A Flexible Multiring Concentric Electrode for Non-Invasive Identification of Intestinal Slow Waves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Biosignal Recordings on the Body Surface
1.2. Intestinal Myoelectrical Activity
2. Materials and Methods
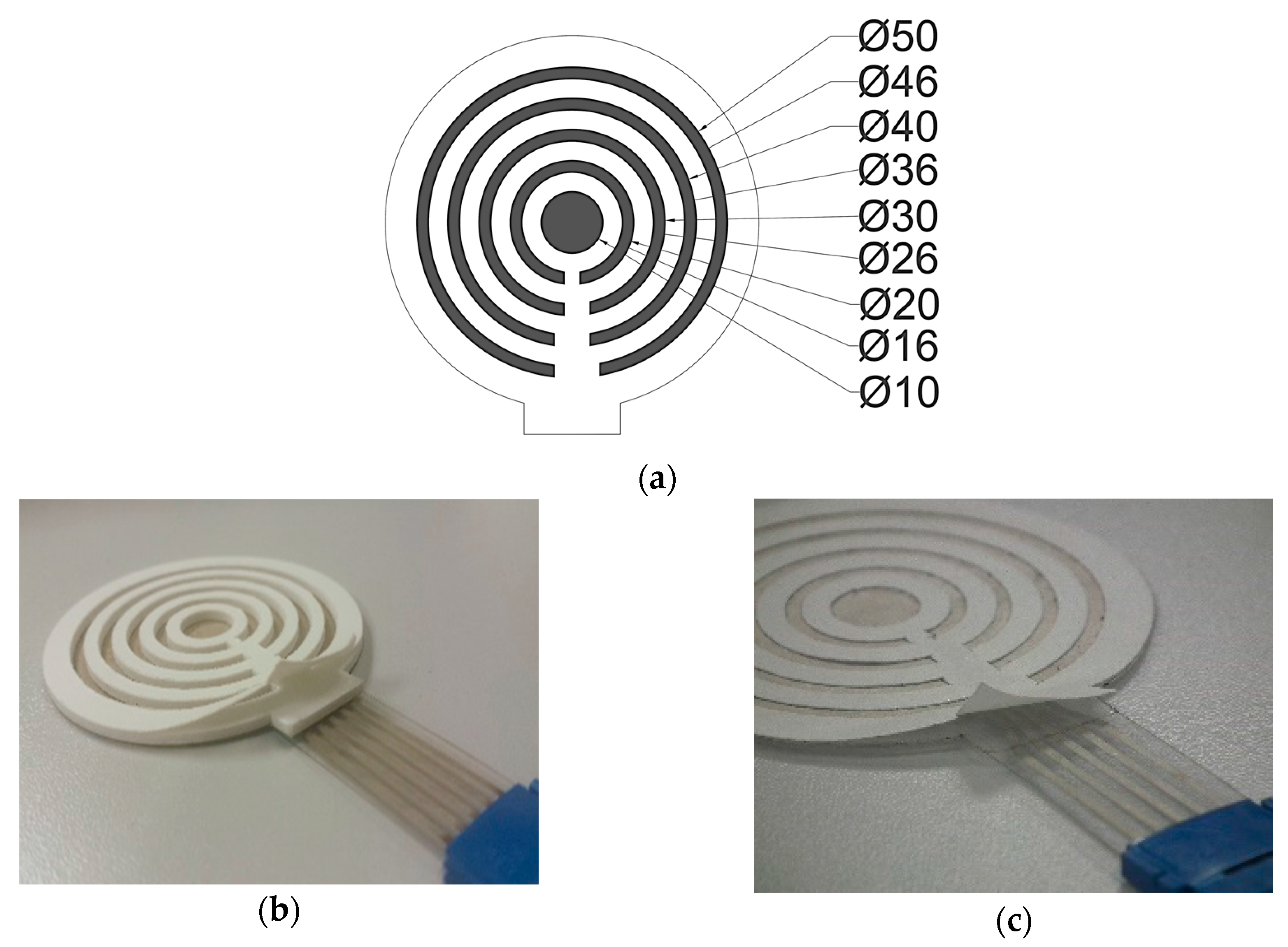
2.1. Sensing Part
2.2. Recording Sessions
2.3. Signal Analysis
- %DFTFSW: defined as the ratio of analyzed windows whose DF is inside the typical frequency range of intestinal SW (8–12 cpm).
