Compressibility of High-Density EEG Signals in Stroke Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Patients’ Description
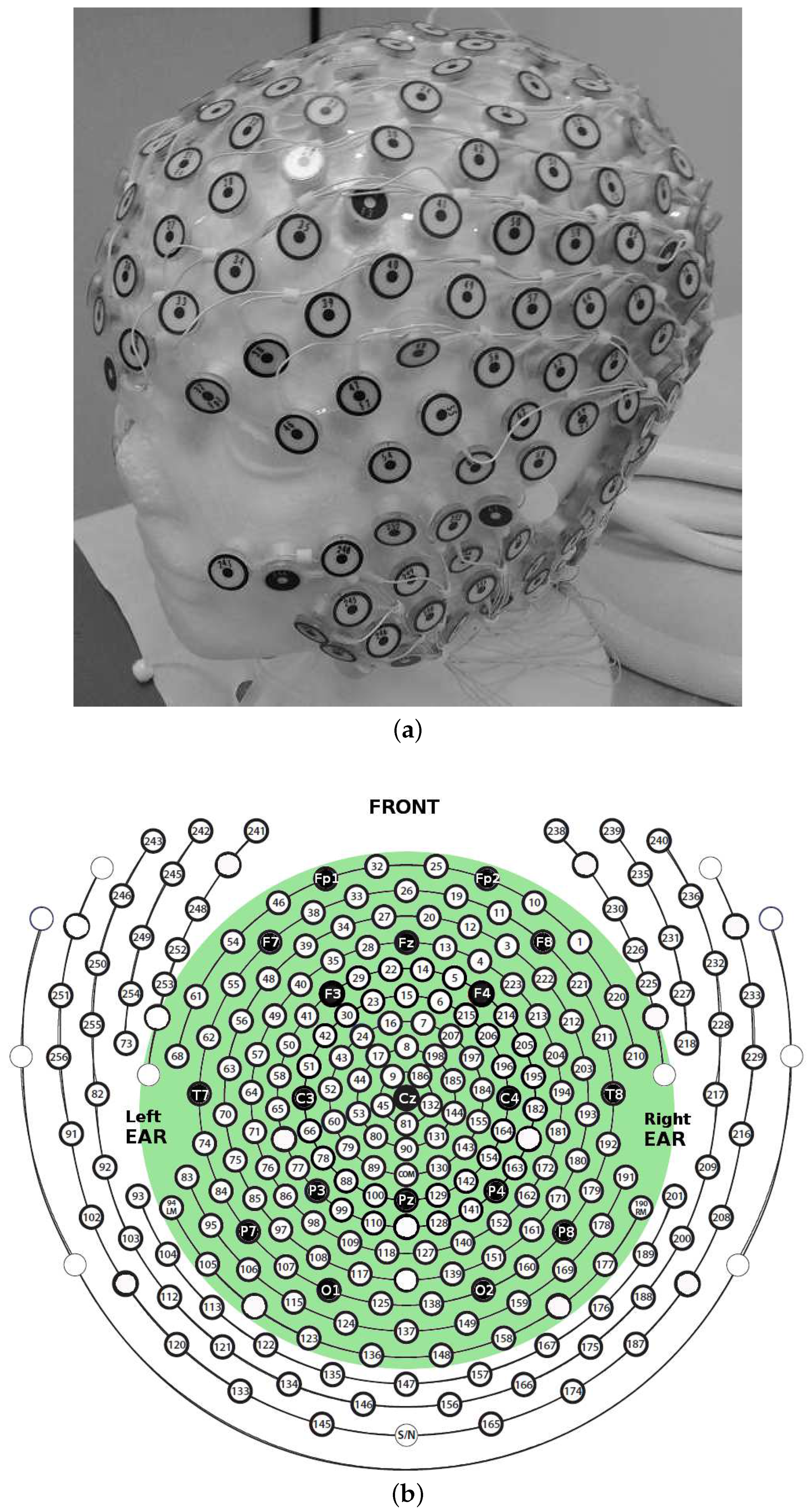
2.2. HD-EEG Recording and Preprocessing
2.3. Compressive Sensing
2.4. Compression of EEG Signals
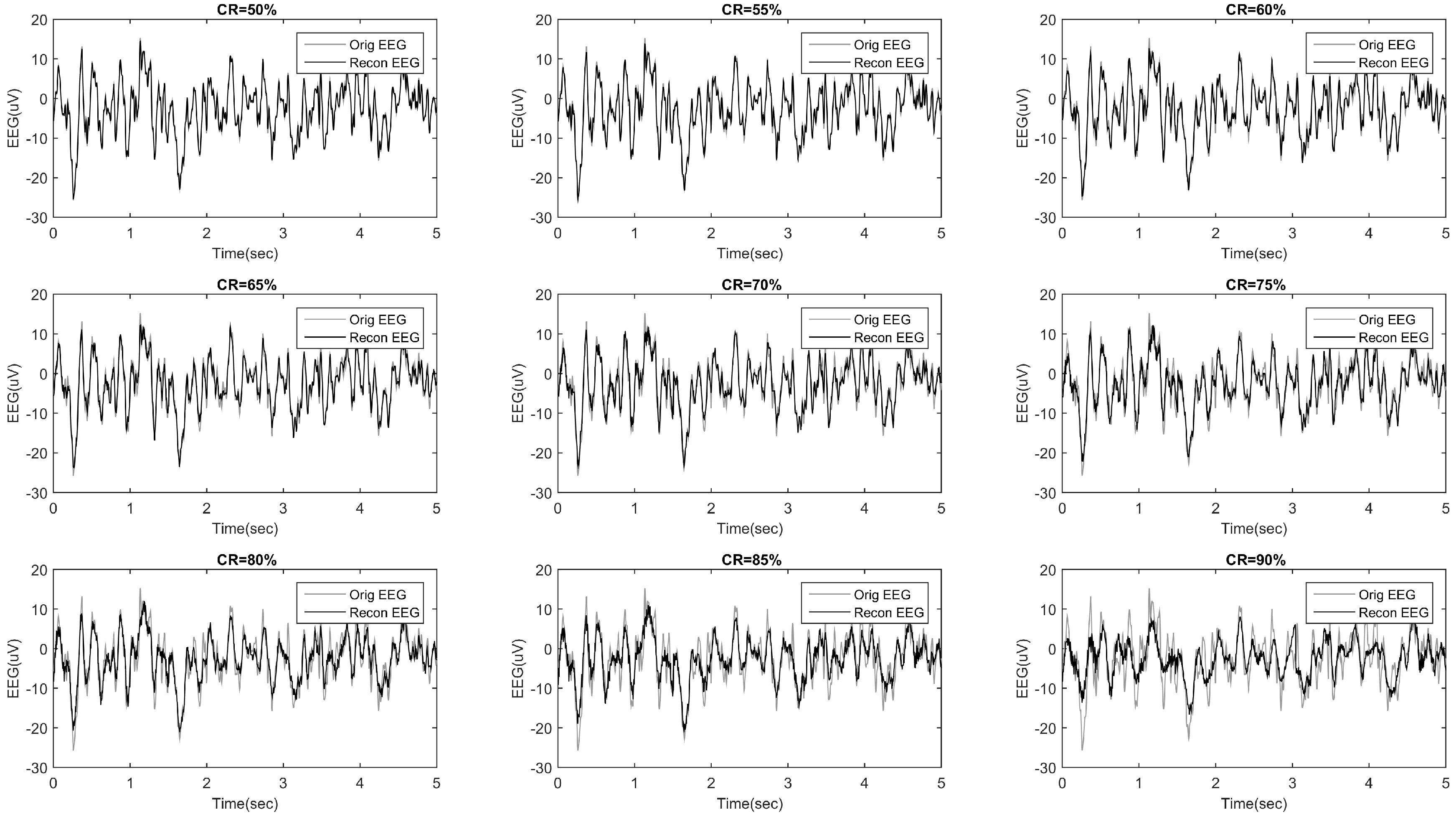
2.4.1. Epoch-Based SSIM Comparison
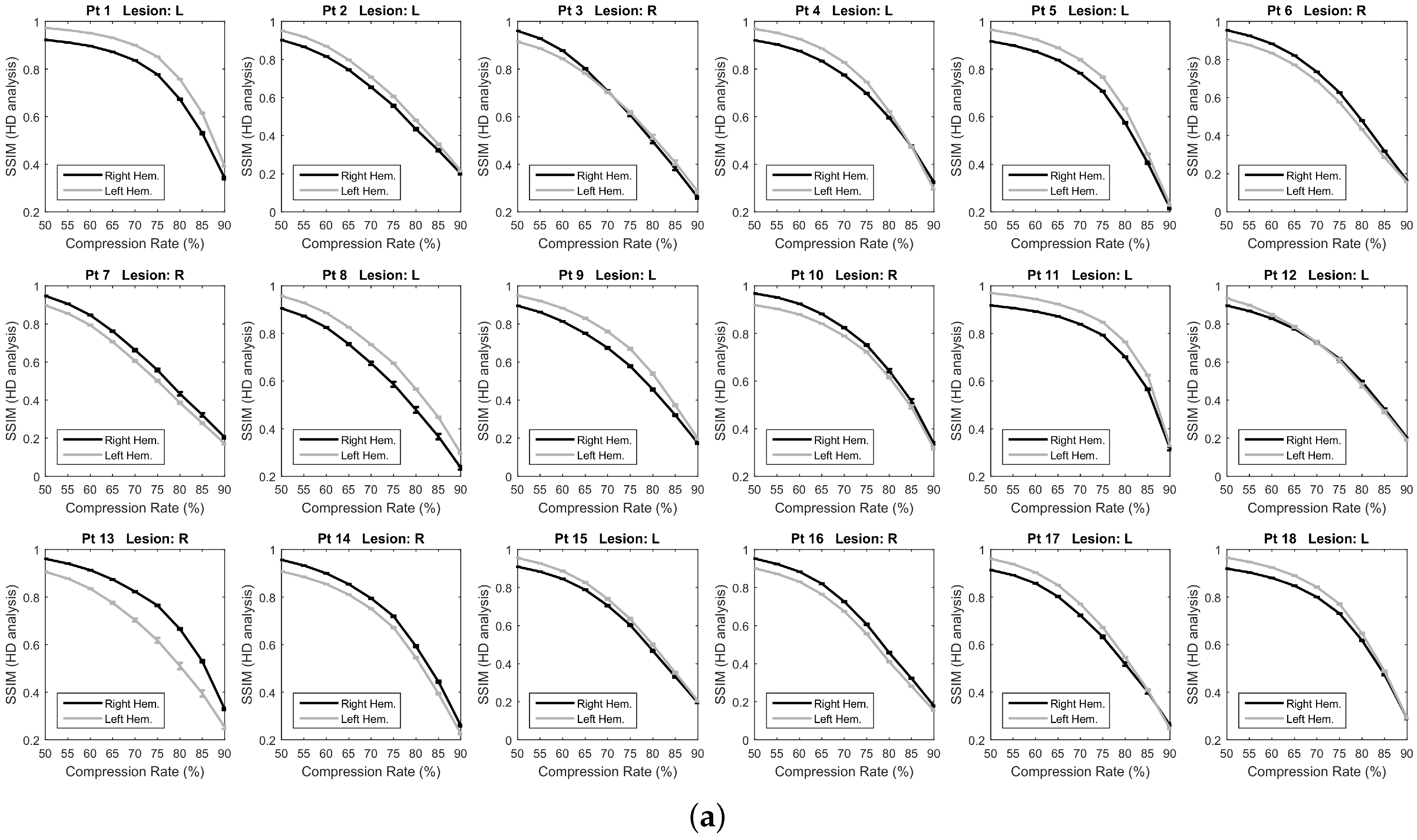
2.4.2. Overall SSIM Comparison
3. Results
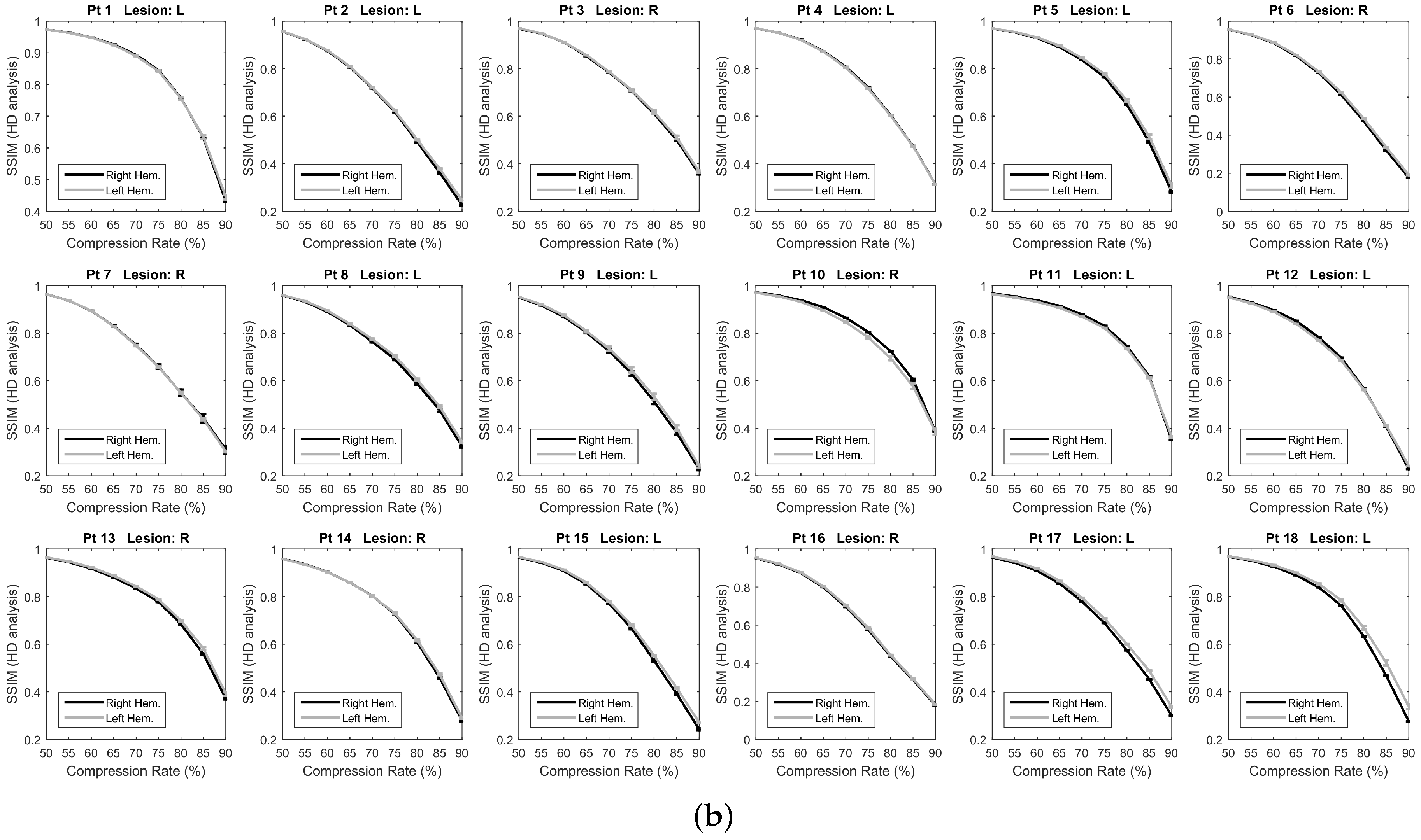
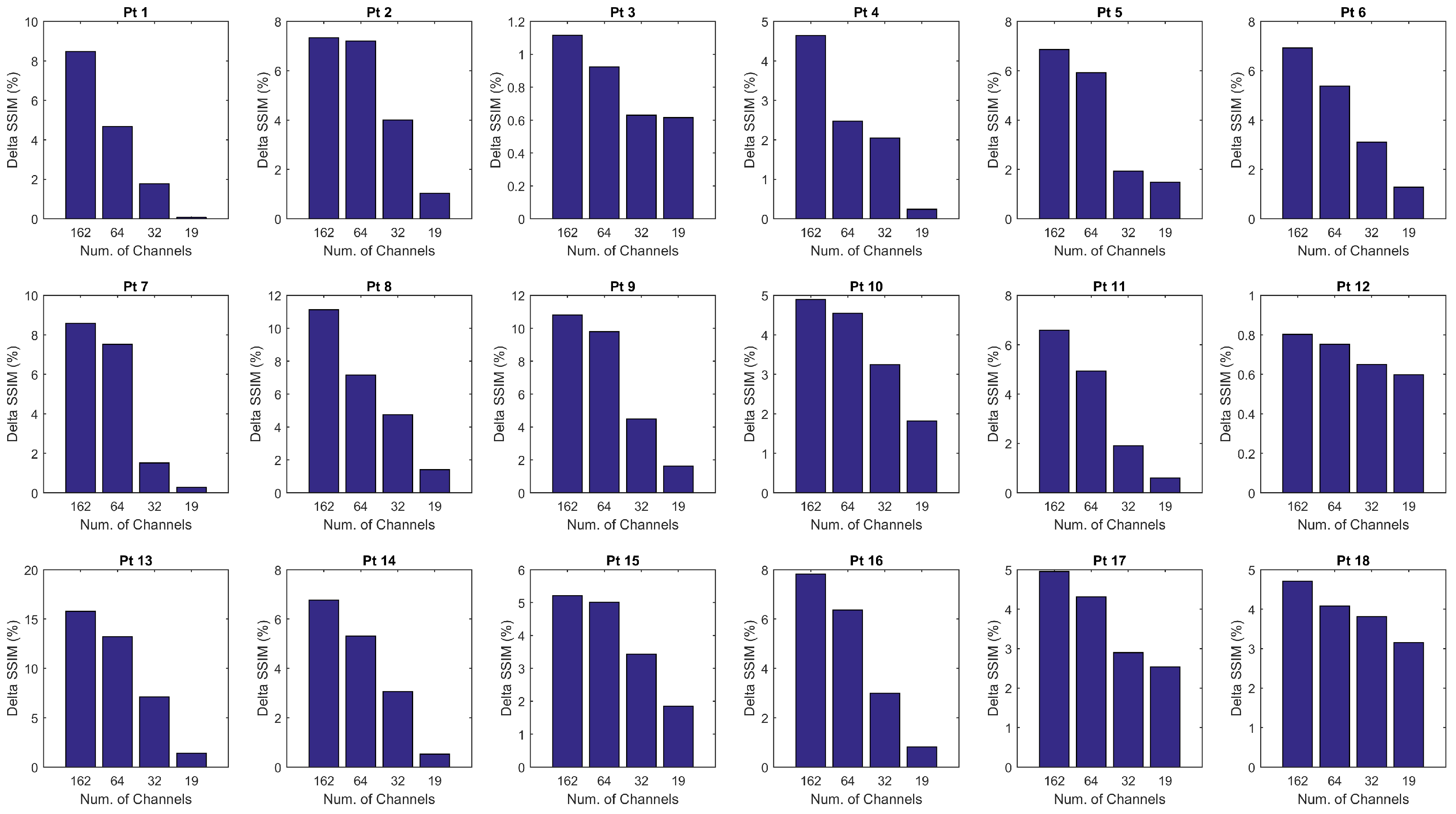
3.1. Epoch-Based SSIM Comparison
3.2. Overall SSIM Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Salvo, S.; Naro, A.; Bonanno, L.; Russo, M.; Muscarà, N.; Bramanti, P.; Marino, S. Assessment of nociceptive system in vegetative and minimally conscious state by using laser evoked potentials. Brain Inj. 2015, 29, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Salvo, S.; Caminiti, F.; Bonanno, L.; De Cola, M.C.; Corallo, F.; Caizzone, A.; Rifici, C.; Bramanti, P.; Marino, S. Neurophysiological assessment for evaluating residual cognition in vegetative and minimally conscious state patients: A pilot study. Funct. Neurol. 2015, 30, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, B.; Zhou, F. Integration of 24 Feature Types to Accurately Detect and Predict Seizures Using Scalp EEG Signals. Sensors 2018, 18, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.C.; Wu, C.T.; Huang, H.C.; Cheng, W.T.; Liu, Y.H. Major depression detection from EEG signals using kernel eigen-filter-bank common spatial patterns. Sensors 2017, 17, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé-Casals, J.; Vialatte, F. Towards semi-automatic artifact rejection for the improvement of Alzheimer’s disease screening from EEG signals. Sensors 2015, 15, 17963–17976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez, P.L.; Srinivasan, R. Electric Fields of the Brain, The Neurophysics of EEG; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ryynanen, O.R.M.; Hyttinen, J.A.K.; Malmivuo, J.A. Effect of measurement noise and electrode density on the spatial resolution of cortical potential distribution with different resistivity values for the skull. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vico Fallani, F.; Astolfi, L.; Cincotti, F.; Mattia, D.; la Rocca, D.; Maksuti, E.; Salinari, S.; Babiloni, F.; Vegso, B.; Kozmann, G.; et al. Evaluation of the brain network organization from EEG signals: A preliminary evidence in stroke patient. Anat. Rec. 2009, 292, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Quinlan, E.B.; Dodakian, L.; McKenzie, A.; Kathuria, N.; Zhou, R.J.; Augsburger, R.; See, J.; Le, V.H.; Srinivasan, R.; et al. Connectivity measures are robust biomarkers of cortical function and plasticity after stroke. Brain 2015, 138, 2359–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grefkes, C.; Fink, G.R. Connectivity-based approaches in stroke and recovery of function. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, S.; Pignat, J.M.; Ptak, R.; Aboulafia, T.; Allet, L.; Gillabert, N.; Magnin, C.; Albert, F.; Momjian-Mayor, I.; Nahum, L.; et al. The behavioral significance of coherent resting-state oscillations after stroke. Neuroimage 2012, 61, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolo, P.; Rizk, S.; Magnin, C.; Pietro, M.D.; Schnider, A.; Guggisberg, A.G. Coherent neural oscillations predict future motor and language improvement after stroke. Brain 2015, 138, 3048–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Srinivasan, R.; Burke Quinlan, E.; Solodkin, A.; Small, S.L.; Cramer, S.C. Utility of EEG measures of brain function in patients with acute stroke. J. Neurophysiol. 2016, 115, 2399–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Dai, G.; Kong, W.; Chen, F.; Wang, L. A Novel Nonlinear Dynamic Method for Stroke Rehabilitation Effect Evaluation Using EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 2488–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliandro, P.; Vecchio, F.; Miraglia, F.; Reale, G.; Della Marca, G.; La Torre, G.; Lacidogna, G.; Iacovelli, C.; Padua, L.; Bramanti, P.; et al. Small-world characteristics of cortical connectivity changes in acute stroke. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2017, 31, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Meng, J.; Wang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yang, J.; Qi, H.; Ming, D. Abnormal EEG complexity and functional connectivity of brain in patients with acute thalamic ischemic stroke. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2016, 2016, 2582478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappasodi, F.; Olejarczyk, E.; Marzetti, L.; Assenza, G.; Pizzella, V.; Tecchio, F. Fractal dimension of EEG activity senses neuronal impairment in acute stroke. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vico Fallani, F.; Clausi, S.; Leggio, M.; Chavez, M.; Valencia, M.; Maglione, A.G.; Babiloni, F.; Cincotti, F.; Mattia, D.; Molinari, M. Interhemispheric connectivity characterizes cortical reorganization in motor-related networks after cerebellar lesions. Cerebellum 2017, 16, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Jung, T.P.; Makeig, S.; Rao, B.D. Compressed sensing of EEG for wireless telemonitoring with low energy consumption and inexpensive hardware. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Rao, B.D. Extension of SBL algorithms for the recovery of block sparse signals with intra-block correlation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrous, H.; Ward, R. Block Sparse Compressed Sensing of Electroencephalogram (EEG) Signals by Exploiting Linear and Non-Linear Dependencies. Sensors 2016, 16, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaran, M.; Kamal, M.H.; Pollo, C.; Vandergheynst, P.; Schmid, A. Compact low-power cortical recording architecture for compressive multichannel data acquisition. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2014, 8, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labate, D.; La Foresta, F.; Palamara, I.; Morabito, G.; Bramanti, A.; Zhang, Z.; Morabito, F.C. EEG complexity modifications and altered compressibility in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. Smart Innov. Syst. Technol. 