Design and Evaluation of FBG-Based Tension Sensor in Laparoscope Surgical Robots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
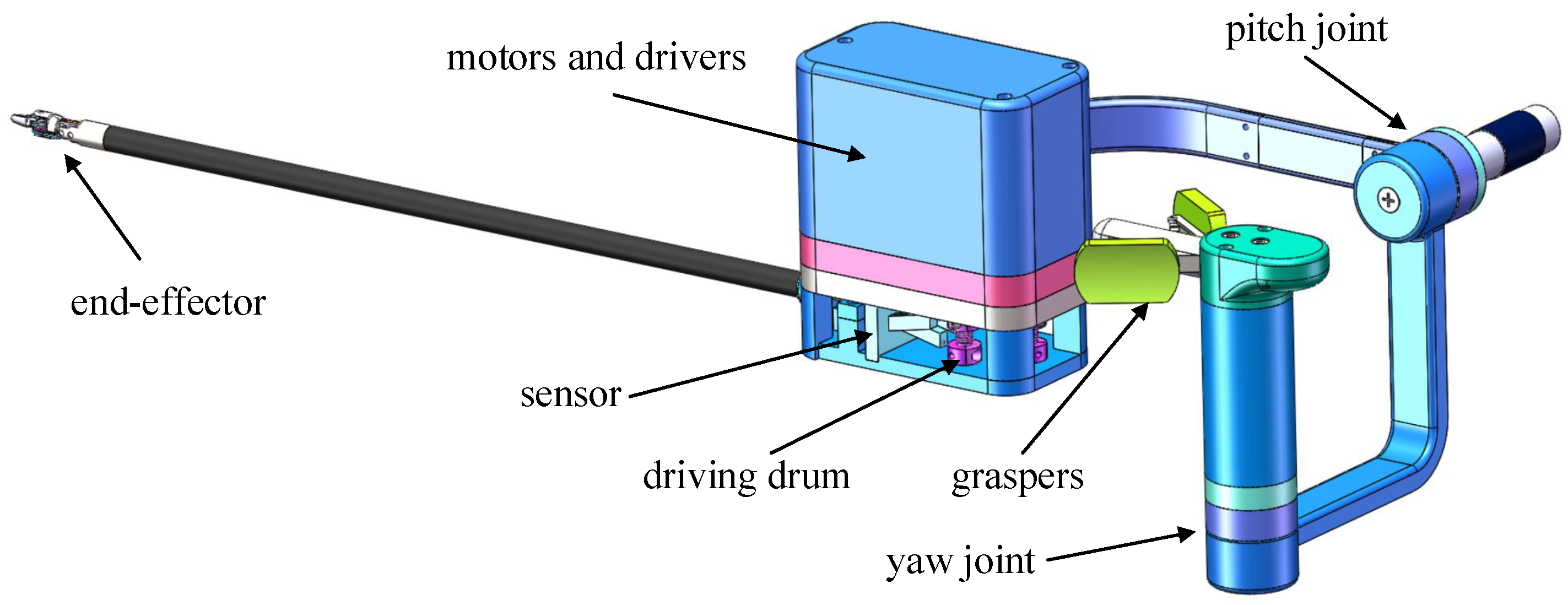
2. Sensor Design
- the structure of the sensor should avoid reducing sharply the stiffness of the transmission system which leads to an obvious hysteresis phenomenon;
- the output of the sensor should be as linearly proportional to the input as possible;
- the dimensions of the sensor should be minimized.
