Disposable Voltammetric Immunosensors Integrated with Microfluidic Platforms for Biomedical, Agricultural and Food Analyses: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
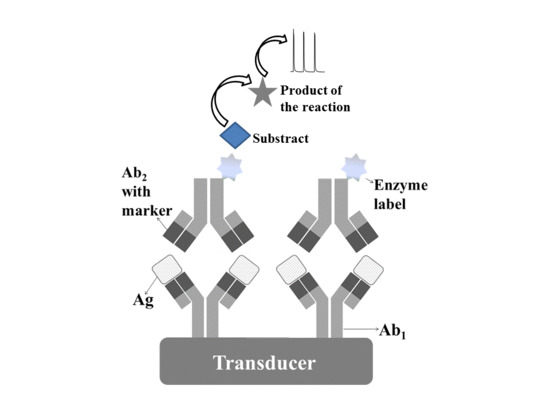
2. Voltammetric Immunosensors
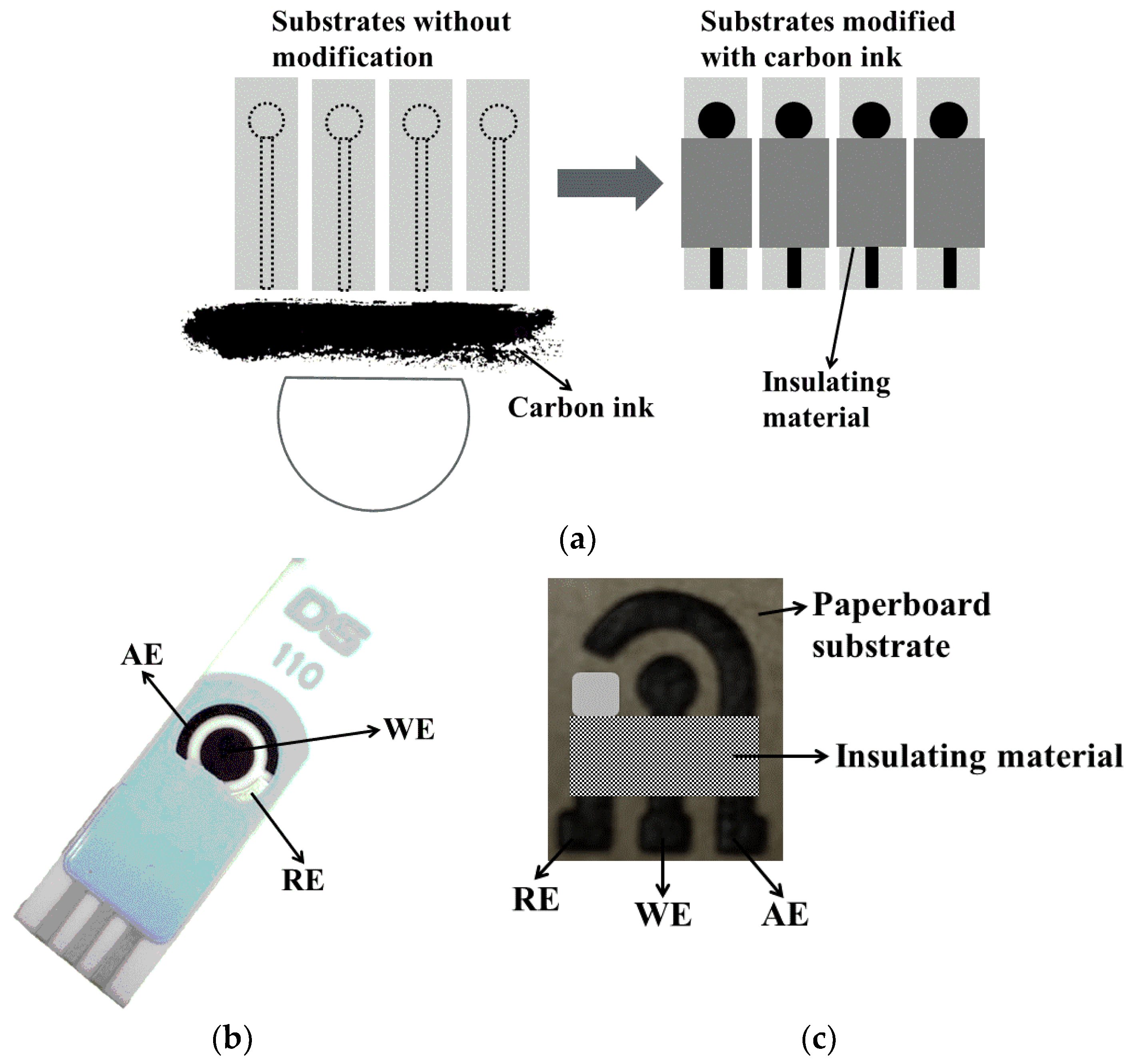
3. Screen-Printed Electrodes (SPEs) for Voltammetric Immunosensors
4. Association of Microfluidic Devices and Disposable Voltammetric Immunosensors
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, L.C.; Lyons, C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadir, E.B.; Sezginturk, M.K. Applications of commercial biosensors in clinical, food, environmental, and biothreat/biowarfare analyses. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 478, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timothy, R.J.; Holford, F.D.; Seamus, P.J.H. Recent trends in antibody based sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 12–24. [Google Scholar]
- Duffy, G.F.; Moore, E.J. Electrochemical immunosensors for food analysis: A review of recent developments. Biosensors 2017, 50, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowicz, M. Impact of nanotechnology on design of advanced screen-printed electrodes for different analytical applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 84, 22–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, F.S.; Angnes, L. Electrochemical immunosensors—A powerful tool for analytical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanez-Sedeno, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarron, J.M. Multiplexed electrochemical immunosensors for clinical biomarkers. Sensors 2017, 17, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, N.B.; Salgado, A.M.; Valdman, B. The evolution and developments of immunosensors for health and environmental monitoring: Problems and perspectives. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Ali, M.A.; Anand, P.; Agrawal, V.V.; John, R.; Maji, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Microfluidic-integrated biosensors: Prospects for point-of-care diagnostics. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 8, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonker, M.; Sahore, V.; Woolley, A.D. Recent advances in microfluidic sample preparation and separation techniques for molecular biomarker analysis: A critical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 986, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, M.I.; Desmulliez, M.P.Y. Lab-on-a-chip based immunosensor principles and technologies for the detection of cardiac biomarkers: A review. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 569–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Pashazadeh, P.; Hejazi, M.; de la Guardia, M.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Recent advances in nanomaterial-mediated bio and immune sensors for detection of aflatoxin in food products. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 87, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strehlitz, B.; Nikolaus, N.; Stoltenburg, R. Protein detection with aptamer biosensors. Sensors 2008, 8, 4296–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Fu, Z.; Yan, F.; Huangxian, J. Biomedical and clinical applications of immunoassays and immunosensors for tumor markers. Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, F.; Adornetto, G.; Palleschi, G. A review of experimental aspects of electrochemical immunosensors. Electrochim. Acta. 2012, 84, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, I.; Cristea, C.; Harceaga, V.; Marrazza, G.