2014, 26, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Britton, J.W.; Frey, L.C.; Hopp, J.L.; Korb, P.; Koubeissi, M.Z.; Lievens, W.E.; Pestana-Knight, E.M.; Louis, E.K.S. Electroencephalography (EEG): An Introductory Text and Atlas of Normal and Abnormal Findings in Adults, Children, and Infants; American Epilepsy Society: Chicago, IL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyaseelan, R.D.; Vargo, M.M.; Chae, J. National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) as an early predictor of poststroke dysphagia. PM R 2015, 7, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morabito, F.C. Independent component analysis and feature extraction techniques for NDT data. Mater. Eval. 2000, 58, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Baraniuk, R.G. Compressive sensing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2007, 24, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.J.; Wakin, M.B. An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orović, I.; Papić, V.; Ioana, C.; Li, X.; Stanković, S. Compressive Sensing in Signal Processing: Algorithms and Transform Domain Formulations. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 7616393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C. Mean squared error: Love it or leave it? A new look at signal fidelity measures. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2009, 26, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a Test of Whether one of Two Random Variables is Stochastically Larger than the Other. Ann. Math. Stat. 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanciullacci, C.; Bertolucci, F.; Lamola, G.; Panarese, A.; Artoni, F.; Micera, S.; Rossi, B.; Chisari, C. Delta Power Is Higher and More Symmetrical in Ischemic Stroke Patients with Cortical Involvement. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kaam, R.C.; Van Putten, M.J.A.M.; Vermeer, S.E.; Hofmeijer, J. Contralesional Brain Activity in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 45, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.E.; Ebert, A.D.; Chatzikonstantinou, A. The use of routine EEG in acute ischemic stroke patients without seizures: Generalized but not focal EEG pathology is associated with clinical deterioration. Int. J. Neurosci. 