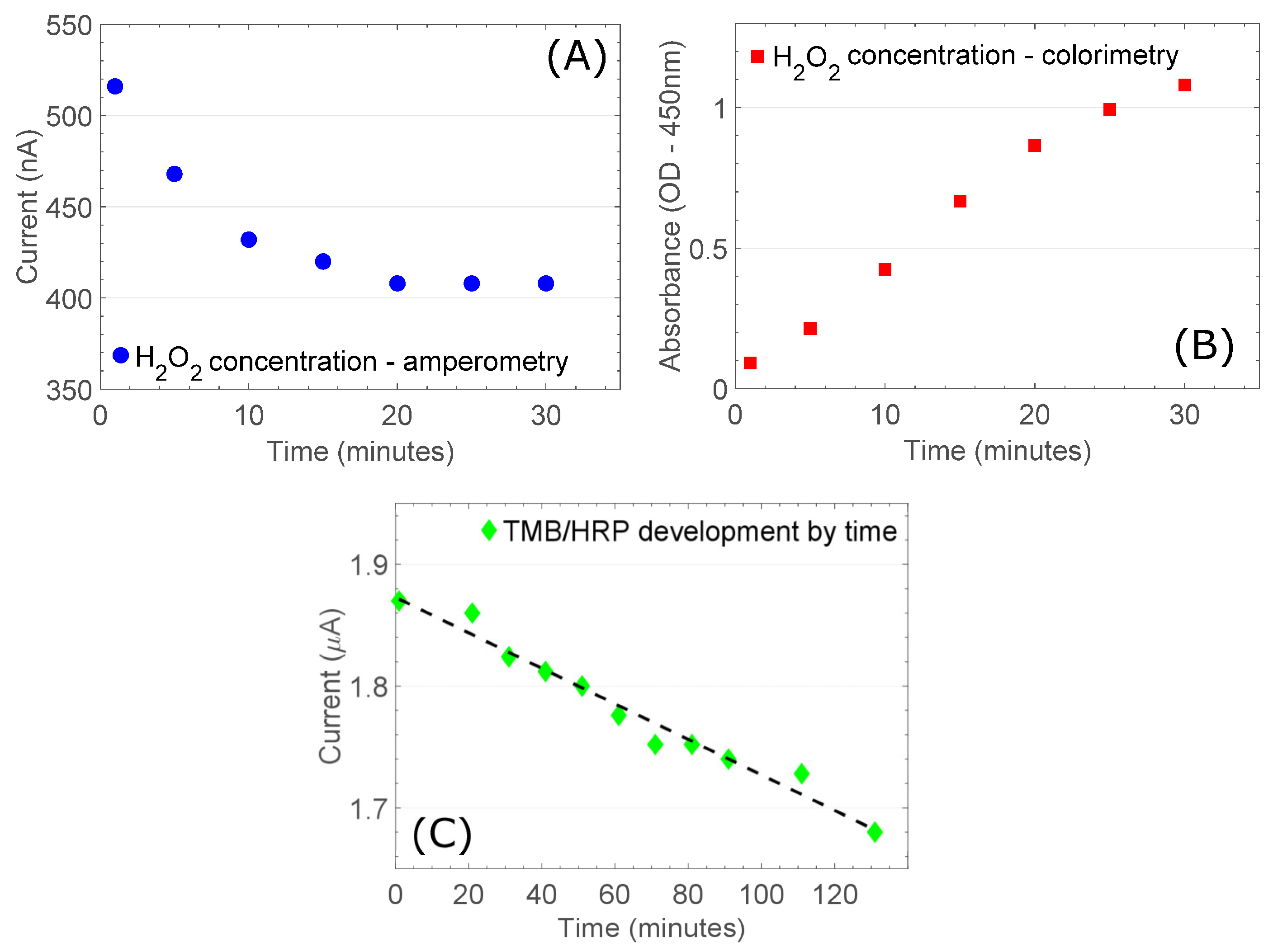
3.2. TMB Measurement Protocol Is Determined by H2O2 Depletion Kinetics
3.3. Prototype IFNγ PoC Detection Assay Demonstration
4. Conclusions
Data Access Statement
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, T.A.; Moraes, F.C.; Janegitz, B.C.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Electrochemical Biosensors Based on Nanostructured Carbon Black: A Review. J. Nanomater. 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Eijk, A.A.; Tintu, A.N.; Hays, J.P. Pre-implementation guidelines for infectious disease point-of-care testing in medical institutions. Future Microbiol. 2017, 12, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mauk, M.; Song, J.; Bau, H.H.; Gross, R.; Bushman, F.D.; Collman, R.G.; Liu, C. Miniaturized devices for point of care molecular detection of HIV. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bissonnette, L.; Bergeron, M.G. Portable devices and mobile instruments for infectious diseases point-of-care testing. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 471–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.I.; Reis, N.M. A critical insight into the development pipeline of microfluidic immunoassay devices for the sensitive quantitation of protein biomarkers at the point of care. Analyst 2017, 142, 858–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawn, S.D.; Mwaba, P.; Bates, M.; Piatek, A.; Alexander, H.; Marais, B.J.; Cuevas, L.E.; McHugh, T.D.; Zijenah, L.; Kapata, N. Advances in tuberculosis diagnostics: the Xpert MTB/RIF assay and future prospects for a point-of-care test. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romeo, A.; Leung, T.; Sanchez, S. Smart biosensors for multiplexed and fully integrated point-of-care diagnostics. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1957–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A.; Tiwari, S.; Jayant, R.D.; Marty, A.; Nair, M. Towards detection and diagnosis of Ebola virus disease at point-of-care. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozel, T.R.; Burnham-Marusich, A.R. Point of Care Testing for Infectious Diseases-Past, Present and Future. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L.; Qin, J. Microfluidic platform towards point-of-care diagnostics in infectious diseases. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1377, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laksanasopin, T.; Guo, T.W.; Nayak, S.; Sridhara, A.A.; Xie, S.; Olowookere, O.O.; Cadinu, P.; Meng, F.; Chee, N.H.; Kim, J. A smartphone dongle for diagnosis of infectious diseases at the point of care. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 273re1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, B.; O’Dell, D.; Finkelstein, J.L.; Lee, S.; Erickson, D.; Mehta, S. IronPhone: Mobile device-coupled point-of-care diagnostics for assessment of iron status by quantification of serum ferritin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, M. Advances in point-of-care technologies for molecular diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, B.; Cortazar, B.; Tseng, D.; Ozkan, H.; Feng, S.; Wei, Q.; Chan, R.Y.L.; Burbano, J.; Farooqui, Q.; Lewinski, M. Cellphone-based hand-held microplate reader for point-of-care testing of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7857–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincer, C.; Bruch, R.; Kling, A.; Dittrich, P.S.; Urban, G.A. Multiplexed Point-of-Care Testing–xPOCT. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syedmoradi, L.; Daneshpour, M.; Alvandipour, M.; Gomez, F.A.; Hajghassem, H.; Omidfar, K. Point of care testing: the impact of nanotechnology. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, C.M.; Augustine, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Nara, S.; Srivastava, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Microfluidics Based Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 1700047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubala, V.; Harris, L.F.; Ricco, A.J.; Tan, M.X.; Williams, D.E. Point of care diagnostics: Status and future. Anal. Chem. 2011, 84, 487–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F. Advances in paper-based point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Zapatero-Rodríguez, J.; Estrela, P.; O’Kennedy, R. Point-of-care diagnostics in low resource settings: Present status and future role of microfluidics. Biosensors 2015, 5, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vashist, S.K.; Luppa, P.B.; Yeo, L.Y.; Ozcan, A.; Luong, J.H. Emerging technologies for next-generation point-of-care testing. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ferrari, M.; Qin, L. Point-of-care technologies for molecular diagnostics using a drop of blood. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Basteiro, A.L.; Di Nardo, A.; Saavedra, B.; Silva, D.R.; Palmero, D.; Gegia, M.; Migliori, G.B.; Duarte, R.; Mambuque, E.; Centis, R.; et al. Point of care diagnostics for tuberculosis. Pulmonology 2018, 24, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urdea, M.; Penny, L.A.; Olmsted, S.S.; Giovanni, M.Y.; Kaspar, P.; Shepherd, A.; Wilson, P.; Dahl, C.A.; Buchsbaum, S.; Moeller, G. Requirements for high impact diagnostics in the developing world. Nature 2006, 444, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Guan, Z.; Song, Y.; Song, E.; Lu, Z.; Liu, D.; An, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Yang, C. Lateral flow assay with pressure meter readout for rapid point-of-care detection of disease-associated protein. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channon, R.B.; Yang, Y.; Feibelman, K.M.; Geiss, B.J.; Dandy, D.S.; Henry, C.S. Development of an Electrochemical Paper-Based Analytical Device for Trace Detection of Virus Particles. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7777–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, S.; Fiore, L.; Massoud, R.; Cortese, C.