A Flexible Interdigital Electrode Used in Skin Penetration Promotion and Evaluation with Electroporation and Reverse Iontophoresis Synergistically
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
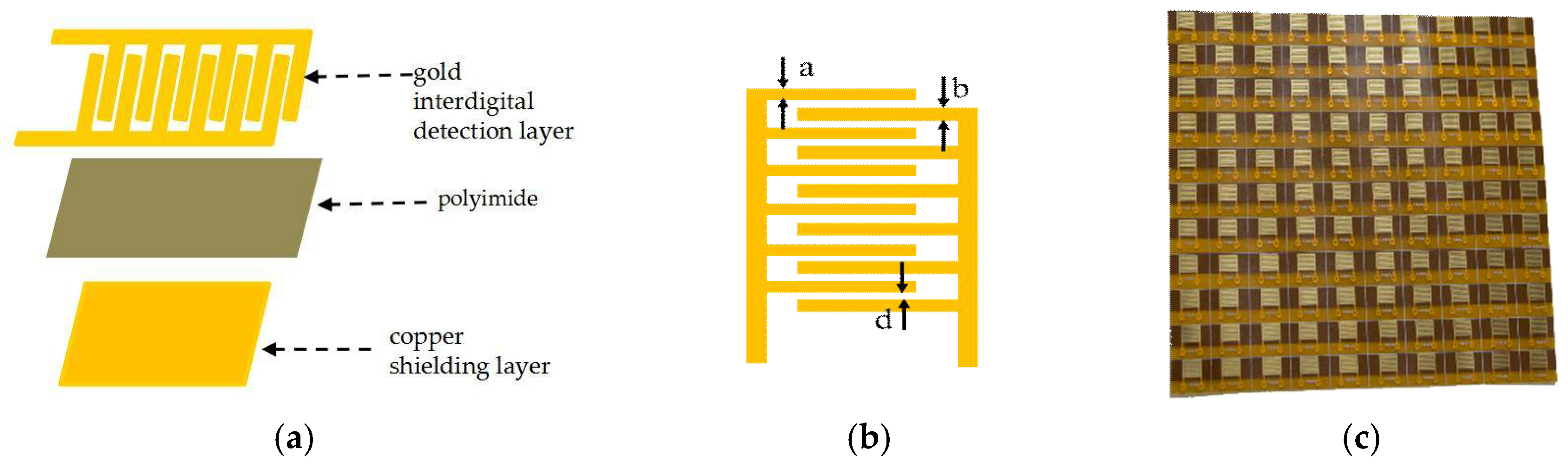
2.1. Fabrication of Flexible Gold Interdigital Microelectrode
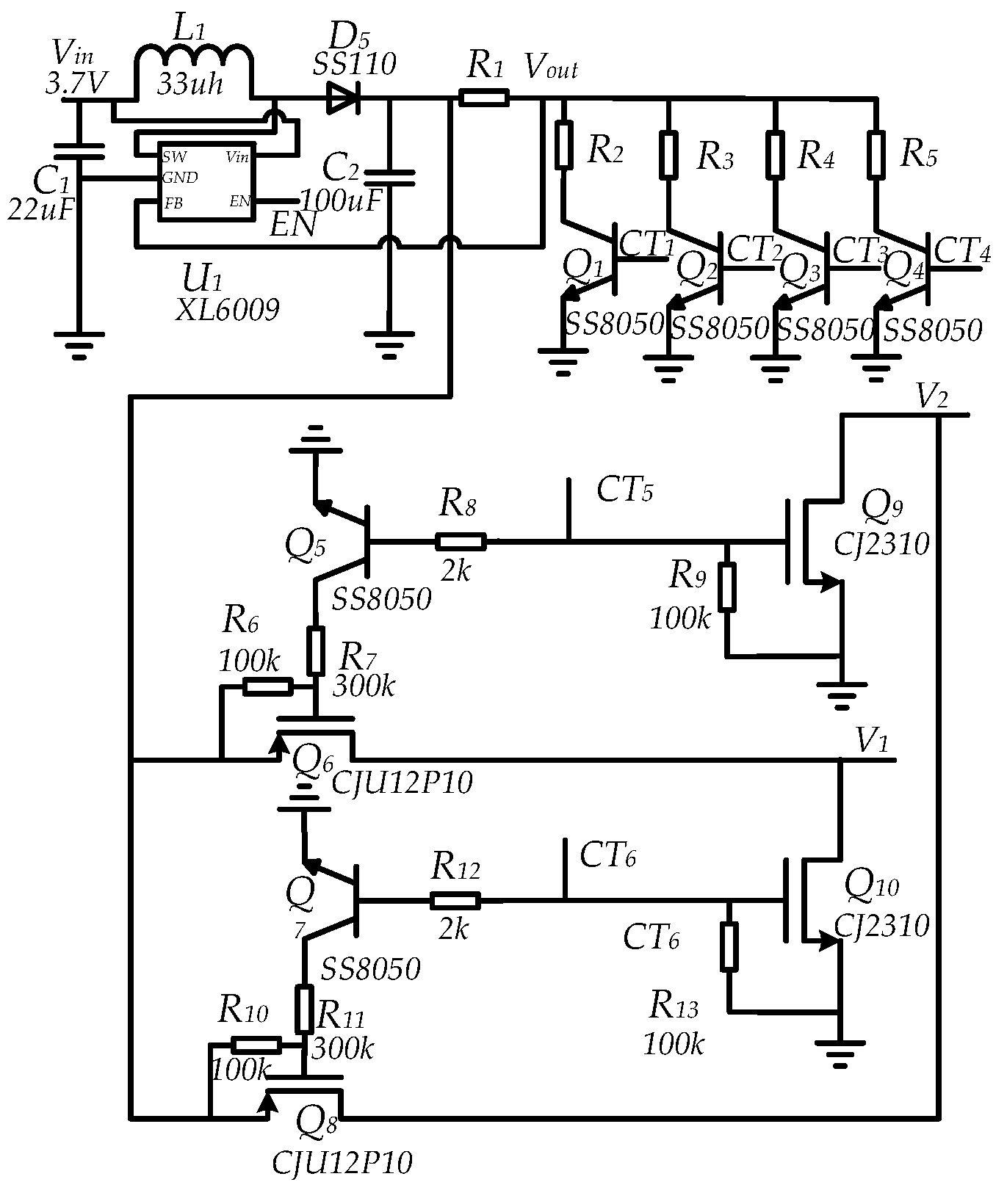
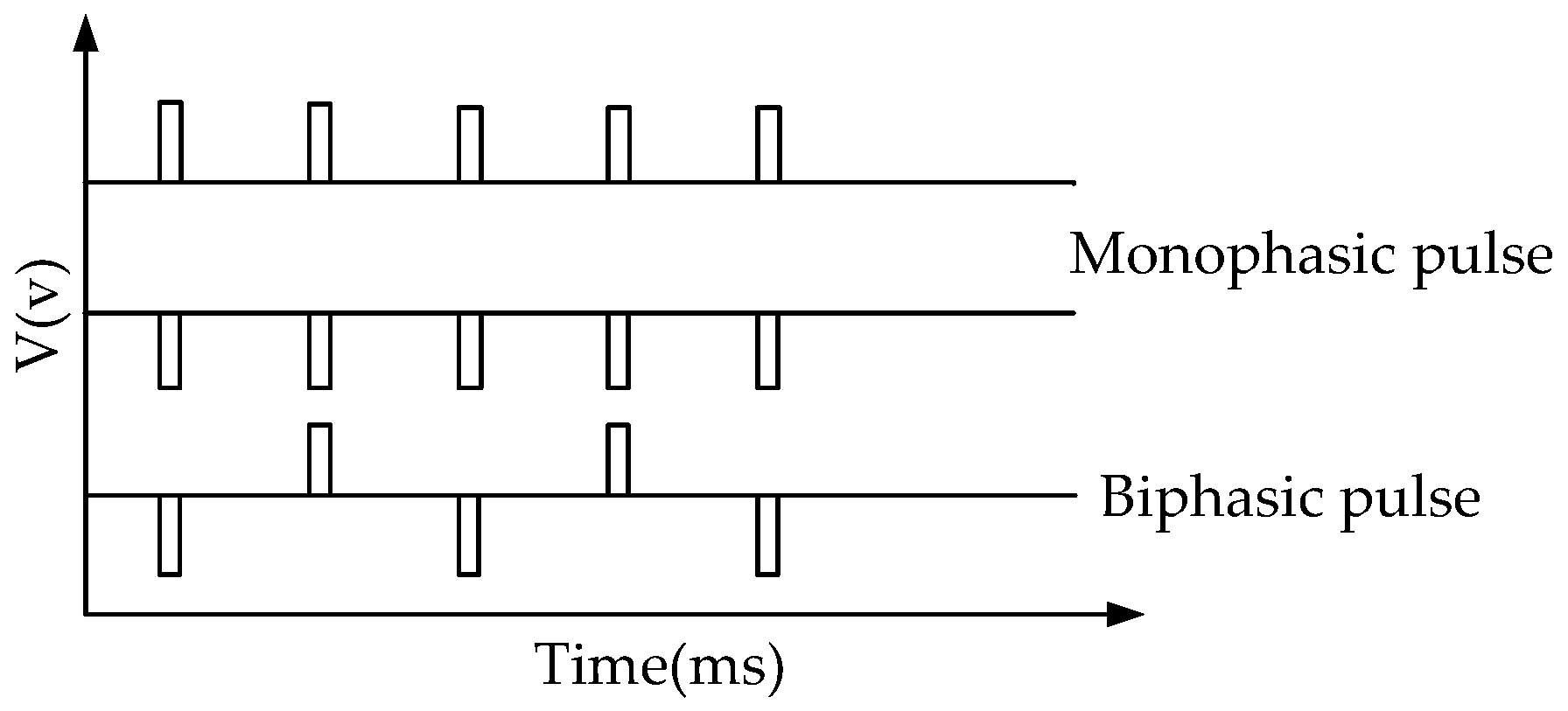
2.2. Circuit Design of the Electroporation
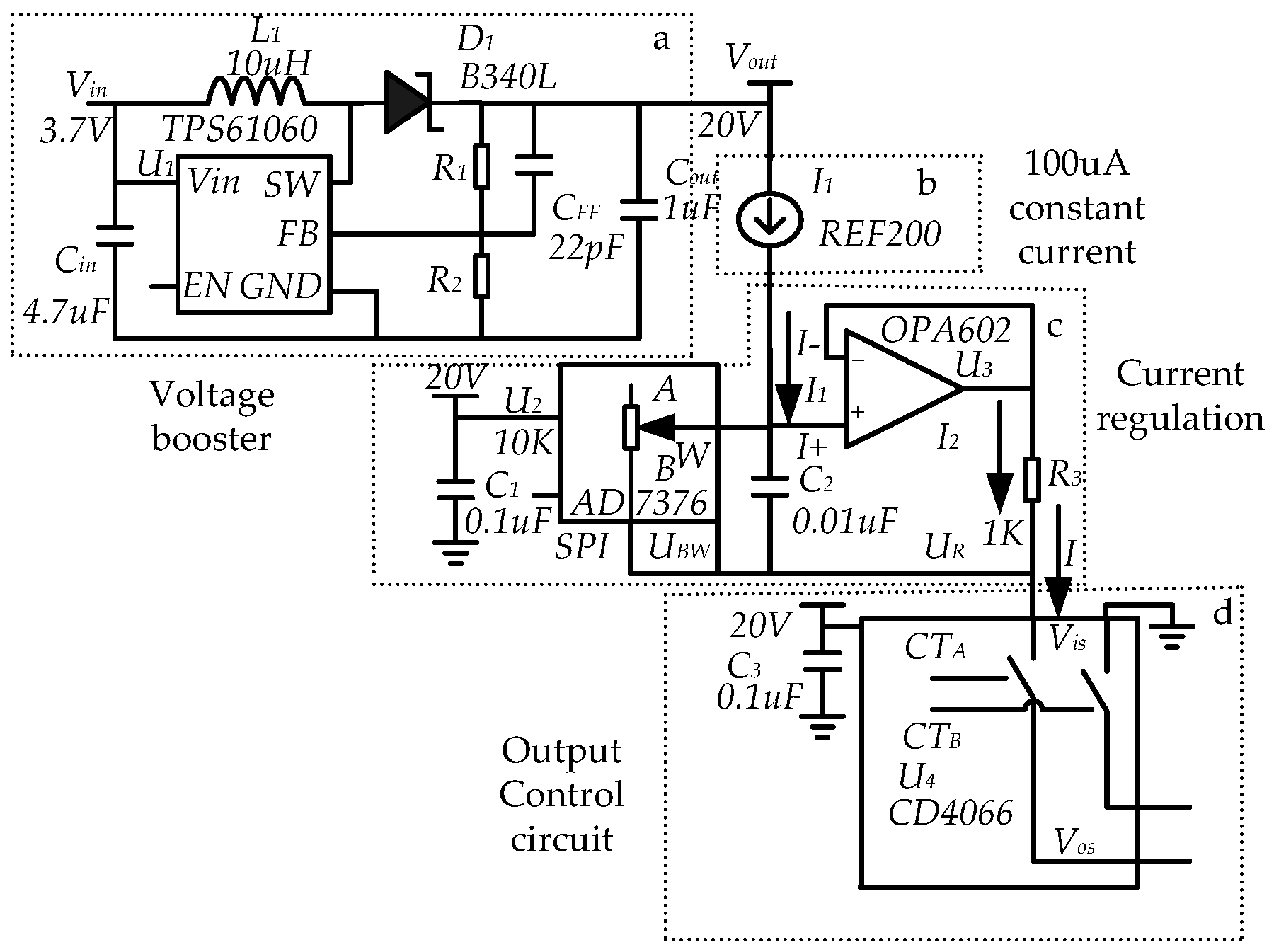
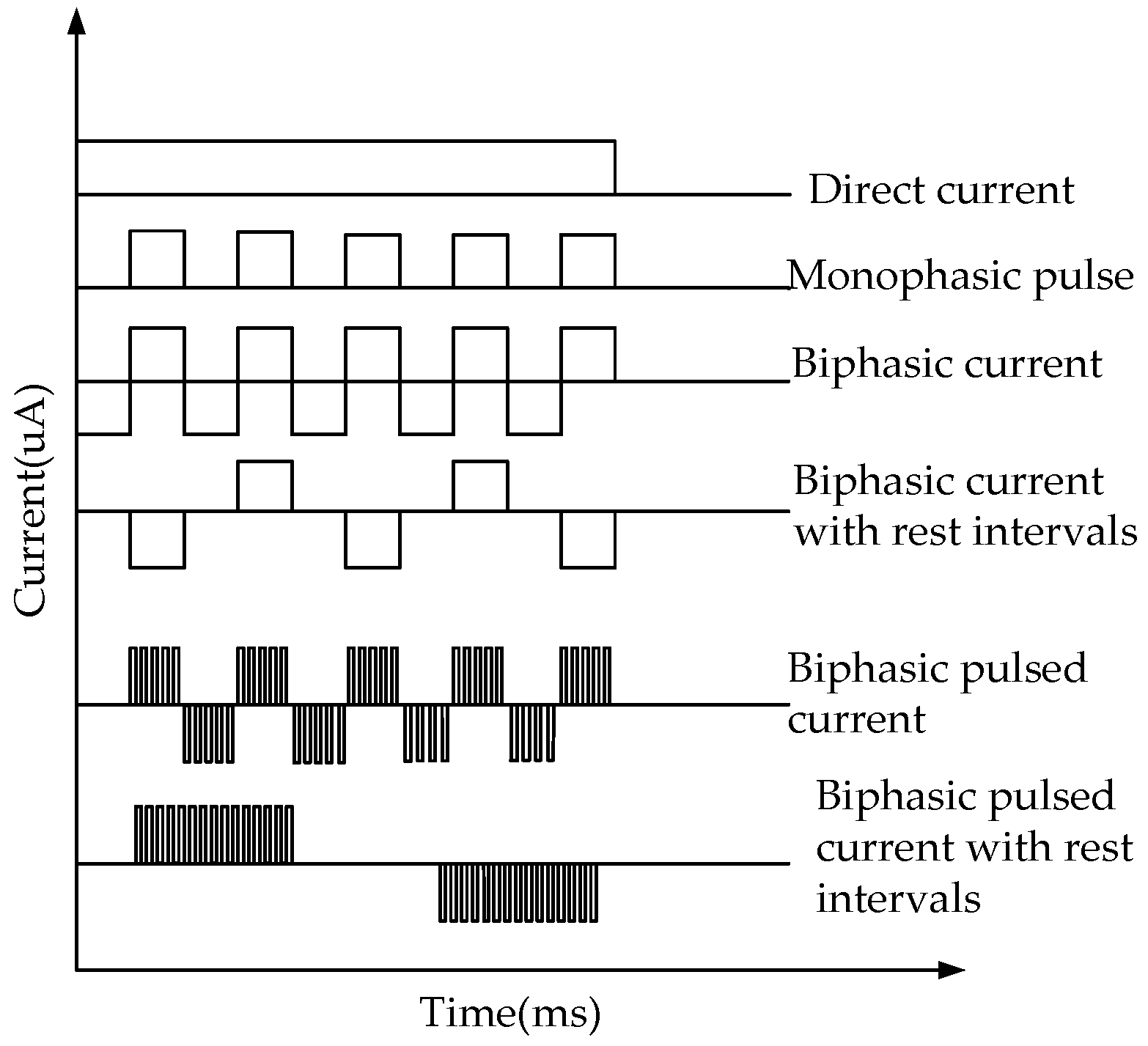
2.3. Circuit Design of the Reverse Iontophoresis
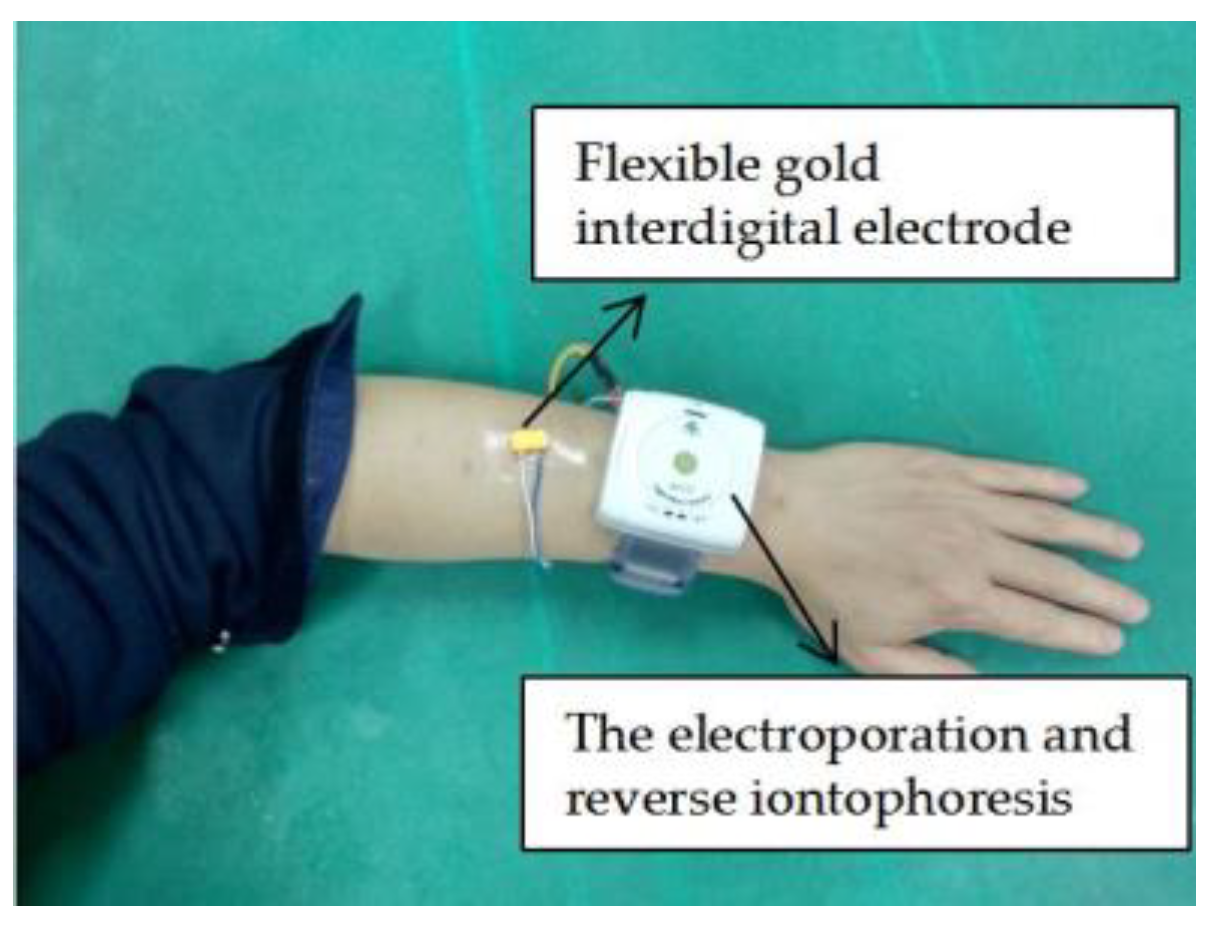
2.4. Experiments on Skin Penetration In Vivo
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of the Circuit of Electroporation and Reverse Iontophoresis
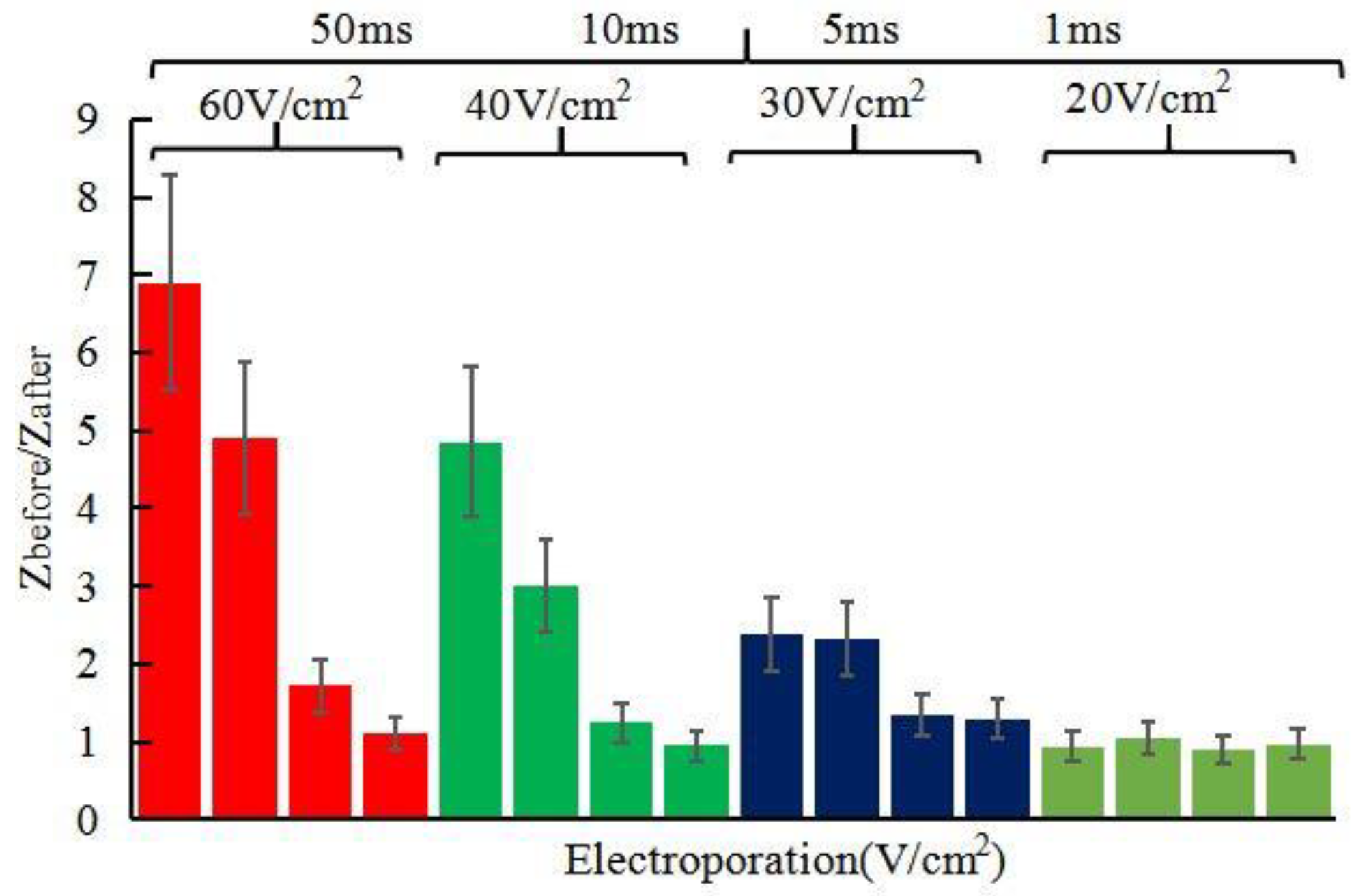
3.2. Evaluation of Electroporation and Reverse Iontophoresis for Promoting Penetration of Skin by Measuring Skin Impedance In Vivo
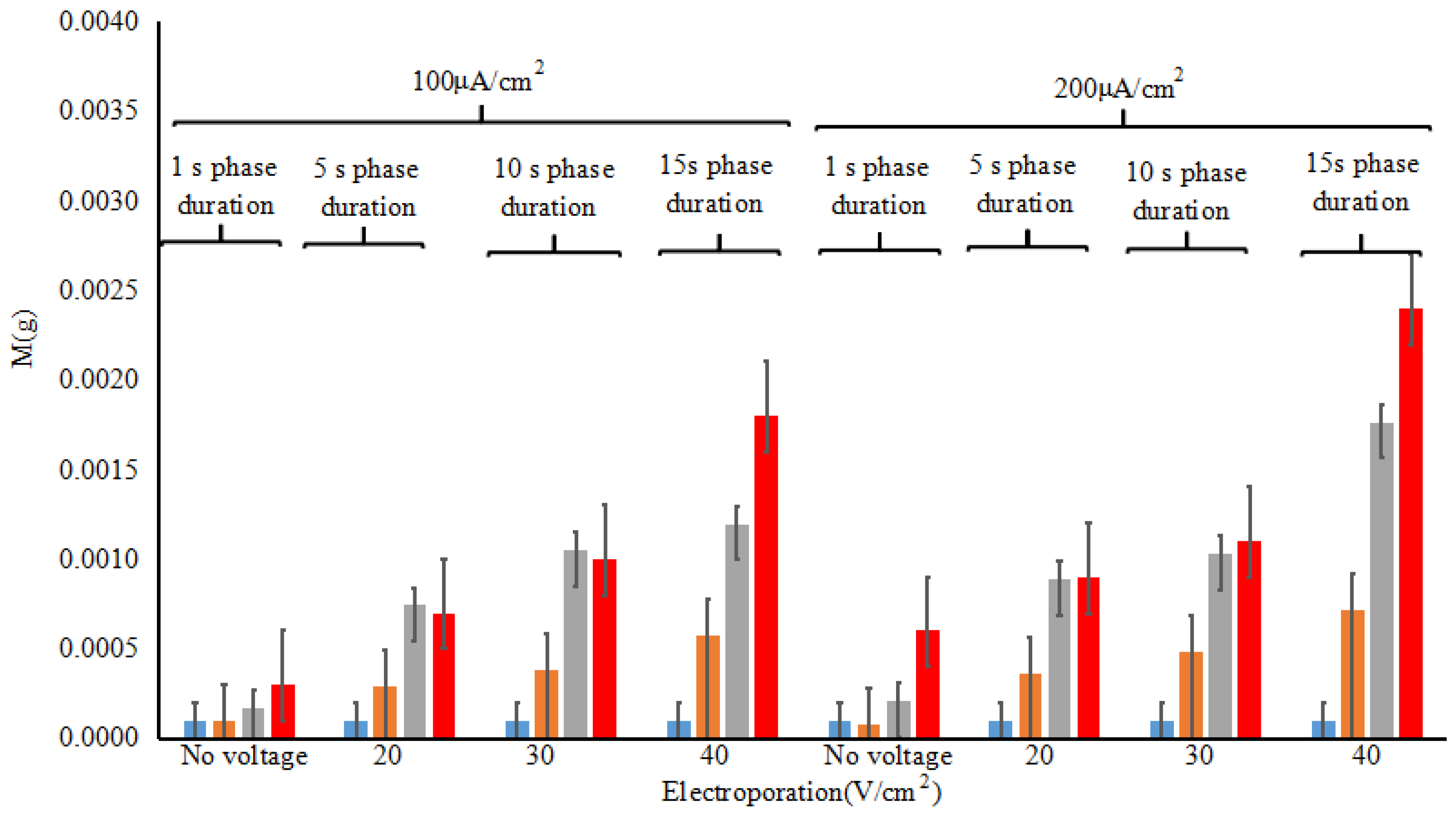
3.3. In Vivo Evaluation of Electroporation and Reverse Iontophoresis Synergistically for ISF Extraction by Weight
