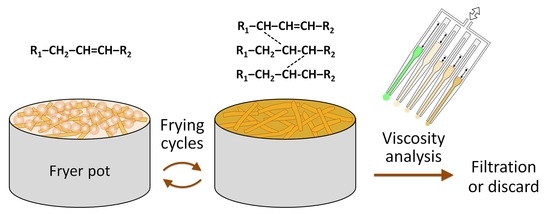
A 3D-Printed Multichannel Viscometer for High-Throughput Analysis of Frying Oil Quality
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Fabrication of the Multichannel Viscometer
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design Principle of the Multichannel Viscometer
3.2. Characterization of the Multichannel Viscometer
3.3. Quantitative Assessment of Frying Oil Degradation
3.4. 10-Plex Measurement of Oil Viscosity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Claeys, W.L.; De Vleeschouwer, K.; Hendrickx, M.E. Quantifying the formation of carcinogens during food processing: Acrylamide. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saguy, I.S.; Dana, D. Integrated approach to deep fat frying: Engineering, nutrition, health and consumer aspects. J. Food Eng. 2003, 56, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal; Isengard, H.-D. Determination of total polar material in frying oil using accelerated solvent extraction. Lipid Technol. 2010, 22, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.L.; Wehling, R.L.; Cuppett, S.L. Near-infrared spectroscopic determination of degradation in vegetable oils used to fry various foods. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2011, 59, 12286–12290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerde, J.A.; Hardy, C.L.; Hurburgh, C.R., Jr.; White, P.J. Rapid Determination of Degradation in Frying Oils with Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2007, 84, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, C.C.; Gonçalves, L.A.G.; Gumerato, H.F.; Mendes, F.M. Study of the effectiveness of quick tests based on physical properties for the evaluation of used frying oil. Food Control 2012, 26, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevc, T.; Cigić, B.; Vidrih, R.; Poklar Ulrih, N.; Šegatin, N. Correlation of basic oil quality indices and electrical properties of model vegetable oil systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11355–11362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertz, C. Chemical and physical parameters as quality indicators of used frying fats. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2000, 102, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.O.; Santos, I.M.G.; Souza, A.G. Effect of heating and cooling on rheological parameters of edible vegetable oils. J. Food Eng. 2005, 67, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKennell, R. Cone-plate viscometer. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 1710–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnin, A.; Piau, J.M. Cone-and-plate rheometry of yield stress fluids. Study of an aqueous gel. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1990, 36, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Burns, M.A. Analysis of non-Newtonian liquids using a microfluidic capillary viscometer. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.; Cai, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, X.; Chen, S. A novel polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic viscometer fabricated using microwire-molding. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2015, 86, 104302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Jee, S.; Atajanov, A.; Yang, S. Micro-Viscometer for Measuring Shear-Varying Blood Viscosity over a Wide-Ranging Shear Rate. Sensors 2017, 17, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Tang, X.; Zheng, B. A PDMS viscometer for microliter Newtonian fluid. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Park, J.K. Microfluidic rheometer for characterization of protein unfolding and aggregation in microflows. Small 2010, 6, 1306–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zheng, B. A PDMS viscometer for assaying endoglucanase activity. Analyst 2011, 136, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J. Continuous and simultaneous measurement of the biophysical properties of blood in a microfluidic environment. Analyst 2016, 141, 6583–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Xie, S.; Ge, J.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Ru, C.; Luo, J.; Sun, Y. Microfluidic Assessment of Frying Oil Degradation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ward, K.R.; Burns, M.A. Viscosity Measurements Using Microfluidic Droplet Length. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3996–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arosio, P.; Hu, K.; Aprile, F.A.; Muller, T.; Knowles, T.P.J. Microfluidic Diffusion Viscometer for Rapid Analysis of Complex Solutions. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3488–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Arratia, P.E. A high-shear, low Reynolds number microfluidic rheometer. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2013, 14, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.E.; Vanapalli, S.A. Multiplexed microfluidic viscometer for high-throughput complex fluid rheology. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 16, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Kim, B.; Lee, J.K.; Choi, S. 3D-printed capillary circuits for rapid, low-cost, portable analysis of blood viscosity. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 259, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, D.N.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, S.-H.; Lee, S. Correlation of fatty acid composition of vegetable oils with rheological behaviour and oil uptake. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostik, V.; Memeti, S.; Bauer, B. Fatty acid composition of edible oils and fats. J. Hyg. Eng. Des. 2013, 4, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, E.; Min, D.B. Chemistry of deep-fat frying oils. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, R77–R86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Chen, J.; Shen, Q. Chemical alterations taken place during deep-fat frying based on certain reaction products: A review. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2012, 165, 662–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisshaar, R. Quality control of used deep-frying oils. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagi, A.; Nakajima, M. Regeneration of used frying oils using adsorption processing. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2003, 80, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakoby, B.; Scherer, M.; Buskies, M.; Eisenschmid, H. An automotive engine oil viscosity sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2003, 3, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichero, J.A. Thickening agents used for dysphagia management: Effect on bioavailability of water, medication and feelings of satiety. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, S.; Kim, B.; Choi, S. A 3D-Printed Multichannel Viscometer for High-Throughput Analysis of Frying Oil Quality. Sensors 2018, 18, 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051625
Oh S, Kim B, Choi S. A 3D-Printed Multichannel Viscometer for High-Throughput Analysis of Frying Oil Quality. Sensors. 2018; 18(5):1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051625
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Sein, Byeongyeon Kim, and Sungyoung Choi. 2018. "A 3D-Printed Multichannel Viscometer for High-Throughput Analysis of Frying Oil Quality" Sensors 18, no. 5: 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051625
APA StyleOh, S., Kim, B., & Choi, S. (2018). A 3D-Printed Multichannel Viscometer for High-Throughput Analysis of Frying Oil Quality. Sensors, 18(5), 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051625