Review of Three-Dimensional Human-Computer Interaction with Focus on the Leap Motion Controller
Abstract
1. Introduction
- currently available three-dimensional interaction devices
- methods of gesture design and recognition
- applications of usage
- state-of-the-art in interaction design
- evaluation methods for these designs
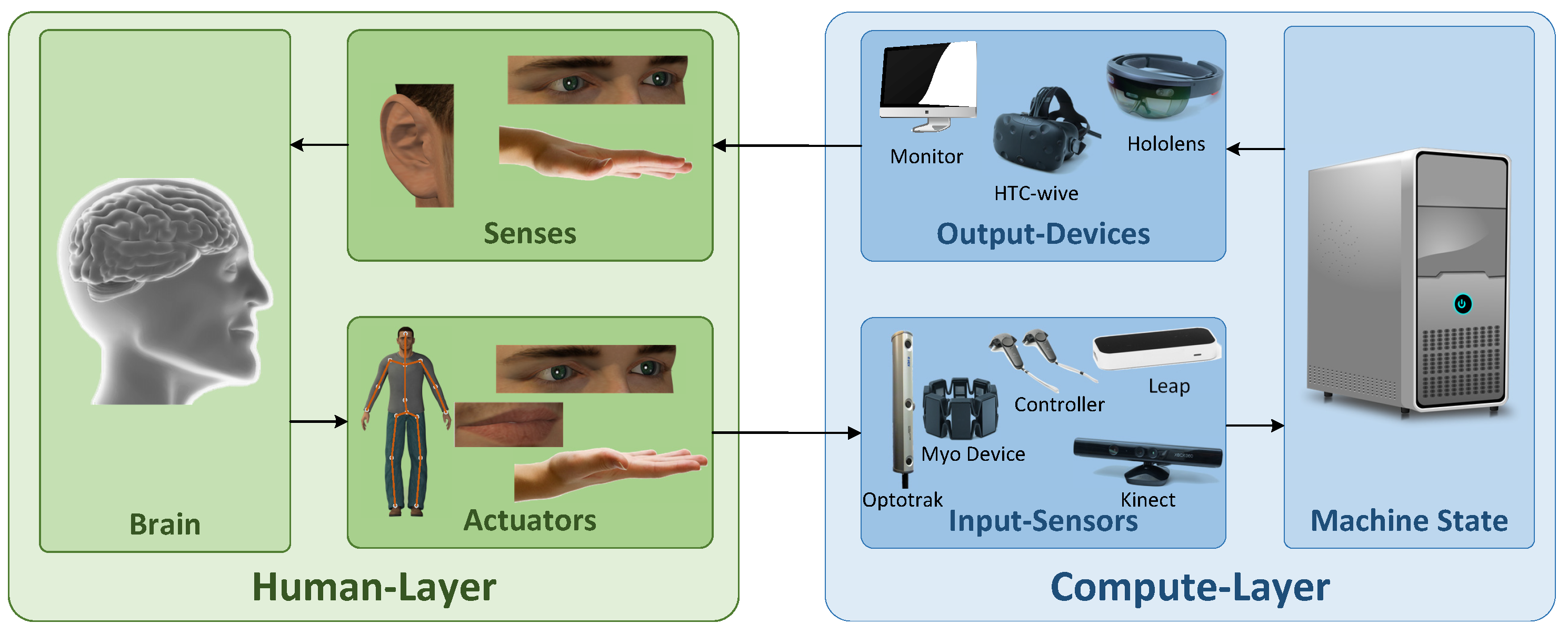
2. Human-Computer Interaction
2.1. User Interfaces
- actuators: output signal of the human user
- input-devices/sensors: channel of signals to the HMI-system
- senses: sensory channel of the human user (sensory organs)
- output-devices/media: output signal of the HMI-system
2.2. Evolution of Interaction Devices
3. Applications and Contexts
3.1. Medical Field
3.2. Human-Robot Interaction
3.3. Text Recognition
3.4. Education and Analysis
3.5. Music
3.6. Games and Gamification
3.7. Authentication and Identification
4. Methods
4.1. Leap Motion Controller
- Data acquisition—transformation between LMC coordinate system and the coordinate system of the scene of interaction, data fusion and smoothing.
- Feature extraction—obtain features of tracked hand(s) or arm(s).
- Gesture definition and recognition—define and recognise gestures to be detected by LMC.
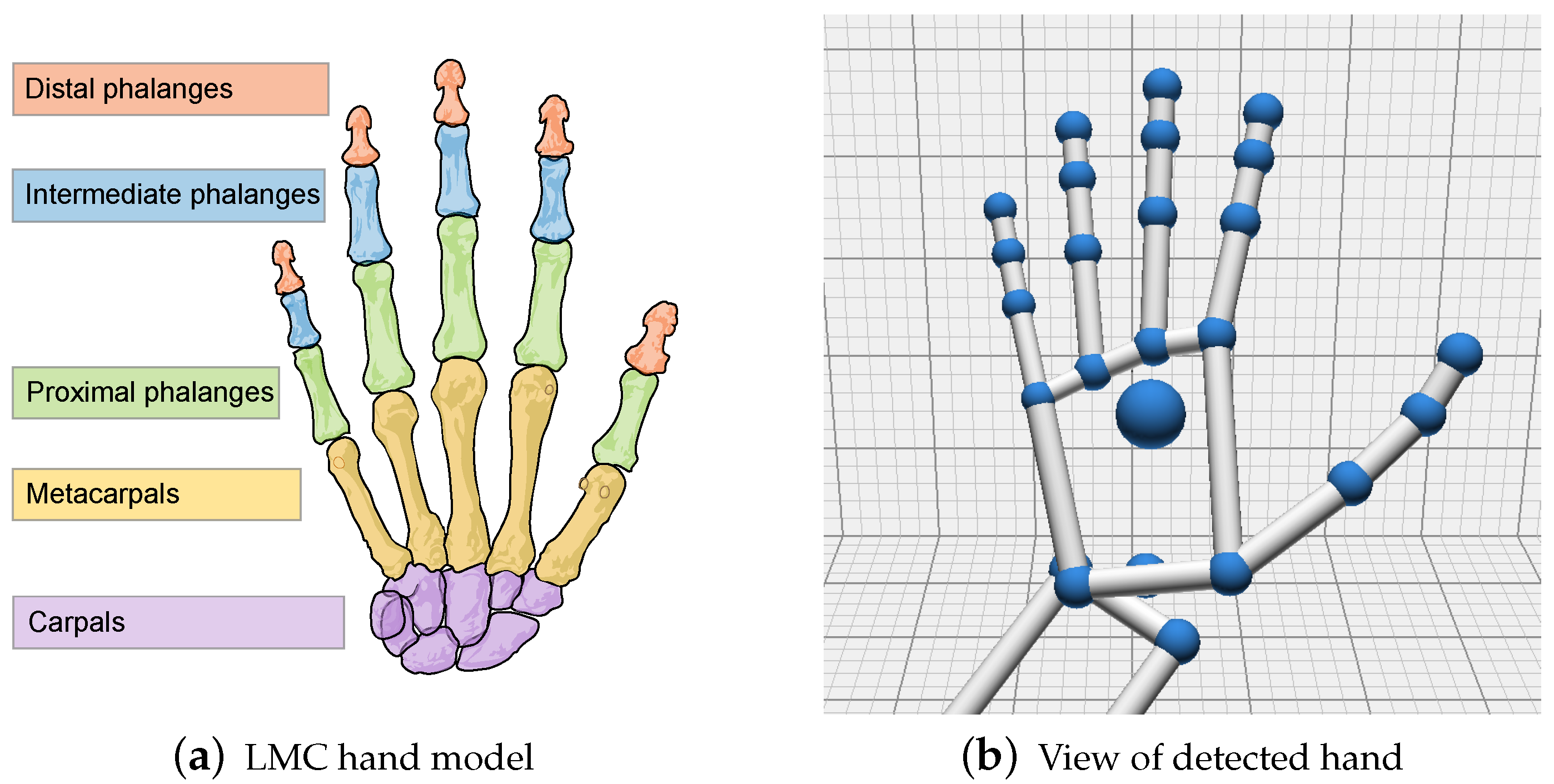
4.1.1. Data Acquisition
4.1.2. Gesture Definition
4.1.3. Feature Extraction and Gesture Recognition
5. Evaluation
5.1. Usability
5.2. User Experience
5.3. Mental Workload
5.4. Experimental Approaches
5.5. System Performance
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krueger, M.W.; Thomas, G.; Hinrichsen, K. VIDEOPLACE—An artificial reality. ACM SIGCHI Bull. 1985, 16, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewett, T.; Baecker, R.; Card, S.; Carey, T.; Gasen, J.; Mantei, M.; Perlman, G.; Strong, G.; Verplank, W. ACM SIGCHI Curricula for Human-Computer Interaction; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- LaViola, J.J., Jr.; Kruijff, E.; McMahan, R.P.; Bowman, D.; Poupyrev, I.P. 3D User Interfaces: Theory and Practice; Addison-Wesley Professional: Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Preece, J.; Rogers, Y.; Sharp, H. Interaction Design; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, J.; Rada, R.; Diaper, D. Interacting with computers. Interact. Comput. 1989, 1, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dix, A. Human-computer interaction. In Encyclopedia of Database Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 1327–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Ogiela, M.; Hachaj, T. Natural User Interfaces for Exploring and Modeling Medical Images and Defining Gesture Description Technology. In Natural User Interfaces in Medical Image Analysis: Cognitive Analysis of Brain and Carotid Artery Images; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 205–279. [Google Scholar]
- Frøkjær, E.; Hertzum, M.; Hornbæk, K. Measuring usability: Are effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction really correlated? In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, The Hague, The Netherlands, 1–6 April 2000; pp. 345–352. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, W.; Tullis, T. Measuring the User Experience: Collecting, Analyzing, and Presenting Usability Metrics; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Duchowski, A.T. Eye Tracking Methodology; Theory and Practice; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; Volume 328. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, A.R.; Castillo, J.R.; Chae, O.O. Local directional number pattern for face analysis: Face and expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 1740–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.Y.; Mian, A.S.; Liu, W.; Krishna, A. Using kinect for face recognition under varying poses, expressions, illumination and disguise. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Tampa, FL, USA, 15–17 January 2013; pp. 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, J.; Rudner, B.; Reichert, M. Gesture-based process modeling using multi-touch devices. Int. J. Inf. Syst. Model. Des. 2013, 4, 48–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Halawani, A.; Feng, S.; Li, H.; Réhman, S.U. Multimodal hand and foot gesture interaction for handheld devices. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 2014, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Fazal, M.A.; Karim, M.S. Multiple Information Communication in Voice-Based Interaction. In Multimedia and Network Information Systems; Zgrzywa, A., Choroś, K., Siemiński, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ogiela, M.; Hachaj, T. Natural User Interfaces in Medical Image Analysis: Cognitive Analysis of Brain and Carotid Artery Images; Springer Publishing Company: Cham, Switzerland; Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.K.; Duin, R.P.W.; Mao, J. Statistical pattern recognition: A review. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 4–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, G.; Kambhamettu, C. Age invariant face recognition using graph matching. In Proceedings of the Fourth IEEE International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Washington, DC, USA, 27–29 September 2010; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Martinez, A. Labeled graph kernel for behavior analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 1640–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoun, N.; Mejdoub, M.; Amar, C. Graph-based approach for human action recognition using spatio-temporal features. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2014, 25, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Miah, M.; Rahman, H.; Bhowmik, A.; Karmaker, D. Face Recognition using Eigenfaces. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 118, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Acharya, T. Gesture recognition: A survey. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C (Appl. Rev.) 2007, 37, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khiyari, H.; Wechsler, H. Face recognition across time lapse using convolutional neural networks. J. Inf. Secur. 2016, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguri, C.; Bunescu, R. Recognition of Dynamic Hand Gestures from 3D Motion Data Using LSTM and CNN Architectures. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Cancun, Mexico, 18–21 December 2017; pp. 1130–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe, A.; Kurniawan, S.; Shin, J.E. A Method and Advisor Tool for Multimedia User Interface Design. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2006, 64, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, M. Multimodal interaction: A review. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014, 36, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptelinin, V.; Nardi, B. Acting with Technology: Activity Theory and Interaction Design; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, B. The graphical user interface. ACM SIGCHI Bull. 1998, 30, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusilovsky, P.; Kobsa, A.; Vassileva, J. Adaptive Hypertext and Hypermedia; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, H.; Abdul-Kareem, S. Human-computer interaction using vision-based hand gesture recognition systems: A survey. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 25, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billinghurst, M.; Clark, A.; Lee, G. A survey of augmented reality. Found. Trends Hum. Comput. Interact. 2015, 8, 73–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milgram, P.; Takemura, H.; Fumio Kishino, A.U. Augmented reality: A class of displays on the reality-virtuality continuum. In Telemanipulator and Telepresence Technologies; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1994; Volume 2351, pp. 282–293. [Google Scholar]
- Hinckley, K.; Jacob, R.K.; Ware, C. Input/Output Devices and Interaction Techniques. In The Computer Science and Engineering Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press, LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; Chapter 20; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, S.; Landay, J.A.; Malkin, J.; Li, X.; Bilmes, J.A. The Vocal Joystick: Evaluation of Voice-based Cursor Control Techniques. In Proceedings of the 8th International ACM SIGACCESS Conference on Computers and Accessibility, Portland, OR, USA, 23–25 October 2006; pp. 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Wuest, H.; Vial, F.; Strieker, D. Adaptive line tracking with multiple hypotheses for augmented reality. In Proceedings of the Fourth IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR’05), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 5–8 October 2005; pp. 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Leung, H.; Shum, H. Human action recognition via skeletal and depth based feature fusion. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Motion in Games, Burlingame, CA, USA, 10–12 October 2016; pp. 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, S.R.; Thuc, H.; Lee, Y.J.; Hwang, J.N.; Yoo, J.H.; Choi, K.H. A review on video-based human activity recognition. Computers 2013, 2, 88–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Nasir, A.; Riaz, O.; Gotoh, Y.; Amiruddin, M. A Statistical Model for Annotating Videos with Human Actions. Pak. J. Stat. 2016, 32, 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Chéron, G.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. P-CNN: Pose-based CNN features for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3218–3226. [Google Scholar]
- Camgöz, N.; Kindiroglu, A.; Akarun, L. Gesture Recognition Using Template Based Random Forest Classifiers. In ECCV Workshops; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 579–594. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, J.W., III. Progress of the Whirlwind Computer Towards an Automatic Programming Procedure. In Proceedings of the 1952 ACM National Meeting (Pittsburgh), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2 May 1952; pp. 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, B.A. A Brief History of Human-Computer Interaction Technology. Interactions 1998, 5, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, A.H. The Evolution of Game Controllers and Control Schemes and Their Effect on Their Games. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-Evolution-of-Game-Controllers-and-Control-and-Cummings/76f3d23b46896af6e602ad28436f9ec774a67d7e (accessed on 4 July 2018).