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kovatchev, B.P. Diabetes Technology: Markers, Monitoring, Assessment, and Control of Blood Glucose Fluctuations in Diabetes. Scientifica 2012, 2012, 283821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortensius, J.; Bijl, J.J.V.D.; Kleefstra, N.; Houweling, S.T.; Bilo, H.J.G. Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose. Diabetes Educ. 2011, 38, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Organization for Standardization. In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems—Requirements for Blood-Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/54976.html (accessed on 4 May 2018).
- Garg, S.K.; Potts, R.O.; Ackerman, N.R.; Fermi, S.J.; Tamada, J.A.; Chase, H.P. Correlation of fingerstick blood glucose measurements with GlucoWatch biographer glucose results in young subjects with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1708–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitzer, K.R.; Desai, S.; Dunn, T.; Edelman, S.; Jayalakshmi, Y.; Kennedy, J.; Tamada, J.A.; Potts, R.O. Detection of hypoglycemia with the GlucoWatch biographer. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ce, F.D.A.; Wolf, B. Current development in non-invasive glucose monitoring. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Mintchev, M.P. Development of Wearable Semi-invasive Blood Sampling Devices for Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Survey. Engineering 2013, 5, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovatchev, B.P.; Shields, D.; Breton, M. Graphical and Numerical Evaluation of Continuous Glucose Sensing Time Lag. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2009, 11, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, T.K.; Chakrabarty, S.; Ghosh, B. Transdermal reverse iontophoresis: A novel technique for therapeutic drug monitoring. J. Control. Release 2016, 246, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, J.; Powell, K.; Tlanger, R. Control of Transport of Molecules across Tissue Using Electroporation. U.S. Patent 5,019,034, 18 May 1991. [Google Scholar]
- White, E.A.; Horne, A.; Runciman, J.; Orazem, M.E.; Navidi, W.C.; Roper, C.S.; Bunge, A.L. On the correlation between single-frequency impedance measurements and human skin permeability to water. Toxicol. Vitro 2011, 25, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwingenschuh, S.; Scharfetter, H.; Martinsen, Ø.G.; Boulgaropoulos, B.; Augustin, T.; Tiffner, K.I.; Dragatin, C.; Raml, R.; Hoefferer, C.; Prandl, E.C.; et