On-Orbit Relative Radiometric Calibration of the Night-Time Sensor of the LuoJia1-01 Satellite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
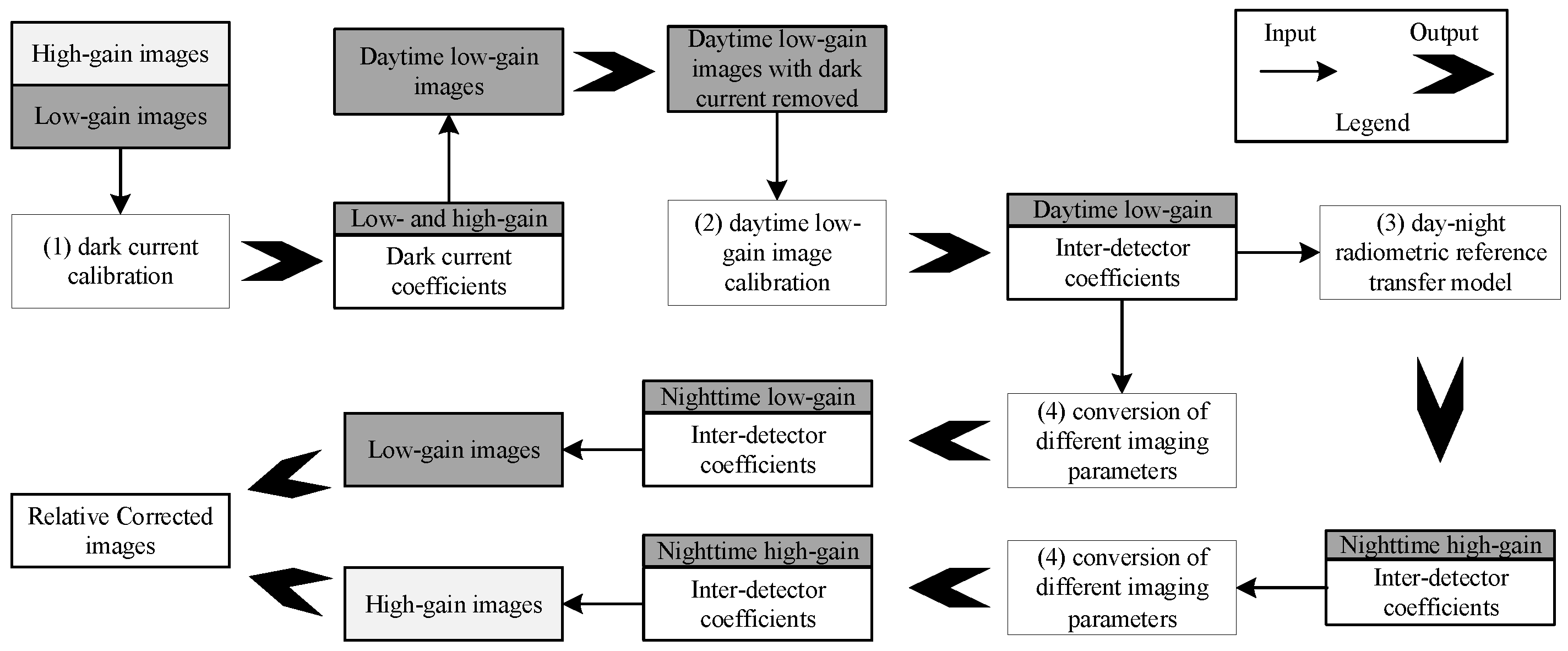
2. Method
2.1. Dark Current Calibration
2.2. Daytime Calibration of Low-Gain Images
