Characteristics of BDS Signal-in-Space User Ranging Errors and Their Effect on Advanced Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Statistics and Overbound of BDS SIS URE
2.1. Data Preprocessing
2.1.1. Data Sources
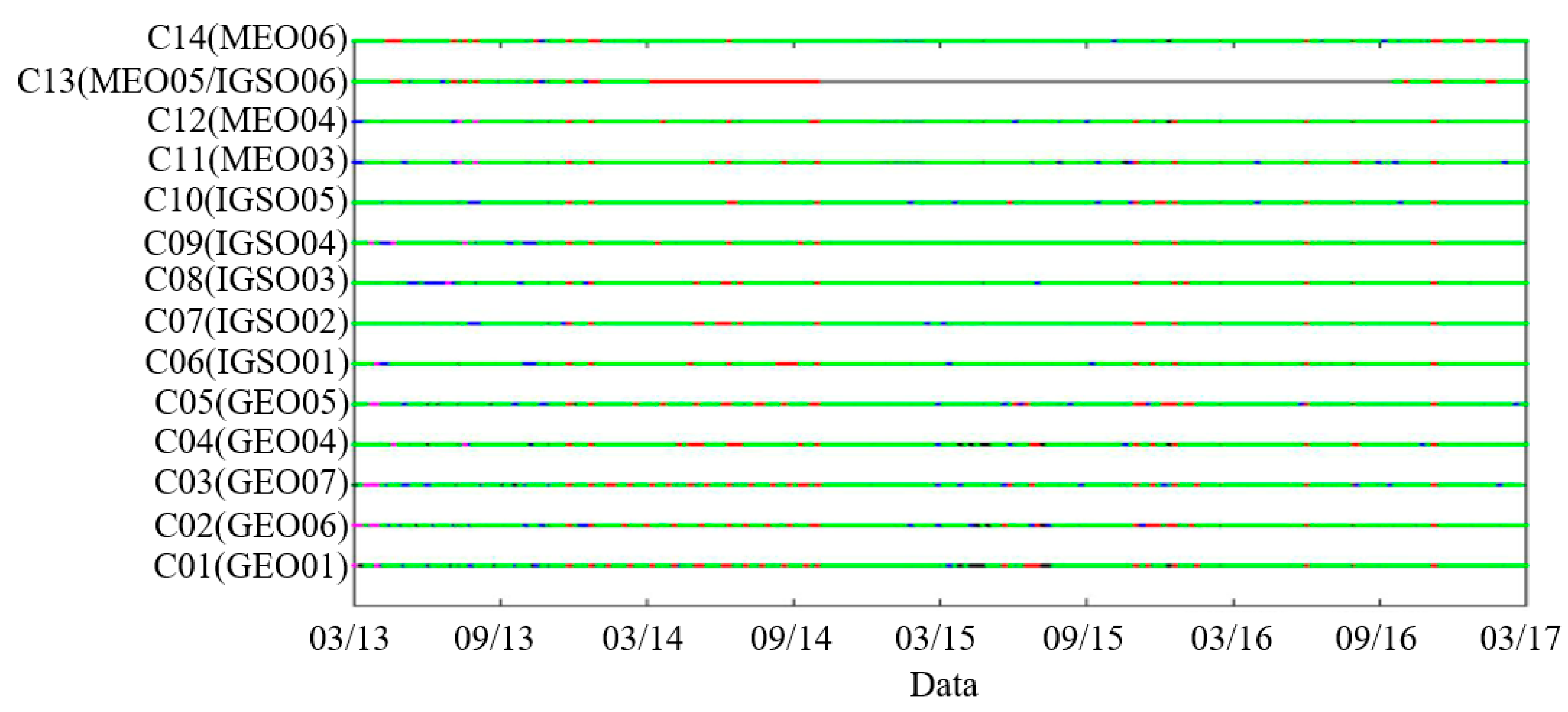
2.1.2. BDS Outlier Filter
- The integrity status word is not zero, or the URA is greater than 48 m.
- The broadcast ephemeris is not within the 4 h period.
- The precise ephemeris/clock is lost.
