Adaptive ISAR Imaging of Maneuvering Targets Based on a Modified Fourier Transform
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Imaging Model of the Maneuvering Target
3. Adaptive Imaging Method Based on a Modified Fourier Transform
3.1. Compensation of Quadratic Phase Terms
- (1)
- For all scatterers on the target, the relative chirp rate is identical.
- (2)
- For scatterers located in the same Doppler cell, their compensation components for the quadratic phase terms are approximately identical.
- (3)
- The values of represent the discrete azimuth positions of scatterers, and they are related to different Doppler cells in ISAR image.
3.2. Doppler Focus Shift
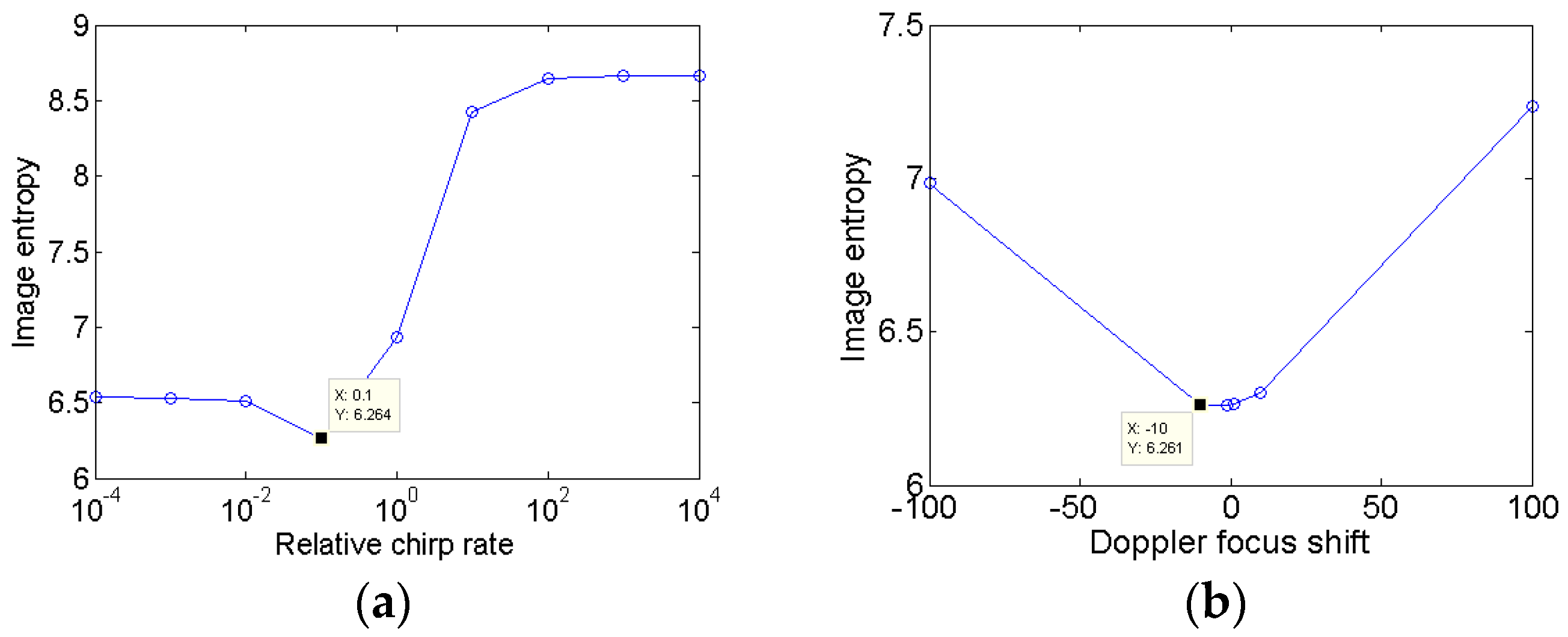
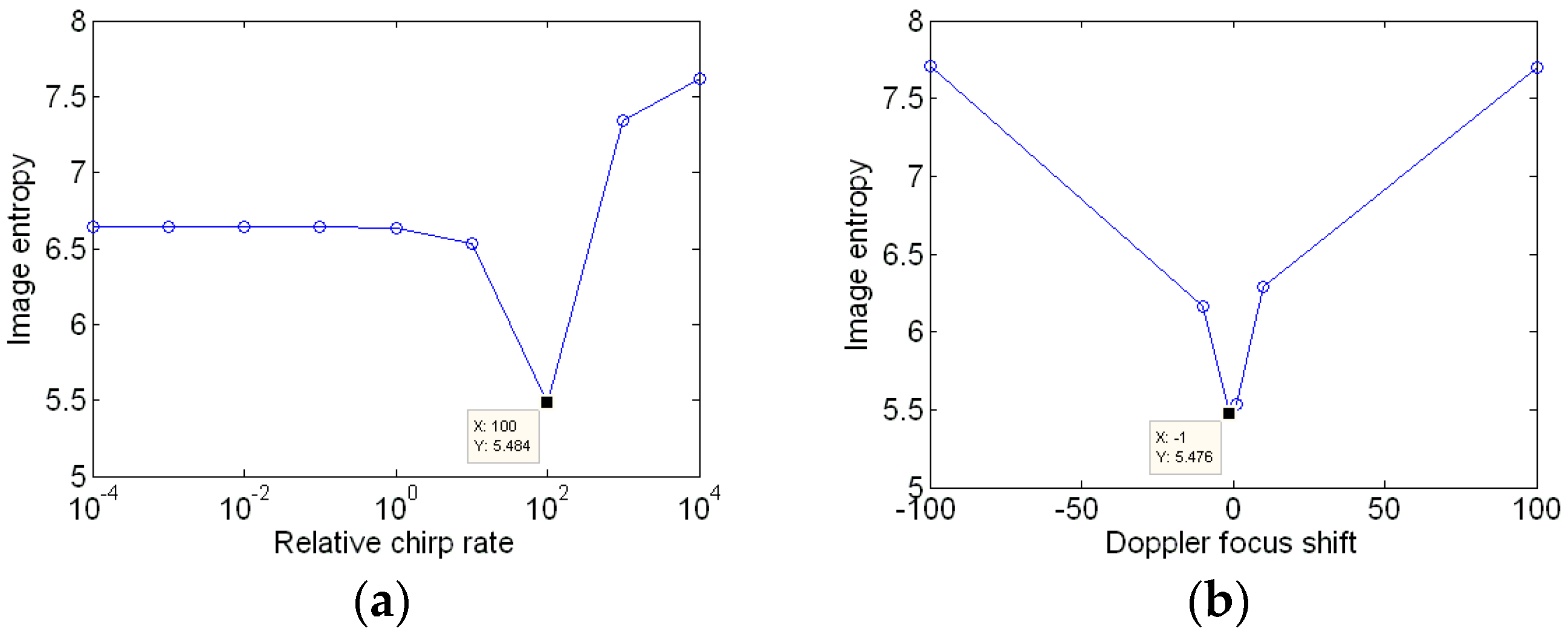
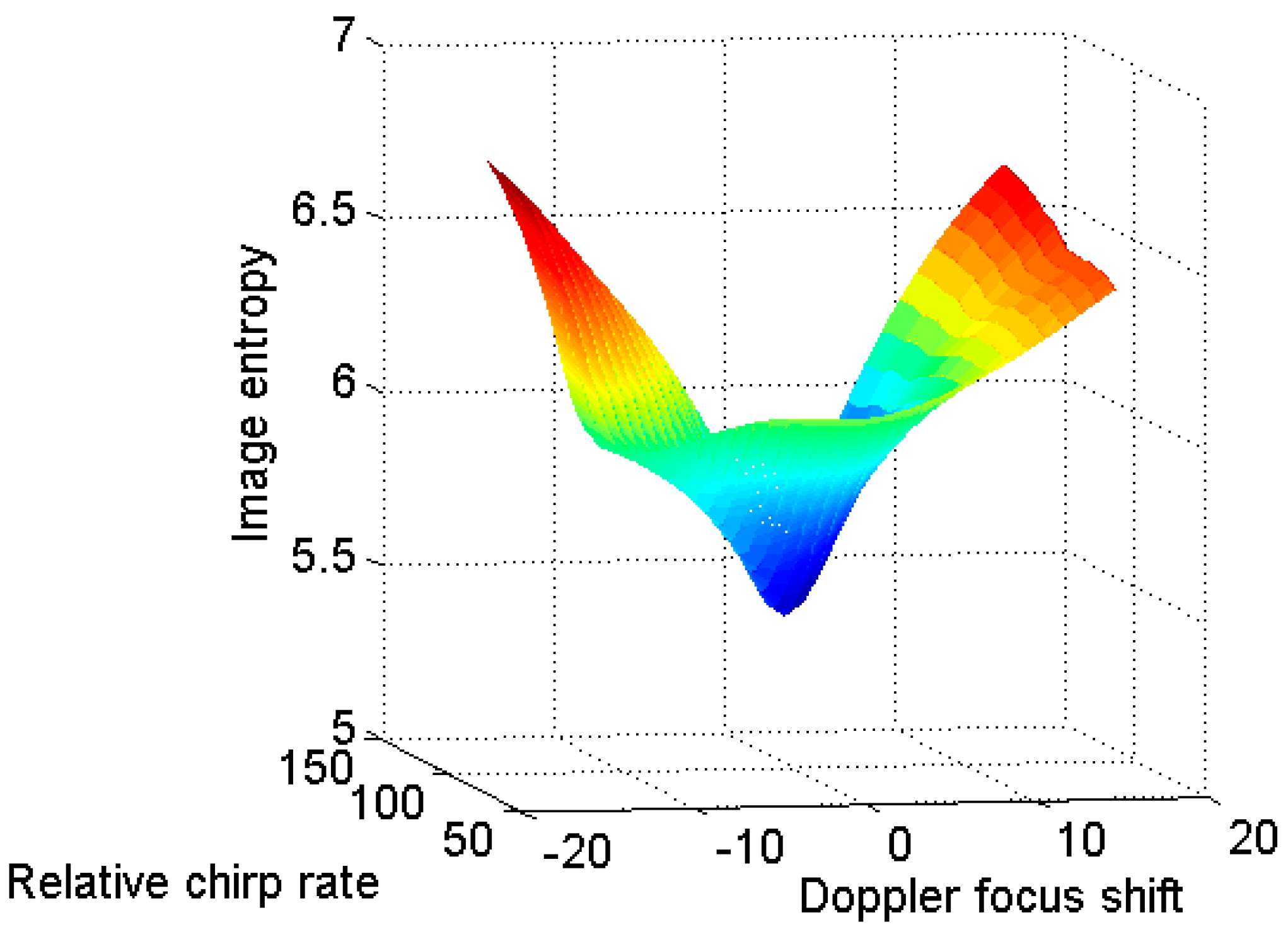
3.3. Parameter Search by the Two-Dimensional Gradient Descent Optimization Scheme
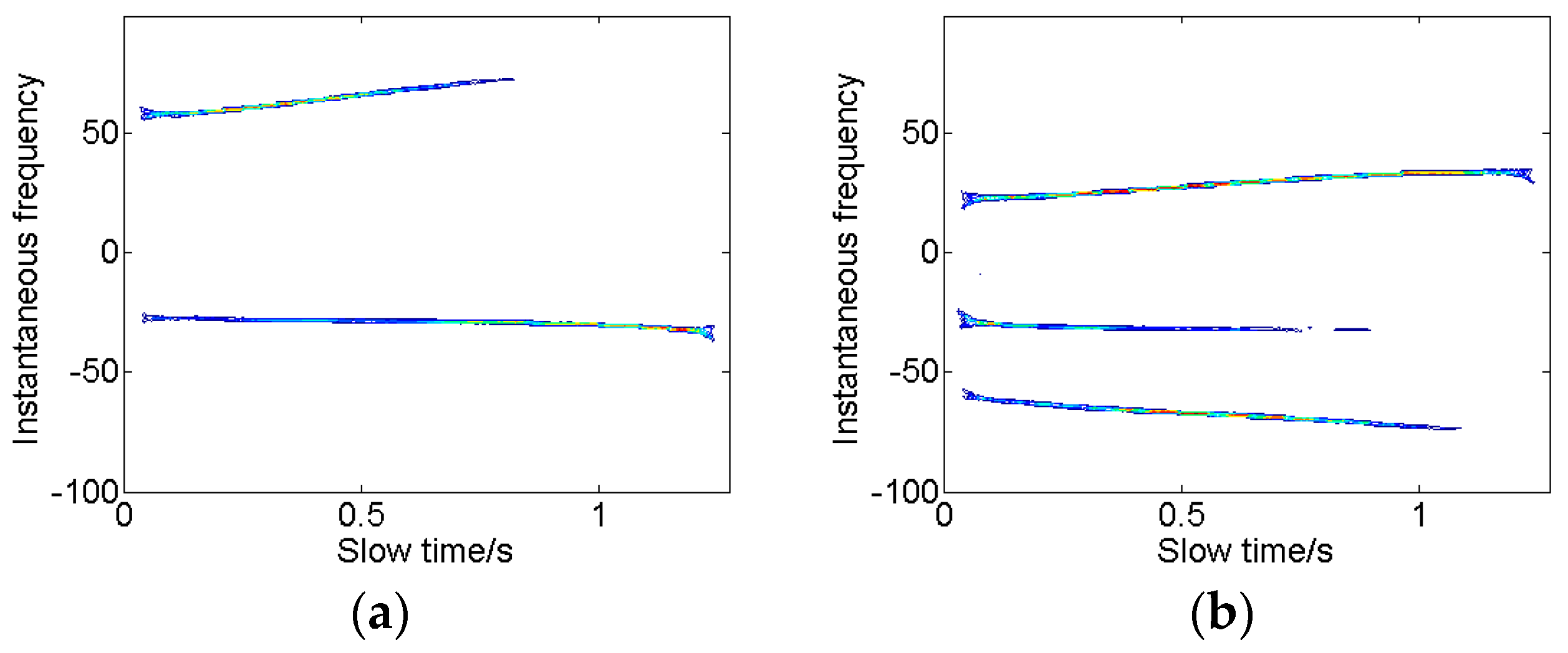
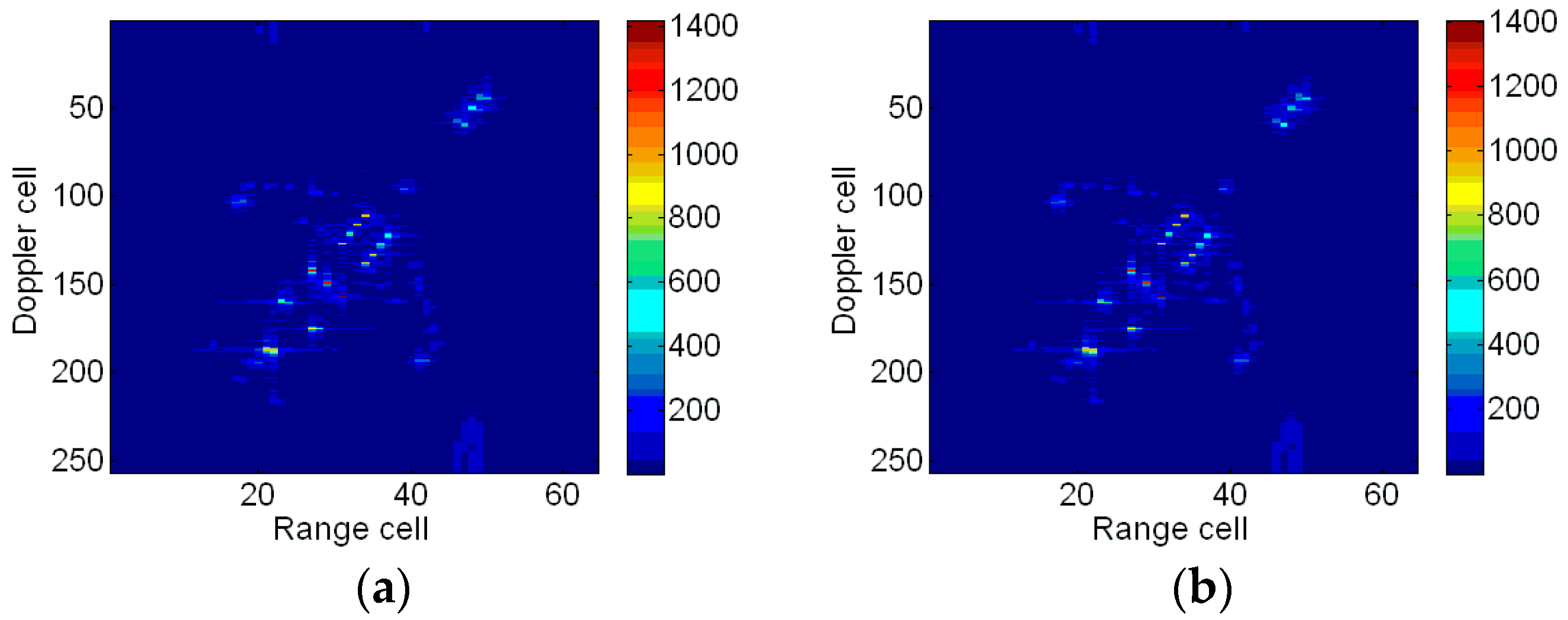
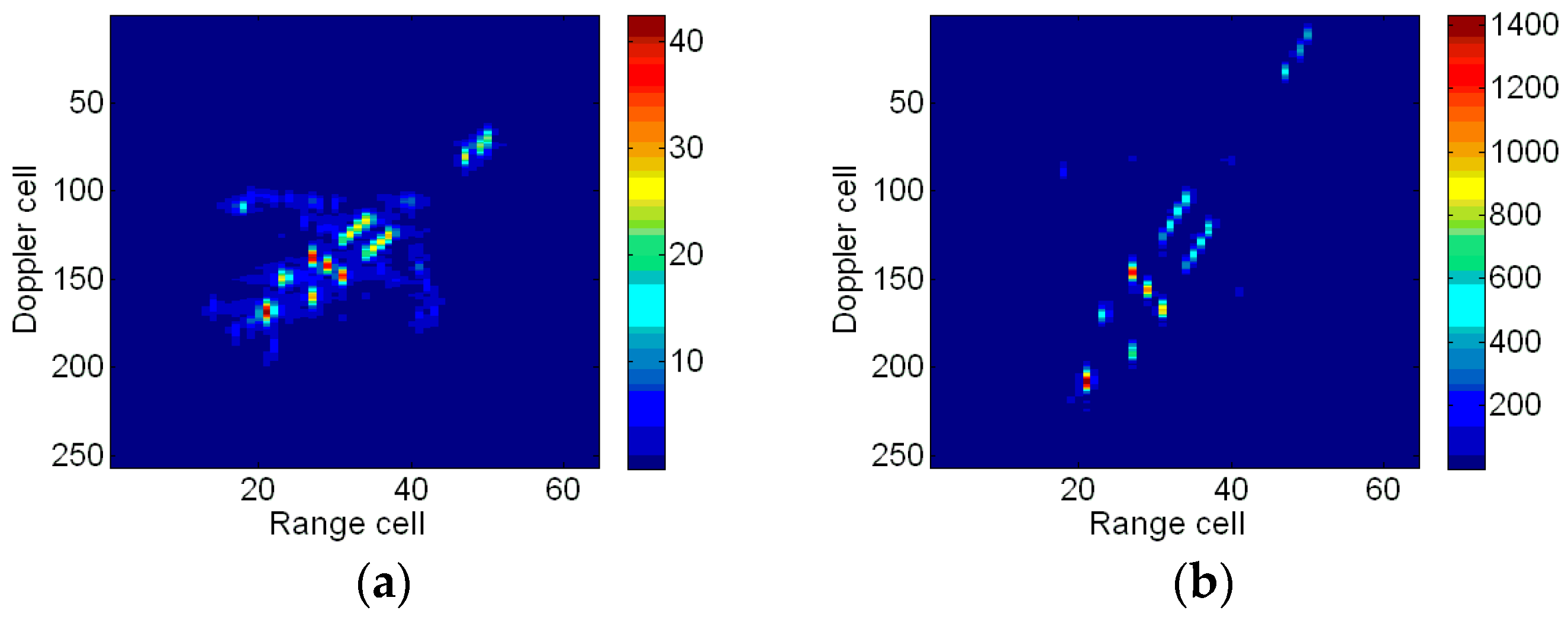
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Results of a Simulated Airplane
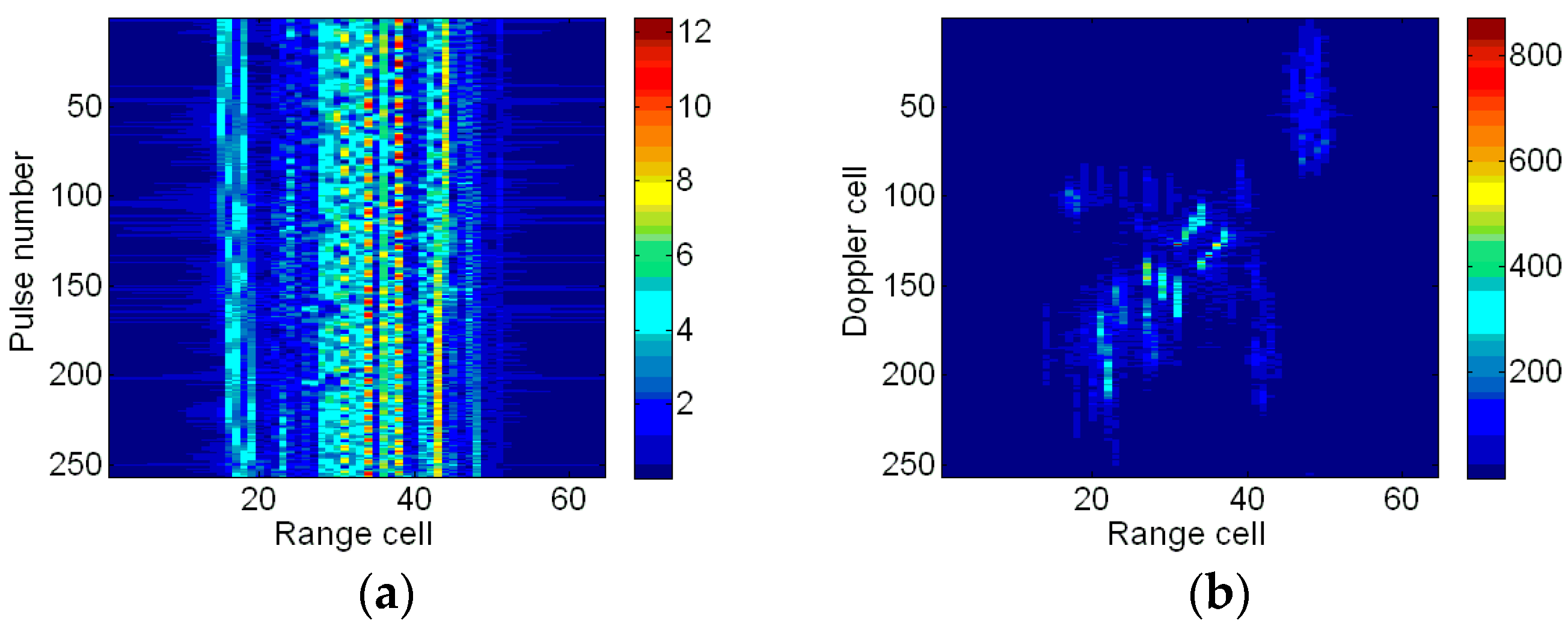
4.2. Results of the Boeing B727