- %DFRESP: defined as the ratio between the number of windows in which the DF of the surface signal is within the DF of respiration (DFRESP) ±1 cpm and the total number of windows
- PRSW/RESP: defined as the ratio between the power within the SW frequency range and the power in the respiratory bandwidth, calculated as follows:
- %DFLF: defined as the ratio between the number of windows in which the DF is within 6–8 cpm and the total number of windows.
- PRSW/LF: defined as the ratio between the power within the SW frequency range and the power in the low frequency bandwidth, calculated as follows:
- %DFOTHERS: defined as the ratio between the number of other cases and the total number of windows. Ideally, this parameter should be 0%.
- %DFSW: defined as the ratio of analyzed windows whose DF after discarding peaks on the low frequency and respiration bandwidth is in the SW range.
- MV (mean variability): defined as the average of the dominant frequency difference between consecutive windows in the range of 8 to 12 cpm, where ‘Ri’ is the dominant frequency of the EEnG signal in the window ‘i’ and ‘N’ is the number of analyzed windows in the session:
2.4. Selecting the Best Combination of Recording Factors of CRE
2.5. Selecting the Best CRE Ring Size and Comparison with Conventional Bipolar Recording
3. Results
3.1. Signal Acquisition and Parameters
3.2. Selection of the Best Combination of CRE Recording Factors
3.3. Selection of the Best Ring Size of CRE and Comparison with Conventional Bipolar Recording
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bradshaw, L.A.; Richards, W.O.; Wikswo, J.P. Volume conductor effects on the spatial resolution of magnetic fields and electric potentials from gastrointestinal electrical activity. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2001, 39, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besio, W.; Aakula, R.; Dai, W. Comparison of bipolar vs. tripolar concentric ring electrode Laplacian estimates. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2004, 3, 2255–2258. [Google Scholar]
- Prats-Boluda, G.; Garcia-Casado, J.; Martinez-de-Juan, J.L.; Ponce, J.L. Identification of the slow wave component of the electroenterogram from Laplacian abdominal surface recordings in humans. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, 1115–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuoka, Y.; Miyazawa, K.; Mori, H.; Miyagi, M.; Nishida, M.; Horiuchi, Y.; Ichikawa, A.; Hoshino, H.; Noshiro, M.; Ueno, A. Development of a compact wireless laplacian electrode module for electromyograms and its human interface applications. Sensors 2013, 13, 2368–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.C.; Feng, W.Y.; Tarjan, P.P. Laplacian electrocardiograms with active electrodes for arrhythmia detection. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 30 October–2 November 1997; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Besio, W.; Prasad, A. Analysis of skin-electrode impedance using concentric ring electrode. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2006, 1, 6414–6417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boudria, Y.; Feltane, A.; Besio, W. Significant improvement in one-dimensional cursor control using Laplacian electroencephalography over electroencephalography. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 11, 35014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufer, M.; Rasquinha, L.; Tarjan, P. Optimization of Multi-ring Sensing Electrode Set. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1–4 November 1990; pp. 612–613. [Google Scholar]