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Sandulescu, R. Electrochemical immunosensors in breast and ovarian cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 424, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piro, B.; Reisberg, S. Recent advances in electrochemical immunosensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munge, B.S.; Stracensky, T.; Gamez, K.; DiBiase, D.; Rusling, J.F. Multiplex immunosensor arrays for electrochemical detection of cancer biomarker proteins. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 2644–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; Pingarron, J.M. Non-invasive breast cancer diagnosis through electrochemical biosensing at different molecular levels. Sensors 2017, 17, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishpon, J.; Rosen, I. The development of an immunosensor for the electrochemical determination of the isoenzyme LDH5. Biosensors 1989, 4, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pang, X.; Du, B.; Li, H.; Wu, D.; Wei, Q. Ultrasensitive sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor based on dual signal amplification strategy using multifunctional graphene nanocomposites as labels for quantitative detection of tissue polypeptide antigen. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 214, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsinke, A.; Benkert, A.; Scheller, F.W. Electrochemical Immunoassays. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 2000, 366, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conzuelo, F.; Montiel, R.V.; Campuzano, S.; Gamella, M.; Torrente-Rodriguez, R.M.; Reviejo, A.J.; Pingarron, J.M. Rapid screening of multiple antibiotic residues in milk using disposable amperometric magnetosensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 820, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Wang, L.; Ma, C.; Zhang, M.; Xie, G. Sandwich immunoassay for hepatitis C virus non-structural 5A protein using a glassy carbon electrode modified with an Au-MoO3/chitosan nanocomposite. Anal. Lett. 2013, 46, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Kang, M.S.; Paik, J.K.; Ku, S.; Cho, H.M.; Irudayaraj, J.; Kim, D.H. Current technologies of electrochemical immunosensors: Perspective on signal amplification. Sensors 2018, 18, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhen, Q.; He, Y.; Chen, X.; Lyu, W.; Han, R.; Ding, M. An electrochemical sensor for indole in plasma based on MWCNTs-chitosan modified screen-printed electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, R.A.S.; Lima, J.I.F.C.; Quinaz, M.B. Recent developments, characteristics and potential applications of screen-printed electrodes in pharmaceutical and biological analysis. Talanta 2016, 146, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleat, Z.; Khoshroo, A.; Mazloum-Ardakani, M. Screen-printed electrodes for biosensing: A review (2008–2013). Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 865–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araujo, W.R.; Frasson, C.M.R.; Ameku, W.A.; Silva, J.R.; Angnes, L.; Paixão, T.R.L.C. Single-step reagentless laser scribing fabrication of electrochemical paper-based analytical devices. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15113–15117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulay, S.B.; Julich, S.; Tomaso, H.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Development of an immunosensor for the detection of Francisella tularensis antibodies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 4685–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohanka, M.; Malir, F.; Roubal, T.; Kuca, K. Detection of aflatoxins in capsicum spice using an electrochemical immunosensor. Anal. Lett. 2008, 41, 2344–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodra, A.; Lopez, M.A.; Escarpa, A. Disposable and reliable electrochemical magnetoimmunosensor for fumonisins simplified determination in maize-based foodstuffs. