Performance Analysis of GPS/BDS Dual/Triple-Frequency Network RTK in Urban Areas: A Case Study in Hong Kong
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hong Kong GNSS Network RTK Service Platform
- Decode the data from Hong Kong SatRef.
- Store observations and ephemeris in the format of RINEX.
- Correct the antenna phase center offset.
- Detect the outlier of the observation and repair cycle slips.
- Fix the double difference ambiguity between the reference stations.
- Estimate the double difference tropospheric delay and ionospheric delay.The tropospheric delay can be divided into two parts: the hydrostatic delay and the non- hydrostatic or wet delay. We declined the first form by using the empirical model. For the wet delay, we estimated it together with ambiguities in the data processing. Once the ambiguity was fixed correctly, the ionospheric delay could be estimated using the following observation combination,where is the ionospheric scale factor defined with respect to the first-order ionospheric delay on the L1 carrier (); ∆∇Φ is the double difference carrier phase observation; is the fixed double difference ambiguity; and λ is the wavelength.
- Generate VRS corrections.VRS corrections include the tropospheric delay, ionospheric delay, orbit error, etc. of the VRS observation.
- Transfer RTCM (Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services) data to users.In this study, the RTCM-3 MSM4 (Multiple Signal Message 4) was applied. This generated RTCM data were sent to the user through a wireless connection, using the Networked Transport of RTCM via the Internet Protocol (NTRIP).
- Allow the processing of data from many GNSS (GPS, BDS, GLONASS, etc.).
- Provide centimeter-level accuracy NRTK service.
3. Ambiguity Resolution for Triple-Frequency Signals
4. Experiment and Analysis
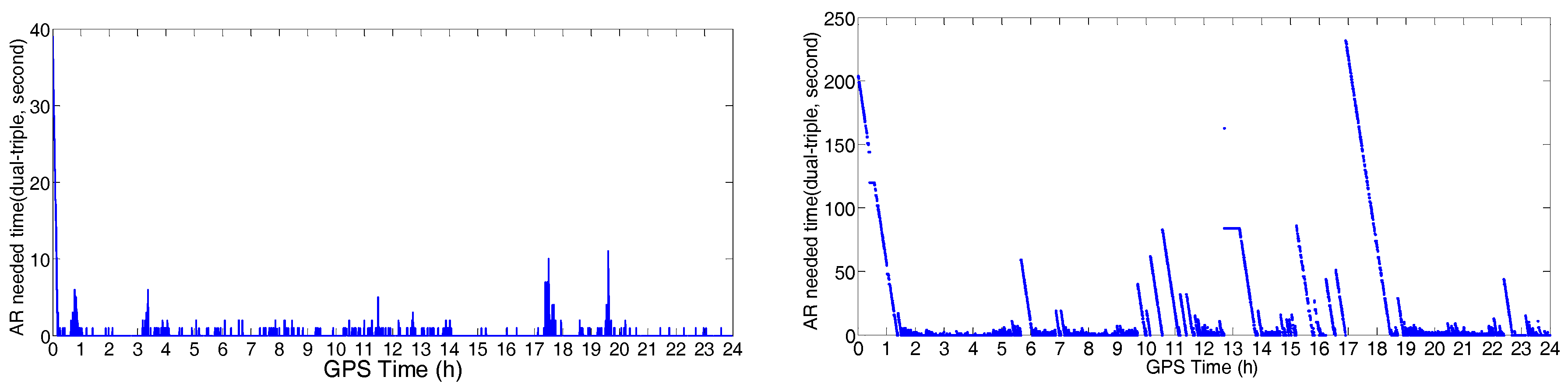
4.1. Initialization Time Test
4.2. Positioning Accuracy Test
4.3. Ambiguity Successfully Fixed Rate Test
4.4. Triple-Frequency GNSS RTK Test
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The initialization time of the NRTK varied with the number of visible satellites and the quality of the observation.
- (2)
- Centimeter-level NRTK service could be provided for users over Hong Kong by using the Hong Kong GNSS Network RTK Service Platform.
- (3)
- In urban areas, GPS/BDS NRTK services for static, walking, and driving users significantly improved the ambiguity successfully fixed rate of NRTK service when compared with that using GPS signal alone. In typical urban environment, the RTK positioning ambiguity successfully fixed rate with GPS/BDS was 33.4–72.4%, which was about 12.7–32.4% with GPS only.