- The SIS UREs exceed the URA by a factor of more than 4.42.
2.2. Statistics of BDS SIS URE
2.2.1. Global Average rms SIS UREs, Orbit-Only rms SIS UREs and Worst-Case SIS UREs
- BDS global average rms SIS UREs. There are three orbits of satellites in BDS: MEO, IGSO and GEO; satellites C01 to C05 are GEO satellites, satellites C06 to C10 are IGSO satellites, and satellites C11 to C14 are MEO satellites. Because of the differences in satellite observation geometry structure, the computational models for the SIS UREs of the three orbits are different and are derived as follows:where R represents the radial errors, A represents the along-track errors, and C represents the cross-track errors. R, A and C are the three directions of the orbit errors. T represents clock errors.
- BDS orbit-only rms SIS UREs. Orbit-only rms SIS UREs are obtained by removing the clock errors according to Equations (1) and (2):
- BDS worst-case SIS UREs. The worst-case SIS UREs are the maximum instantaneous SIS UREs calculated by the broadcast ephemeris. The worst-case SIS UREs play a crucial role in the SIS performance evaluation. The worst-case SIS UREs can be calculated either from the instantaneous SIS UREs or from radial errors, along-track errors, cross-track errors and clock errors. The present study uses the latter approach [14]:where γ is the latitude of the edge of satellite coverage.
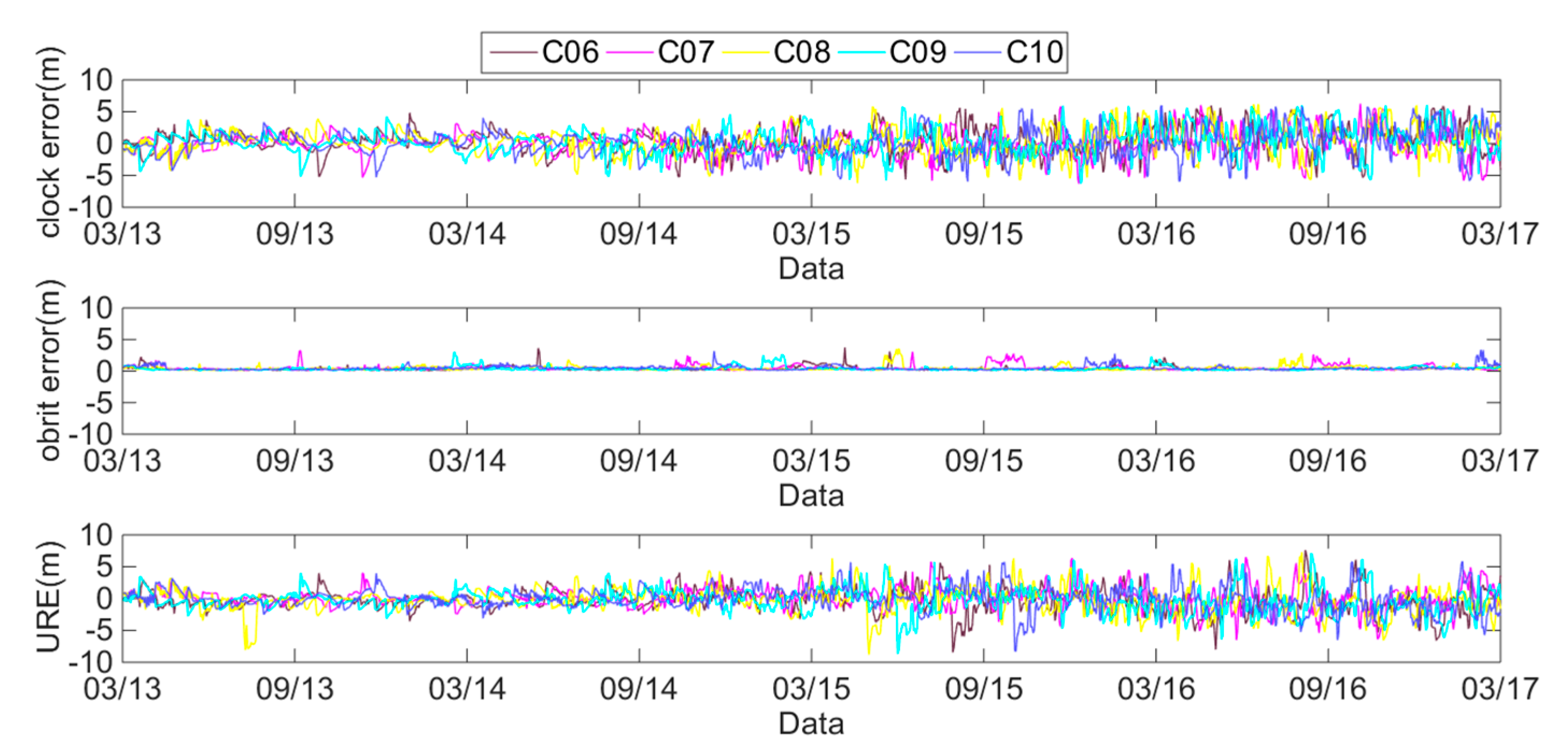
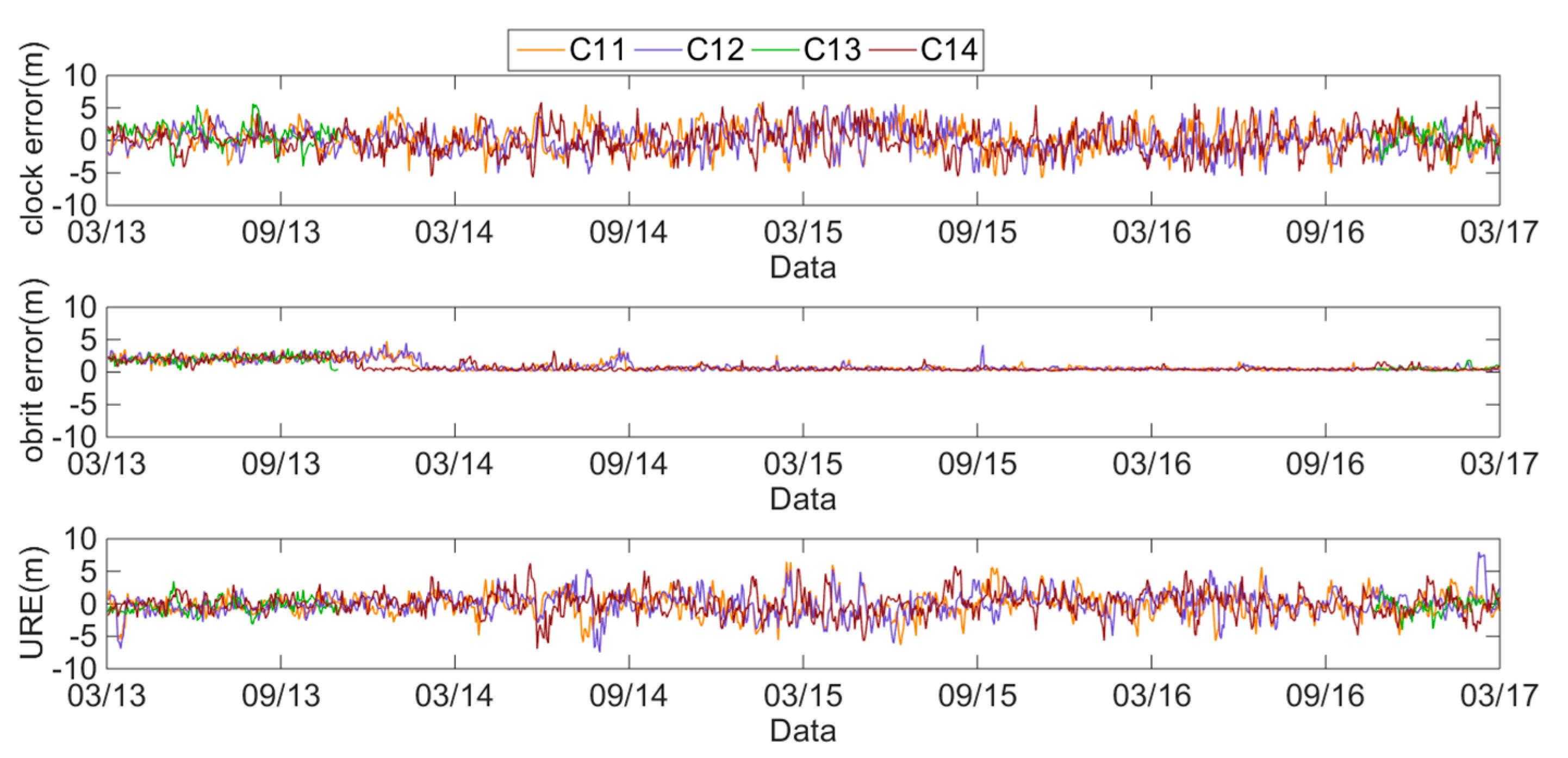
2.2.2. Analysis of BDS Clock Errors, Orbit Errors and SIS UREs
2.3. Overbound BDS SIS UREs
3. Effect of BDS URA on ARAIM
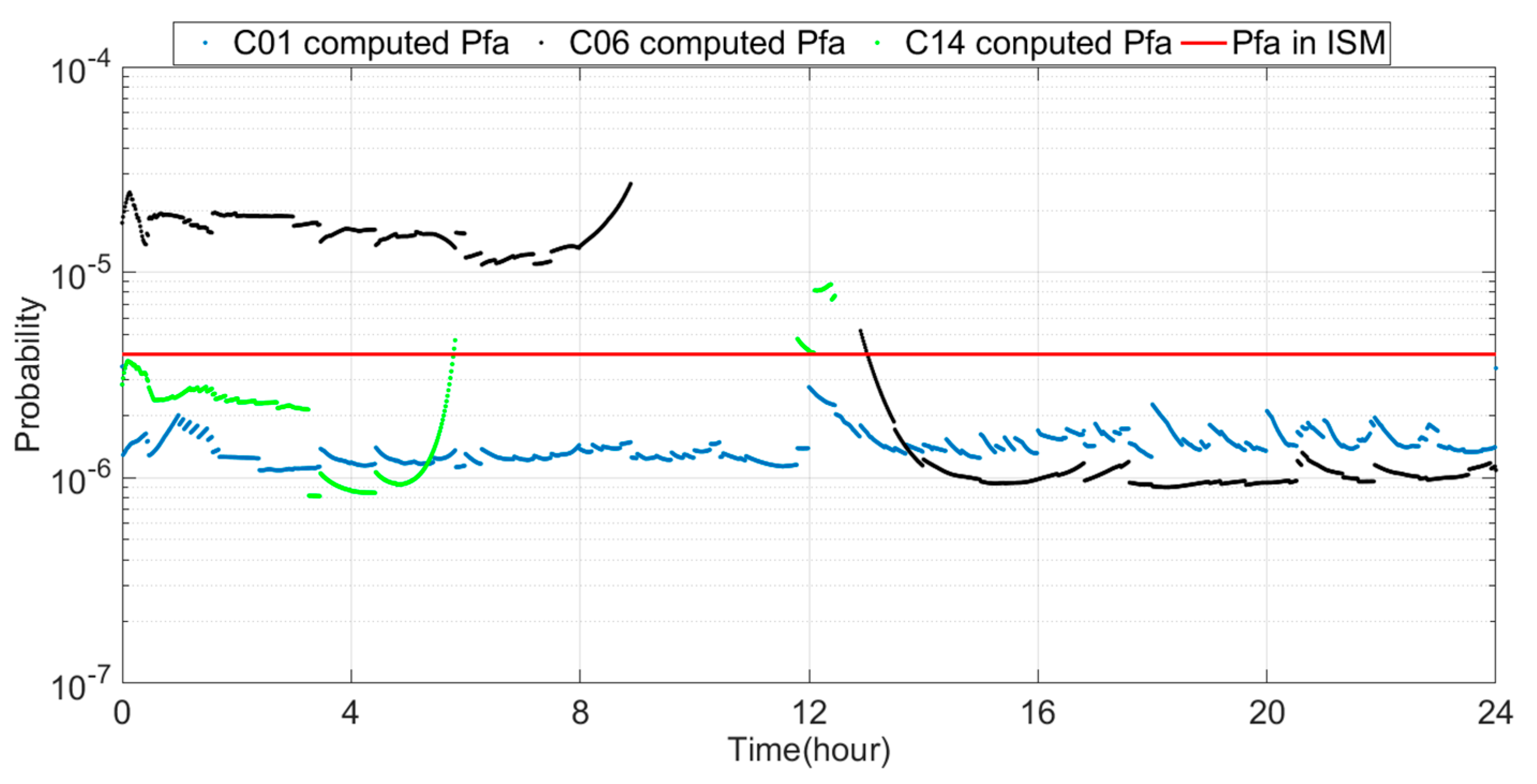
3.1. Effect of BDS URA on Pfa