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khafaji, Q.A.M.; Harris, M.; Tombelli, S.; Laschi, S.; Turner, A.P.F.; Mascini, M.; Marrazza, G. An electrochemical immunoassay for HER2 detection. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarocka, U.; Sawicka, R.; Gora-Sochacka, A.; Sirko, A.; Dehaen, W.; Radecki, J.; Radecka, H. An electrochemical immunosensor based on a 4,4’-thiobisbenzenethiol self-assembled monolayer for the detection of hemagglutinin from avian influenza virus H5N1. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 228, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.; Tlili, C.; L’Hocine, L.; Zourob, M. Electrochemical immunosensor for the milk allergen β-lactoglobulin based on electrografting of organic film on graphene modified screen-printed carbon electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Ahlawat, W.; Kumar, R.; Dilbaghi, N. Graphene, carbon nanotubes, zinc oxide and gold as elite nanomaterials for fabrication of biosensors for healthcare. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, T.T.N.; Takamura, Y.; Tamiya, E.; Vestergaard, M.C. Modified screen printed electrode for development of a highly sensitive label-free impedimetric immunosensor to detect amyloid beta peptides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 892, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.S.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, L.S.; Wang, J.F. Electrochemical immunoassay for procalcitonin antigen detection based on signal amplification strategy of multiple nanocomposites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 51, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.Y.; Liu, Q.; Wu, X.W.; Jiang, X.Y.; Yu, J.G.; Chen, X.Q. Chiral electrochemical recognition of tryptophan enantiomers at a multi-walled carbon nanotube-chitosan composite modified glassy carbon electrode. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 98020–98025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brondani, D.; Piovesan, J.V.; Westphal, E.; Gallardo, H.; Dutra, R.A.F.; Spinelli, A.; Vieira, I.C. A label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on an ionic organic molecule and chitosan-stabilized gold nanoparticles for the detection of cardiac troponin T. Analyst 2014, 139, 5200–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.M.S.; Dias, A.C.M.S.; Cordeiro, M.T.; Marques, E., Jr.; Goulart, M.O.F.; Dutra, R.F. A thiophene-modified screen printed electrode for detection of dengue virus NS1 protein. Talanta 2014, 128, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, K.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y. Magnetic beads-based electrochemical immunosensor for detection of pseudorabies virus antibody in swine serum. Talanta 2011, 87, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Dominguez-Renedo, O. Screen-printed biosensors in drugs analysis. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2017, 13, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, F.S.; Angnes, L. Fast and accurate analysis of drugs using amperometry associated with flow injection analysis. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4784–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzoni, A.M.; Mudadu, A.G.; Lorenzoni, G.; Soro, B.; Bardino, N.; Arras, I.; Sanna, G.; Vodret, B.; Bazzardi, R.; Marongiu, E.; et al. Detection of Dinophysis species and associated okadaic acid in farmed shellfish: A two-year study from the western Mediterranean area. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, R.B.; Hayat, A.; Sassolas, A.; Alonso, G.A.; Munoz, R.; Marty, J.L. Automated flow-through amperometric immunosensor for highly sensitive and on-line detection of okadaic acid in mussel sample. Talanta 2012, 99, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Tang, J.; Dai, Z.; Yan, F.; Ju, H.; Murr, N.E. A disposable electrochemical immunosensor for flow injection immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thunkhamrak, C.; Reanpang, P.; Ounnunkad, K.; Jakmunee, J. Sequential injection system with amperometric immunosensor for sensitive determination of human immunoglobulin G. Talanta 2017, 171, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, A.C.V.; Masini, J.C. A análise por injeção sequencial (SIA): Vinte anos em uma perspectiva brasileira. Quim. Nova 2010, 33, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskeyfield, D.E.H.; Davis, F.; Magan, N.; Tothill, I.E. A membrane-based immunosensor for the analysis of the herbicide isoproturon. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 699, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeravik, J.; Skadal, P. Screen-printed amperometric immunosensor for repeated use in the flow-through mode. Electroanalysis 1999, 11, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscay, J.; Garcia, M.B.G.; Garcia, A.C. Flow injection analysis system using magnetic beads, screen printed electrodes and magnets. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Balso, M.A.; Messina, G.A.; Sanz, M.I.; Raba, J. Screen-printed immunosensor modified with carbon nanotubes in a continuous-flow system for the Botrytis cinerea determination in apple tissues. Talanta 2009, 79, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Feng, J.; Fang, Z.; Xu, J.; Lu, X. Application of microfluidic “lab-on-a-chip” for the detection of mycotoxins in food. Trends Food Technol. 2015, 46, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkus, B. Applying the miniaturization technologies for biosensor design. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bange, A.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Microfluidic immunosensor systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2488–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Errachid, A. Analytical microsystems for biomedical and environmental applications. Biocyb. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 31, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kant, K.; Shahbazi, M.A.; Dave, V.P.; Ngo, T.A.; Chidambara, V.A.; Than, L.Q.; Bang, D.D.; Wolff, A. Microfluidic devices for sample preparation and rapid detection of foodborne pathogens. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1003–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothbauer, M.; Zirath, H.; Ertl, P. Recent advances in microfluidic technologies for cell-to-cell interactions studies. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, B.; Pandey, B.; Neupane, B.; Ligler, F.S. Signal amplification strategies for microfluidic immunoassays. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervas, M.; Lopez, M.A.; Escarpa, A. Electrochemical microfluidic chips coupled to magnetic bead-based ELISA to control allowable levels of zearalenone in baby foods using simplified calibration. Analyst 2009, 134, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervas, M.; Lopez, M.A.; Escarpa, A. Integrated electrokinetic magnetic bead-based electrochemical immunoassay on microfluidic chips for reliable control of permitted levels of zearalenone in infant foods. Analyst 2011, 136, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regiart, M.; Rinaldi-Tosi, M.; Aranda, P.R.; Bertolino, F.A.; Villarroel-Rocha, J.; Sapag, K.; Messina, G.A.; Raba, J.; Fernandez-Baldo, M.A. Development of a nanostructured immunosensor for early and in situ detection of Xanthomonas arboricola in agricultural food production. Talanta 2017, 175, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervas, M.; Lopez, M.A.; Escarpa, A. Electrochemical immunosensing on board microfluidic chip platforms. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 31, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyazi, T.