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, V.C.; Qian, S. Joint time–frequency transform for radar range Doppler imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1998, 34, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kasilingam, D. Global range alignment for ISAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Sueda, H.; Watanabe, Y. Motion compensation for ISAR via centroid tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1996, 32, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Zou, J.W.; Xu, S.Y.; Chen, Z.P. Squint model interferometric ISAR imaging based on respective reference range selection and squint iteration improvement. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2015, 9, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.B.; Liu, H.W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q.H. ISAR imaging of ship targets based on an integrated cubic phase bilinear autocorrelation function. Sensors 2017, 17, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.J.; Xu, S.Y.; Wu, W.Z.; Tian, B.; Chen, Z.P. IAA-based high-resolution ISAR imaging with small rotational angle. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1978–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Z.; Hu, P.J.; Xu, S.Y.; Chen, Z.P.; Chen, J. Image registration for InISAR based on joint translational motion compensation. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarov, A.; Minchev, C. ISAR geometry, signal model, and image processing algorithms. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.C.; Martorella, M. Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging: Principles, Algorithms and Applications; SciTech: Edison, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Sheng, J.L.; Duan, J.; Xing, M.D.; Qiao, Z.J.; Bao, Z. Translational motion compensation for ISAR imaging under low SNR by minimum entropy. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2013, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, W.; Thayaparan, T. Focusing inverse synthetic aperture radar images with high-order motion error using the adaptive joint-time frequency algorithm optimized with the genetic algorithm and the particle swarm optimization algorithm C comparison and results. IET Signal Process. 2010, 4, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorella, M.; Berizzi, F.; Haywood, B. Contrast maximization based technique for 2-D ISAR autofocusing. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2005, 4, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, D.E. Phase gradient autofocus robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Liu, X.Z. Improved global range alignment for ISAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhan, M.Y.; Liu, H.Q.; Liao, G.S.; Liao, Y. A robust translational motion compensation method for ISAR imaging based on keystone transform and fractional Fourier transform under low SNR environment. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 2140–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Andrews, H.C. Target-motion-induced radar imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1980, 16, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Bao, Z.; Sun, X.B. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of non-uniformly rotating targets. Opt. Eng. 1996, 35, 3007–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, B. ISAR imaging of maneuvering target based on the quadratic frequency modulated signal model with time-varying amplitude. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayaparan, T.; Brinkman, W.; Lampropoulos, G. Inverse synthetic aperture radar image focusing using fast adaptive joint time–frequency and three-dimensional motion detection on experimental radar data. IET Signal Process. 2010, 4, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Sun, C.; Xing, M.D. Time-frequency approaches to ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets and their limitations. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2001, 48, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, V.C.; Miceli, W.J. Time-varying spectral analysis for radar imaging of maneuvering targets. IET Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 1998, 145, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.D.; Wu, R.B.; Li, Y.C.; Bao, Z. New ISAR imaging algorithm based on modified Wigner Ville distribution, IET Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2009, 3, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berizzi, F.; Mese, E.D.; Diani, M.; Martorella, M. High-resolution ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets by means of the range instantaneous Doppler technique: Modeling and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auger, F.; Flandrin, P. Improving the readability of time-frequency and time-scaled representations by the reassignment method. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1995, 43, 1068–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Wu, Y.; Jia, X.; Ye, W. Novel ISAR imaging algorithm for maneuvering targets based on a modified keystone transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Su, T.; Zheng, J.B.; He, X.H. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of targets with nonsevere maneuverability based on the centroid frequency chirp rate distribution. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.C.; Wang, X.S.; Wang, G.Y. Scaled Radon-Wigner transform imaging and scaling of maneuvering target. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 2043–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Deng, B.; Wang, Y. Research progress of the fractional Fourier transform in signal processing. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2006, 49, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.W.; Tian, B.; Chen, Z.P. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging compensation method based on coherent processing of intermediate frequency direct sampling data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.H.; Alice, H.W.C.; Yeo, S.Y. Fast minimum entropy phase compensation for ISAR imaging. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2004, 26, 1656–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.L.; Bi, G.A.; Wan, C.R. Lv’s distribution: Principle, implementation, properties, and performance. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 35, 1240–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z. Minimum-entropy phase adjustment for ISAR. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2004, 151, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarov, A. ISAR Signal Formation and Image Reconstruction as Complex Spatial Transforms; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 27–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.Y.; Xu, C.X.; Zhu, D.T. Optimization Method; High Education Publisher: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 112–139. [Google Scholar]
- Jorge, N.; Wright, S. Numerical Optimization; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 30–62. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Liu, H.Q.; Gui, X.G.; Zhang, X.Z. An efficient ISAR imaging method for maneuvering target based on synchrosqueezing transform. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Setting Value | Parameter | Setting Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 10 GHz | Bandwidth | 500 MHz |
| Pulse width | 50 µs | Complex sampling rate | 500 MHz |
| Pulse repeat frequency | 200 Hz | Pulse number | 256 |
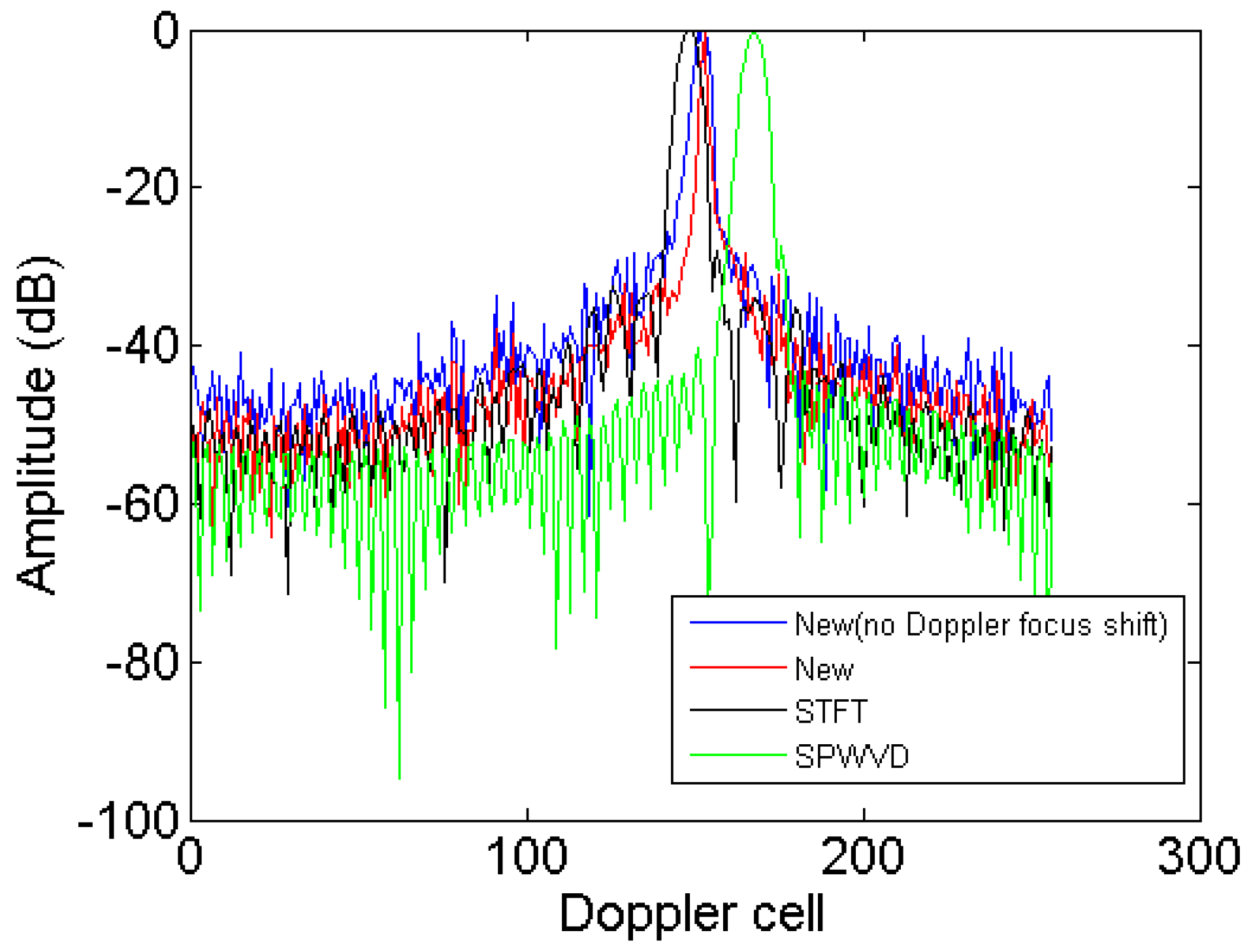
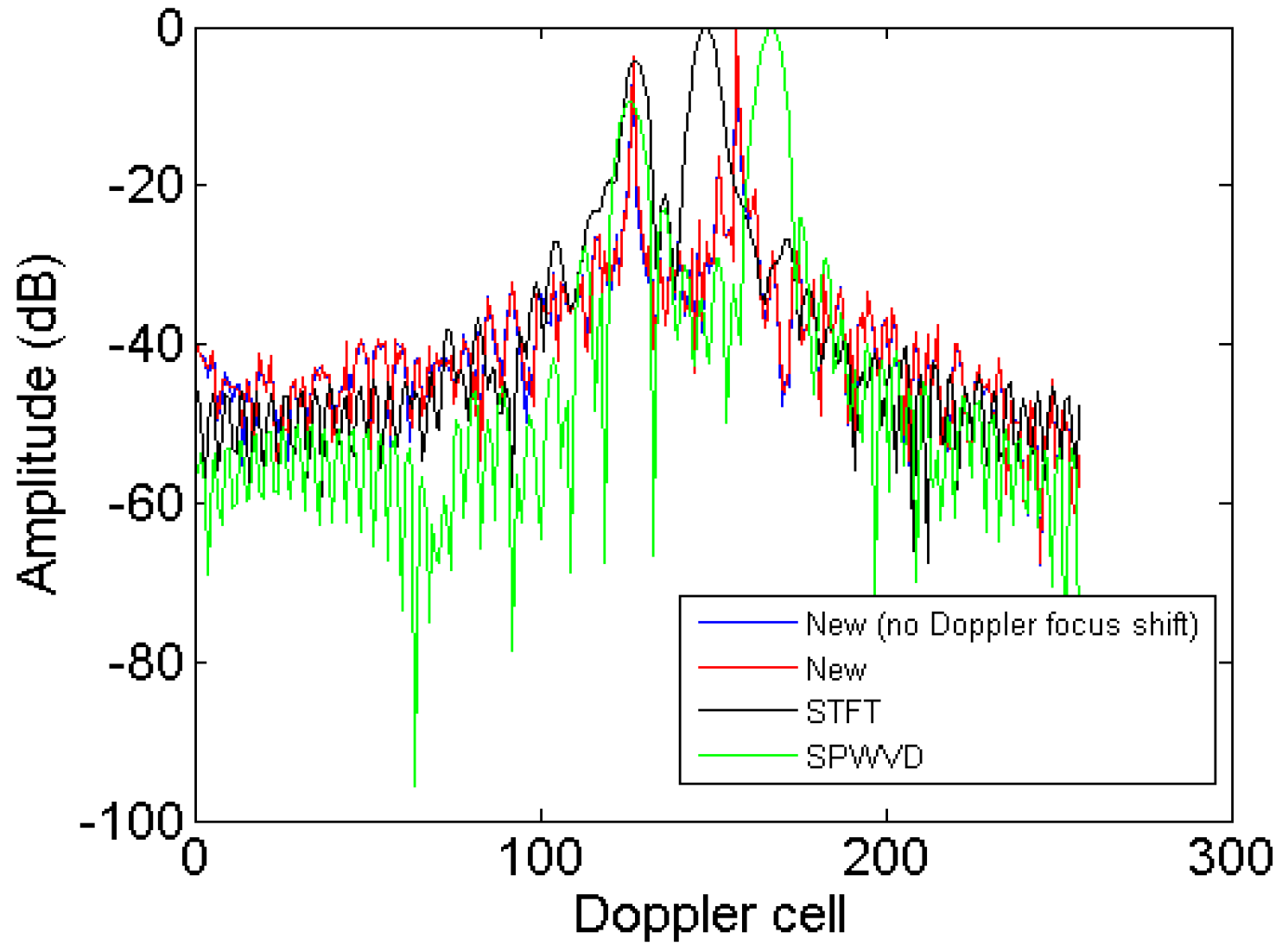
| Method | Figure | Entropy | Contrast |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD | Figure 3b | 6.75 | 4.09 |
| New (no Doppler focus shift) | Figure 6b | 6.11 | 4.59 |
| New | Figure 7b | 5.84 | 4.80 |
| STFT | Figure 8a | 6.70 | 4.55 |
| SPWVD | Figure 8b | 6.38 | 5.85 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Xu, S.; Wu, W.; Hu, P.; Chen, Z. Adaptive ISAR Imaging of Maneuvering Targets Based on a Modified Fourier Transform. Sensors 2018, 18, 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051370
Wang B, Xu S, Wu W, Hu P, Chen Z. Adaptive ISAR Imaging of Maneuvering Targets Based on a Modified Fourier Transform. Sensors. 2018; 18(5):1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051370
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Binbin, Shiyou Xu, Wenzhen Wu, Pengjiang Hu, and Zengping Chen. 2018. "Adaptive ISAR Imaging of Maneuvering Targets Based on a Modified Fourier Transform" Sensors 18, no. 5: 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051370
APA StyleWang, B., Xu, S., Wu, W., Hu, P., & Chen, Z. (2018). Adaptive ISAR Imaging of Maneuvering Targets Based on a Modified Fourier Transform. Sensors, 18(5), 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051370