2017, 127, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bönstrup, M.; Schulz, R.; Schön, G.; Cheng, B.; Feldheim, J.; Thomalla, G.; Gerloff, C. Parietofrontal network upregulation after motor stroke. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 18, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mégevand, P.; Spinelli, L.; Genetti, M.; Brodbeck, V.; Momjian, S.; Schaller, K.; Michel, C.M.; Vulliemoz, S.; Seeck, M. Electric source imaging of interictal activity accurately localises the seizure onset zone. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patient ID | AGE | GEN | Sev. Scale | Stroke Type | Stroke Site | Lesion Site |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt 1 | 53 | M | 13 | Ischemic | Silvian artery, Fronto-Temporal-Parietal Areas | Left |
| Pt 2 | 37 | M | 12 | Hemorrhagic | Pontine hemorrhage | Left |
| Pt 3 | 27 | M | 11 | Hemorrhagic | Frontal Lobe | Right |
| Pt 4 | 73 | F | 12 | Ischemic | Silvian artery, Fronto-Temporal-Parietal Areas | Left |
| Pt 5 | 86 | M | 14 | Ischemic | Thalamus, Posterior limb internal capsule | Left |
| Pt 6 | 61 | F | 12 | Hemorrhagic | Frontal Lobe | Right |
| Pt 7 | 76 | M | 12 | Ischemic | Periventricular and cortical white matter lesions | Right |
| Pt 8 | 59 | M | 11 | Hemorrhagic | Posterior limb internal capsule | Left |
| Pt 9 | 66 | M | 12 | Hemorrhagic | Anterior cerebral artery and Frontal lobe | Left |
| Pt 10 | 72 | M | 14 | Ischemic | Pontine | Right |
| Pt 11 | 81 | M | 14 | Ischemic | Silvian artery, Fronto-Temporal-Parietal Areas | Left |
| Pt 12 | 66 | M | 12 | Hemorrhagic | Pontine hemorrhage | Left |
| Pt 13 | 76 | M | 15 | Ischemic | Complete middle cerebral artery stroke | Right |
| Pt 14 | 72 | M | 12 | Hemorrhagic | Thalamus, Posterior limb internal capsule | Right |
| Pt 15 | 71 | M | 13 | Ischemic | Pontine | Left |
| Pt 16 | 55 | M | 14 | Hemorrhagic | Thalamus, Posterior limb internal capsule | Right |