2.3. Day-Night Radiometric Reference Transfer
2.4. Conversion of Calibration Coefficients under Different Imaging Parameters
3. Experiment and Results
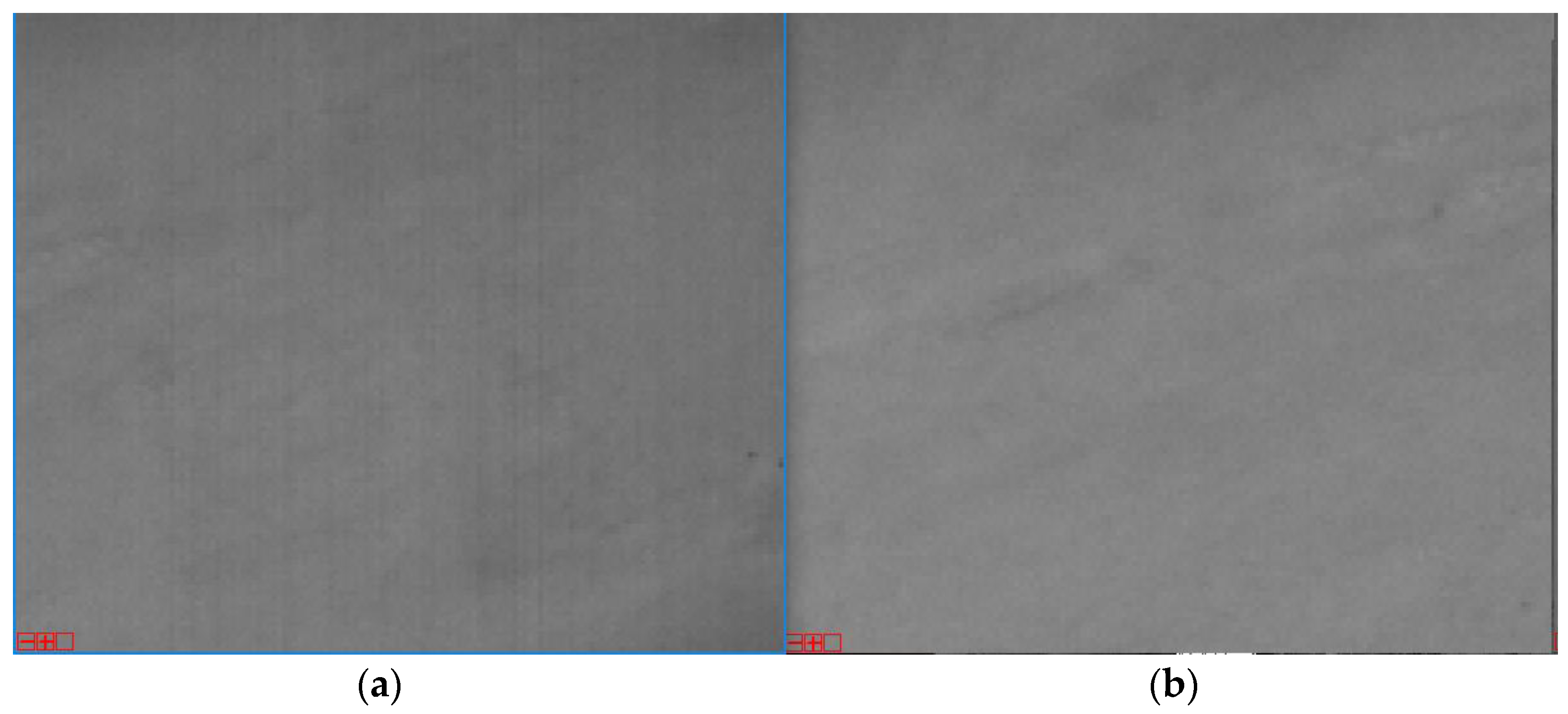
3.1. Data Introduction
3.2. Results of Dark Current Calibration