- (4)
- The BDS triple-frequency observation significantly improved the initialization time and positioning accuracy of RTK in Hong Kong. For a baseline of about 20 km, the initialization time was reduced to 1 s with triple-frequency data, compared with 23 s with dual-frequency data.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, G. GPS: Theory, Algorithms and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; ISBN 9783540727149. [Google Scholar]
- Rizos, C. Alternatives to current GPS-RTK services and some implications for CORS infrastructure and operations. GPS Solut. 2007, 11, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skone, S.; Hoyle, V. Canadian GPS Network for Ionosphere Monitoring (CANGIM). GPS Solut. 2005, 9, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twilley, R.J.; Digney, P.W. The Australian regional GPS network. Phys. Chem. Earth Part A Solid Earth Geod. 2001, 26, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, J.E.J.; McCallum, J.N.; Reid, P.B.; McCulloch, P.M.; Baynes, B.E.; Dickey, J.M.; Shabala, S.S.; Watson, C.S.; Titov, O.; Ruddick, R.; et al. The AuScope geodetic VLBI array. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholarin, E.A.; Awange, J.L. Global navigation satellite system (GNSS). In Environmental Project Management; Environmental Science and Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-27649-6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.M.; Wang, Q.; You, X.Z. Numerical analysis of contemporary horizontal tectonic deformation fields in China from GPS data. Acta Seismol. Sin. 2005, 18, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mageed, K.M.A. Comparison of GPS commercial software packages to processing static baselines up to 30 km. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2015, 10, 10640–10650. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Ji, S. Data quality assessment and the positioning performance analysis of BeiDou in Hong Kong. Surv. Rev. 2015, 47, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ji, S.; Chen, W.; Weng, D. A new ionosphere-free ambiguity resolution method for long-range baseline with GNSS triple-frequency signals. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 1600–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Li, J.L.; Xu, J.Y.; Tang, J.; Guo, H.R.; He, H.B. Contribution of the Compass satellite navigation system to global PNT users. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 2813–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Deng, J.; Lu, X.; Song, Z.; Xu, Y. A New GNSS Single-Epoch Ambiguity Resolution Method Based on Triple-Frequency Signals. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhu, B. Detection and Correction of Cycle Slip in Triple-Frequency GNSS Positioning. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 12584–12595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Chen, W.; Ding, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Hu, C. Potential benefits of GPS/GLONASS/GALILEO integration in an urban canyon—Hong Kong. J. Navig. 2010, 63, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Rizos, C. Three Carrier Approaches for Future Global, Regional and Local GNSS Positioning Services: Concepts and Performance Perspectives. In Proceedings of the 18th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2005), Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2005; pp. 2277–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y. GNSS three carrier ambiguity resolution using ionosphere-reduced virtual signals. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 847–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, Z.; Liu, J. Precise relative positioning using real tracking data from COMPASS GEO and IGSO satellites. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadarajah, N.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Raziq, N. BeiDou inter-satellite-type bias evaluation and calibration for mixed receiver attitude determination. Sensors 2013, 13, 9435–9463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Teunissen, P.; Nakamura, S. Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Odolinski, R.; Odijk, D. Instantaneous BeiDou+GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles. J. Geod. 2014, 88, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O. Orbit and clock analysis of Compass GEO and IGSO satellites. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.R.; Khoo, H.S.; Goh, P.C.; Law, C.L. Development and assessment of GPS virtual reference stations for RTK positioning. J. Geod. 2003, 77, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizos, C. Network RTK Research and Implementation: A Geodetic Perspective. J. Glob. Position. Syst. 2002, 1, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dao, T.H.D.; Alves, P.; Lachapelle, G. Performance Evaluation of Multiple Reference Station GPS RTK for a Medium Scale Network. Positioning 2004, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, Y.; Rizos, C. Locata-based precise point positioning for kinematic maritime applications. GPS Solut. 2014, 19, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forssell, B.; Martin-Neira, M.; Harrisz, R. A Carrier phase ambiguity resolution in GNSS-2. Proc. ION GPS 1997, 10, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar]