- Ware, C.; Mikaelian, H.H. An Evaluation of an Eye Tracker as a Device for Computer Input2. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI/GI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems and Graphics Interface, Toronto, ON, Canada, 5–9 April 1987; pp. 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Shotton, J.; Fitzgibbon, A.; Cook, M.; Sharp, T.; Finocchio, M.; Moore, R.; Kipman, A.; Blake, A. Real-time human pose recognition in parts from single depth images. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 1297–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Sarbolandi, H.; Lefloch, D.; Kolb, A. Kinect Range Sensing: Structured-Light versus Time-of-Flight Kinect. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2015, 139, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capes, T.; Coles, P.; Conkie, A.; Golipour, L.; Hadjitarkhani, A.; Hu, Q.; Huddleston, N.; Hunt, M.; Li, J.; Neeracher, M.; et al. Siri On-Device Deep Learning-Guided Unit Selection Text-to-Speech System. Proc. Interspeech 2017, 2017, 4011–4015. [Google Scholar]
- Zander, T.O.; Kothe, C. Towards passive brain–computer interfaces: Applying brain–computer interface technology to human–machine systems in general. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, D.; Wolpaw, J. EEG-based brain–computer interfaces. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 4, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Deng, Q. CUDA-based real-time hand gesture interaction and visualization for CT volume dataset using leap motion. Vis. Comput. 2016, 32, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.N.W.; Kassim, N.L.A.; Jhawar, A.; Shurkri, N.M.; Baharin, N.A.K.; Chan, C.S. User acceptance of a touchless sterile system to control virtual orthodontic study models. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 149, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, G.M.; Elizondo, M.L. Use of a gesture user interface as a touchless image navigation system in dental surgery: Case series report. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2014, 44, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestorov, N.; Hughes, P.; Healy, N.; Sheehy, N.; OHare, N. Application of Natural User Interface Devices for Touch-Free Control of Radiological Images During Surgery. In Proceedings of the IEEE 29th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Dublin, Ireland, 20–24 June 2016; pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Hettig, J.; Saalfeld, P.; Luz, M.; Becker, M.; Skalej, M.; Hansen, C. Comparison of gesture and conventional interaction techniques for interventional neuroradiology. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 1643–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, L.C.; Flach, P.M.; Thali, M.J.; Ross, S. Out of touch—A plugin for controlling OsiriX with gestures using the leap controller. J. Forensic Radiol. Imaging 2014, 2, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzotto, N.; Costanzo, A.; Bizzotto, L.; Regis, D.; Sandri, A.; Magnan, B. Leap Motion Gesture Control with OsiriX in the Operating Room to Control Imaging. Surg. Innov. 2014, 21, 655–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipshagen, T.; Graw, M.; Tronnier, V.; Bonsanto, M.; Hofmann, U.G. Touch- and marker-free interaction with medical software. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Munich, Germany, 7–12 September 2009; pp. 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Chophuk, P.; Chumpen, S.; Tungjitkusolmun, S.; Phasukkit, P. Hand Postures for Evaluating Trigger Finger Using Leap Motion Controller. In Proceedings of the 2015 Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON-201S), Pattaya, Thailand, 25–27 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Martono, N.P.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ohwada, H. Utilizing finger movement data to cluster patients with everyday action impairment. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 15th International Conference on Cognitive Informatics & Cognitive Computing (ICCI*CC), Palo Alto, CA, USA, 22–23 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alagha, M.A.; Alagha, M.A.; Dunstan, E.; Sperwer, O.; Timmins, K.A.; Boszczyk, B.M. Development of a new assessment tool for cervical myelopathy using hand-tracking sensor: Part 1: Validity and reliability. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracegirdle, A.; Mitrovic, T. Investigating the Usability of the Leap Motion Controller: Gesture-Based Interaction with a 3D Virtual Environment Final Report; Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence: Seattle, WA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Rau, P.L.P.; Choe, P.; Gulrez, T. Leap-Motion Based Online Interactive System for Hand Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Cross-Cultural Design, Crete, Greece, 2–7 August 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9181, pp. 338–347. [Google Scholar]
- Placidi, G.; Cinque, L.; Petracca, A.; Polsinelli, M.; Spezialetti, M. A Virtual Glove System for the Hand Rehabilitation Based on Two Orthogonal LEAP Motion Controllers. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods, Porto, Portugal, 24–26 February 2017; pp. 184–192. [Google Scholar]
- Grubisic, I.; Kavanagh, H.S.; Grazio, S. Novel approaches in hand rehabilitation. Period. Biol. 2015, 117, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, D.E.; Charles, D.K.; Morrow, P.J.; McClean, S.; McDonough, S.M. Using Fitt’s Law to Model Arm Motion Tracked in 3D by a Leap Motion Controller for Virtual Reality Upper Arm Stroke Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 29th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Dublin, Ireland, 20–24 June 2016; pp. 335–336. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Fernández, C.; Morán, A.L.; García-Canseco, E. Haptic feedback in motor hand virtual therapy increases precision and generates less mental workload. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare (PervasiveHealth), Istanbul, Turkey, 20–23 May 2015; pp. 280–286. [Google Scholar]
- Gieser, S.N.; Boisselle, A.; Makedon, F. Real-Time Static Gesture Recognition for Upper Extremity Rehabilitation Using the Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Human Modeling and Applications in Health, Safety, Ergonomics and Risk Management, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2–7 August 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9185, pp. 144–154. [Google Scholar]
- Baldominos, A.; Saez, Y.; Pozo, C.G.D. An Approach to Physical Rehabilitation Using State-of-the-art Virtual Reality and Motion Tracking Technologies. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 64, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommalapati, R.; Michmizos, K.P. Virtual reality for pediatric neuro-rehabilitation: Adaptive visual feedback of movement to engage the mirror neuron system. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 5849–5852. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, J.M.; Jorge, J.C.M.; Duarte, J.B.F.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. Complementary Treatment for Children with Cerebral Palsy Based on Virtual Reality. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2016, 14, 3820–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, C.B.; Ojeda-Castelo, J.J.; Piedra-Fernandez, J.A. Art activities with Kinect to Students with Cognitive Disabilities: Improving all Motor Skills. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2017, 237, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.J.; Chen, C.H.; Chang, K.P. Augmented reality technology combined with three-dimensional holography to train the mental rotation ability of older adults. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 65, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, F.; Brennan, P.; Hennessey, I.; Hughes, M.; Partridge, R. The LEAP™ gesture interface device and take-home laparoscopic simulators: A study of construct and concurrent validity. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 23 (Suppl. 1), 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, M.I.P.H.; Taekman, J.M.; Zomorodi, A.R.; Gonzalez, L.F.; Turner, D.A. Simulation in Neurosurgery—A Brief Review and Commentary. World Neurosurg. 2016, 89, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travaglini, T.A.; Swaney, P.J.; Weaver, K.D.; Webster, R.J., III. Initial Experiments with the Leap Motion as a User Interface in Robotic Endonasal Surgery. In Robotics and Mechatronics; Mechanisms and Machine Science; Zeghloul, S., Laribi, M., Gazeau, J.P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 37, pp. 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, A.; Adão, T.; Magalhães, L.; Peres, E. A Myographic-based 5HCI6 Solution Proposal for Upper Limb Amputees. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 100, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyanarayanan, M.; Rajan, S. MYO Armband for physiotherapy healthcare: A case study using gesture recognition application. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks (COMSNETS), Bangalore, India, 5–10 January 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sathiyanarayanan, M.; Rajan, S. Understanding the use of leap motion touchless device in physiotherapy and improving the healthcare system in India. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks (COMSNETS), Bangalore, India, 4–8 January 2017; pp. 502–507. [Google Scholar]
- Erdoğan, K.; Durdu, A.; Yilmaz, N. Intention Recognition Using Leap Motion Controller and Artificial Neural Networks; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. Interval model control of human welder’s movement in machine-assisted manual GTAW torch operation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 86, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ma, H.; Yang, C.; Fu, M. Hand Gesture Based Robot Control System Using Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, Portsmouth, UK, 24–27 August 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9244, pp. 581–591. [Google Scholar]
- Gojare, B.; Kanawade, S.Y.; Bodhak, K.; Surve, S. Leap Motion Control Using Virtual Automation. Int. J. Adv. Res. Ideas Innov. Technol. 2017, 3, 322–325. [Google Scholar]