al. Assessment of skin penetration to topically applied drugs by skin impedance and admittance. Physiol. Meas. 2017, 38, N138–N150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, R.; Yu, H.; Li, G.; Sun, Y.; Liang, W.; Xu, K. A Method for Measuring the Volume of Transdermally Extracted Interstitial Fluid by a Three-Electrode Skin Resistance Sensor. Sensors 2014, 14, 7084–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, A.; Kim, J.Y.; Jo, S.; Jee, J.H.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Bhagat, Y.A.; Kim, I.; Cho, J. Smartphone-Based Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Devices for Daily Obesity Management. Sensors 2015, 15, 22151–22166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Pu, Z.; Liang, W.; Liu, T.; Wang, R.; Yu, H.; Xu, K. Non-invasive measurement of normal skin impedance for determining the volume of the transdermally extracted interstitial fluid. Measurement 2015, 62, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanic, R.; Novotny, I.; Rehacek, V.; Tvarozek, V.; Weis, M. Thin film non-symmetric microelectrode array for impedance monitoring of human skin. Thin Solid Films 2003, 433, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamishev, A.V.; Sundararajan, K.; Yang, F.; Du, Y.; Zahn, M. Interdigital sensors and transducers. Proc. IEEE 2016, 92, 808–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Yamamoto, Y. Electrical properties of the epidermal stratum corneum. Med. Biol. Eng. 1976, 14, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Lu, F.; Wang, C.; Zhao, R.; Du, L.; Fang, Z. Evaluation of Skin Permeability Based on Impedance Detection by Microsensor Technology. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2018, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizmadzhev, Y.A.; Indenborn, A.V.; Kuzmin, P.I.; Galichenko, S.V.; Weaver, J.C.; Potts, R.O. Electrical properties of skin at moderate voltages: Contribution of appendageal macropores. Biophys. J. 1998, 74, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, T.S.; Fu, L.S.; Sun, T.P.; Hsu, T.H.; Chang, K.M. Use of electroporation and reverse iontophoresis for extraction of transdermal multibiomarkers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, C.T.S.; Buisson, Y.; Connolly, P. The effect of pulsed bipolar dc on the simultaneous extraction