| Pt 17 | 72 | M | 12 | Hemorrhagic | Cerebellum | Left |
| Pt 18 | 79 | M | 14 | Hemorrhagic | Frontal-Temporal-Parietal areas | Left |
| Patient | CR = 50% | CR = 55% | CR = 60% | CR = 65% | CR = 70% | CR = 75% | CR = 80% | CR = 85% | CR = 90% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt 1 | 4.41E-28 | 7.68E-28 | 2.93E-25 | 1.95E-22 | 9.12E-21 | 1.01E-19 | 1.25E-15 | 2.05E-10 | 7.62E-05 |
| Pt 2 | 3.12E-23 | 1.72E-16 | 3.96E-11 | 6.11E-07 | 1.20E-05 | 2.51E-04 | 7.90E-04 | 1.53E-02 | 1.91E-01 |
| Pt 3 | 9.50E-20 | 1.78E-05 | 2.68E-01 | 3.15E-01 | 3.66E-02 | 7.67E-03 | 1.20E-02 | 1.56E-02 | 8.30E-03 |
| Pt 4 | 7.68E-28 | 2.52E-24 | 1.34E-21 | 1.77E-16 | 1.12E-11 | 2.82E-07 | 9.66E-02 | 1.06E-01 | 8.66E-08 |
| Pt 5 | 4.63E-27 | 2.50E-20 | 1.30E-13 | 1.31E-09 | 1.59E-08 | 2.64E-08 | 6.82E-10 | 9.95E-06 | 1.68E-01 |
| Pt 6 | 5.50E-28 | 2.80E-24 | 3.87E-20 | 5.07E-16 | 9.91E-11 | 6.40E-10 | 3.32E-08 | 4.45E-06 | 6.90E-01 |
| Pt 7 | 1.93E-15 | 6.67E-08 | 1.51E-05 | 1.85E-04 | 1.14E-03 | 1.86E-03 | 1.41E-02 | 1.79E-02 | 1.85E-02 |
| Pt 8 | 1.67E-25 | 6.96E-18 | 5.16E-09 | 7.17E-06 | 9.65E-05 | 1.71E-04 | 2.03E-04 | 8.76E-05 | 3.73E-05 |
| Pt 9 | 2.73E-25 | 2.61E-19 | 3.78E-15 | 1.26E-12 | 1.44E-10 | 7.27E-10 | 1.94E-08 | 5.43E-05 | 6.08E-03 |
| Pt 10 | 1.79E-27 | 2.46E-19 | 1.98E-08 | 3.53E-03 | 1.68E-01 | 4.88E-01 | 5.35E-01 | 6.75E-01 | 7.03E-01 |
| Pt 11 | 6.62E-28 | 5.89E-25 | 2.01E-22 | 2.17E-19 | 1.87E-16 | 1.71E-14 | 7.25E-16 | 6.06E-14 | 2.72E-03 |
| Pt 12 | 8.25E-06 | 1.39E-01 | 8.88E-01 | 4.12E-01 | 2.96E-01 | 1.15E-01 | 2.42E-02 | 2.61E-02 | 4.10E-03 |
| Pt 13 | 2.19E-26 | 7.71E-23 | 2.17E-19 | 2.54E-16 | 2.22E-14 | 1.12E-14 | 3.71E-13 | 1.32E-10 | 2.14E-06 |
| Pt 14 | 8.21E-26 | 6.15E-16 | 1.53E-07 | 2.32E-04 | 2.20E-03 | 9.34E-04 | 6.26E-04 | 7.20E-05 | 1.88E-03 |
| Pt 15 | 6.76E-18 | 7.74E-08 | 8.40E-05 | 3.45E-03 | 3.66E-02 | 8.69E-02 | 1.01E-01 | 4.82E-01 | 9.39E-01 |
| Pt 16 | 7.42E-27 | 2.24E-19 | 3.81E-13 | 6.43E-09 | 9.26E-05 | 6.71E-05 | 1.46E-05 | 1.21E-06 | 6.26E-05 |