- Makris, S.; Tsarouchi, P.; Matthaiakis, A.S.; Athanasatos, A.; Chatzigeorgiou, X.; Stefos, M.; Giavridis, K.; Aivaliotis, S. Dual arm robot in cooperation with humans for flexible assembly. CIRP Ann. 2017, 66, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruusamäe, K.; Pryor, M. High-Precision Telerobot with Human-Centered Variable Perspective and Scalable Gestural Interface. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Human System Interactions (HSI), Portsmouth, UK, 6–8 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, D.; Büchele, K.; Meschtscherjakov, A. Pointing at the HUD: Gesture Interaction Using a Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the AutomotiveUI (Adjunct), Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 24–26 October 2016; pp. 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Devine, S.; Rafferty, K.; Ferguson, S. Real time robotic arm control using hand gestures with multiple end effectors. In Proceedings of the UKACC International Conference on Control (UKACC Control 2016), Belfast, UK, 31 August–2 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hernoux, F.; Béarée, R.; Gibaru, O. Investigation of dynamic 3D hand motion reproduction by a robot using a Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the 2015 Virtual Reality International Conference, Laval, France, 8–10 April 2015; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, N.; Argyrou, A.; Nägele, F.; Ubis, F.; Campos, U.E.; Zarate, M.O.D.; Wilterdink, R. AR-Enhanced Human-Robot-Interaction-Methodologies, Algorithms, Tools. Procedia CIRP 2016, 44, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarouchi, P.; Athanasatos, A.; Makris, S.; Chatzigeorgiou, X.; Chryssolouris, G. High Level Robot Programming Using Body and Hand Gestures. Procedia CIRP 2016, 55, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manawadu, U.E.; Kamezaki, M.; Ishikawa, M.; Kawano, T.; Sugano, S. A Haptic Feedback Driver-Vehicle Interface for Controlling Lateral and Longitudinal Motions of Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Banff, AB, Canada, 12–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.L.; Liu, H.B. Examples of quadrocopter control on ROS. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Conference on Anti-Counterfeiting, Security, and Identification (ASID), Xiamen, China, 25–27 September 2015; pp. 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, A.; Patel, K.A.; Ram, R.G.; Capoor, G.K. Gesture Control of Drone Using a Motion Controller; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez Fernández, R.A.; Sanchez-Lopez, J.L.; Sampedro, C.; Bavle, H.; Molina, M.; Campoy, P. Natural User Interfaces for Human-Drone Multi-Modal Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Arlington, VA, USA, 7–10 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Peshkova, E.; Hitz, M.; Kaufmann, B. Natural Interaction Techniques for an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle System. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2017, 16, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshkova, E.; Hitz, M.; Ahlström, D.; Alexandrowicz, R.W.; Kopper, A. Exploring intuitiveness of metaphor-based gestures for UAV navigation. In Proceedings of the 2017 26th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Lisbon, Portugal, 28 August–1 September 2017; pp. 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Peshkova, E.; Hitz, M. Coherence Evaluation of Input Vocabularies to Enhance Usability and User Experience. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCHI Symposium on Engineering Interactive Computing Systems, Lisbon, Portugal, 26–29 June 2017; pp. 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Monajjemi, M.; Bruce, J.; Sadat, S.A.; Wawerla, J.; Vaughan, R. UAV, do you see me? Establishing mutual attention between an uninstrumented human and an outdoor UAV in flight. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 3614–3620. [Google Scholar]
- Monajjemi, M.; Mohaimenianpour, S.; Vaughan, R. UAV, come to me: End-to-end, multi-scale situated HRI with an uninstrumented human and a distant UAV. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 4410–4417. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, C.C.; Wang, R.H.; Chen, B.R. Recognizing arbitrarily connected and superimposed handwritten numerals in intangible writing interfaces. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.J.; Garcia-Hernando, G.; Tang, D.; Kim, T.K. Spatio-Temporal Hough Forest for efficient detection–localisation–recognition of fingerwriting in egocentric camera. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2016, 148, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wang, W.; Qu, X. On-line Sample Generation for In-air Written Chinese Character Recognition Based on Leap Motion Controller. In Proceedings of the Pacific Rim Conference on Multimedia, Gwangju, Korea, 16–18 September 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9314, pp. 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Fan, X.; He, X.; Jia, Q.; Gao, R. Online gesture-based interaction with visual oriental characters based on manifold learning. Signal Process. 2015, 110, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, K.; Miyao, H.; Maruyama, M. Handwritten Character Recognition in the Air by Using Leap Motion Controller. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2–7 August 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 528, pp. 534–538. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; AlRegib, G.; Juang, B.H. Air-Writing Recognition-Part II: Detection and Recognition of Writing Activity in Continuous Stream of Motion Data. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2016, 46, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, C.; Dogra, D.P.; Saini, R.; Roy, P.P. Segmentation and recognition of text written in 3D using Leap motion interface. In Proceedings of the 2015 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 3–6 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Saini, R.; Roy, P.P.; Dogra, D.P. 3D text segmentation and recognition using leap motion. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 16491–16510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, K.Y.; Ganganath, N.; Cheng, C.T.; Tse, C.K. A Real-Time ASL Recognition System Using Leap Motion Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Cyber-Enabled Distributed Computing and Knowledge Discovery, Xi’an, China, 17–19 September 2015; pp. 411–414. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Gauba, H.; Roy, P.P.; Dogra, D.P. Coupled HMM-based multi-sensor data fusion for sign language recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, 86, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.R.; Ong, H.F.; Bahar, N. A Sign Language to Text Converter Using Leap Motion. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2016, 6, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, L.E.; Araullo, J.; Carter, L. The Leap Motion controller: A view on sign language. In Proceedings of the 25th Australian Computer-Human Interaction Conference: Augmentation, Application, Innovation, Collaboration, Adelaide, Australia, 25–29 November 2013; pp. 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Aliyu, S.; Mohandes, M.; Deriche, M.; Badran, S. Arabie sign language recognition using the Microsoft Kinect. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals Devices (SSD), Leipzig, Germany, 21–24 March 2016; pp. 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Simos, M.; Nikolaidis, N. Greek sign language alphabet recognition using the leap motion device. In Proceedings of the 9th Hellenic Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Thessaloniki, Greece, 18–20 May 2016; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Naglot, D.; Kulkarni, M. ANN based Indian Sign Language numerals recognition using the leap motion controller. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Coimbatore, India, 26–27 August 2016; Volume 2, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nájera, R.O.R.; Sánchez, M.L.; Serna, J.G.G.; Tapia, R.P.; Llanes, J.Y.A. Recognition of Mexican Sign Language through the Leap Motion Controller. In Proceedings of the 2016 World Congress in Computer Science, Computer Engineering and Applied Computing, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–28 July 2016; pp. 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, P.; Rodrigues, H.; Rocha, T.; Francisco, M.; Morgado, L. Accessible Options for Deaf People in e-Learning Platforms: Technology Solutions for Sign Language Translation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 67, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirjon, S.; Gummeson, J.; Gelb, D.; Kim, K.H. TypingRing: A Wearable Ring Platform for Text Input. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Florence, Italy, 18–22 May 2015; pp. 227–239. [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty, B.; Lennon, E.; DiCola, F.; Buzby, K.; Manzella, M.; Hromada, E. Utilizing Depth Based Sensors and Customizable Software Frameworks for Experiential Application. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2012, 12, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chifor, M.; Stefanut, T. Immersive Virtual Reality Application Using Google Cardboard and Leap Motion Technologies. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Immersive-Virtual-Reality-application-using-Google-Chifor-Stefanut/0a309a7eb032c07c15a40275685d689e435e73bf (accessed on 4 July 2018).
- Häfner, P.; Häfner, V.; Ovtcharova, J. Teaching Methodology for Virtual Reality Practical Course in Engineering Education. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2013, 25, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainggolan, F.L.; Siregar, B.; Fahmi, F. Anatomy Learning System on Human Skeleton Using Leap Motion Controller. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCOINS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 15–17 August 2016; Volume 3, pp. 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, A.K.; Aras, R. Potential of multimodal and multiuser interaction with virtual holography. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2015, 81, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, A.; Licari, D.; Mancini, G.; Brogni, A.; Mitri, N.D.; Barone, V. Graphical Interfaces and Virtual Reality for Molecular Sciences. In Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Morse, P.; Reading, A.; Lueg, C.; Kenderdine, S. TaggerVR: Interactive Data Analytics for Geoscience—A Novel Interface for Interactive Visual Analytics of Large Geoscientific Datasets in Cloud Repositories. In 2015 Big Data Visual Analytics (BDVA); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, S.; Dass, N.; Chau, D.H.P. NaturalMotion: Exploring Gesture Controls for Visualizing Time-Evolving Graphs. In Proceedings of IEEE VIS; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rittitum, P.; Vatanawood, W.; Thongtak, A. Digital scrum board using leap motion. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ACIS 15th International Conference on Computer and Information Science (ICIS), Okayama, Japan, 26–29 June 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, E.S.; de Abreu, J.A.O.; de Almeida, J.H.P.; Teichrieb, V.; Ramalho, G.L. A Preliminary Evaluation of the Leap motion Sensor as Controller of New Digital Musical Instruments. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/e0ec/447d7b97f80cd17f947eeea2c5094d698121.pdf (accessed on 4 July 2018).