3.2. Effect of BDS URA on ARAIM Availability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blanch, J.; Walter, T.; Enge, P. Optimal Positioning for Advanced RAIM. In Proceedings of the ION ITM 2012, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 30–31 January 2012; pp. 1624–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Paternostro, S.; Moore, T.; Atkin, C.H.J.; Morvan, H.P. Evaluation of Advanced Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring Performance on Predicted Aircraft Trajectories. In Proceedings of the IEEE Position, Location and Navigation Symposium, Savannah, GA, USA, 11–16 April 2016; pp. 842–856. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, M.; Qu, L.; Hu, Z.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Initial results of precise orbit and clock determination for COMPASS navigation satellite system. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanch, J.; Walter, T.; Enge, P.; Burns, J.; Alexander, K.; Boyero, J.P.; Lee, Y.; Pervan, B.; Joerger, M.; Khanafseh, S.; et al. Progress on Working Group-C Activities on Advanced RAIM. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS+ 2015, Tampa, FL, USA, 14–18 September 2015; pp. 629–638. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.C.; Bian, B. Analysis of Advanced RAIM Performance Degradation Caused by Integrity Support Message Parameter Errors and Neglecting Nominal Bias Errors. In Proceedings of the ION ITM 2017, Monterey, CA, USA, 30 January–1 February 2017; pp. 210–225. [Google Scholar]
- Heng, L.; Gao, G.X.; Walter, T.; Enge, P. Statistical Characterization of GPS Signal-In-Space Errors. In Proceedings of the ION ITM 2011, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–26 January 2011; pp. 312–319. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, S.P.; Meurer, M.; Rippl, M.; Belabbas, B.; Joerger, M.; Pervan, B. URA/SISA Analysis for GPS-Galileo ARAIM Integrity Support Message. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS+2015, Tampa, FL, USA, 14–18 September 2015; pp. 735–745. [Google Scholar]