| Pt 17 | 1.77E-22 | 1.78E-15 | 3.37E-10 | 8.50E-08 | 5.43E-05 | 1.31E-02 | 2.32E-01 | 8.70E-01 | 1.61E-01 |
| Pt 18 | 2.92E-26 | 2.10E-17 | 6.41E-12 | 2.26E-08 | 4.90E-06 | 2.58E-04 | 5.71E-02 | 8.99E-01 | 3.91E-01 |
| Patient | CR = 50% | CR = 55% | CR = 60% | CR = 65% | CR = 70% | CR = 75% | CR = 80% | CR = 85% | CR = 90% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt 1 | 6.45E-01 | 9.59E-01 | 6.45E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 4.42E-01 | 4.42E-01 | 7.98E-01 | 7.98E-01 | 8.78E-01 |
| Pt 2 | 7.98E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 9.59E-01 | 8.78E-01 | 8.78E-01 | 8.78E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 4.42E-01 | 3.28E-01 |
| Pt 3 | 3.82E-01 | 5.05E-01 | 7.98E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 8.78E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 6.45E-01 | 7.98E-01 | 4.42E-01 |
| Pt 4 | 8.78E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 9.59E-01 | 9.59E-01 | 9.59E-01 | 6.45E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 9.59E-01 |
| Pt 5 | 9.59E-01 | 6.45E-01 | 6.45E-01 | 8.78E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 8.78E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 9.59E-01 |
| Pt 6 | 6.45E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 7.98E-01 | 5.05E-01 | 5.05E-01 | 3.82E-01 | 3.82E-01 | 1.61E-01 | 1.61E-01 |
| Pt 7 | 9.59E-01 | 9.59E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 9.59E-01 | 9.59E-01 | 8.78E-01 | 7.98E-01 | 6.45E-01 | 6.45E-01 |
| Pt 8 | 9.59E-01 | 5.05E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 6.45E-01 | 6.45E-01 | 7.98E-01 | 6.45E-01 | 8.78E-01 | 6.45E-01 |
| Pt 9 | 5.74E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 5.05E-01 | 7.98E-01 | 9.59E-01 |
| Pt 10 | 7.98E-01 | 7.98E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 8.78E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 9.59E-01 |
| Pt 11 | 2.34E-01 | 2.79E-01 | 2.34E-01 | 2.34E-01 | 2.34E-01 | 4.42E-01 | 3.28E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 6.45E-01 |