- Howell, M.J.; Moore, A.G. Wedge: A Musical Interface for Building and Playing Composition-Appropriate Immersive Environments. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Symposium on 3D User Interfaces (3DUI), Arles, France, 23–24 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Perdana, I. Teaching elementary school students new method of music performance with Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Virtual Systems & Multimedia (VSMM), Hong Kong, China, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 273–277. [Google Scholar]
- Hemery, E.; Manitsaris, S.; Moutarde, F.; Volioti, C.; Manitsaris, A. Towards the Design of a Natural User Interface for Performing and Learning Musical Gestures. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 3, 6329–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volioti, C.; Hemery, E.; Manitsaris, S.; Teskouropoulou, V.; Yilmaz, E.; Moutarde, F.; Manitsaris, A. Music Gestural Skills Development Engaging Teachers, Learners and Expert Performers. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 3, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonteles, J.H.; Sousa, E.S.; Rodrigues, M.A.F. Visual and Interactive Performance of Particles Conducted by the Leap Motion for an Orchestral Arrangement. In Proceedings of the 2015 XVII Symposium on Virtual and Augmented Reality, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 25–28 May 2015; pp. 255–264. [Google Scholar]
- Kapp, K.M. The Gamification of Learning and Instruction: Game-Based Methods and Strategies for Training and Education, 1st ed.; Pfeiffer & Company: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pirker, J.; Pojer, M.; Holzinger, A.; Gütl, C. Gesture-Based Interactions in Video Games with the Leap Motion Controller. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–4 July 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10271, pp. 620–633. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Cai, S.; Ma, Y.; Liu, E. A Series of Leap Motion-Based Matching Games for Enhancing the Fine Motor Skills of Children with Autism. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 15th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies, Hualien, Taiwan, 6–9 July 2015; pp. 430–431. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, O.H.; Lee, S.T. A Study about Honey Bee Dance Serious Game for Kids Using Hand Gesture. Int. J. Multimedia Ubiquitous Eng. 2014, 9, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardovelli, T.A.; Frère, A.F. The design and evaluation of a peripheral device for use with a computer game intended for children with motor disabilities. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2015, 118, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chastine, J.; Kosoris, N.; Skelton, J. A study of gesture-based first person control. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Computer Games, Louisville, KY, USA, 30 July–1 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, V.T.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Jeong, Y.S. Easy-to-use virtual brick manipulation techniques using hand gestures. J. Supercomput. 2016, 72, 2752–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pastor, O.M. Operating Virtual Panels with Hand Gestures in Immersive VR Games: Experiences with the Leap Motion Controller. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality and Computer Graphics, Ugento, Italy, 12–15 June 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10324, pp. 299–308. [Google Scholar]
- Yanaka, K.; Ishiguro, D. Natural User Interface for Board Games Using Lenticular Display and Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2–7 August 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 528, pp. 552–557. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, F.; Esteves, J.S.; Carvalho, V.; Moreira, C.; Lourenço, P. Sign Language Learning Using the Hangman Videogame. In Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Ultra Modern Telecommunications and Control Systems and Workshops (ICUMT), Brno, Czech Republic, 6–8 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Xu, W.; Sweeney, L.; Li, Y.; Gross, R.; Yurovsky, D. New Directions in Contact Free Hand Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, San Antonio, TX, USA, 16 September–19 October 2007; pp. 389–392. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.M.; Hsia, C.H.; Liu, Y.F.; Yu, J.C.; Chu, M.H.; Le, T.N. Contact-free hand geometry-based identification system. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 11728–11736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Contact-free and pose-invariant hand-biometric-based personal identification system using RGB and depth data. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. C 2014, 15, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutellaa, E.; Hadid, A.; Bengherabi, M.; Ait-Aoudia, S. On the use of Kinect depth data for identity, gender and ethnicity classification from facial images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2015, 68, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, A.; Yadav, S.; Nigam, I.; Singh, R.; Vatsa, M. A Leap Password based Verification System. In Proceedings of the IEEE 7th International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Arlington, VA, USA, 8–11 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardos, A.M.; Sanchez, J.M.; Portillo, J.I.; Wang, X.; Besada, J.A.; Casar, J.R. Design and deployment of a contactless hand-shape identification system for smart spaces. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2016, 7, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.; Halevi, T.; Memon, N.D. Leap Motion Controller for Authentication via Hand Geometry and Gestures. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human Aspects of Information Security, Privacy, and Trust, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2–7 August 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9190, pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kamaishi, S.; Uda, R. Biometric Authentication by Handwriting Using Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication, Danang, Vietnam, 4–6 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guerra-Segura, E.; Travieso, C.M.; Alonso, J.B. Study of the variability of the Leap Motion’s measures for its use to characterize air strokes. Measurement 2017, 105, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigdor, D.; Wixon, D. Brave NUI World: Designing Natural User Interfaces for Touch and Gesture, 1st ed.; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Gauba, H.; Roy, P.P.; Dogra, D.P. A multimodal framework for sensor based sign language recognition. Neurocomputing 2017, 259, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Xi, B.; Zheng, N.; Fan, J. Training more discriminative multi-class classifiers for hand detection. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, G.; Lin, Y. A novel finger and hand pose estimation technique for real-time hand gesture recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 49, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautaray, S.S.; Agrawal, A. Vision based hand gesture recognition for human computer interaction: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2015, 43, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, J.; Murphy, R.R. Hand gesture recognition with depth images: A review. In Proceedings of the IEEE RO-MAN: The 21st IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Paris, France, 9–12 September 2012; pp. 411–417. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Mastnik, S.; André, E. EMG-based Hand Gesture Recognition for Realtime Biosignal Interfacing. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Gran Canaria, Spain, 13–16 January 2008; pp. 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Georgi, M.; Amma, C.; Schultz, T. Recognizing Hand and Finger Gestures with IMU based Motion and EMG based Muscle Activity Sensing. Biosignals 2015, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyali, A.; Hashimoto, N. Spectral Collaborative Representation based Classification for hand gestures recognition on electromyography signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2016, 24, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Rahaman, A.; Shuvo, M.F.; Ovi, M.A.S.; Rahman, M.M. Human hand gesture detection based on EMG signal using ANN. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Informatics, Electronics Vision (ICIEV), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 23–24 May 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z. Survey on 3D Hand Gesture Recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2016, 26, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichert, F.; Bachmann, D.; Rudak, B.; Fisseler, D. Analysis of the accuracy and robustness of the leap motion controller. Sensors 2013, 13, 6380–6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeragliuolo, A.H.; Hill, N.J.; Disla, L.; Putrino, D. Validation of the Leap Motion Controller using markered motion capture technology. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, J.Y.; Lulic, T.; Gonzalez, D.A.; Tran, J.; Dickerson, C.R.; Roy, E.A. Evaluation of a portable markerless finger position capture device: Accuracy of the Leap Motion controller in healthy adults. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guna, J.; Jakus, G.; Pogacnik, M.; Tomazic, S.; Sodnik, J. An analysis of the precision and reliability of the leap motion sensor and its suitability for static and dynamic tracking. Sensors 2014, 14, 3702–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitão, P.M.O. Analysis and Evaluation of Gesture Recognition Using LeapMotion. In Proceedings of the 10th Doctoral Symposium in Informatics Engineering, Porto, Portugal, 29–30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Uchidiuno, U.A.; Feng, Y.; Mentis, H.M.; Zahiri, H.; Park, A.E.; George, I.M. Efficiency and Accuracy of Kinect and Leap Motion Devices Compared to the Mouse for Intraoperative Image Manipulation; AMIA: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Gold, N. Lessons Learned in Exploring the Leap MotionTM Sensor for Gesture-Based Instrument Design; Goldsmiths University of London: London, UK, 2014; pp. 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, D.; Weichert, F.; Rinkenauer, G. Evaluation of the Leap Motion Controller as a New Contact-Free Pointing Device. Sensors 2015, 15, 214–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonizzi Barsanti, S.; Caruso, G.; Micoli, L.L.; Covarrubias Rodriguez, M.; Guidi, G. 3D Visualization of Cultural Heritage Artefacts with Virtual Reality devices. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-5/W7, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, N.; Horan, B.; McKenzie, S. Taking the LEAP with the Oculus HMD and CAD—Plucking at thin Air? Procedia Technol. 2015, 20, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsanti, S.G.; Caruso, G.; Guidi, G. Virtual navigation in the ancient Egyptian funerary rituals. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Virtual System & Multimedia (VSMM), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–21 October 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Caggianese, G.; Gallo, L.; Neroni, P. An Investigation of Leap Motion Based 3D Manipulation Techniques for Use in Egocentric Viewpoint. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality and Computer Graphics, Otranto, Italy, 15–18 June 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9769, pp. 318–330. [Google Scholar]