2.1. Sensor Structure
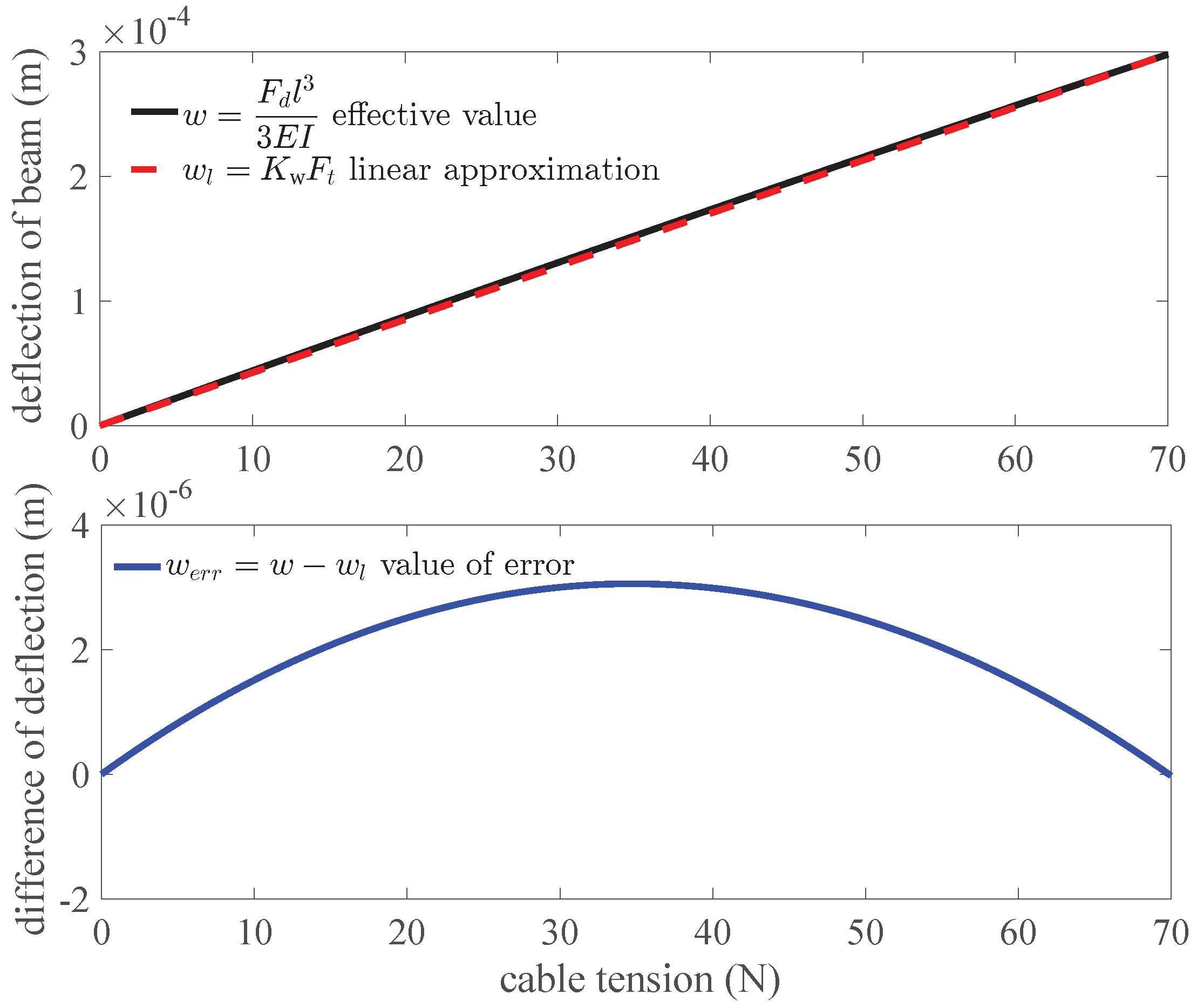
2.2. Parameters of Sensor Optimization
3. Sensor Calibration and Testing
3.1. Calibration of the Sensor
3.2. Testing of the Sensor
4. Estimation of the Grasping Force Based on the Sensor
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lanfranco, A.R.; Castellanos, A.E.; Desai, J.P.; Meyers, W.C. Robotic surgery: A current perspective. Ann. Surg. 2004, 239, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemiti, N.; Morel, G.; Ortmaier, T.; Bonnet, N. Mechatronic design of a new robot for force control in minimally invasive surgery. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2007, 12, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Du, Z.; Wang, W.; Sun, L. A Novel Position Compensation Scheme for Cable-Pulley Mechanisms Used in Laparoscopic Surgical Robots. Sensors 2017, 17, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenk Çavuşoğlu, M.; Williams, W.; Tendick, F.; Shankar Sastry, S. Robotics for telesurgery: Second generation Berkeley/UCSF laparoscopic telesurgical workstation and looking towards the future applications. Ind. Robot Int. J. 2003, 30, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejos, A.; Patel, R.; Naish, M. Force sensing and its application in minimally invasive surgery and therapy: A survey. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2010, 224, 1435–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Kenngott, H.G.; Müller-Stich, B.P.; Reiter, M.A.; Rassweiler, J.; Gutt, C.N. Robotic suturing: Technique and benefit in advanced laparoscopic surgery. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2008, 17, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, W.; Lim, S.C. Inferring Interaction Force from Visual Information without Using Physical Force Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hannaford, B. Gaussian process regression for sensorless grip force estimation of cable-driven elongated surgical instruments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviles, A.I.; Alsaleh, S.; Sobrevilla, P.; Casals, A. Exploring the effects of dimensionality reduction in deep networks for force estimation in robotic-assisted surgery. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2016: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling, San Diego, CA, USA, 27 February–3 March 2016; Volume 9786, p. 97861X. [Google Scholar]
- Aviles, A.I.; Alsaleh, S.M.; Hahn, J.K.; Casals, A. Towards Retrieving Force Feedback in Robotic-Assisted Surgery: A Supervised Neuro-Recurrent-Vision Approach. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2017, 10, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gessert, N.; Beringhoff, J.; Otte, C.; Schlaefer, A. Force estimation from OCT volumes using 3D CNNs. Int. J. Comput. Assisted Radiol. Surg. 2018, 13, 107–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, Y.; Ishii, C. Estimation of the grasping torque of robotic forceps using the robust reaction torque observer. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Bali, Indonesia, 5–10 December 2014; pp. 1650–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.C.; Kim, C.Y.; Yao, B.; Peine, W.J.; Song, Y.E. Reaction force estimation of surgical robot instrument using perturbation observer with SMCSPO algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Montreal, ON, Canada, 6–9 July 2010; pp. 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, U.; Lee, D.H.; Yoon, W.J.; Hannaford, B.; Choi, H.R. Force sensor integrated surgical forceps for minimally invasive robotic surgery. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y.; Seok, D.Y.; Choi, H. A novel 6-axis force/torque sensor for robotic applications. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 22, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.; Kim, Y.B.; So, J.; Seok, D.Y.; Choi, H.R. Sensorized Surgical Forceps for Robotic-assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.H.; Culjat, M.O.; Franco, M.L.; Bisley, J.W.; Carman, G.P.; Dutson, E.P.; Grundfest, W.S. A multielement tactile feedback system for robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2009, 2, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dargahi, J.; Parameswaran, M.; Payandeh, S. A micromachined piezoelectric tactile sensor for an endoscopic grasper-theory, fabrication and experiments. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2000, 9, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasaimeh, M.A.; Sokhanvar, S.; Dargahi, J.; Kahrizi, M. PVDF-based microfabricated tactile sensor for minimally invasive surgery. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2009, 18, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.B.; Jo, Y.H. Design and evaluation of 2-DOF compliant forceps with force-sensing capability for minimally invasive robot surgery. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Kim, U.; Moon, H.; Koo, J.C.; Yoon, W.J.; Choi, H.R. Preliminary design of multi-axial contact force sensor for minimally invasive robotic surgery grasper. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 1019–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.H.; Kim, U.; Gulrez, T.; Yoon, W.J.; Hannaford, B.; Choi, H.R. A laparoscopic grasping tool with force sensing capability. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 130–141. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, M.S.; Hoffmann, L.; Buck, T.C.; Koch, A.W. Fiber Bragg Grating-Based Force-Torque Sensor with Six Degrees of Freedom. Int. J. Optomechatron. 2009, 3, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer, H.; Nagy, I.; Knoll, A.; Schirmbeck, E.U.; Bauernschmitt, R. The Endo [PA] R system for minimally invasive robotic surgery. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004; Volume 4, pp. 3637–3642. [Google Scholar]
- Tholey, G.; Desai, J.P. A modular, automated laparoscopic grasper with three-dimensional force measurement capability. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Roma, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 250–255. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuishi, M.; Sugita, N.; Pitakwatchara, P. Force-feedback augmentation modes in the laparoscopic minimally invasive telesurgical system. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2007, 12, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibold, U.; Kubler, B.; Hirzinger, G. Prototype of instrument for minimally invasive surgery with 6-axis force sensing capability. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 496–501. [Google Scholar]
- Fontanelli, G.; Buonocore, L.; Ficuciello, F.; Villani, L.; Siciliano, B. A novel force sensing integrated into the trocar for minimally invasive robotic surgery. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.D.; Rosen, J. Computer-Controlled Motorized Endoscopic Grasper for In Vivo Measurement of Soft Tissue. Med. Meets Virtual Real. Dig. Upgrades Appl. Moore’s Law Health 2002, 85, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, M.; Yokoi, K.; Tanie, K. On a new torque sensor for tendon drive fingers. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1990, 6, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotti, F.; Tiezzi, P.; Vassura, G.; Biagiotti, L.; Palli, G.; Melchiorri, C. Development of UB hand 3: Early results. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 4488–4493. [Google Scholar]