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Benito-Lopez, F. Review on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices towards commercialization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1001, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettakppnpitak, J.; Boehle, K.; Nantaphol, S.; Teengam, P.; Adkins, J.A.; Srisa-Art, M.; Henry, C.S. Electrochemistry on paper-based analytical devices: A review. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1420–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Bhirde, A.A.; Morgan, N.Y.; Eden, H.S.; Chen, X. Electrochemical immunosensors for detection of cancer protein biomarkers. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6546–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungchai, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. Electrochemical detection for paper-based microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5821–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Louis, P. Status of point-of-care testing: Promise, realities, and possibilities. Clin. Biochem. 2000, 33, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busin, V.; Wells, B.; Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M.; Shu, W.; Burgess, S.T.G. Opportunities and challenges for the application of microfluidic technologies in point-of-care veterinary diagnostics. Mol. Cell. Probes 2016, 30, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Kong, Z.; Jin, H.; Cai, X. Electrochemical integrated paper-based immunosensor modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposites for point-of-care testing of 17β-estradiol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.I.; Reis, N.M. A critical insight into the development pipeline of microfluidic immunoassay devices for the sensitive quantification of protein biomarkers at the point of care. Analyst 2017, 142, 858–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, R.A.G.; Materon, E.M.; Melendez, M.E.; Carvalho, A.L.; Faria, R.C. Disposable microfluidic immunoarray device for sensitive breast cancer biomarker detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27433–27440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uliana, C.V.; Peverari, C.R.; Afonso, A.S.; Cominetti, M.R.; Faria, R.C. Fully disposable microfluidic electrochemical device for detection of estrogen receptor alpha breast cancer biomarker. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Mani, V.; Patel, V.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Microfluidic electrochemical immunoarray for ultrasensitive detection of two cancer biomarker proteins in serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4477–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otieno, B.A.; Krause, C.E.; Latus, A.; Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Faria, R.C.; Rusling, J.F. On-line protein capture on magnetic beads for ultrasensitive microfluidic immunoassays of cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Xu, H.; Xu, S.; Cai, X. A wireless point-of-care testing system for the detection of neuron-specific enolase with microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 95, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Fang, C.; Zeng, R.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z. Paper-based microfluidic devices for electrochemical immunofiltration analysis of human chorionic gonadotropin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, Z.; Akgun, M.; Kokturk, G.; Uludag, Y. A fully automated microfluidic-based electrochemical sensor for real-time bacteria detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Zhi, X.; Su, H.; Wang, K.; Yan, Z.; He, N.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D.; Cui, D. A novel electrochemical microfluidic chip combined with multiple biomarkers for early diagnosis of gastric cancer. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Hong, S.; Jang, J. Label-free detection of influenza viruses using a reduced graphene oxide-based electrochemical immunosensor integrated with a microfluidic platform. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eletxigerra, U.; Martinez-Perdiguero, J.; Merino, S. Disposable microfluidic immuno-biochip for rapid electrochemical detection of tumor necrosis factor alpha biomarker. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 221, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Fang, C.; Zeng, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z. A disposable paper-based microfluidic immunosensor based on reduced graphene oxide-tetraethylene pentamine/Au nanocomposite decorated carbon screen-printed electrodes. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 252, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piguillem, S.V.; Ortega, F.G.; Raba, J.; Messina, G.A.; Fernandez-Baldo, M.A. Development of a nanostructured electrochemical immunosensor applied to the early detection of invasive aspergillosis. Microchem. J. 2018, 139, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinawang, P.D.; Rai, V.; Ionescu, R.E.; Marks, R.S. Electrochemical lateral flow immunosensor for detection and quantification of dengue NS1 protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kling, A.; Chatelle, C.; Armbrecht, L.; Qelibari, E.; Kieninger, J.; Dincer, C.; Weber, W.; Urban, G. Multianalyte antibiotic detection on an electrochemical microfluidic platform. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10036–10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Ge, L.; Yan, M.; Song, X.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. Paper-based three-dimensional electrochemical immunodevice based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized paper for sensitive point-of-care testing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 32, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillehoj, P.B.; Huang, M.C.; Truong, N.; Ho, C.M. Rapid electrochemical detection on a mobile phone. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2950–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthuppu, B.; Heiskanen, A.; Kofoed, D.; Aamand, J.; Jorgensen, C.; Dufva, M.; Jakobsen, M.H. Micro-flow-injection analysis (µFIA) immunoassay of herbicide residue 2,6-dicholorobenzamide—towards automated at-line monitoring using modular microfluidics. Analyst 2015, 140, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regiart, M.; Fernandez-Baldo, M.A.; Spotorno, V.G.; Bertolino, F.A.; Raba, J. Ultra sensitive microfluidic immunosensor for determination of clenbuterol in bovine hair samples using electrodeposited gold nanoparticles and magnetic micro particles as bio-affinity platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, T.R.; Martucci, D.H.; Faria, R.C. Simple disposable microfluidic device for Salmonella typhimurium detection by magneto-immunoassay. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 255, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Baldo, M.A.; Bertolino, F.A.; Fernandez, G.; Messina, G.A.; Sanz, M.I.; Raba, J. Determination of ochratoxin A in apples contamined with Aspergillus achraceus by using a microfluidic competitive immunosensor with magnetic nanoparticles. Analyst 2011, 136, 2756–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Baldo, M.A.; Messina, G.A.; Sanz, M.I.; Raba, J. Microfluidic immunosensor with micromagnetic beads coupled to carbon-based screen-printed electrodes (SPCEs) for determination of Botrytis cinerea in tissue of fruits. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2010, 58, 11201–11206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. An electrochemical immunosensor based on microfluidic chip for detection of chlorpyrifos. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 8750–8758. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y. Magnetic control of an electrochemical microfluidic device with an arrayed immunosensor for simultaneous multiple immunoassays. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Analyte | Transducer | Detection Limit | Sample | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Okadaic acid (toxin) | SPCE modified with MBs | 0.15 µg·mL−1 | Mussel | [46] |