- Headleand, C.J.; Day, T.; Pop, S.R.; Ritsos, P.D.; John, N.W. A Cost-Effective Virtual Environment for Simulating and Training Powered Wheelchairs Manoeuvres. Stud. Health Technol. Inf. 2016, 220, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Avola, D.; Cinque, L.; Levialdi, S.; Petracca, A.; Placidi, G.; Spezialetti, M. Markerless Hand Gesture Interface Based on LEAP Motion Controller. In DMS; Knowledge Systems Institute Graduate School: Skokie, IL, USA, 2014; pp. 260–266. [Google Scholar]
- Rossol, N.; Cheng, I.; Shen, R.; Basu, A. Touchfree medical interfaces. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 6597–6600. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, M. GPU-Based Realtime Hand Gesture Interaction and Rendering for Volume Datasets Using Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Cyberworlds, Santander, Spain, 6–8 October 2014; pp. 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Bercu, Z.L.; Patil, V.V.; Patel, R.S.; Kim, E.; Nowakowski, S.F.; Lookstein, R.A.; Fischman, A.M. Abstract No. 426—Use of hands free gesture-based imaging control for vessel identification during hepatic transarterial chemoembolization and selective internal radiotherapy procedures. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, S186–S187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Santos, F.; Fonseca, I.; Tavares, T. ATreVEE IN: Using Natural Interaction in Procedure Simulator for Training in the Electricity Sector. In Proceedings of the 14th Brazilian Symposium on Computer Games and Digital Entertainment (SBGames), Piaui, Brazil, 11–13 November 2015; pp. 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias, M.; Bordegoni, M.; Cugini, U. A hand gestural interaction system for handling a desktop haptic strip for shape rendering. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 233, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcao, C.; Lemos, A.C.; Soares, M. Evaluation of Natural User Interface: A Usability Study Based on the Leap Motion Device. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 3, 5490–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsabasis, P.; Vosinakis, S. Adult and Children User Experience with Leap Motion in Digital Heritage: The Cycladic Sculpture Application. In Proceedings of the Euro-Mediterranean Conference, Nicosia, Cyprus, 31 October–5 November 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 10058, pp. 350–361. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Kuijper, A.; Sourin, A. Exploration of Natural Free-Hand Interaction for Shape Modeling Using Leap Motion Controller. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Cyberworlds (CW), Chongqing, China, 28–30 September 2016; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Fellner, D.W.; Kuijper, A.; Sourin, A. Mid-Air Gestures for Virtual Modeling with Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Distributed, Ambient, and Pervasive Interactions, Toronto, ON, Canada, 17–22 July 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9749, pp. 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Shiba, Y.; Sasakura, M. Visual Interface and Interaction Design for Self-Service Orders at a Restaurant. In Proceedings of the 2016 20th International Conference Information Visualisation (IV), Lisbon, Portugal, 19–22 July 2016; pp. 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama, S.; Shibata, M.; Hiratsuka, S. A study of displaying 3D electronic text using augmented reality via Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Budapest, Hungary, 9–12 October 2016; pp. 3015–3020. [Google Scholar]
- Virag, I.; Stoicu-Tivadar, L.; Crişan-Vida, M. Gesture-Based Interaction in Medical Interfaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th International Symposium on Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics (SACI), Timisoara, Romania, 12–14 May 2016; pp. 519–523. [Google Scholar]
- Vosinakis, S.; Koutsabasis, P.; Makris, D.; Sagia, E. A Kinesthetic Approach to Digital Heritage Using Leap Motion: The Cycladic Sculpture Application. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Games and Virtual Worlds for Serious Applications (VS-Games), Barcelona, Spain, 7–9 September 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Seah, H.S. Interaction in marker-less augmented reality based on hand detection using leap motion. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Virtual-Reality Continuum and Its Applications in Industry, Zhuhai, China, 3–4 December 2016; pp. 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Kyto, M.; Dhinakaran, K.; Martikainen, A.; Hamalainen, P. Improving 3D Character Posing with a Gestural Interface. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2017, 37, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantecón, T.; del-Blanco, C.R.; Jaureguizar, F.; García, N. Hand Gesture Recognition Using Infrared Imagery Provided by Leap Motion Controller. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2016, 10016, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Strang, G. Introduction to Linear Algebra, 4th ed.; Wellesley-Cambridge Press: Wellesley, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kalman, R.E. A New Approach to Linear Filtering And Prediction Problems. ASME J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.C.P.; Clua, E.W.G.; Montenegro, A.A. Sensor Data Fusion for Full Arm Tracking Using Myo Armband and Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the 14th Brazilian Symposium on Computer Games and Digital Entertainment (SBGAMES), Piauí, Brazil, 11–13 November 2015; pp. 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X. Markerless Human-Manipulator Interface Using Leap Motion with Interval Kalman Filter and Improved Particle Filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2016, 12, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, G.; Dominio, F.; Zanuttigh, P. Hand gesture recognition with jointly calibrated Leap Motion and depth sensor. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2016, 75, 14991–15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Y. Hand fine-motion recognition based on 3D Mesh MoSIFT feature descriptor. Neurocomputing 2015, 151, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Jiang, N.; Chang, J.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J.J. Understanding the impact of multimodal interaction using gaze informed mid-air gesture control in 3D virtual objects manipulation. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2017, 105, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, J. Hand Gesture Recognition in Multi-space of 2D/3D. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 2015, 15, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Nagamune, K.; Uozumi, Y.; Sakai, Y. Automation of the Simple Test for Evaluating Hand Function Using Leap Motion Controller. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2016, 9738, 312–319. [Google Scholar]
- Vivian, R. Propositions for a Mid-Air Interactions System Using Leap-Motion for a Collaborative Omnidirectional Immersive Environment. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Distributed, Ambient, and Pervasive Interactions, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–14 July 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10291, pp. 203–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zaiti, I.A.; Pentiuc, S.G.; Vatavu, R.D. On free-hand TV control: Experimental results on user-elicited gestures with Leap Motion. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2015, 19, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempel, D.; Camilleri, M.J.; Lee, D.L. The design of hand gestures for human—Computer interaction: Lessons from sign language interpreters. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2014, 72, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pititeeraphab, Y.; Choitkunnan, P.; Thongpance, N.; Kullathum, K.; Pintavirooj, C. Robot-arm control system using LEAP motion controller. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Engineering (BME-HUST), Hanoi, Vietnam, 5–6 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sartori, E.; Fiorini, P.; Muradore, R. Cutaneous Feedback in Teleoperated Robotic Hands; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Sun, L.; Lu, X.; Hao, J.; Liu, J. A practical, fast, and low-cost kinematic calibration scheme for a deformable manipulator by using Leap Motion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Qingdao, China, 3–7 December 2016; pp. 719–724. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Control of human arm movement in machine-human cooperative welding process. Control Eng. Pract. 2014, 32, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, I.; Uhl, A.; Meschtscherjakov, A.; Tscheligi, M. Design and Exploration of Mid-Air Authentication Gestures. ACM Trans. Interact. Intell. Syst. 2016, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerefeyn, S.; Maleshkov, S. Manipulation of virtual objects through a LeapMotion optical sensor. Int. J. Comput. Sci. 2015, 12, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chuan, C.H.; Regina, E.; Guardino, C. American Sign Language Recognition Using Leap Motion Sensor. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Detroit, MI, USA, 3–6 December 2014; pp. 541–544. [Google Scholar]
- Vamsikrishna, K.M.; Dogra, D.P.; Desarkar, M.S. Computer-Vision-Assisted Palm Rehabilitation with Supervised Learning. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 2016, 63, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Tong, Z.; Chu, J. Dynamic Hand Gesture Recognition with Leap Motion Controller. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuri, F.; Piumatti, G. A preliminary study of a hybrid user interface for augmented reality applications. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Intelligent Technologies for Interactive Entertainment (INTETAIN), Turin, Italy, 10–12 June 2015; pp. 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Avola, D.; Del Buono, A.; Gianforme, G.; Paolozzi, S.; Wang, R. SketchML a Representation Language for Novel Sketch Recognition Approach. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, Corfu, Greece, 9–13 June 2009; p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Nymoen, K.; Haugen, M.R.; Jensenius, A.R. MuMYO—Evaluating and Exploring the MYO Armband for Musical Interaction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on New Interfaces For Musical Expression, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 31 May–3 June 2015; pp. 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, L.C.; Hatch, G.; Ampanozi, G.; Thali, M.J.; Ross, S. You Can’t Touch This. Surg. Innov. 2012, 19, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardos, A.M.; Sánchez, J.M.; Portillo, J.I.; Besada, J.A.; Casar, J.R. A Contactless Identification System Based on Hand Shape Features. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 52, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Zhang, P. A Markerless Human-Robot Interface Using Particle Filter and Kalman Filter for Dual Robots. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 2257–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heloir, A.; Nunnari, F. Toward an intuitive sign language animation authoring system for the deaf. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2016, 15, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oropesa, I.; de Jong, T.L.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, P.; Dankelman, J.; Gomez, E.J. Feasibility of tracking laparoscopic instruments in a box trainer using a Leap Motion Controller. Measurement 2016, 80, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahanas, V.; Loukas, C.; Georgiou, K.; Lababidi, H.; Al-Jaroudi, D. Virtual reality-based assessment of basic laparoscopic skills using the Leap Motion controller. Surg. Endosc. 2017, 31, 5012–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güttler, J.; Shah, R.; Georgoulas, C.; Bock, T. Unobtrusive Tremor Detection and Measurement via Human-Machine Interaction. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 63, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, M.; Hondori, H.M.; McKenzie, A.; Dodakian, L.; Lopes, C.V.; Cramer, S.C. Free-hand interaction with leap motion controller for stroke rehabilitation. In CHI Extended Abstracts; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1663–1668. [Google Scholar]