- Gunning, K.; Walter, T.; Enge, P. Characterization of GLONASS Broadcast Clock and Ephemeris: Nominal Performance and Fault Trends for ARAIM. In Proceedings of the ION ITM 2017, Monterey, CA, USA, 30 January–1 February 2017; pp. 170–183. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, T.; Gunning, K.; Blanch, J. Keynote: Validation of the Unfaulted Error Bounds for ARAIM. In Proceedings of the ION Pacific PNT Meeting 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 1–4 May 2017; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Sui, L.; Jia, X.; Zhu, Y. SIS Error Statistical Analysis of Beidou Satellite Navigation System; Geomatics & Information Science of Wuhan University: Wuhan, China, 2014; Volume 423, pp. 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- Mistrapau, F.; Bija, B.; Cueto-Felgueroso, G.; Odriozola, M.; Azaola, M.; Cezón, A.; Amarillo-Fernández, F. GPS SISRE/URA Integrity Analysis for ARAIM. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS+ 2016, Portland, OR, USA, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 1793–1803. [Google Scholar]
- US DoD. Global Positioning System Standard Positioning Service Performance Standard, 4th ed.; US DoD: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Jia, R.; Dong, X.; Shang, C.; Wang, J. Analysis on URE and Positioning Accuracy of BeiDou Navigation System. Mod. Electron. Tech. 2014, 37, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Heng, L.; Gao, G.X.; Walter, T.; Enge, P. Statistical Characterization of GLONASS Broadcast Clock Errors and Signal-in-Space Errors. In Proceedings of the ION ITM 2012, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 30 January–1 February 2012; pp. 1697–1707. [Google Scholar]