| CEA (tumor marker) | SPCE modified with CEA/colloidal Au/chitosan film | 0.22 ng·mL−1 0.45 ng·mL−1 | Serum | [47] |
| HIgG (biomarker) | SPCE modified with GO | 1.70 ng·mL−1 | Urine | [48] |
| Isoproturon (herbicide) | SPCE | 0.84 ng·mL−1 | Soil | [50] |
| 2,4-D (herbicide) | Gold-SPE modified with cysteamine | 0.12 µg·mL−1 | Water and food | [51] |
| Biotin (vitamin) | SPCE | 10−14 mol·L−1 | Clinical | [52] |
| Botrytis cinerea (fungus) | SPCE modified with MWCNT | 0.02 µg·mL−1 | Fruit | [53] |
| Application | Analyte | SPE Modified with | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomedical | 17-E2 (hormone) | MWCNTs/THi/AuNPs | 10 pg·mL−1 | [73] |
| CA15-3 (biomarker) | - | 6.0 µU·mL−1 | [75] | |
| ER α (biomarker) | PDDA/GSH-AuNPs/DNA | 10 fg·mL−1 | [76] | |
| PSA (biomarker) | Glutathione/AuNPs | 0.23 pg·mL−1 | [77] | |
| IL-6 and IL-8 proteins (biomarkers) | AuNPs | 5.0 fg·mL−1 (IL-6) and 7.0 fg·mL−1 (IL-8) | [78] | |
| NSE (biomarker) | NH2-G/THi/AuNPs | 10 pg·mL−1 | [79] | |
| HCG (biomarker) | - | 0.36 mIU·mL−1 | [80] | |
| Biomedical | E. coli (bacteria) | AuNPs | 50 cfu·mL−1 and 2.0 × 104 cfu·mL−1 (standard immunoassay) | [81] |
| CEA, CA 19-9, H.P., P53, PGI and PGII (biomarkers) | - | 0.37 ng·mL−1 (CEA), 10.75 U·mL−1 (CA 19-9), 5.0 U·L−1 (H.P.), 35 pg·mL−1 (P53), 37.5 ng·mL−1 (PGI) and 2.5 ng·mL−1 (PGII) | [82] | |
| H1N1 (virus) | rGO/EDC-NHS | 0.5 PFU·mL−1 | [83] | |
| TNFα (Biobmarker) | - | 4.1 ng·mL−1 | [84] | |
| AFP (biomarker) | rGO-TEPA/AuNPs | 0.005 ng·mL−1 | [85] | |
| GMN (aspergillosis) | CuNPs-PVP | 0.23 ng·mL−1 | [86] | |
| Dengue NS1 protein | - | 0.5 ng·mL−1 | [87] | |
| Tetracycline and pristinamycin (antibiotics) | - | 6.33 ng·mL−1 (tetracycline) and 9.22 ng·mL−1 (pristinamycin) | [88] | |
| CA 125, CEA (biomarkers) | MWCNTs | 0.2 mU·mL−1 (CA 125) and 0.01 ng·mL−1 (CEA) | [89] | |
| PfHRP2 (biomarker) | - | 16 ng·mL−1 | [90] | |
| BAM (herbicide) | - | Not found | [91] | |
| Food | CLB (2-agonist) | AuNPs | 0.008 ng·mL−1 | [92] |
| S. typhi (bacterium) | - | 7.7 cells·mL−1 | [93] | |
| Agricultural Food | XA (toxin) | - | 1.5 × 102 CFU·mL−1 | [64] |
| OTA (mycotoxin) | - | 0.05 µg·Kg−1 | [94] | |
| B. cinerea (fungus) | - | 0.008 µg·mL−1 | [95] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Felix, F.S.; Baccaro, A.L.B.; Angnes, L. Disposable Voltammetric Immunosensors Integrated with Microfluidic Platforms for Biomedical, Agricultural and Food Analyses: A Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124124
Felix FS, Baccaro ALB, Angnes L. Disposable Voltammetric Immunosensors Integrated with Microfluidic Platforms for Biomedical, Agricultural and Food Analyses: A Review. Sensors. 2018; 18(12):4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124124
Chicago/Turabian StyleFelix, Fabiana S., Alexandre L. B. Baccaro, and Lúcio Angnes. 2018. "Disposable Voltammetric Immunosensors Integrated with Microfluidic Platforms for Biomedical, Agricultural and Food Analyses: A Review" Sensors 18, no. 12: 4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124124
APA StyleFelix, F. S., Baccaro, A. L. B., & Angnes, L. (2018). Disposable Voltammetric Immunosensors Integrated with Microfluidic Platforms for Biomedical, Agricultural and Food Analyses: A Review. Sensors, 18(12), 4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124124