- Petracca, A.; Carrieri, M.; Avola, D.; Moro, S.B.; Brigadoi, S.; Lancia, S.; Spezialetti, M.; Ferrari, M.; Quaresima, V. A virtual ball task driven by forearm movements for neuro-rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Virtual Rehabilitation Proceedings (ICVR), Valencia, Spain, 9–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, C.; Lau, J.; Huynh, D.; Albertson, S.; Beem, J.; Qian, E. Capturing the Perceived Phantom Limb through Virtual Reality. Adv. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrieri, M.; Petracca, A.; Lancia, S.; Moro, S.B.; Brigadoi, S.; Spezialetti, M.; Ferrari, M.; Placidi, G.; Quaresima, V. Prefrontal Cortex Activation upon a Demanding Virtual Hand-Controlled Task: A New Frontier for Neuroergonomics. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetna Naidu, A.G. Hand Gesture Recognition Using Leap Motion Controller. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2016, 5, 436–441. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, G.L.; Quesada, L.; Guerrero, L.A. A Gesture-Based Interaction Approach for Manipulating Augmented Objects Using Leap Motion. In IWAAL; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; Volume 9455, pp. 231–243. [Google Scholar]
- McCartney, R.; Yuan, J.; Bischof, H.P. Gesture Recognition with the Leap Motion Controller. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, Computer Vision, & Pattern Recognition, Sydney, Australia, 10–11 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Toghiani-Rizi, B.; Lind, C.; Svensson, M.; Windmark, M. Static Gesture Recognition Using Leap Motion. arxiv, 2017; arXiv:1705.05884. [Google Scholar]
- Qingchao, X.; Jiangang, C. The Application of Leap Motion in Astronaut Virtual Training. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2015; Volume 187. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Horie, R. An Improved Computer Interface Comprising a Recurrent Neural Network and a Natural User Interface. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 60, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, J.; Menin, A.; Nedel, L. Lossless Multitasking: Using 3D Gestures Embedded in Mouse Devices. In Proceedings of the 2016 XVIII Symposium on Virtual and Augmented Reality (SVR), Gramado, Brazil, 21–24 June 2016; pp. 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J. Multi-LeapMotion sensor based demonstration for robotic refine tabletop object manipulation task. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2016, 1, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, D.; Kruijff, E.; LaViola, J.J., Jr.; Poupyrev, I.P. 3D User Interfaces: Theory and Practice, CourseSmart eTextbook; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Swan, J.E.; Moser, K.R. Evaluation of User-Centric Optical See-Through Head-Mounted Display Calibration Using a Leap Motion Controller. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium on 3D User Interfaces (3DUI), Greenville, SC, USA, 19–20 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vosinakis, S.; Koutsabasis, P. Evaluation of visual feedback techniques for virtual grasping with bare hands using Leap Motion and Oculus Rift. Virtual Real. 2018, 22, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, J. SUS-A Quick and Dirty Usability Scale. Usability Eval. Ind. 1996, 189, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bangor, A.; Kortum, P.; Miller, J. Determining What Individual SUS Scores Mean: Adding an Adjective Rating Scale. J. Usability Stud. 2009, 4, 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.R.; Sauro, J. The Factor Structure of the System Usability Scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human Centered Design, San Diego, CA, USA, 19–24 July 2009; Kurosu, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 94–103. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, J.C.; Verbeek, F.J. Pointing task evaluation of leap motion controller in 3d virtual environment. Creating Differ. 2014, 78, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, L.; Bruno, F.; Muzzupappa, M. Virtual museum system evaluation through user studies. J. Cult. Heritage 2017, 26, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standardization, I.O.F. Ergonomics of Human-System Interaction—Part 210: Human-Centred Design for Interactive Systems; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikarla, V.K.; Sodnik, J.; Szolgay, P.; Jakus, G. Exploring direct 3D interaction for full horizontal parallax light field displays using leap motion controller. Sensors 2015, 15, 8642–8663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laugwitz, B.; Held, T.; Schrepp, M. Construction and Evaluation of a User Experience Questionnaire. In Proceedings of the Symposium of the Austrian HCI and Usability Engineering Group, Graz, Austria, 20–21 November 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Gewrmany, 2008; pp. 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Schrepp, M.; Hinderks, A.; Thomaschewski, J. Design and Evaluation of a Short Version of the User Experience Questionnaire (UEQ-S). Int. J. Interact. Multimedia Artif. Intell. 2017, 4, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.Y. Hybrid reality-based user experience and evaluation of a context-aware smart home. Comput. Ind. 2016, 76, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, B. A Review of the Mental Workload Literature; Defense Technical Information Center: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Moustafa, K.; Luz, S.; Longo, L. Assessment of Mental Workload: A Comparison of Machine Learning Methods and Subjective Assessment Techniques. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Human Mental Workload: Models and Applications, Dublin, Ireland, 28–30 June 2017; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 30–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, S.G.; Staveland, L.E. Development of NASA-TLX (Task Load Index): Results of Empirical and Theoretical Research. Adv. Psychol. 1988, 52, 139–183. [Google Scholar]
- Wickens, C.D. Multiple resources and performance prediction. Theor. Issues Ergon. Sci. 2002, 3, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.R.; Tangermann, M.; Dornhege, G.; Krauledat, M.; Curio, G.; Blankertz, B. Machine learning for real-time single-trial EEG-analysis: From brain—Computer interfacing to mental state monitoring. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 167, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajani, H.; Garbey, M.; Omurtag, A. Measuring Mental Workload with EEG+fNIRS. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unni, A.; Ihme, K.; Surm, H.; Weber, L.; Lüdtke, A.; Nicklas, D.; Jipp, M.; Rieger, J.W. Brain activity measured with fNIRS for the prediction of cognitive workload. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Infocommunications (CogInfoCom), Gyor, Hungary, 19–21 October 2015; pp. 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- McDuff, D.J.; Hernandez, J.; Gontarek, S.; Picard, R.W. COGCAM: Contact-free Measurement of Cognitive Stress During Computer Tasks with a Digital Camera. In Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 7–12 May 2016; pp. 4000–4004. [Google Scholar]
- Procházka, A.; Schätz, M.; Vyšata, O.; Vališ, M. Microsoft kinect visual and depth sensors for breathing and heart rate analysis. Sensors 2016, 16, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burno, R.A.; Wu, B.; Doherty, R.; Colett, H.; Elnaggar, R. Applying Fitts’ Law to Gesture Based Computer Interactions. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 3, 4342–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramcharitar, A.; Teather, R.J. A Fitts’ Law Evaluation of Video Game Controllers: Thumbstick, Touchpad and Gyrosensor. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 6–11 May 2017; pp. 2860–2866. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, F.R.; Abyarjoo, F.; Barreto, A.; Rishe, N.; Adjouadi, M. Interaction Design for 3D User Interfaces: The World of Modern Input Devices for Research, Applications, and Game Development; A. K. Peters, Ltd.: Natick, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fitts, P.M. The information capacity of the human motor system in controlling the amplitude of movement. J. Exp. Psychol. 1954, 47, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukoreff, R.W.; MacKenzie, I.S. Towards a standard for pointing device evaluation, perspectives on 27 years of Fitts’ law research in HCI. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2004, 61, 751–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windolf, M.; Götzen, N.; Morlock, M. Systematic accuracy and precision analysis of video motion capturing systems—Exemplified on the Vicon-460 system. J. Biomech. 2008, 41, 2776–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.T.; Pathirana, P.N. Deducing the reachable space from fingertip positions. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; Volume 2015, pp. 7578–7581. [Google Scholar]
- Wachs, J.P.; Kölsch, M.; Stern, H.; Edan, Y. Vision-based Hand-gesture Applications. Commun. ACM 2011, 54, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J. Usability Engineering; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wickens, C.D. The effects of control dynamics on performance. In Handbook of Perception and Human Performance; Cognitive Processes and Performance; John Wiley & Sons: Oxford, UK, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Teather, R.J.; Pavlovych, A.; Stuerzlinger, W.; MacKenzie, I.S. Effects of tracking technology, latency, and spatial jitter on object movement. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Symposium on 3D User Interfaces, Lafayette, LA, USA, 14–15 March 2009; pp. 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- BS ISO 9241-960. Ergonomics of Human-System Interaction-Part 960: Framework and Guidance for Gesture Interactions. Available online: https://www.techstreet.com/standards/iso-9241-960-2017?product_id=1993768 (accessed on 4 July 2018).