of glucose and lactate by reverse iontophoresis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Load = 100 k, Pulse Width = 1 ms | Load = 100 k, Pulse Width = 5 ms | Load = 100 k, Pulse Width = 10 ms | Load = 100 k, Pulse Width = 50 ms | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulses per Second = 10 PPS | Pulses per Second = 10 PPS | Pulses per Second = 10 PPS | Pulses per Second = 10 PPS | ||||||||||||||
| VoltageSetting (V) | 20 | 30 | 40 | 60 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 60 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 60 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 60 | |
| Measured voltage (V) | Mean | 19.76 | 29.68 | 39.53 | 59.27 | 19.86 | 29.62 | 39.56 | 59.47 | 19.79 | 29.68 | 39.73 | 59.57 | 19.86 | 29.88 | 39.73 | 59.37 |
| SD | 0.26 | 0.41 | 0.64 | 0.87 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.61 | 0.82 | 0.20 | 0.35 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.20 | 0.41 | 0.44 | 0.67 | |
| Error (%) | 2.50 | 2.43 | 2.78 | 2.67 | 2.25 | 2.54 | 2.62 | 2.25 | 2.05 | 2.23 | 2.05 | 1.83 | 1.70 | 1.77 | 1.78 | 2.17 | |
| Parameters | Load = 100 k, Pulse Voltage = 1 ms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulses per Second = 10 PPS | |||||