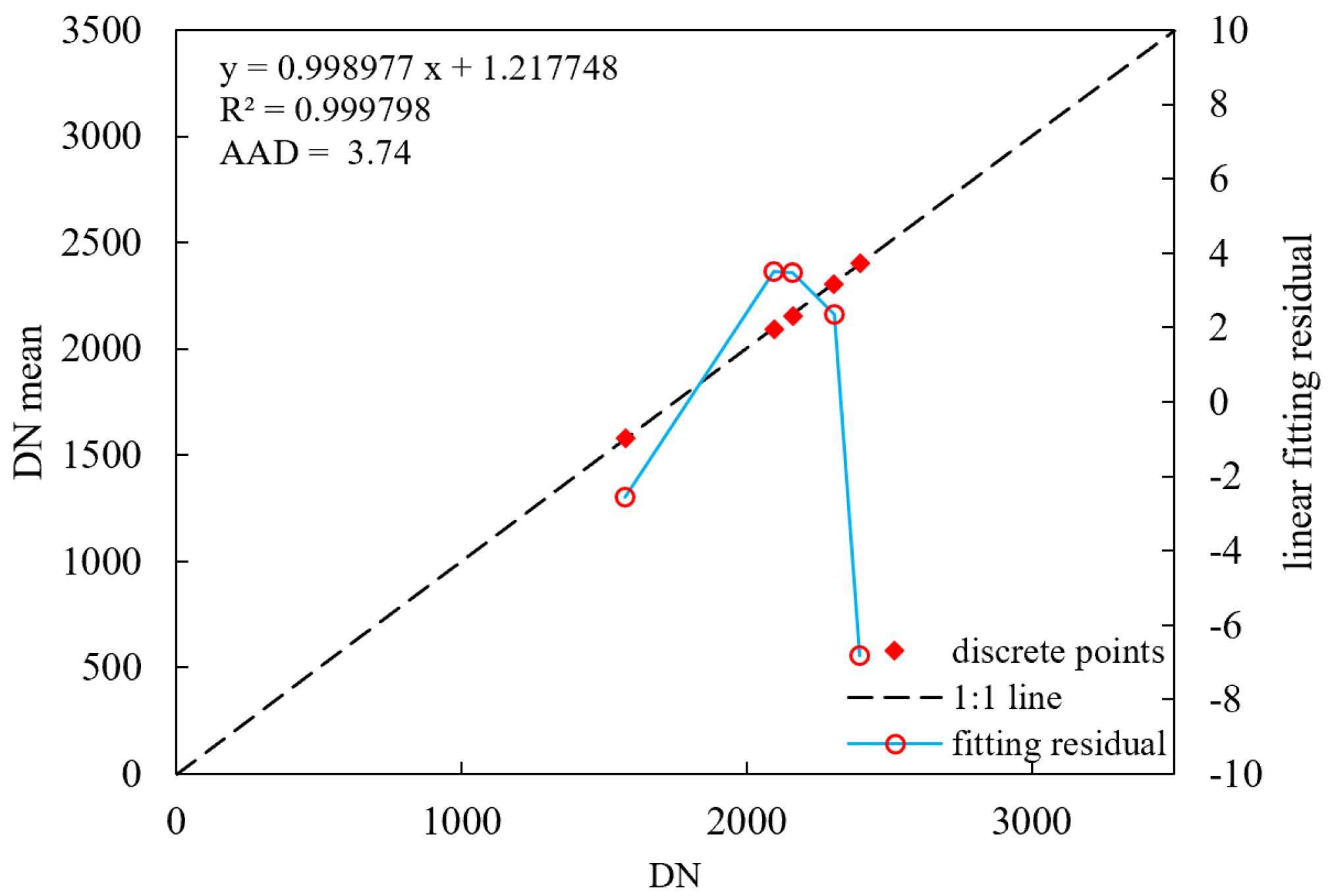
3.3. Daytime Low-Gain Calibration
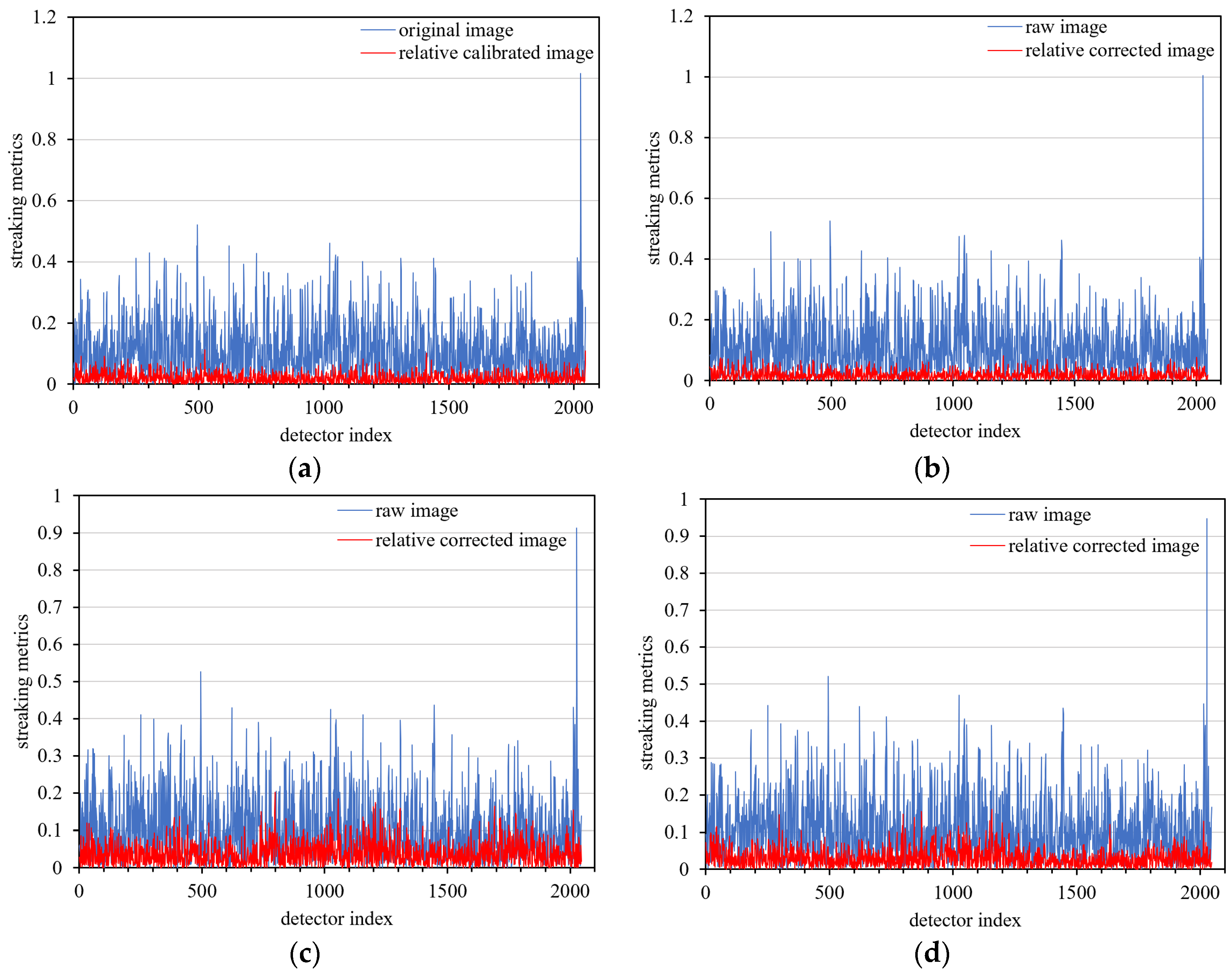
3.4. Day-Night Radiometric Reference Transfer
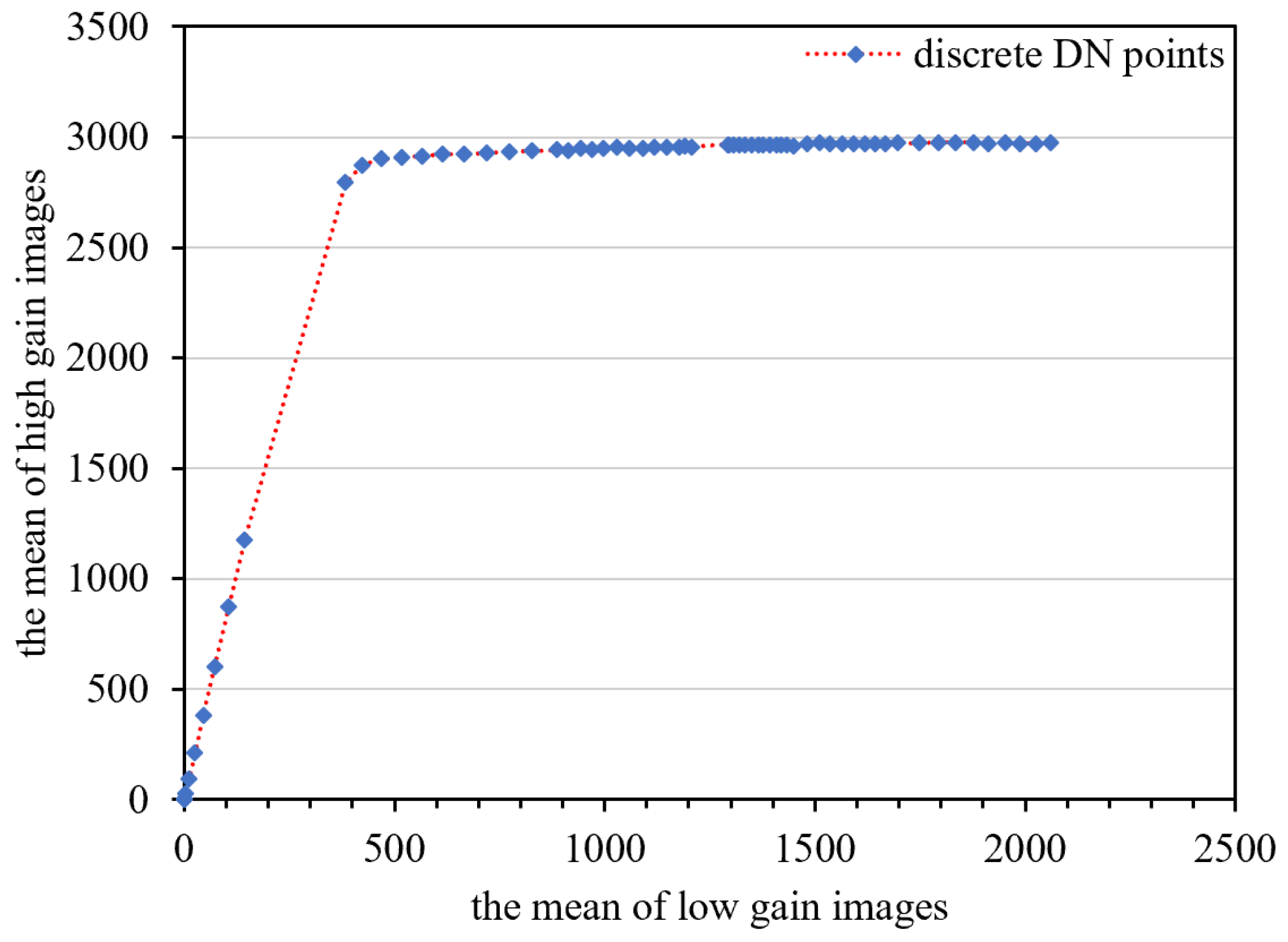
3.4.1. Parameter Solving for the High-Gain and Low-Gain Response Model
Preflight Calibration Data