- Fleckenstein, P.; Oigaard, A. Electrical spike activity in the human small intestine. A multiple electrode study of fasting diurnal variations. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 1978, 23, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, E.M. Disturbances in small bowel motility. Baillieres. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1999, 13, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vantrappen, G. Small intestinal motility and bacteria. In Gastrointestinal Motility; Heidt, P.J., Rusch, V., Eds.; Old Herborn University: Herborn, Germany, 1997; Volume 67, pp. 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, X.; Li, S.; Foreman, R.; Farber, J.; Lin, L.; Yin, J.; Chen, J.D.Z. Hyperglycemia-induced small intestinal dysrhythmias attributed to sympathovagal imbalance in normal and diabetic rats. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, E.M. Gastric and small intestinal motility in health and disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 1996, 25, 113–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somarajan, S.; Muszynski, N.D.; Cheng, L.K.; Bradshaw, L.A.; Naslund, T.C.; Richards, W.O. Noninvasive biomagnetic detection of intestinal slow wave dysrhythmias in chronic mesenteric ischemia. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G52–G58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, L.; Allos, S.; Wikswo, J.P., Jr.; Richards, W. Correlation and comparison of magnetic and electric detection of small intestinal electrical activity. Am. J. 1997, 272, G1159–G1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.D.; Schirmer, B.D.; McCallum, R.W. Measurement of electrical activity of the human small intestine using surface electrodes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1993, 40, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.D.; Lin, Z. Adaptive cancellation of the respiratory artifact in surface recording of small intestinal electrical activity. Comput. Biol. Med. 1993, 23, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats-Boluda, G.; Garcia-Casado, J.; Martinez-de-Juan, J.L.; Ye-Lin, Y. Active concentric ring electrode for non-invasive detection of intestinal myoelectric signals. Med. Eng. Phys. 2011, 33, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Casado, J.; Zena-Gimenez, V.; Prats-Boluda, G.; Ye-Lin, Y. Enhancement of non-invasive recording of electroenterogram by means of a flexible array of concentric ring electrodes. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 42, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Casado, J.; Zena, V.; Perez, J.J.; Prats-Boluda, G.; Ye-Lin, Y.; Garcia-Breijo, E. Opened-Ring Electrode Array for Enhanced Non-invasive Monitoring of Bioelectrical Signals: Application to Surface EEnG Recording. In Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies; Fernández-Chimeno, M., Fernandes, P.L., Alvarez, S., Stacey, D., Solé-Casals, J., Fred, A., Gamboa, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 452, pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Prats-Boluda, G.; Ye-Lin, Y.; Garcia-Breijo, E.; Ibañez, J.; Garcia-Casado, J. Active flexible concentric ring electrode for non-invasive surface bioelectrical recordings. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 125703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.G. Medical Instrumentation: Application and Design, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 189–215. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-T.; Liao, L.-D.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wang, I.-J.; Lin, B.-S.; Chang, J.-Y. Novel dry polymer foam electrodes for long-term EEG measurement. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gruetzmann, A.; Hansen, S.; Müller, J. Novel dry electrodes for ECG monitoring. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meziane, N.; Webster, J.G.; Attari, M.; Nimunkar, A.J. Dry electrodes for electrocardiography. Physiol. Meas. 2013, 34, R47–R69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Casado, J.; Martinez-de-Juan, J.L.; Ponce, J.L. Adaptive filtering of ECG interference on surface EEnGs based on signal averaging. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye-Lin, Y.; Garcia-Casado, J.; Martinez-de-Juan, J.L.; Prats-Boluda, G.; Ponce, J.L. The detection of intestinal spike activity on surface electroenterograms. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 663–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Yin, J.; Liu, J.; Pasricha, P.J.; Chen, J.D.Z. In vivo gastric and intestinal slow waves in W/Wv mice. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2005, 50, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Breijo, E.; Prats-Boluda, G.; Lidon-Roger, J.V.; Ye-Lin, Y.; Garcia-Casado, J. A comparative analysis of printing techniques by using an active concentric ring electrode for bioelectrical recording. Microelectron. Int. 2015, 32, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zena-Gimenez, V.; Garcia-Casado, J.; Prats-Boluda, G.; Ye-Lin, Y. Effects of Configuration and Dimension of Conecnetric Ring Electrodes in EEnG Recordin Applications. In Proceedings of the 10th International join Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2017), Porto, Portugal, 21–23 February 2017; Volume 1, pp. 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, F.Y.F. Electrogastrography: Basic knowledge, recording, processing and its clinical applications. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 20, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye-Lin, Y.; Alberola-Rubio, J.; Prats-Boluda, G.; Barrachina, J.M.B.; Perales, A.; Valero, J.; Desantes, D.; Garcia-Casado, J. Non-invasive electrohysterogram recording using flexible concentric ring electrode. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 4050–4053. [Google Scholar]
- Ye-Lin, Y.; Alberola-Rubio, J.; Prats-Boluda, G.; Perales, A.; Desantes, D.; Garcia-Casado, J. Feasibility and Analysis of Bipolar Concentric Recording of Electrohysterogram with Flexible Active Electrode. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 43, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye-Lin, Y.; Bueno-Barrachina, J.M.; Prats-boluda, G.; Rodriguez de Sanabria, R.; Garcia-Casado, J. Wireless sensor node for non-invasive high precision electrocardiographic signal acquisition based on a multi-ring electrode. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2017, 97, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats-Boluda, G.; Ye-Lin, Y.; Bueno Barrachina, J.M.; Senent, E.; Rodriguez de Sanabria, R.; Garcia-Casado, J. Development of a portable wireless system for bipolar concentric ECG recording. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 75102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huigen, E.; Peper, A.; Grimbergen, C.A. Investigation into the origin of the noise of surface electrodes. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2002, 40, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhagen, M.A.M.T.; Van Schelven, L.J.; Samsom, M.; Smout, A.J.P.M. Pitfalls in the analysis of electrogastrographic recordings. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberola-Rubio, J.; Prats-Boluda, G.; Ye-Lin, Y.; Valero, J.; Perales, A.; Garcia-Casado, J. Comparison of non-invasive electrohysterographic recording techniques for monitoring uterine dynamics. Med. Eng. Phys. 2013, 35, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besio, W.; Aakula, R.; Koka, K.; Dai, W. Development of a tri-polar concentric ring electrode for acquiring accurate Laplacian body surface potentials. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 34, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makeyev, O.; Ding, Q.; Besio, W.G. Improving the accuracy of Laplacian estimation with novel multipolar concentric ring electrodes. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2016, 80, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prats-Boluda, G.; Ye-Lin, Y.; Bueno-Barrachina, J.; Rodriguez de Sanabria, R.; Garcia-Casado, J. Towards the clinical use of concentric electrodes in ECG recordings: Influence of ring dimensions and electrode position. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2016, 27, 25705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, L.; Torres, A.; Garcia-Casado, J.; Prats-Boluda, G.; Ye-Lin, Y.; Jane, R. Evaluation of Laplacian diaphragm electromyographic recording in a dynamic inspiratory maneuver. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2014, 2014, 2201–2204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Estrada, L.; Torres, A.; Sarlabous, L.; Jané, R. Evaluation of sternocleidomastoid muscle activity by electromyography recorded with concentric ring electrodes. In Proceedings of the XXXIII Congreso Anual la Socieded Española Ingeniería Biomédica (CASEIB 2015), Madrid, Spain, 4–6 November 2015; pp. 183–186. [Google Scholar]






| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Solids Contents (%) | 81.14–83.14 |
| Vicosity (Pa.s) | 2.0–5.5 |
| Curing condition (°C) | 80 °C/10 min |
| Sheet resistivity (25 µm) | < 30 mΩ/sq |
| Y | Improvement Ratio (IRY) | Weight (WY) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | %DFTFSW | 0.25 |
| 2 | %DFSW | 0.125 |
| 3 | PRECG | 0.125 |
| 4 | PRSW/RESP | 0.0625 |
| 5 | PRSW/LF | 0.0625 |
| 6 | %RS | 0.0625 |
| 7 | %DFRESP | 0.0625 |
| 8 | %DFLF | 0.0625 |
| 9 | %DFOTHERS | 0.125 |
| 10 | MV | 0.0625 |
| MC-EEnG (n = 50) | BC-EEnG (n = 40) | BIP (n = 10) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foam | Adh | Foam | Adh | Foam | Adh | |
| %DFTFSW (%) | 56.0 ± 12.6 | 56.1 ± 9.5 | 54.1 ± 8.3 | 57.3 ± 12.7 | 53.4 ± 17.2 | 58.7 ± 11.5 |
| %DFRESP (%) | 19.7 ± 14.1 | 16.1 ± 9.2 | 14.6 ± 9.8 | 14.4 ± 11.2 | 23.9 ± 22.1 | 21.7 ± 9.5 |
| PRSW/RESP (dB) | 5.01 ± 1.82 | 4.74 ± 1.74 | 5.59 ± 1.76 | 5.19 ± 2.20 | 3.81 ± 2.03 | 4.07 ± 2.21 |
| %DFLF (%) | 16.6 ± 7.1 | 16.7 ± 7.6 | 24.6 ± 10.0 | 21.6 ± 9.3 | 12.5 ± 11.3 | 9.6 ± 3.8 |
| PRSW/LF (dB) | 3.78 ± 1.44 | 3.86 ± 0.92 | 2.86 ± 1.45 | 3.55 ± 1.25 | 4.25 ± 1.58 | 4.97 ± 1.47 |
| %DFOTHERS (%) | 7.9 ± 4.3 | 11.1 ± 5.5 | 6.7 ± 5.3 | 6.7 ± 3.9 | 10.2 ± 12.9 | 9.9 ± 8.2 |
| PRECG (dB) | 6.39 ± 3.89 | 6.13 ± 1.82 | 11.17 ± 4.32 | 19.77 ± 4.90 | 7.93 ± 4.91 | 6.57 ± 3.55 |
| %DFSW (%) | 92.1 ± 4.2 | 88.8 ± 5.5 | 93.2 ± 5.3 | 93.2 ± 3.9 | 87.0 ± 12.1 | 89.6 ± 8.5 |
| DFSW (cpm) | 9.97 ± 0.26 | 9.84 ± 0.35 | 9.99 ± 0.21 | 9.72 ± 0.49 | 9.49 ± 0.48 | 9.64 ± 0.20 |
| RS (%) | 58.9 ± 15.5 | 54.5 ± 21.7 | 58.8 ± 14.3 | 56.4 ± 22.8 | 60.9 ± 26.3 | 72.6 ± 28.8 |
| MV (cpm) | 0.38 ± 0.07 | 0.39 ± 0.10 | 0.41 ± 0.09 | 0.40 ± 0.11 | 0.38 ± 0.23 | 0.30 ± 0.26 |
| MC-EEnG (n = 50) | BC-EEnG (n = 40) | BIP (n = 10) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foam | Adh | Foam | Adh | Foam | Adh | |
| %DFTFSW (%) | 45.9 ± 21.0 | 57.8 ± 14.9 | 32.9 ± 11.4 | 57.0 ± 12.5 | 49.3 ± 10.7 | 50.1 ± 10.2 |
| %DFRESP (%) | 25.9 ± 23.0 | 19.6 ± 18.1 | 24.8 ± 18.4 | 12.3 ± 11.1 | 29.8 ± 14.3 | 25.6 ± 14.0 |
| PRSW/RESP (dB) | 4.23 ± 2.92 | 4.14 ± 2.13 | 2.58 ± 1.77 | 4.98 ± 2.18 | 3.83 ± 1.83 | 3.51 ± 1.94 |
| %DFLF (%) | 18.8 ± 12.4 | 8.8 ± 5.9 | 29.8 ± 16.3 | 15.9 ± 10.1 | 13.5 ± 8.1 | 14.1 ± 8.6 |
| PRSW/LF (dB) | 3.69 ± 1.90 | 5.15 ± 0.81 | 2.11 ± 1.55 | 4.16 ± 1.84 | 5.16 ± 1.26 | 4.63 ± 1.37 |
| %DFOTHERS(%) | 9.40 ± 8.6 | 13.8 ± 7.8 | 12.4 ± 8.4 | 14.8 ± 10.2 | 7.4 ± 4.4 | 10.2 ± 8.8 |
| PRECG(dB) | 7.82 ± 3.96 | 4.44 ± 2.94 | 11.83 ± 6.65 | 14.43 ± 6.17 | 6.13 ± 4.49 | 4.52 ± 2.03 |
