Polymer Optical Fiber Goniometer: A New Portable, Low Cost and Reliable Sensor for Joint Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Analysis
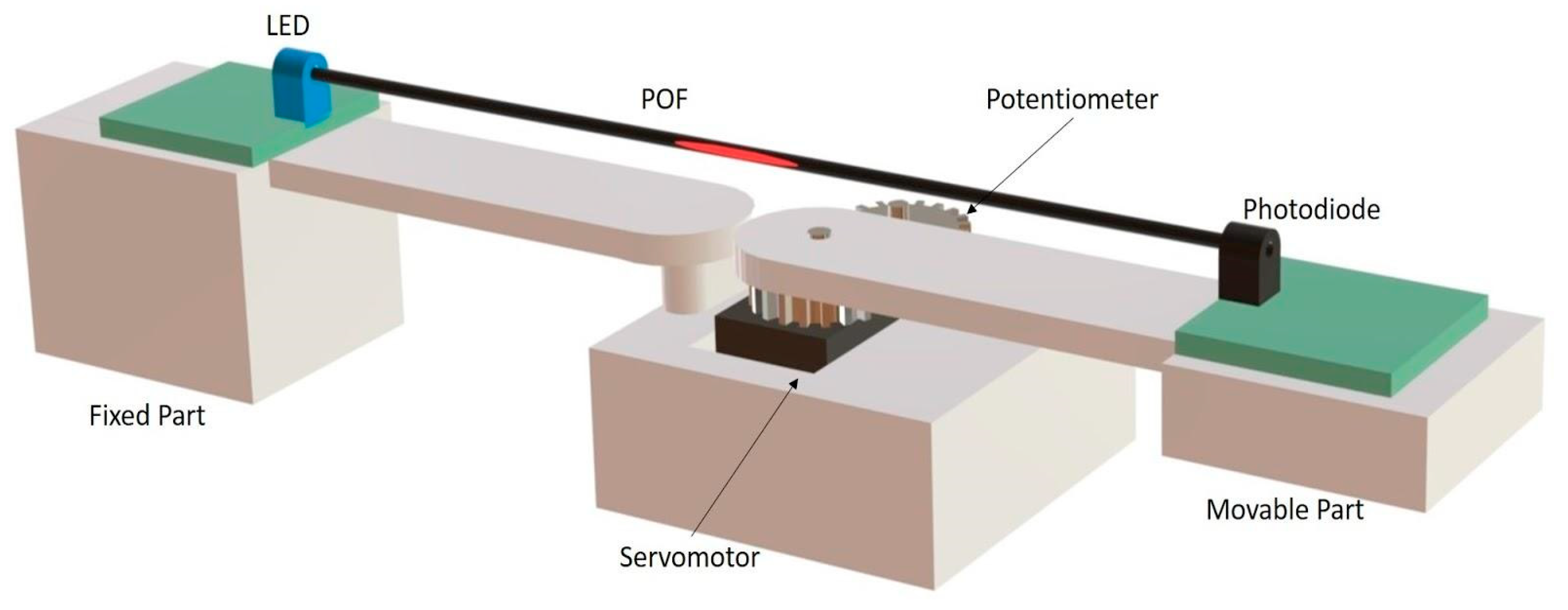
2.1. Test Bench
2.2. Joint Angle Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Test Bench
3.2. Joint Angle Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verrall, G.M.; Slavotinek, J.P.; Barnes, P.G.; Esterman, A.; Oakeshott, R.D.; Spriggins, A.J. Hip joint range of motion restriction precedes athletic chronic groin injury. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2007, 10, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanese, S.; Gordon, S.; Buettner, P.; Flavell, C.; Ruston, S.; Coe, D.; O’Sullivan, W.; McCormack, S. Reliability and concurrent validity of knee angle measurement: Smartphone app versus universal goniometer used by experienced and novice clinicians. Man. Ther. 2014, 19, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhea, M.R.; Kenn, J.G.; Peterson, M.D.; Massey, D.; Simão, R.; Marin, P.J.; Favero, M.; Cardozo, D.; Krein, D. Joint-angle specific strength adaptations influence improvements in power in highly trained athletes. Hum. Mov. 2016, 17, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Frizera, A.; Pontes, M.J. Compensation technique for environmental and light source power variations applied in a polymer optical fiber curvature sensor for wearable devices. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 34, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesh, S.; Padma, S.; Srinivas, T.; Asokan, S. Fiber bragg grating goniometer for joint angle measurement. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donno, M.; Palange, E.; Di Nicola, F.; Di Nicola, G.; Ciancetta, F. A new flexible optical fiber goniometer for dynamic angular measurements: Application to human joint movement monitoring. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2008, 57, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.T.; King, C.E.; Do, A.H.; Nenadic, Z. A durable, low-cost electrogoniometer for dynamic measurement of joint trajectories. Med. Eng. Phys. 2011, 33, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picerno, P.; Cereatti, A.; Cappozzo, A. A spot check for assessing static orientation consistency of inertial and magnetic sensing units. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gohary, M.; McNames, J. Shoulder and elbow joint angle tracking with inertial sensors. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 2635–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, A.R.; Leal-Junior, A.G.; Marques, C.; Leite, S.; de Sena, G.L.; Machado, L.C.; Frizera, A.; Ribeiro, M.R.N.; Pontes, M.J. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) recycling for the production of optical fiber sensor systems. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 30051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K. Polymer optical fiber sensors: A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 013002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Frizera, A.; Avellar, L.M.; Pontes, M.J. Design considerations, analysis, and application of a low-cost, fully portable, wearable polymer optical fiber curvature sensor. Appl. Opt. 2017, 57, 6927–6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, L.E.; Walsh, P.; Hermann, S.; Smyth, B.; Caulfield, B. Wearable monitoring of seated spinal posture. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2008, 2, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilro, L.; Oliveira, J.G.; Pinto, J.L.; Nogueira, R.N. A reliable low-cost wireless and wearable gait monitoring system based on a plastic optical fiber sensor. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 045801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Di, H.; Liu, R. Light intensity modulation fiber-optic sensor for curvature measurement. Opt. Laser Technol. 2010, 42, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Frizera, A.; Pontes, M.J. Sensitive zone parameters and curvature radius evaluation for polymer optical fiber curvature sensors. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 100, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Frizera, A.; Marques, C.; Sanchez, M.R.A.; dos Santos, W.M.; Siqueira, A.A.G.; Segatto, M.V.; Pontes, M.J. Polymer optical fiber for angle and torque measurements of a series elastic actuator’s spring. J. Lightwave Technol. 2018, 36, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Jang, K.W.; Yoo, W.J.; Shin, S.H.; Cho, S.; Lee, B. Feasibility study on fiber-optic goniometer for measuring knee joint angle. Opt. Rev. 2014, 21, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupar, D.Z.; Bajic, J.S.; Manojlovic, L.M.; Slankamenac, M.P.; Joza, A.V.; Zivanov, M.B. Wearable low-cost system for human joint movements monitoring based on fiber-optic curvature sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 3424–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Junior, A.G.; Frizera, A.; Pontes, M.J. Analytical model for a polymer optical fiber under dynamic bending. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 93, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, M.S.; Djordjevich, A.; Nikezic, D. Analytical Optimization of optical fiber curvature gauges. IEEE Sens. J. 2008, 8, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Valencia, L.S.; Elias, A.; Rocon, E.; Bastos-Filho, T.; Frizera, A. An IMU-to-body alignment method applied to human gait analysis. Sensors 2016, 16, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OptiTrack. Available online: https://optitrack.com/ (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- EMGSystem. Available online: http://www.emgsystem.com.br/p/goniometros/ (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Biometrics. Available online: http://www.biometricsltd.com/ (accessed on 21 November 2018).