On-Orbit Data
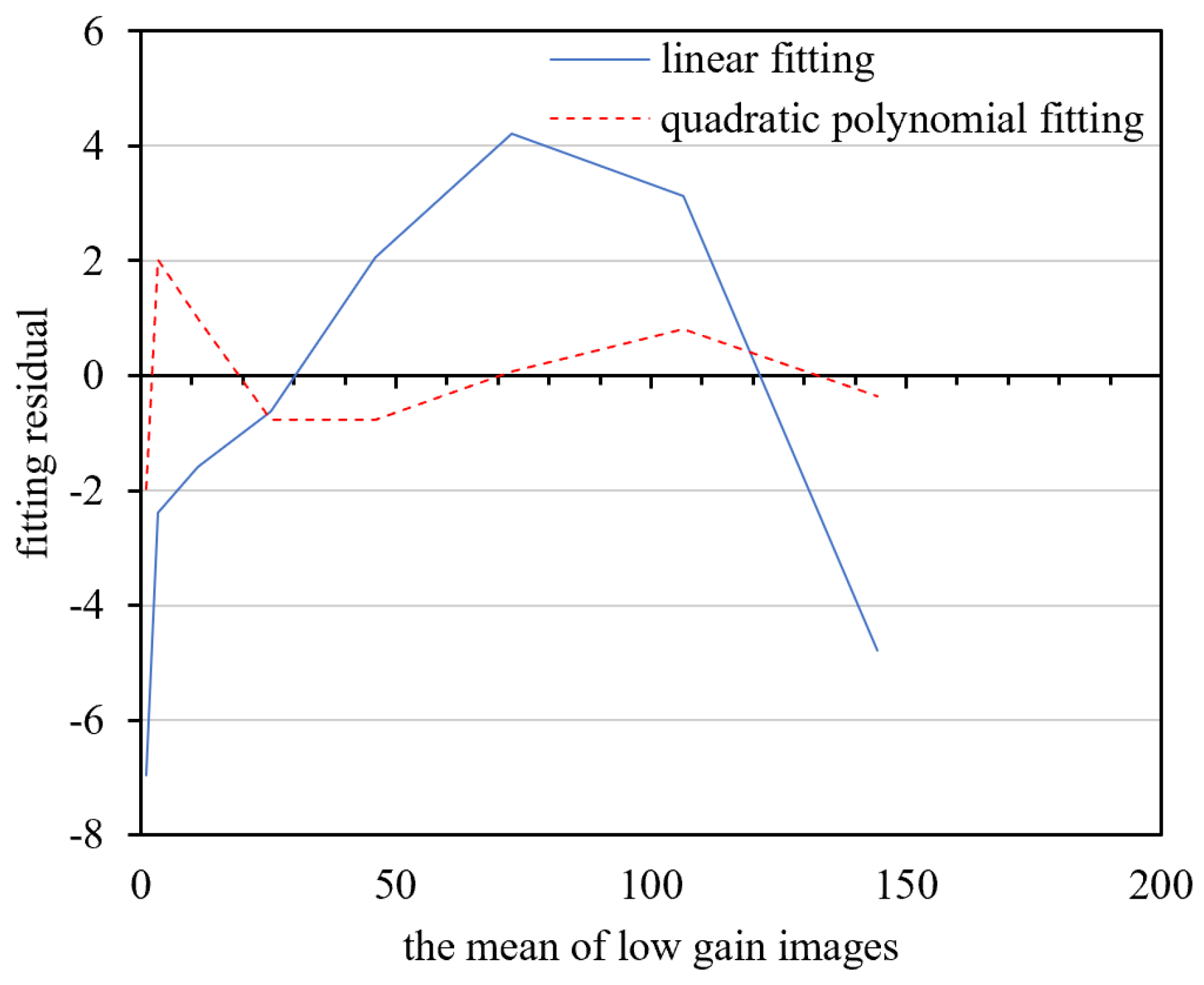
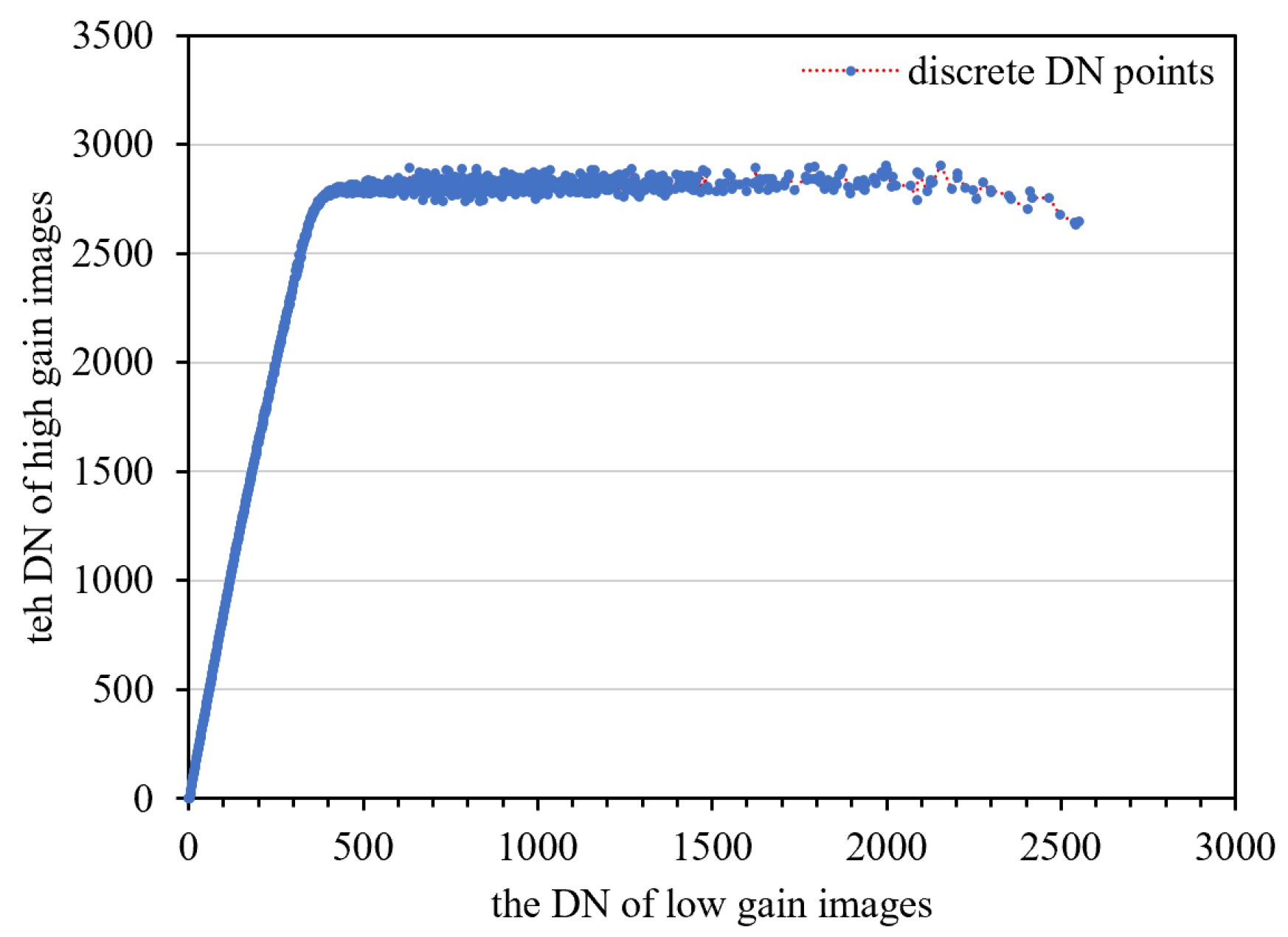
Model Parameter-Solving
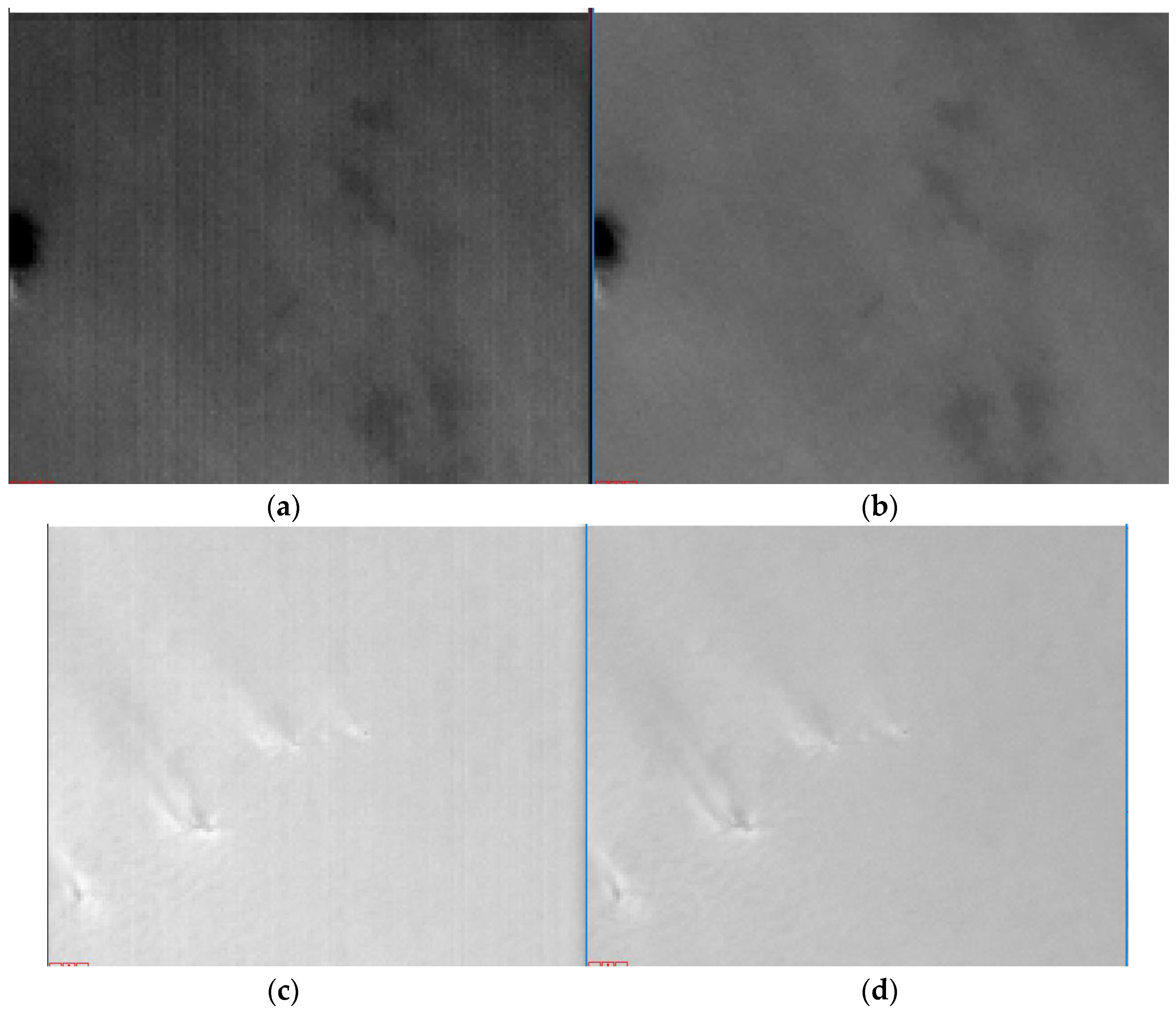
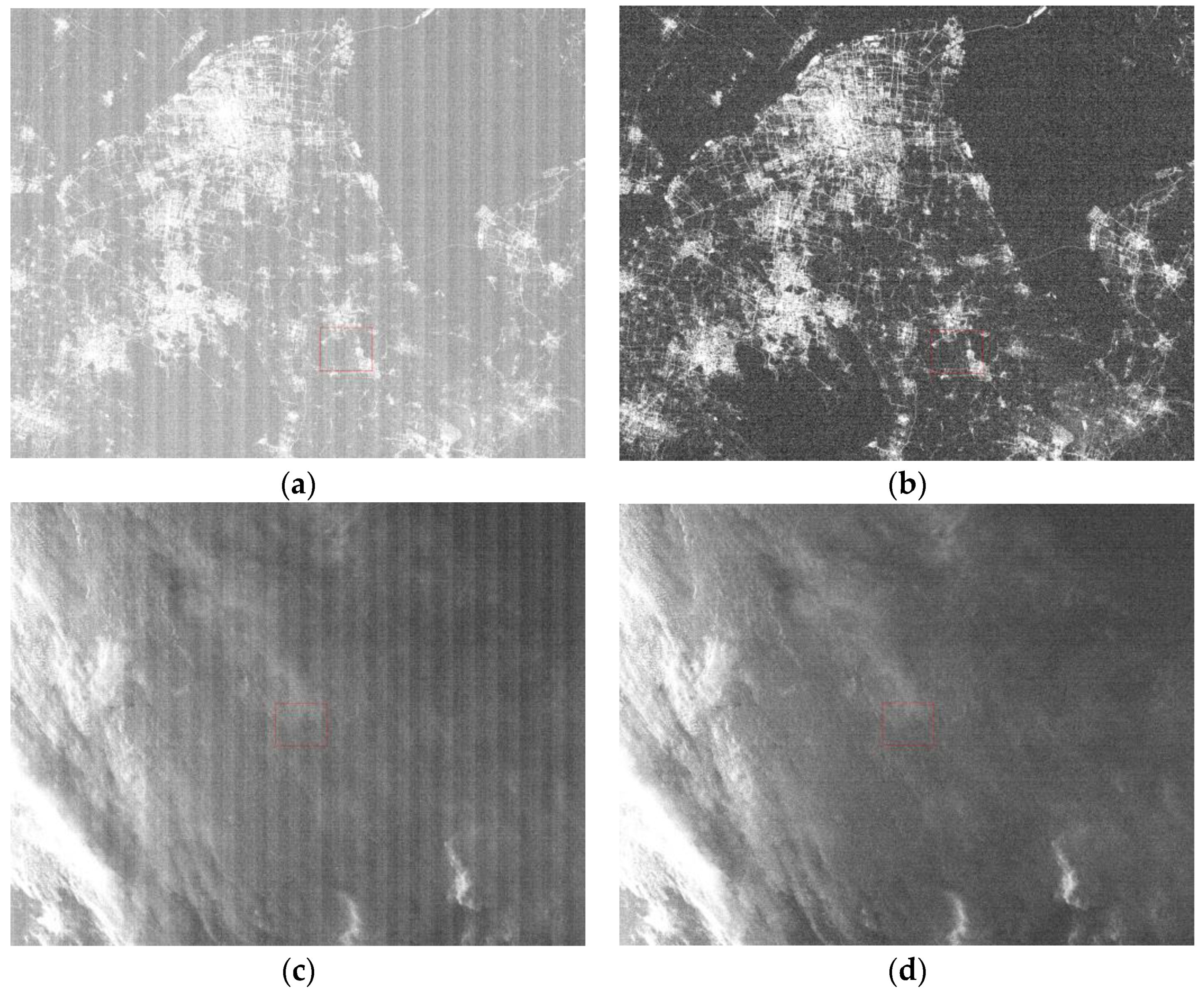
3.4.2. Nighttime Correction
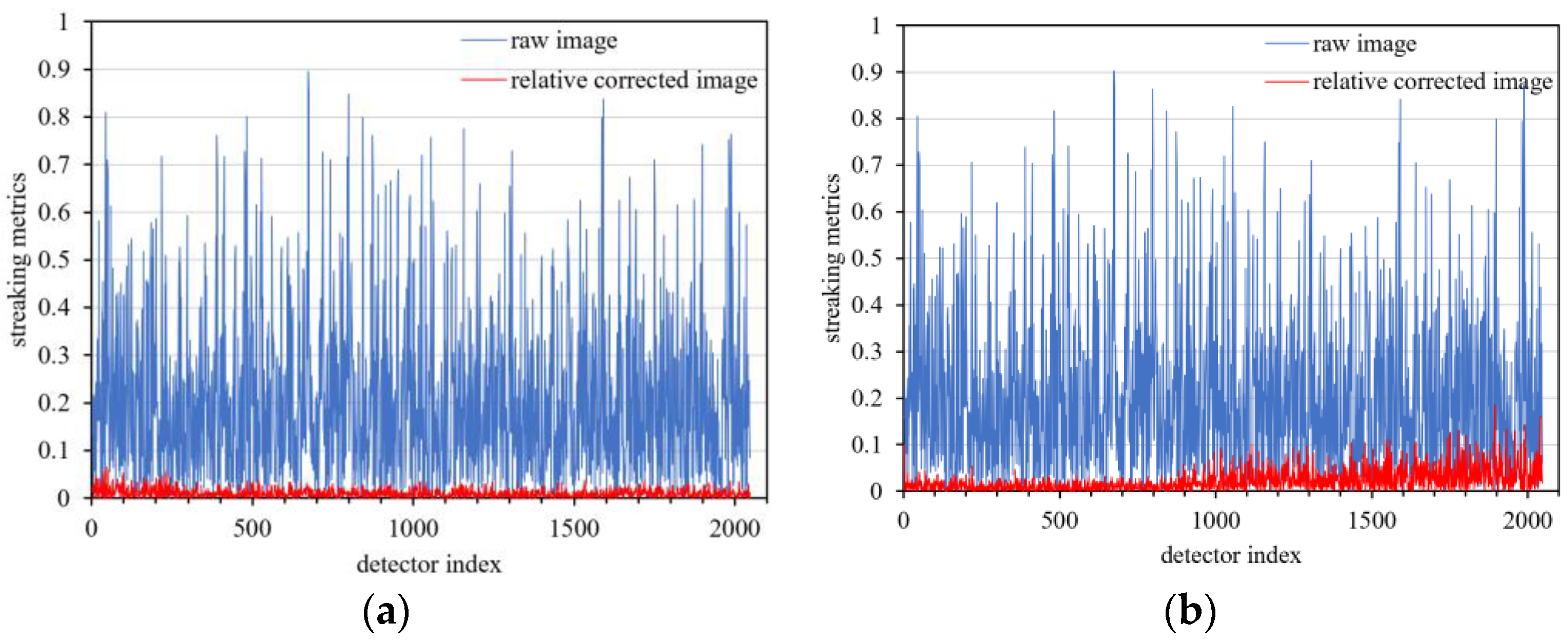
3.5. Validating Different Correction Coefficients under Different Imaging Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- 1)
- The root mean square of the mean for each detector in low (high) gain images is better than 0.04 (0.07) DN after dark current correction.