- Vollath, U.; Birnbach, S.; Landau, H.; Fraile-Ordonez, J.M.; Martin-Neira, M. Analysis of three-carrier ambiguity resolution (TCAR) technique for precise relative positioning in GNSS-2. In Proceedings of the 2nd European symposium on Global Navigation Satellite Systems, Toulouse, France, 20–23 October 1998. [Google Scholar]
- De Jonge, P.J.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Jonkman, N.F.; Joosten, P. The distributional dependence of the range on triple frequency GPS ambiguity resolution. In Proceedings of the ION-NTM 2000, Anaheim, CA, USA, 26–28 January 2000; Volume 5, pp. 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hatch, R.; Jung, J.; Enge, P.; Pervan, B. Civilian GPS: The benefits of three frequencies. GPS Solut. 2000, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: A method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J. Geod. 1995, 70, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Joosten, P.; Tiberius, C. A comparison of TCAR, CIR and LAMBDA GNSS ambiguity resolution. In Proceedings of the 15th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 2002), Portland, OR, USA, 24–27 September 2002; pp. 2799–2808. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Li, B. A benefit of multiple carrier GNSS signals: Regional scale network-based RTK with doubled inter-station distances. J. Spat. Sci. 2008, 53, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Feng, Y.; Shen, Y. Three carrier ambiguity resolution: Distance-independent performance demonstrated using semi-generated triple frequency GPS signals. GPS Solut. 2010, 14, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Deng, C.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Triple-frequency carrier ambiguity resolution for Beidou navigation satellite system. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skone, S.; Shrestha, S.M. Limitations in DGPS positioning accuracies at low latitudes during solar maximum. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 81-1–81-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gao, S.; Hu, C.; Chen, Y.; Ding, X. Effects of ionospheric disturbances on GPS observation in low latitude area. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.P.; Tu, Y.M.; Ji, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Weng, D.; Ding, X.; Hu, T. A 2-d ionospheric model for low latitude area-Hong Kong. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Verhagen, S. The GNSS ambiguity ratio-test revisited: A better way of using it. Surv. Rev. 2009, 41, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. The ratio test for future GNSS ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkins, A. Increasing GNSS RTK availability with a new single-epoch batch partial ambiguity resolution algorithm. GPS Solut. 2011, 15, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






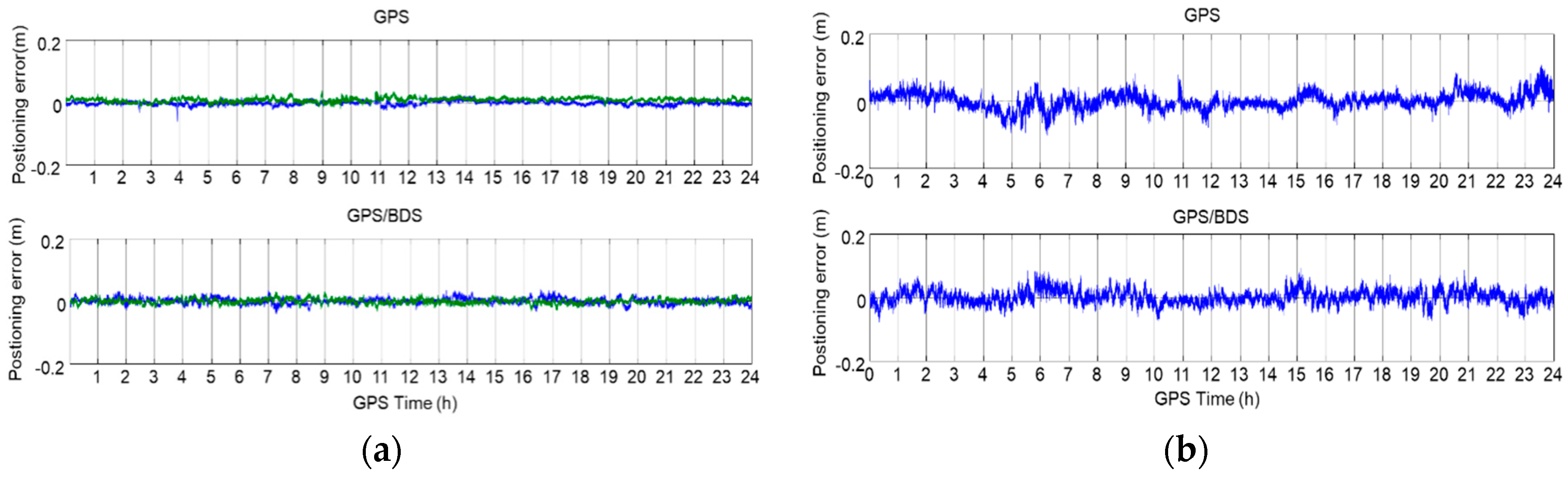


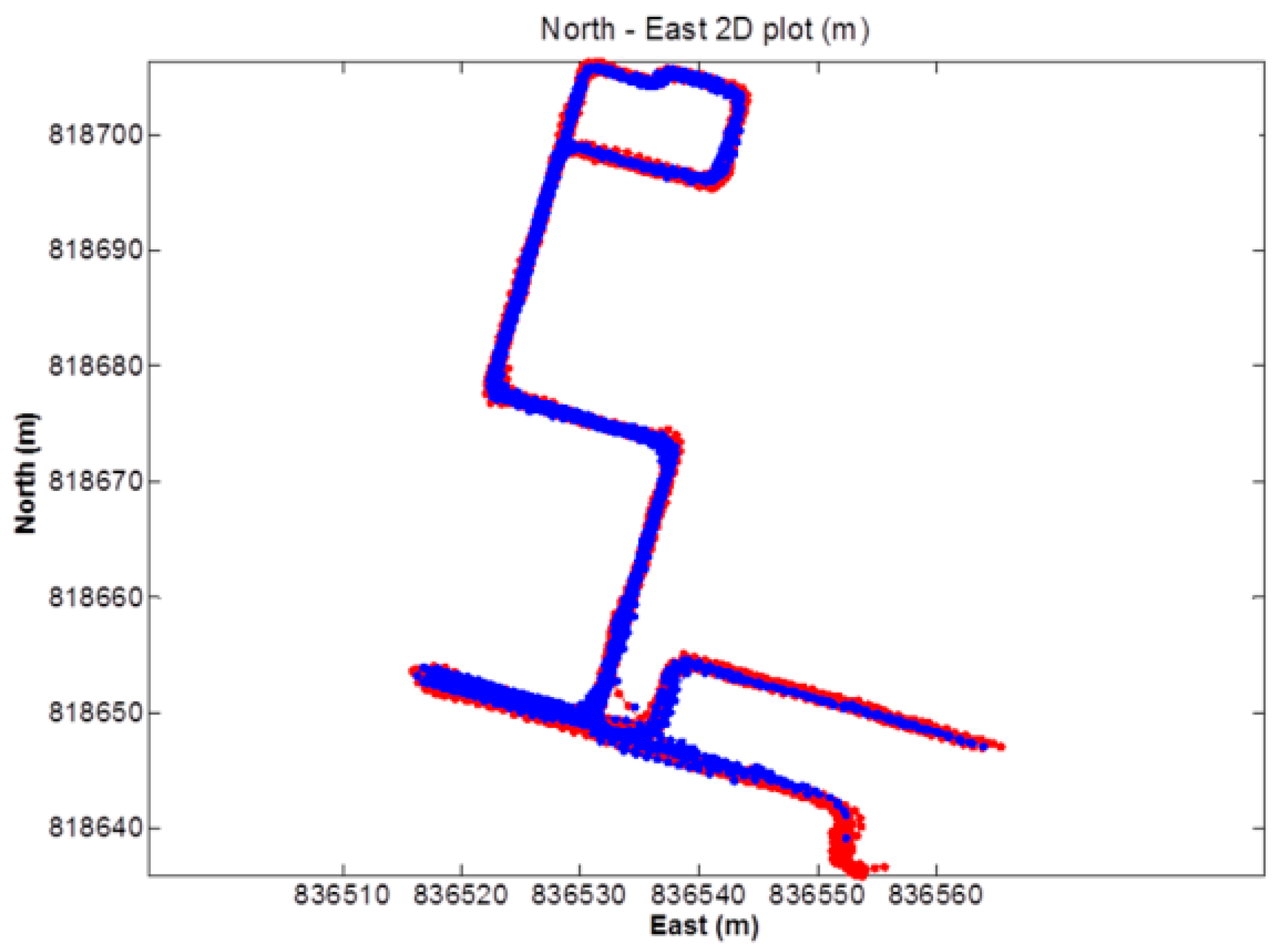


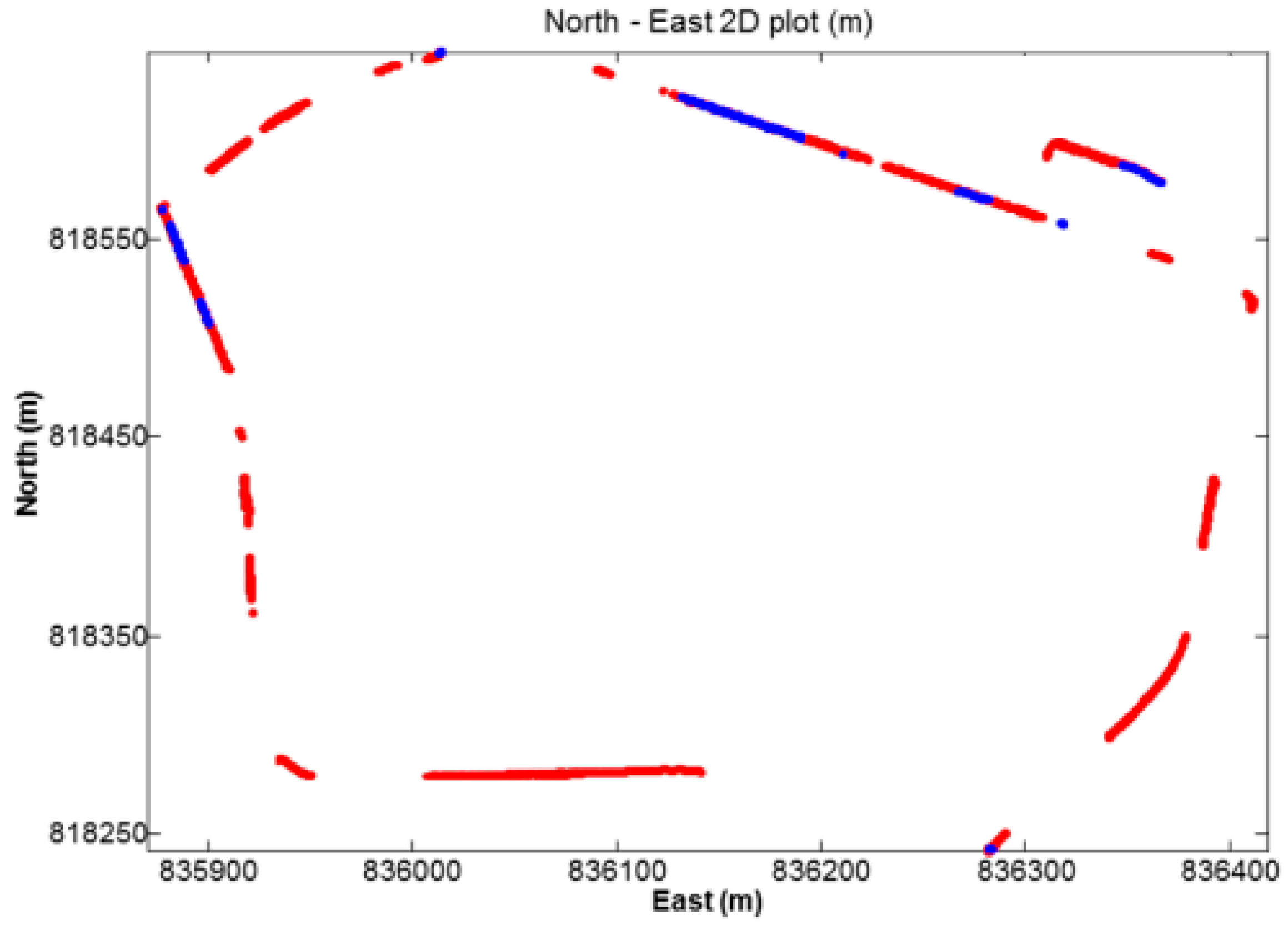


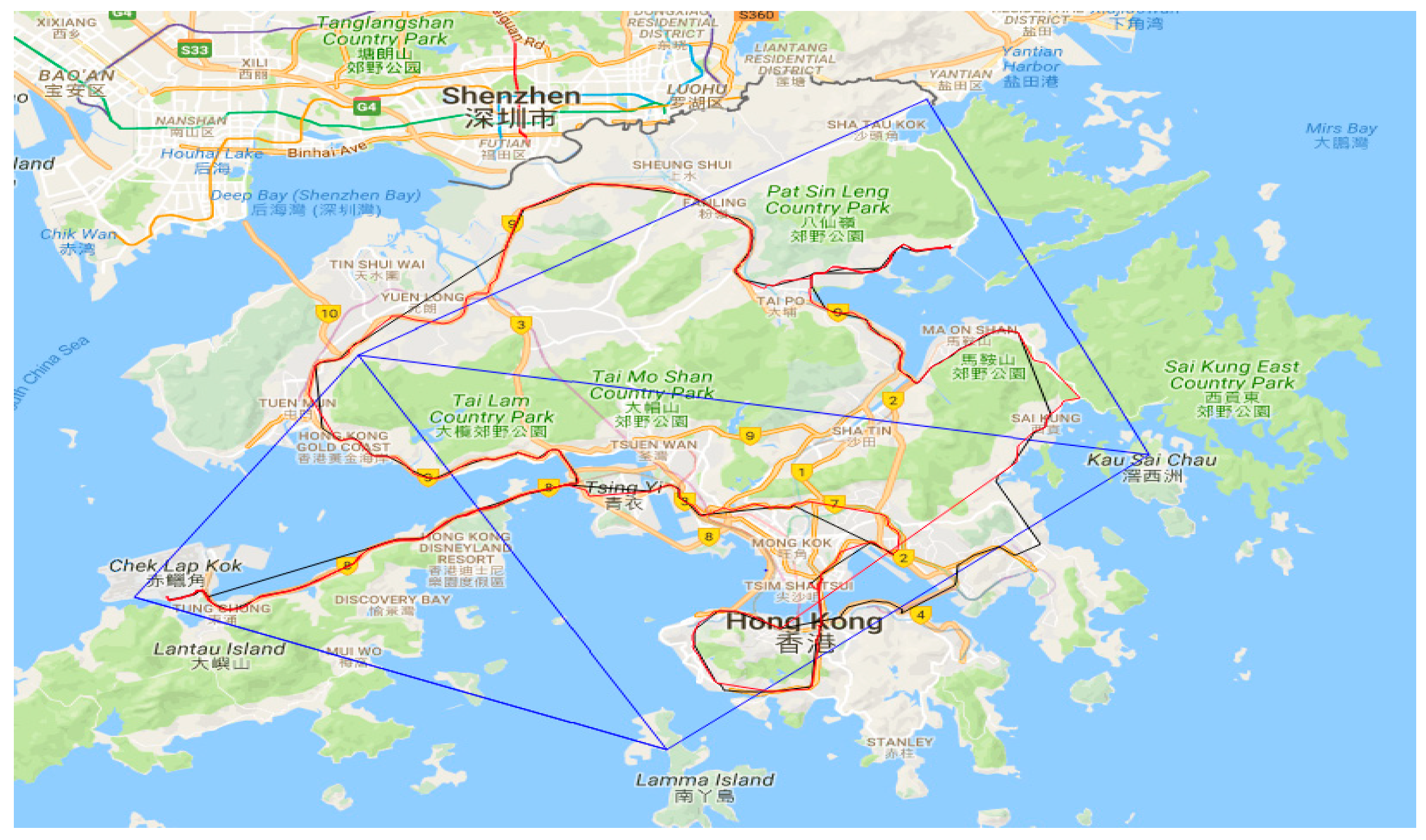


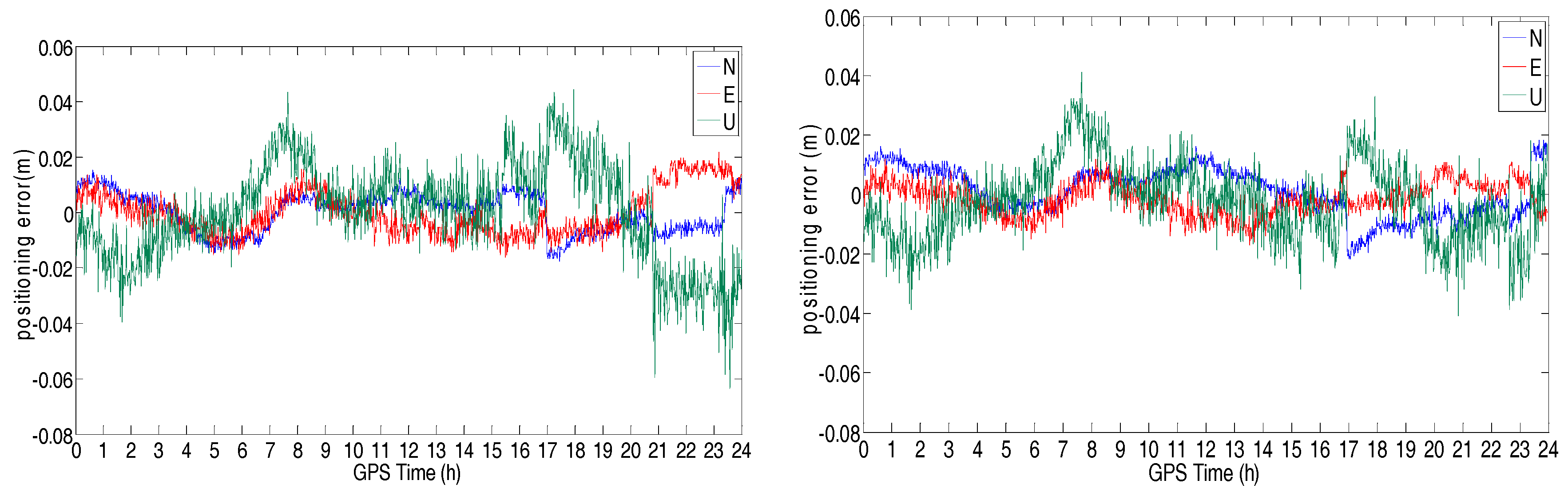
| System | N(m) | E(m) | U(m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.023 |
| GPS/BDS | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0.021 |
| Number of Points | Environment | Horizontal Direction | Vertical Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | Good environment | 1–2 cm | 2–4 cm |
| 3 | Constrained environments | 2–3 cm | 3–6 cm |
| System | Number of Epoch | Number of Unfixed Epoch | POLYU |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS | 85575 | 531 | 99.38% |