- Dins, A.; Ye, P.; Schipper, B. Statistical characterization of Beidou and GPS SIS errors in the Asian region. In Proceedings of the IEEE Digital Avionics Systems Conference, Prague, Czech Republic, 13–17 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, W.K.; Ren, J.; Lou, Y.D.; Dai, X.L.; Fang, X. Long-term behavior and statistical characterization of BeiDou signal-in-space errors. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1907–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, J. Research of the Coordinate Conversion between WGS84 and CGCS2000. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P. The BeiDou Navigation Message. In Proceedings of the IGNSS 2013, Outrigger Gold Coast, Qld, Australia, 16–18 July 2013; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, S.P.; Meurer, M.; Martini, I.; Rippl, M.; Joerger, M.; Pervan, B. Nominal Range Error Analysis to Support ARAIM. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS+ 2016, Portland, OR, USA, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 1726–1735. [Google Scholar]
- CSNO. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document; BeiDou SIS ICD; China Satellite Navigation Office: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Ge, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y. Reduced ARAIM monitoring subset method based on satellites in different orbital planes. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohenour, C.; Graas, F.V. GPS Orbit and Clock Error Distributions. Navigation 2011, 58, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Working Group C. Milestone 2 Report of the EU/US Cooperation on Satellite Navigation Released. FAA, 2015. Available online: http://www.gps.gov/policy/cooperation/europe/2015/working-group-c/823 (accessed on 11 February 2015).
- Blanch, J.; Walter, T.; Enge, P.; Lee, Y.; Pervan, B. Advanced RAIM User Algorithm Description: Integrity Support Message Processing, Fault Detection, Exclusion, and Protection Level Calculation. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2012, Nashville, TN, USA, 17–21 September 2012; pp. 2828–2849. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Lu, Z. Mixed Beidou Constellation DOP Value and Positioning Performance Analysis. GNSS World China 2016, 41, 6–10. [Google Scholar]