| %DFSW(%) | 90.5 ± 8.6 | 86.1 ± 7.8 | 87.5 ± 8.4 | 85.1 ± 10.2 | 89.4 ± 4.3 | 88.5 ± 8.8 |
| DFSW(cpm) | 9.98 ± 0.32 | 10.29 ± 0.70 | 9.69 ± 0.51 | 9.69 ± 0.55 | 10.04 ± 0.26 | 9.59 ± 0.28 |
| RS (%) | 52.8 ± 29.2 | 80.1 ± 20.1 | 40.3 ± 30.0 | 54.5 ± 30.4 | 56.1 ± 10.7 | 47.5 ± 23.6 |
| MV (cpm) | 0.35 ± 0.16 | 0.34 ± 0.21 | 0.46 ± 0.11 | 0.44 ± 0.15 | 0.49 ± 0.11 | 0.37 ± 0.08 |
| Below Navel | Above Navel | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foam | Adhesive | Foam | Adhesive | |||||
| BC | MC | BC | MC | BC | MC | BC | MC | |
| BCFoBN | MCFoBN | BCAdBN | MCAdBN | BCFoAN | MCFoAN | BCAdAN | MCAdAN | |
| %DFTFSW | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.96 | 1.00 |
| %DFRESP | 0.83 | 0.46 | 0.84 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.86 |
| PRSW/RESP | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.72 | 0.00 | 0.54 | 0.79 | 0.52 |
| %DFLF | 0.24 | 0.62 | 0.39 | 0.62 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 0.66 | 1.00 |
| PRSW/LF | 0.24 | 0.54 | 0.47 | 0.57 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 1.00 |
| %DFOTHERS | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.99 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.66 | 0.00 | 0.11 |
| PRECG | 0.44 | 0.12 | 1.00 | 0.11 | 0.48 | 0.22 | 0.65 | 0.00 |
| %DFSW | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.99 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.66 | 0.00 | 0.11 |
| RS | 0.55 | 0.59 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.00 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 1.00 |
| MV (cpm) | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.11 | 1.00 |
| IRGlobal | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.69 | 0.51 | 0.10 | 0.39 | 0.54 | 0.60 |
 | ||||||||
| Best (1) Poor (0) | ||||||||
| BC1-EEnG | BC2-EEnG | BC3-EEnG | BC4-EEnG | BIP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %DFTFSW | 0.84 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.21 | 0.68 |
| %DFRESP | 1.00 | 0.83 | 0.35 | 0.00 | 0.05 |
| PRRESP | 1.00 | 0.91 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.00 |
| %DFLF | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 0.59 | 1.00 |
| PRLF | 0.00 | 0.31 | 0.42 | 0.53 | 1.00 |
| %DFOTHERS | 0.51 | 1.00 | 0.45 | 0.59 | 0.00 |
| PRECG | 0.67 | 0.91 | 0.47 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| %DFSW | 0.53 | 1.00 | 0.49 | 0.62 | 0.00 |
| %RS | 0.14 | 0.38 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.00 |
| MV | 0.40 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| IRGlobal | 0.58 | 0.80 | 0.34 | 0.46 | 0.36 |
 | |||||
| Best (1) Poor (0) | |||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zena-Giménez, V.; Garcia-Casado, J.; Ye-Lin, Y.; Garcia-Breijo, E.; Prats-Boluda, G. A Flexible Multiring Concentric Electrode for Non-Invasive Identification of Intestinal Slow Waves. Sensors 2018, 18, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020396
Zena-Giménez V, Garcia-Casado J, Ye-Lin Y, Garcia-Breijo E, Prats-Boluda G. A Flexible Multiring Concentric Electrode for Non-Invasive Identification of Intestinal Slow Waves. Sensors. 2018; 18(2):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020396
Chicago/Turabian StyleZena-Giménez, Victor, Javier Garcia-Casado, Yiyao Ye-Lin, Eduardo Garcia-Breijo, and Gema Prats-Boluda. 2018. "A Flexible Multiring Concentric Electrode for Non-Invasive Identification of Intestinal Slow Waves" Sensors 18, no. 2: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020396
APA StyleZena-Giménez, V., Garcia-Casado, J., Ye-Lin, Y., Garcia-Breijo, E., & Prats-Boluda, G. (2018). A Flexible Multiring Concentric Electrode for Non-Invasive Identification of Intestinal Slow Waves. Sensors, 18(2), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020396