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Arduini, F. Low-cost and reagent-free paper-based device to detect chloride ions in serum and sweat. Talanta 2018, 179, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-Gálvez, A.; Morales-Narváez, E.; Romero, J.; Merkoçi, A. Photoluminescent lateral flow based on non-radiative energy transfer for protein detection in human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Yang, H.; Gong, Y.; You, M.; Liu, Z.; Choi, J.R.; Wen, T.; Qu, Z.; Mei, Q.; Xu, F. A fully disposable and integrated paper-based device for nucleic acid extraction, amplification and detection. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Akay, A.; Wei, H.; Wang, S.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Erlandsson, B.E.; Li, X.; Lee, W.; Hu, J.; Wang, L. Advances in smartphone-based point-of-care diagnostics. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, S.K.; van Oordt, T.; Schneider, E.M.; Zengerle, R.; Von Stetten, F.; Luong, J.H. A smartphone-based colorimetric reader for bioanalytical applications using the screen-based bottom illumination provided by gadgets. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashist, S.K.; Schneider, E.M.; Zengerle, R.; Von Stetten, F.; Luong, J.H. Graphene-based rapid and highly-sensitive immunoassay for C-reactive protein using a smartphone-based colorimetric reader. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oncescu, V.; O’Dell, D.; Erickson, D. Smartphone based health accessory for colorimetric detection of biomarkers in sweat and saliva. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3232–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.; Wambach, T.; Venkatesh, A.G.; Hall, D.A. A low-cost smartphone-based electrochemical biosensor for point-of-care diagnostics. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS) Proceedings, Lausanne, Switzerland, 22–24 October 2014; pp. 312–315. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Deng, W.; Su, J.; Chen, S.; Song, H.; Aldalbahi, A.; Zuo, X.; Song, S.; Shi, J. Portable detection of clenbuterol using a smartphone-based electrochemical biosensor with electric field-driven acceleration. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 781, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Chao, R.; Ren, Y.; Hu, C.; Xu, Z.; Liu, G.L. Smartphone based portable bacteria pre-concentrating microfluidic sensor and impedance sensing system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammerink, T.S.; Spiering, V.; Elwenspoek, M.; Fluitman, J.; Van den Berg, A. Modular concept for fluid handling systems. A demonstrator micro analysis system. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Workshop on Micro Electromechanical Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–15 February 1996; pp. 389–394. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Merkel, T.; Graeber, M.; Pagel, L. A new technology for fluidic microsystems based on PCB technology. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1999, 77, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Marshall, L.A.; Babikian, S.; Han, C.M.; Santiago, J.G. A printed circuit board based microfluidic system for point-of-care diagnostics applications. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences, Seattle, WA, USA, 2–6 October 2011; pp. 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Aracil, C.; Perdigones, F.; Moreno, J.M.; Luque, A.; Quero, J.M. Portable Lab-on-PCB platform for autonomous micromixing. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 131, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.H.; Yang, J.; Lenigk, R.; Bonanno, J.; Grodzinski, P. Self-contained, fully integrated biochip for sample preparation, polymerase chain reaction amplification, and DNA microarray detection. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaßmann, S.; Ibendorf, I.; Pagel, L. Realization of a flow injection analysis in PCB technology. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 133, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdallo, I.; Jimenez-Jorquera, C.; Fernández-Sánchez, C.; Baldi, A. Integration of microelectronic chips in microfluidic systems on printed circuit board. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 105022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, P.; Rainbow, J.; Regoutz, A.; Estrela, P.; Moschou, D. A PNA-based Lab-on-PCB diagnostic platform for rapid and high sensitivity DNA quantification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 123, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilakis, N.; Moschou, D.; Carta, D.; Morgan, H.; Prodromakis, T. Long-lasting FR-4 surface hydrophilisation towards commercial PCB passive microfluidics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 368, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prodromakis, T.; Liu, Y.; Toumazou, C. A Low-Cost Disposable Chemical Sensing Platform Based on Discrete Components. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2011, 32, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechlivanidis, N.G.; Papadimitriou, K.I.; Evans, D.; Vasilakis, N.; Prodromakis, T. Towards a smartphone-aided electronic ELISA for real-time electrochemical monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Baltimore, MD, USA, 28–31 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, W.; Han, J.; Choi, J.-W.; Ahn, C.H. Point-of-care testing (POCT) diagnostic systems using microfluidic lab-on-a-chip technologies. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 132, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschou, D.; Greathead, L.; Pantelidis, P.; Kelleher, P.; Morgan, H.; Prodromakis, T. Amperometric IFN-γ immunosensors with commercially fabricated PCB sensing electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.; Papadimitriou, K.I.; Greathead, L.; Vasilakis, N.; Pantelidis, P.; Kelleher, P.; Morgan, H.; Prodromakis, T. An Assay System for Point-of-Care Diagnosis of Tuberculosis using Commercially Manufactured PCB Technology. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschou, D.; Tserepi, A. The lab-on-PCB approach: tackling the μTAS commercial upscaling bottleneck. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1388–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papadimitriou, K.I.; Evans, D.; Morgan, H.; Prodromakis, T. A PCB-Based Electronic ELISA System For Rapid, Portable Infectious Disease Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (Biocas), Shanghai, China, 17–19 October 2016; pp. 252–255. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilakis, N.; Papadimitriou, K.I.; Evans, D.; Morgan, H.; Prodromakis, T. The Lab-on-PCB Framework for Affordable, Electronic-Based Point-of-Care Diagnostics: from Design to Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Healthcare Innovation Point-of-Care Technologies Conference (Hi-Poct), Cancun, Mexico, 9–11 November 2016; pp. 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilakis, N.; Papadimitriou, K.I.; Morgan, H.; Prodromakis, T. High-performance PCB-based capillary pumps for affordable point-of-care diagnostics. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2017, 21, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalvani, A. Diagnosing tuberculosis infection in the 21st century—New tools to tackle an old enemy. Chest 2007, 131, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, K.I.; Wang, C.; Rogers, M.L.; Gowers, S.A.N.; Leong, C.L.; Boutelle, M.G.; Drakakis, E.M. High-Performance Bioinstrumentation for Real-Time Neuroelectrochemical Traumatic Brain Injury Monitoring. Front. Human Neurosci. 2016, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldous, L.; Silvester, D.S.; Villagran, C.; Pitner, W.R.; Compton, R.G.; Lagunas, M.C.; Hardacre, C. Electrochemical studies of gold and chloride in ionic liquids. New J. Chem. 2006, 30, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruecha, N.; Shin, K.; Chailapakul, O.; Rodthongkum, N. Label-free Paper-based Electrochemical Impedance Immunosensor for Human Interferon Gamma Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 279, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mazurek, G.H.; Alocilja, E.C. Measurement of interferon gamma concentration using an electrochemical immunosensor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, B140–B145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ye, X.; Yan, Y.; Huang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Tan, S.; Cai, X. Electrochemical immunosensor for interferon-γ based on disposable ITO detector and HRP-antibody-conjugated nano gold as signal tag. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Jin, R.; Wei, H.; Yang, W.; Goldys, E.M.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, G.; Liu, G. Graphene Oxide Based Recyclable in Vivo Device for Amperometric Monitoring of Interferon-γ in Inflammatory Mice. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33078–33087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Mosher, C.; Lee, X.Y.; Das, S.R.; Cargill, A.A.; Tang, X.; Chen, B.; McLamore, E.S.; Gomes, C.; Hostetter, J.M. Rapid and label-free detection of interferon gamma via an electrochemical aptasensor comprising a ternary surface monolayer on a gold interdigitated electrode array. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