| Pulse width Setting (ms) | 1.00 | 5.00 | 10.00 | 50.00 | |
| Measured pulse width (ms) | Mean | 1.002 | 5.004 | 10.015 | 50.045 |
| SD | 0.007 | 0.049 | 0.065 | 0.089 | |
| Error (%) | 0.900 | 0.980 | 0.650 | 0.178 | |
| Program Setting Stored Inside the Microprocessor Current Strength (μA) | Resistance of Resistor (k) | Measured Parameters | |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Current Strength of the Accuracy (μA) | The Pulse and Bipolar Current Error Timing (t > 1 μS) | ||
| 100 (dc) | 10 | 100 ± 0.65% | - |
| 300 (dc) | 10 | 300 ± 0.73% | - |
| 1100 (dc) | 10 | 1100 ± 1.5% | - |
| 300 (pulse) | 10 | 300 ± 0.83% | <1.1% |
| 300 (bipolar) | 10 | 300 ± 0.83% | <1.3% |
| 100 (dc) | 100 | 100 ± 0.85% | - |
| 300 (dc) | 100 | 200 ± 1.24% | - |
| 1.1 (dc) | 100 | 200 ± 1.24% | - |
| 100 (pulse) | 100 | 100 ± 0.85% | <1.2% |
| 100 (bipolar) | 100 | 100 ± 0.85% | <1.5% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, R.; Wang, C.; Lu, F.; Du, L.; Fang, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.-T.; Chen, C.-J.; Zhao, Z. A Flexible Interdigital Electrode Used in Skin Penetration Promotion and Evaluation with Electroporation and Reverse Iontophoresis Synergistically. Sensors 2018, 18, 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051431
Zhao R, Wang C, Lu F, Du L, Fang Z, Guo X, Liu J-T, Chen C-J, Zhao Z. A Flexible Interdigital Electrode Used in Skin Penetration Promotion and Evaluation with Electroporation and Reverse Iontophoresis Synergistically. Sensors. 2018; 18(5):1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051431
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Rongjian, Chenshuo Wang, Fei Lu, Lidong Du, Zhen Fang, Xiuhua Guo, Jen-Tsai Liu, Ching-Jung Chen, and Zhan Zhao. 2018. "A Flexible Interdigital Electrode Used in Skin Penetration Promotion and Evaluation with Electroporation and Reverse Iontophoresis Synergistically" Sensors 18, no. 5: 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051431
APA StyleZhao, R., Wang, C., Lu, F., Du, L., Fang, Z., Guo, X., Liu, J.-T., Chen, C.-J., & Zhao, Z. (2018). A Flexible Interdigital Electrode Used in Skin Penetration Promotion and Evaluation with Electroporation and Reverse Iontophoresis Synergistically. Sensors, 18(5), 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051431