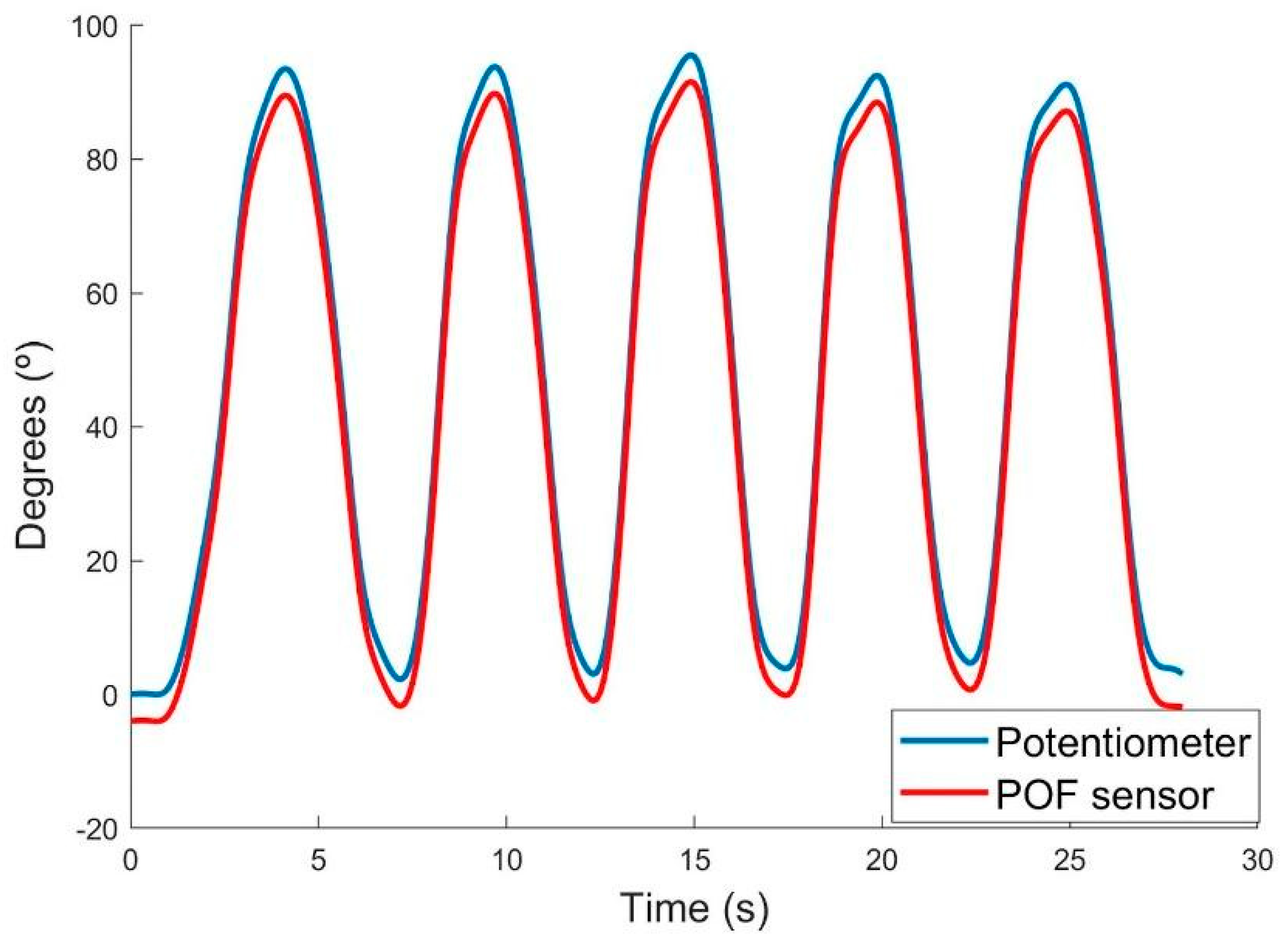
| Angular Velocity | Difference (°) | Standard Deviation (°) | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18°/s | 5.75 | 4.18 | 0.989 |
| 36°/s | 5.71 | 4.54 | 0.987 |
| 50°/s | 4.95 | 3.97 | 0.989 |
| 80°/s | 6.03 | 4.35 | 0.989 |
| 100°/s | 6.48 | 4.48 | 0.989 |
| 140°/s | 7.48 | 4.06 | 0.989 |
| 200°/s | 7.93 | 4.17 | 0.989 |
| Mean | 6.33 | 4.25 | 0.989 |
| Difference (°) | Standard Deviation (°) | Correlation Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Participant 1 | 4.66 | 3.35 | 0.991 |
| Participant 2 | 6.4 | 4.31 | 0.973 |
| Participant 3 | 6.06 | 6.06 | 0.989 |
| Participant 4 | 6.44 | 3.77 | 0.982 |
| Participant 5 | 6.08 | 4.32 | 0.981 |
| Participant 6 | 4.68 | 3.71 | 0.995 |
| Participant 7 | 5.07 | 4.89 | 0.984 |
| Participant 8 | 4.45 | 3.03 | 0.989 |
| Participant 9 | 4.06 | 0.36 | 0.999 |
| Participant 10 | 5.2 | 3.31 | 0.989 |
| Mean | 5.31 | 3.71 | 0.987 |
| Low-Cost | Portable | No Calibration Required | Good Repeatability | No Electromagnetic Interferences | No Reference System | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vargas-Valencia et al. [22] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Arnaldo et al. [12] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Umesh et al. [5] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| OptiTrack [23] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| EMGSystem [24] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Biometrics [25] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Proposed sensor | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezende, A.; Alves, C.; Marques, I.; Silva, M.A.; Naves, E. Polymer Optical Fiber Goniometer: A New Portable, Low Cost and Reliable Sensor for Joint Analysis. Sensors 2018, 18, 4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124293
Rezende A, Alves C, Marques I, Silva MA, Naves E. Polymer Optical Fiber Goniometer: A New Portable, Low Cost and Reliable Sensor for Joint Analysis. Sensors. 2018; 18(12):4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124293
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezende, Andressa, Camille Alves, Isabela Marques, Marco Aurélio Silva, and Eduardo Naves. 2018. "Polymer Optical Fiber Goniometer: A New Portable, Low Cost and Reliable Sensor for Joint Analysis" Sensors 18, no. 12: 4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124293
APA StyleRezende, A., Alves, C., Marques, I., Silva, M. A., & Naves, E. (2018). Polymer Optical Fiber Goniometer: A New Portable, Low Cost and Reliable Sensor for Joint Analysis. Sensors, 18(12), 4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124293