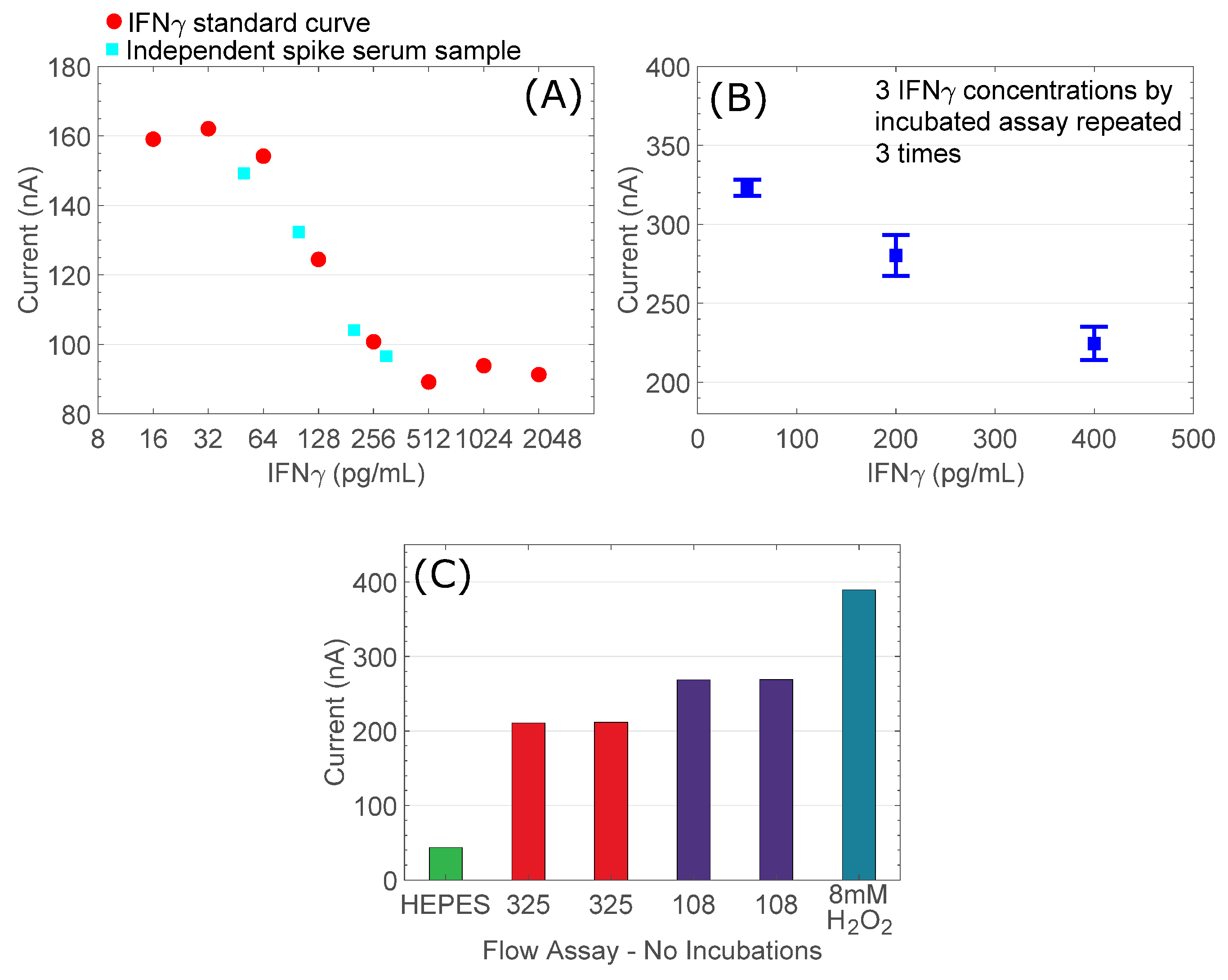
| Sample (pg/mL) | Predicted Value (nA) | Measured Value (nA) | |%Difference| |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 157.610 | 149.260 | 5.300 |
| 100 | 141.560 | 132.340 | 6.510 |
| 200 | 97.370 | 104.120 | 6.920 |
| 300 | 93.680 | 96.620 | 3.130 |
| Mean difference: 5.465% | |||
| Repeat | 50 pg/mL | 200 pg/mL | 400 pg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.326 | 0.264 | 0.222 |
| 2 | 0.325 | 0.294 | 0.236 |
| 3 | 0.317 | 0.277 | 0.215 |
| mean | 0.323 | 0.278 | 0.224 |
| Standard deviation | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.010 |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.015 | 0.054 | 0.045 |
| Ref. | Detection Limit (pg/mL) | Detection Range (pg/mL) | Method/Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| [58] | 3.4 | 5–1000 | Impedance immunosensor/Paper-based. |
| [59] | 0.4 | 0.4–40 | Square wave anodic stripping voltammetry/MNPs & AuNPs. |
| [60] | 0.048 | 0.1–10,000 | PDDA/AuNPs. |
| [61] | 1.3 | 1.3–210 | Amperometry/GO & structure-switching aptamers. |
| [62] | 520 | 1000–5000 | Label-free EIS/Au IDE. |
| This work | 40 | 16–2048 | Amperometry/PCB. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evans, D.; Papadimitriou, K.I.; Vasilakis, N.; Pantelidis, P.; Kelleher, P.; Morgan, H.; Prodromakis, T. A Novel Microfluidic Point-of-Care Biosensor System on Printed Circuit Board for Cytokine Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 4011. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114011
Evans D, Papadimitriou KI, Vasilakis N, Pantelidis P, Kelleher P, Morgan H, Prodromakis T. A Novel Microfluidic Point-of-Care Biosensor System on Printed Circuit Board for Cytokine Detection. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):4011. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114011
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvans, Daniel, Konstantinos I. Papadimitriou, Nikolaos Vasilakis, Panagiotis Pantelidis, Peter Kelleher, Hywel Morgan, and Themistoklis Prodromakis. 2018. "A Novel Microfluidic Point-of-Care Biosensor System on Printed Circuit Board for Cytokine Detection" Sensors 18, no. 11: 4011. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114011
APA StyleEvans, D., Papadimitriou, K. I., Vasilakis, N., Pantelidis, P., Kelleher, P., Morgan, H., & Prodromakis, T. (2018). A Novel Microfluidic Point-of-Care Biosensor System on Printed Circuit Board for Cytokine Detection. Sensors, 18(11), 4011. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114011