- 2)
- The DN relationship between the low and high-gain image conforms to the quadratic polynomial mode.
- 3)
- The streaking metrics are better than 0.2%, after relative calibration.
- 4)
- The nighttime sensor has the same relative correction parameters at different exposure times for the same gain parameters.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Algorithm 1: Description of the dark current calibration of the LJ1-01 nighttime sensor |
| Input: from dark current calibration data includes the low- and high-gain images, i = 1, 2, 3, … N, j = 1, 2, 3, … M |
| Output: the dark current calibration results and |
| for each j = 1 to M do |
| Compute the average value of each frame of data: |
| end for |
| Eliminate the gross error and compute the valid : |
| for each i = 1 to N do |
| Compute the dark current value of each detector: |
| end for |
| Compute the dark current correction reference: |
| Use the calibration results and to correct the of each single frame: |
| return, . |
| Algorithm 2: Description of the relative calibration of the LJ1-01 nighttime sensor |
| Input: dark current calibration results , i = 1, 2, 3, … N Input: dark current correction reference |
| Input: daytime low-gain calibration data , j = 1, 2, 3, … M Input: model relationship between low- and high-gain DNs of LJ1-01 in HDR mode, , |
| Output: relative calibration coefficients and for low-gain images and relative correction model for high-gain images |
| for each j = 1 to M do for each i = 1 to N do |
| Correct the dark current: |
| end for |
| end for |
| Compute the average values of all detectors for the uniform daytime calibration data (j = 1): |
| for each i = 1 to N do |
| Compute the response difference coefficient : |
| end for |
| Compute the average value of the interest zone (9 × 9) of each frame: Compute the reference detector relative calibration coefficients: and |
| for each i = 1 to N do |
| Compute the relative calibration coefficients of the other detectors for low-gain images: |
| end for |
| Based on the , , and the correction model of the low-gain images: |
| When the polynomial is of order n = 2, the relative correction model for high-gain images is: |
| return , , and . |
References
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Dietz, J.B.; Bland, T.; Sutton, P.C.; Kroehl, H.W. Radiance Calibration of DMSP-OLS Low-Light Imaging Data of Human Settlements. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 68, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, S.; Elvidge, C.; Hendy, M.V. Radiometric calibration of DMSP-OLS sensor using VIIRS day/night band. In Proceedings of the Earth Observing Missions and Sensors: Development, Implementation, and Characterization III, Beijing, China, 13–16 October 2014; p. 92640A. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A. Mapping sub-pixel urban expansion in China using MODIS and DMSP/OLS nighttime lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Spatiotemporally enhancing time-series DMSP/OLS nighttime light imagery for assessing large-scale urban dynamics. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Joshi, P.K.; Seto, K.C. Monitoring urbanization dynamics in India using DMSP/OLS night time lights and SPOT-VGT data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, T.R.K.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Elvidge, C.D.; Tuttle, B.T. Spatial characterization of electrical power consumption patterns over India using temporal DMSP-OLS night-time satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.; Tuttle, B.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.; Erwin, E.; Zhizhin, M. A Fifteen Year Record of Global Natural Gas Flaring Derived from Satellite Data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S. A very high-resolution (1 km × 1 km) global fossil fuel CO2 emission inventory derived using a point source database and satellite observations of nighttime lights. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.-C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Matsuno, Y. Exploring and estimating in-use steel stocks in civil engineering and buildings from night-time lights. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 34, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyba, C.; Garz, S.; Kuechly, H.; de Miguel, A.; Zamorano, J.; Fischer, J.; Hölker, F. High-Resolution Imagery of Earth at Night: New Sources, Opportunities and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, C.; Bai, Y. Quantitative Analysis of VIIRS DNB Nightlight Point Source for Light Power Estimation and Stability Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11915–11935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levin, N.; Duke, Y. High spatial resolution night-time light images for demographic and socio-economic studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Schaaf, C.; Seto, K.C. The Vegetation Adjusted NTL Urban Index: A new approach to reduce saturation and increase variation in nighttime luminosity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Phinn, S. Illuminating the capabilities of Landsat 8 for mapping night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 182, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.; Zhizhin, M.; Baugh, K.; Hsu, F.