| GPS/BDS | 86264 | 0 | 100.00% |
| Walking Test | Car-Driving Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| System | POLYU | Jordan | Sha Tin | Hong Kong |
| GPS | 32.4% | 19.1% | 12.7% | 24.2% |
| GPS/BDS | 72.4% | 53.2% | 69.0% | 33.4% |
| 2.44 m | EWL | WL | NL | 21.29 km | EWL | WL | NL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Method | 1.054 | Traditional Method | 19.09 | ||||
| Proposed Technique | 1.001 | 1.003 | 1.003 | Proposed Technique | 1.003 | 1.006 | 1.107 |
| 2.44 m | N(m) | E(m) | U(m) | 21.29 km | N(m) | E(m) | U(m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triple-frequency | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.011 | Triple-frequency | 0.010 | 0.005 | 0.013 |
| Dual-frequency | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.013 | Dual-frequency | 0.011 | 0.008 | 0.018 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Chen, W. Performance Analysis of GPS/BDS Dual/Triple-Frequency Network RTK in Urban Areas: A Case Study in Hong Kong. Sensors 2018, 18, 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082437
Xu Y, Chen W. Performance Analysis of GPS/BDS Dual/Triple-Frequency Network RTK in Urban Areas: A Case Study in Hong Kong. Sensors. 2018; 18(8):2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082437
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ying, and Wu Chen. 2018. "Performance Analysis of GPS/BDS Dual/Triple-Frequency Network RTK in Urban Areas: A Case Study in Hong Kong" Sensors 18, no. 8: 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082437
APA StyleXu, Y., & Chen, W. (2018). Performance Analysis of GPS/BDS Dual/Triple-Frequency Network RTK in Urban Areas: A Case Study in Hong Kong. Sensors, 18(8), 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082437