- Berselli, G.; Borghesan, G.; Brandi, M.; Melchiorri, C.; Natale, C.; Palli, G.; Pirozzi, S.; Vassura, G. Integrated mechatronic design for a new generation of robotic hands. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2009, 42, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Liu, H.; Luo, S.; Seneviratne, L.D.; Althoefer, K. Fiber optics tactile array probe for tissue palpation during minimally invasive surgery. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 2539–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Wanninayake, I.B.; Dasgupta, P.; Seneviratne, L.D.; Althoefer, K. Air-float palpation probe for tissue abnormality identification during minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 2735–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, J. Development of optical fiber Bragg grating force-reflection sensor system of medical application for safe minimally invasive robotic surgery. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 82, 074301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Balicki, M.A.; Kang, J.U.; Gehlbach, P.L.; Handa, J.T.; Taylor, R.H.; Iordachita, I.I. Force sensing micro-forceps with integrated fiber bragg grating for vitreoretinal surgery. In Proceedings of the International Society for Optics and Photonics Optical Fibers and Sensors for Medical Diagnostics and Treatment Applications XII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 21–26 January 2012; Volume 8218, p. 82180W. [Google Scholar]
- Natale, C.; Pirozzi, S. Minimally invasive torque sensor for tendon-driven robotic hands. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Palli, G.; Pirozzi, S. Force sensor based on discrete optoelectronic components and compliant frames. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 165, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, G.; Pirozzi, S. A miniaturized optical force sensor for tendon-driven mechatronic systems: Design and experimental evaluation. Mechatronics 2012, 22, 1097–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, G.; Hosseini, M.; Melchiorri, C. A simple and easy-to-build optoelectronics force sensor based on light fork: Design comparison and experimental evaluation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 269, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Ren, B.; Yan, Z.; Du, Z. A cable-pulley system modeling based position compensation control for a laparoscope surgical robot. Mech. Mach. Theory 2017, 118, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, G.H.; Moll, F. The da Vinci telerobotic surgical system: the virtual operative field and telepresence surgery. Surg. Clin. 2003, 83, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Yang, M.; Dong, W.; Zhang, D. Static deformation modeling and analysis of flexure hinges made of a shape memory alloy. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 115029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
















© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, R.; Ren, B.; Huang, J.; Yan, Z.; Du, Z. Design and Evaluation of FBG-Based Tension Sensor in Laparoscope Surgical Robots. Sensors 2018, 18, 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072067
Xue R, Ren B, Huang J, Yan Z, Du Z. Design and Evaluation of FBG-Based Tension Sensor in Laparoscope Surgical Robots. Sensors. 2018; 18(7):2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072067
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Renfeng, Bingyin Ren, Jiaqing Huang, Zhiyuan Yan, and Zhijiang Du. 2018. "Design and Evaluation of FBG-Based Tension Sensor in Laparoscope Surgical Robots" Sensors 18, no. 7: 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072067
APA StyleXue, R., Ren, B., Huang, J., Yan, Z., & Du, Z. (2018). Design and Evaluation of FBG-Based Tension Sensor in Laparoscope Surgical Robots. Sensors, 18(7), 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072067