-C. Automatic Boat Identification System for VIIRS Low Light Imaging Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3020–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falchi, F.; Cinzano, P.; Duriscoe, D.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Portnov, B.A.; Rybnikova, N.A.; Furgoni, R. The new world atlas of artificial night sky brightness. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kyba, C.C.M.; Kuester, T.; Miguel, A.S.D.; Baugh, K.; Jechow, A.; Hölker, F.; Bennie, J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Gaston, K.J.; Guanter, L. Artificially lit surface of Earth at night increasing in radiance and extent. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hänel, A.; Posch, T.; Ribas, S.J.; Aubé, M.; Duriscoe, D.; Jechow, A.; Kollath, Z.; Lolkema, D.E.; Moore, C.; Schmidt, N.; et al. Measuring night sky brightness: Methods and challenges. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 205, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; He, G.; Long, T.; Guo, H.; Yin, R.; Leng, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, G. Potentiality of Using Luojia 1-01 Nighttime Light Imagery to Investigate Artificial Light Pollution. Sensors 2018, 18, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; He, G.; Long, T. Ongoing Conflict Makes Yemen Dark: From the Perspective of Nighttime Light. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, D.; Xu, H. Mapping Urban Extent Using Luojia 1-01 Nighttime Light Imagery. Sensors 2018, 18, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GPIXEL, Inc. 4 Megapixels Scientific CMOS Image Sensor; GPIXEL, Inc.: Changchun, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Markham, B.; Barsi, J.; Kvaran, G.; Ong, L.; Kaita, E.; Biggar, S.; Czapla-Myers, J.; Mishra, N.; Helder, D. Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager Radiometric Calibration and Stability. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12275–12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pascal, V.; Lebegue, L.; Meygret, A.; Laubies, M.; Hourcastagnou, J.; Hillairet, E. SPOT5 first in-flight radiometric image quality results. In Proceedings of the Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites VI, Crete, Greece, 23–27 September 2002; pp. 200–211. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Erivesb, H.; Xiongb, S.; Xieb, X.; Espositob, J.; Sunb, J.; Barnesc, W. Performance of Terra MODIS solar diffuser and solar diffuser stability monitor. In Proceedings of the Earth Observing Systems X, San Diego, CA, USA, 31 July–4 August 2005; p. 58820S. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Barnes, W. An overview of MODIS radiometric calibration and characterization. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 23, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, B.L.; Boncyk, W.C.; Barker, J.L.; Kaita, E.; Helder, D.L. Landsat-7 Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus In-Flight Radiometric Calibration. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience & Remote Sensing Symposium, Lincoln, NE, USA, 31–31 May 1996; pp. 1273–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Morfitt, R.; Barsi, J.; Levy, R.; Markham, B.; Micijevic, E.; Ong, L.; Scaramuzza, P.; Vanderwerff, K. Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) Radiometric Performance On-Orbit. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2208–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, P.; Meygret, A. Calibration of HRVIR and vegetation cameras on SPOT4. Adv. Space Res. 2001, 28, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, M.; Oaku, H.; Oguma, H.; Green, R.O.; Miyachi, Y.; Shimoda, H. Calibration of advanced visible and near infrared radiometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnutti, M.; Ryan, R.E.; Kelly, M.; Holekamp, K.; Zanoni, V.; Thome, K.; Schiller, S. Radiometric characterization of IKONOS multispectral imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pesta, F.; Bhatta, S.; Helder, D.; Mishra, N. Radiometric Non-Uniformity Characterization and Correction of Landsat 8 OLI Using Earth Imagery-Based Techniques. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 430–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horn, B.K.P.; Woodham, R.J. Destriping LANDSAT MSS images by histogram modification. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1979, 10, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, A.K. Relative Gain Characterization and Correction for Pushbroom Sensors Based on Lifetime Image Statistics and Wavelet Filtering. Master’s Thesis, South Dakota State University, Brookings, SD, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Geis, J.; Florio, C.; Moyer, D.; Rausch, K.; Luccia, F.D. VIIRS day-night band gain and offset determination and performance. In Proceedings of the Earth Observing Systems XVII, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–16 August 2012; p. 851012. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, S.; Miller, S.D. VIIRS Day-Night Band (DNB) calibration methods for improved uniformity. In Proceedings of the Earth Observing Systems XIX, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–21 August 2014; p. 921809. [Google Scholar]