| PRN | 68% Overbounds of Worst-Case UREs(m) |
|---|---|
| C01 | 2.208 |
| C02 | 2.027 |
| C03 | 2.069 |
| C04 | 1.878 |
| C05 | 1.722 |
| C06 | 1.777 |
| C07 | 1.567 |
| C08 | 1.743 |
| C09 | 1.688 |
| C10 | 1.689 |
| C11 | 1.844 |
| C12 | 1.843 |
| C13 | 1.629 |
| C14 | 2.135 |
| Parameter | Setting |
|---|---|
| GPS URA/URE | 1/0.667 |
| BDS URA/URE | 2/1.333 (broadcast) 2.4/1.6 (computed) |
| bnom | 0.75 |
| Psat,GPS/Psat,BDS | 10−5 |
| Pconst,GPS/Pconst,BDS | 10−4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Shao, W.; Li, R.; Song, D.; Li, T. Characteristics of BDS Signal-in-Space User Ranging Errors and Their Effect on Advanced Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring Performance. Sensors 2018, 18, 4475. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124475
Wang Z, Shao W, Li R, Song D, Li T. Characteristics of BDS Signal-in-Space User Ranging Errors and Their Effect on Advanced Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring Performance. Sensors. 2018; 18(12):4475. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124475
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhipeng, Wei Shao, Rui Li, Dan Song, and Tinglin Li. 2018. "Characteristics of BDS Signal-in-Space User Ranging Errors and Their Effect on Advanced Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring Performance" Sensors 18, no. 12: 4475. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124475
APA StyleWang, Z., Shao, W., Li, R., Song, D., & Li, T. (2018). Characteristics of BDS Signal-in-Space User Ranging Errors and Their Effect on Advanced Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring Performance. Sensors, 18(12), 4475. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124475