| Pt 12 | 1.61E-01 | 1.95E-01 | 2.34E-01 | 1.95E-01 | 3.82E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 7.98E-01 | 8.78E-01 | 9.59E-01 |
| Pt 13 | 1.00E+00 | 6.45E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 4.42E-01 | 3.82E-01 | 4.42E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 8.78E-01 | 9.59E-01 |
| Pt 14 | 1.00E+00 | 1.00E+00 | 8.78E-01 | 8.78E-01 | 9.59E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 5.74E-01 | 3.28E-01 | 5.74E-01 |
| Pt 15 | 5.05E-01 | 6.45E-01 | 4.42E-01 | 3.28E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 3.82E-01 | 3.82E-01 | 5.05E-01 | 3.82E-01 |
| Pt 16 | 4.42E-01 | 7.21E-01 | 9.59E-01 | 7.98E-01 | 9.59E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 8.78E-01 | 9.59E-01 | 9.59E-01 |
| Pt 17 | 3.28E-01 | 2.34E-01 | 1.61E-01 | 1.05E-01 | 1.05E-01 | 1.61E-01 | 1.95E-01 | 8.30E-02 | 8.30E-02 |
| Pt 18 | 5.74E-01 | 4.42E-01 | 1.95E-01 | 1.61E-01 | 1.05E-01 | 1.30E-01 | 1.95E-01 | 2.34E-01 | 1.61E-01 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mammone, N.; De Salvo, S.; Ieracitano, C.; Marino, S.; Cartella, E.; Bramanti, A.; Giorgianni, R.; Morabito, F.C. Compressibility of High-Density EEG Signals in Stroke Patients. Sensors 2018, 18, 4107. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124107
Mammone N, De Salvo S, Ieracitano C, Marino S, Cartella E, Bramanti A, Giorgianni R, Morabito FC. Compressibility of High-Density EEG Signals in Stroke Patients. Sensors. 2018; 18(12):4107. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124107
Chicago/Turabian StyleMammone, Nadia, Simona De Salvo, Cosimo Ieracitano, Silvia Marino, Emanuele Cartella, Alessia Bramanti, Roberto Giorgianni, and Francesco C. Morabito. 2018. "Compressibility of High-Density EEG Signals in Stroke Patients" Sensors 18, no. 12: 4107. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124107
APA StyleMammone, N., De Salvo, S., Ieracitano, C., Marino, S., Cartella, E., Bramanti, A., Giorgianni, R., & Morabito, F. C. (2018). Compressibility of High-Density EEG Signals in Stroke Patients. Sensors, 18(12), 4107. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124107