- Fiete, R.D.; Tantalo, T. Comparison of SNR image quality metrics for remote sensing systems. Opt. Eng. 2001, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.; Visvanathan, V. CMOS op-amp sizing using a geometric programming formulation. IEEE Trans. Comput. Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2001, 20, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, U. Characterization of CMOS Image Sensor. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kar, S. MOSFET: Basics, Characteristics, and Characterization. High Permittivity Gate Dielectr. Mater. 2013, 43, 47–152. [Google Scholar]
- Markham, B.L.; Storey, J.C.; Irons, J.R. Landsat Data Continuity Mission, now Landsat-8: Six months on-orbit. In Proceedings of the Earth Observing Systems XVIII, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–29 August 2013; p. 88661B. [Google Scholar]
- Helder, D.L.; Basnet, B.; Morstad, D.L. Optimized identification of worldwide radiometric pseudo-invariant calibration sites. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerace, A.D.; Schott, J.R.; Brown, S.D.; Gartley, M.G.; Lewis, P.E. Using DIRSIG to identify uniform sites and demonstrate the utility of the side-slither calibration technique for Landsat’s new pushbroom instruments. In Proceedings of the Algorithms and Technologies for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery XVIII, Baltimore, MD, USA, 23–27 April 2012; p. 83902A. [Google Scholar]




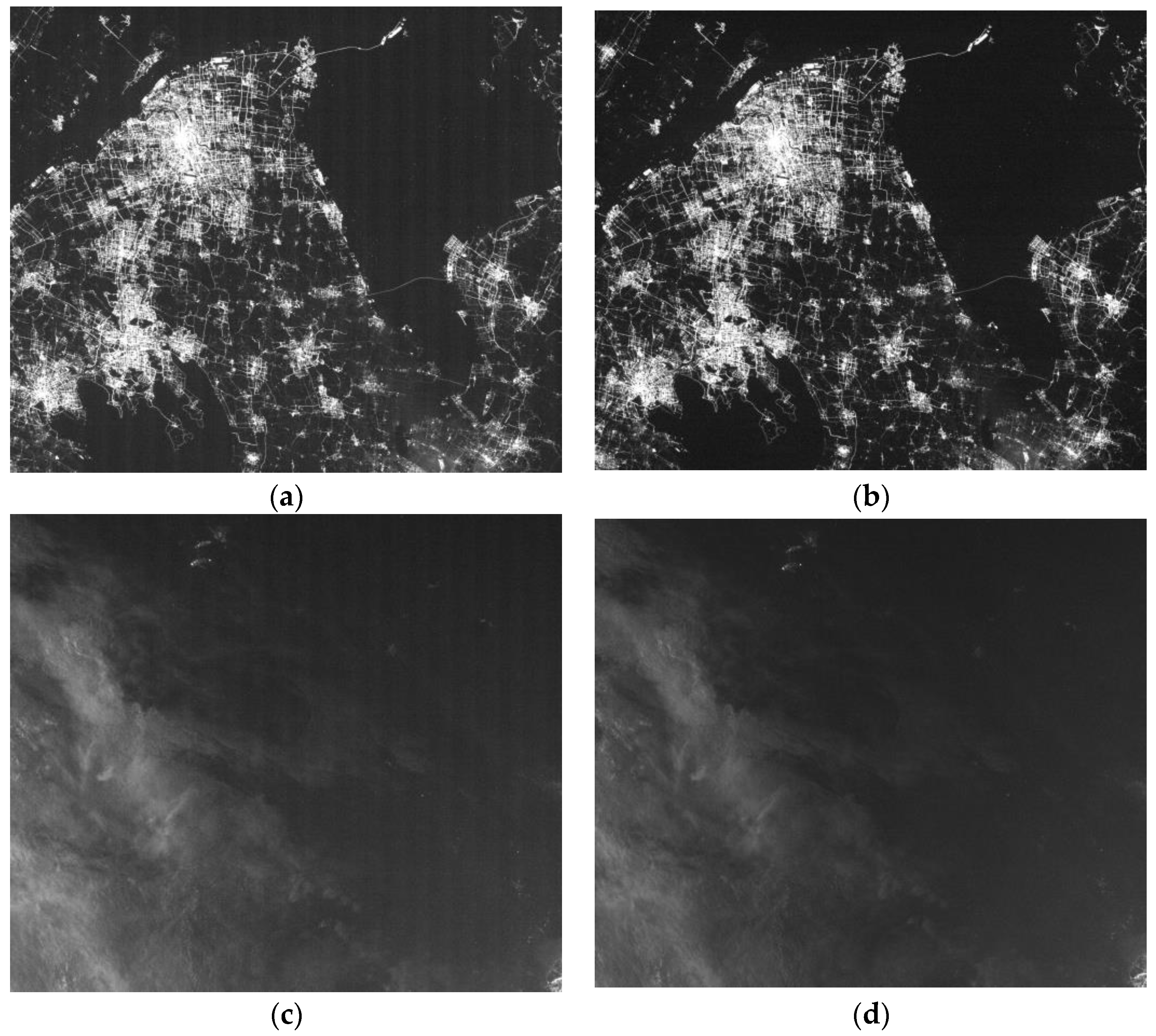

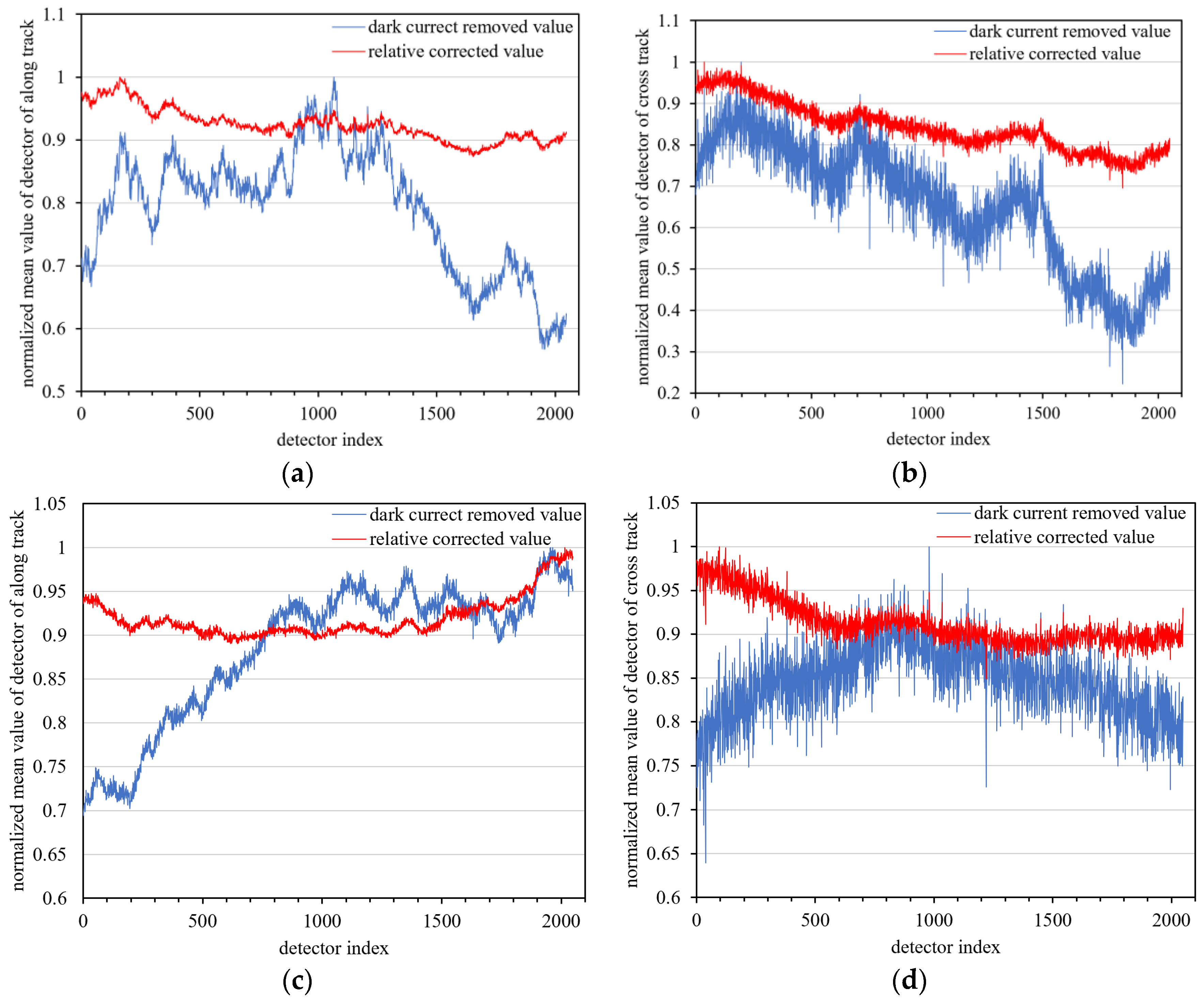

| Sensor Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of active detectors | 2048 × 2048 |
| Detector size | 11 µm × 11 µm |
| Imaging mode | Standard (STD) mode High dynamic range (HDR) mode |
| Spectral range | 460–980 nm |
| Resolution | 129 m |
| Shutter type | Electronic rolling shutter |
| Quantization bits | 12-bit, processing to 15bit @HDR mode |
| Frame rate | 24 fps @HDR mode 48 fps @STD mode |
| Daytime | Nighttime | |
|---|---|---|
| Exposure times (ms) | 0.049 | 17.089 |
| Gain multiplier | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Pseudo-Invariant Calibration Sites | Latitude (Degree) | Longitude (Degree) |
|---|---|---|
| Arabia 2, Middle East | 20.24 | 51.03 |
| Niger 2, Sahara | 21.36 | 10.59 |
| Mauritania 2, Sahara | 20.23 | −8.77 |
| Egypt 2, Sahara | 22.94 | 28.79 |
| Calibration Mission | Imaging Time/Gain and Exposure Time | Imaging Region | LJ1-01 Images | Google Maps and Locations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dark current calibration | 20 July 2018/0.6 + 17.089 ms | Mauritania 2, Sahara | 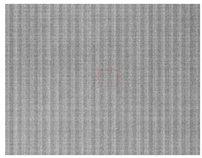 | 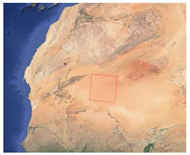 |
| Non-uniformity calibration | 20 July 2018/0.6 + 17.089 ms | Egypt 2, Sahara |  | 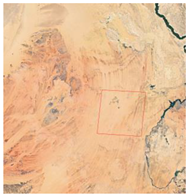 |
| 22 July 2018/0.6 + 17.089 ms | Mauritania 2, Sahara |  |  | |
| 23 July 2018/0.6 + 17.089 ms | Niger 2, Sahara | 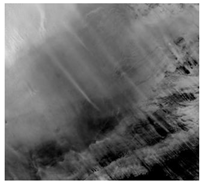 |  | |
| 18 August 2018/0.6 + 17.089 ms | Arabia 2, Middle East |  |  |
| Mean (DN) | Maximum (DN) | Minimum (DN) | Std. (DN) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low gain | 186.8194 | 186.9709 | 186.6585 | 0.041482 |
| High gain | 176.5858 | 176.8145 | 176.4118 | 0.066167 |
| Goodness of Fit (R2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Middle-radiance range | −3.046475 | 8.428720 | −0.001721 | 0.999992 |
| High-radiance range | 2851.017690 | 0.132141 | −0.000036 | 0.979314 |
| Streaking Metrics (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Maximum | Minimum | Std. | |
| Zone 1 | 0.021093 | 0.111714 | 0.0 | 0.016453 |
| Zone 2 | 0.018854 | 0.097228 | 0.0 | 0.014664 |
| Zone 3 | 0.030947 | 0.162012 | 0.0 | 0.024042 |
| Zone 4 | 0.039596 | 0.202831 | 0.0 | 0.030460 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, D. On-Orbit Relative Radiometric Calibration of the Night-Time Sensor of the LuoJia1-01 Satellite. Sensors 2018, 18, 4225. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124225
Zhang G, Li L, Jiang Y, Shen X, Li D. On-Orbit Relative Radiometric Calibration of the Night-Time Sensor of the LuoJia1-01 Satellite. Sensors. 2018; 18(12):4225. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124225
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guo, Litao Li, Yonghua Jiang, Xin Shen, and Deren Li. 2018. "On-Orbit Relative Radiometric Calibration of the Night-Time Sensor of the LuoJia1-01 Satellite" Sensors 18, no. 12: 4225. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124225
APA StyleZhang, G., Li, L., Jiang, Y., Shen, X., & Li, D. (2018). On-Orbit Relative Radiometric Calibration of the Night-Time Sensor of the LuoJia1-01 Satellite. Sensors, 18(12), 4225. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124225