| Device | Application | Methods | References | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myo | Gesture Recognition | Spectral CRC recognition vs. Myo-SDK recognition | [159] | 97.3% accuracy |
| Myo & LMC | Myo-SDK gestures and LMC-SDK gestures | [54] | n/a | |
| LMC evaluated with optical motion capture system. EMG data compared with BioFlex EMG sensors. | [215] | n/a | ||
| Data Fusion and Tracking | Data fusion using Kalman filter | [194] | n/a | |
| Kinect | Gesture Recognition | Kumar et al. provide a detailed survey on Kinect based gesture recognition systems | [152] | – |
| SLR | Gaussian skin colour model; LDA dimension reduction and classification | [111] | 99.8% | |
| NUI | Thresholding and blob search | [216] | n/a | |
| LMC | Authentication | Finger length and distance to palm; NB, RDF and NN | [146] | Acceptance rate (1% false positive): 75.78% (NB), 78.04% (RDF), 78.55% (NN) |
| Normalization scheme and DTW to calculate distance between gestures | [208] | 86%–91% accuracy | ||
| LMC hand model and circle gesture, RDFC | [148] | 99% static, 98% dyn. accuracy. Equal Error Rate (EER) | ||
| LMC SDK-Hand model values; k-NN, NN, SVM, logistic regression, functional trees, logic trees | [217] | ≥90% correct classified instances | ||
| Human-Robot Interaction | Rotation gesture and grab strength; inverse kinematics | [81] | n/a | |
| Hand position tracking, map gestures to robot commands | [91,92,93] | n/a | ||
| Hand tracking. Particle filter and Kalman filter | [218] | n/a | ||
| LMC hand tracking, Tool Center Point (TCP) mapped to hand position | [84] | Tracking Error ≤ | ||
| Fingertip Positions (FPs) mapped to robot TCP | [87] | Repeatability 1 | ||
| SLR | FPs, position of joints, tip velocity, pinch strength. Recognition with machine learning | [210] | 72.78% (k-NN), 79.83% (SVM) recognition rate | |
| Multi LMC, covariance intersection and Kalman (fusion), FPs, joints HMM(recognition ) | [107] | Accuracy: Multi LMC ≥ 84.68%, Single LMC ≥ 68.78% | ||
| Leap Trainer (LeapTrainer: https://github.com/roboleary/LeapTrainer.js (accessed on 12 March 2018)) for gesture design. Motion tracking, GTM, ANN, CC for recognition 3d FPs, ANN for | [109] | 52.56% (GTM), 44.87% (ANN), 35.90% (CC) accuracy | ||
| Palm translation (phalanges to palm distance), bone translation (phalanges to next phalanges start). Classification with SVM | [112] | Palm translation 99.28%, bone translation 98.96% accuracy | ||
| Kinect & LMC | FPs and direction, palm of hand. HMM, BLSTM-NN based sequential classifiers and combination of both | [152] | Overall accuracy (97.85%, 94.55%) (single handed, double handed) combined, (97.38%, 93.64%) HMM, (87.63%, 83.49%) BLSTM-NN | |
| Sign Language Training and Transmission | Kinect for FaceShift and LMC to capture hand movements | [219] | n/a | |
| Leap Trainer for gesture, pose learning and recognition | [141] | n/a | ||
| LMC | Surgery Training | Speed, acceleration, smoothness, distance between hands | [73] | Tracking loss 31.9% |
| Track positions of instrument over LMC | [220,221] | static precision ≤ , dynamic ≥ 2 ≤ 15 | ||
| NUI (VR) | Hand gesture interface based on LMC-SDK | [69,105,118,121,123,127,139,170,171,172,173,174] | n/a | |
| NUI (Desktop) | Hand gesture interface based on LMC-SDK | [53,55,56,93,120,124,126,128,133,137,168,175,176,177,178,179,180,181,182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189,190] | n/a | |
| Rehabilitation | LMC hand tracking, UNITY, evaluation against Novint Falcon | [66] | device evaluation | |
| Joints of fingers, angles between them | [58] | error: ≥ 2.5° ≤ 9.02° | ||
| FPs, direction of forearm and hand, palm normal, joint angle of wrist and knuckles, static. Decision-tree, k-NN, and SVM classification | [67] | Re substitution error: Decision-tree ≤ 23.04%, k-NN ≤ 0.49%, SVM ≤ 2.1% | ||
| FPs, roll, pitch, yaw Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) | [222] | feasibility study | ||
| Generate hand-model of FPs direction vectors (inverse kinematics) | [223] | tracking issues | ||
| LMC hand tracking and gestures | [70,200,224,225] | n/a | ||
| Palm tracking, distance between FPs and palm, angle between fingertip vector and vector from wrist to palm. LDA, SVM, CRF, HMM and combinations for classification | [211] | SVM 88.44%, LDA 87.67%, SVM+CRF 98.74%, LDA+CRF 99.42%, SVM+HMM 98.56%, LDA+HMM 98.96% | ||
| Rehabilitation / Fusion | Multi LMC, motion tracking; Iterative Closest Point (ICP) | [63] | n/a | |
| Prefrontal Cortex Activation (Immersive Environments) | LMC-SDK hand orientation and FPs, 20 channels FNIRS, heart rate; Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) | [226] | user experiment | |
| Gesture Recognition | Distance of FPs to palm; comparing to reference vector in database | [227] | Accuracy with Cosine similarity metric 90%, Euclidean 88.22%, Jaccard 86%, dice similarity 83.11% | |
| FPs ANN | [79] | accuracy ≥ 70.52% ≤ 87.6% | ||
| FPs, scikit-learn (scikit-learn, http://scikit-learn.org/stable/ (accessed on 12 March 2018)) (SVM) | [228] | Accuracy: ≥ 75% | ||
| Palm direction, palm normal, FPs, palm centre. HCNF classifier | [212] | Two datasets: 95% and 89.5% accuracy | ||
| FPs tracking. Built-in gestures | [213] | accuracy at 400 and 800 dynamic 78%, static 90%, > 1000 : dynamic 2%, static 85% | ||
| Motion tracking, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and time series recognition with HMMs for gesture detection | [229] | CNN 92.4%, HMMs 50% for time series | ||
| Distance between palm centre and fingertips, k-NN, Multi Layer Perceptron (MLP), Multinomial Logistic Regression (MLR) classification (static) | [230] | k-NN ≥ 70% ≤ 95%, MLP 70% ≤ 90%, MLR 85% ≤ 90% | ||
| LMC hand tracking, threshold-based gestures | [138] | ≥93% | ||
| Grammar of air gestures | [201] | Extended Backus-Naur | ||
| LMC-SDK skeletal tracking | [231] | Mathematical model of hand occlusion | ||
| Centre position of hand, Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) classification | [232] | Recognition rate ≥ 77% | ||
| Hardware Design | LMC on top of mouse device. Built-in gestures | [233] | Hardware design, user experiment | |
| Multiple Leap Motions | Sum of angles of first three joints and the lateral movement angle of each finger; Self-Calibration | [234] | simple kinematic model of finger |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bachmann, D.; Weichert, F.; Rinkenauer, G. Review of Three-Dimensional Human-Computer Interaction with Focus on the Leap Motion Controller. Sensors 2018, 18, 2194. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072194
Bachmann D, Weichert F, Rinkenauer G. Review of Three-Dimensional Human-Computer Interaction with Focus on the Leap Motion Controller. Sensors. 2018; 18(7):2194. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072194
Chicago/Turabian StyleBachmann, Daniel, Frank Weichert, and Gerhard Rinkenauer. 2018. "Review of Three-Dimensional Human-Computer Interaction with Focus on the Leap Motion Controller" Sensors 18, no. 7: 2194. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072194
APA StyleBachmann, D., Weichert, F., & Rinkenauer, G. (2018). Review of Three-Dimensional Human-Computer Interaction with Focus on the Leap Motion Controller. Sensors, 18(7), 2194. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072194





