A Label-Free Fluorescent Assay for the Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Adenosine Deaminase Activity and Inhibition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Fluorescent Detection of ADA
2.3. Selectivity Assay
2.4. Inhibition of ADA Activity
3. Results and Discussion
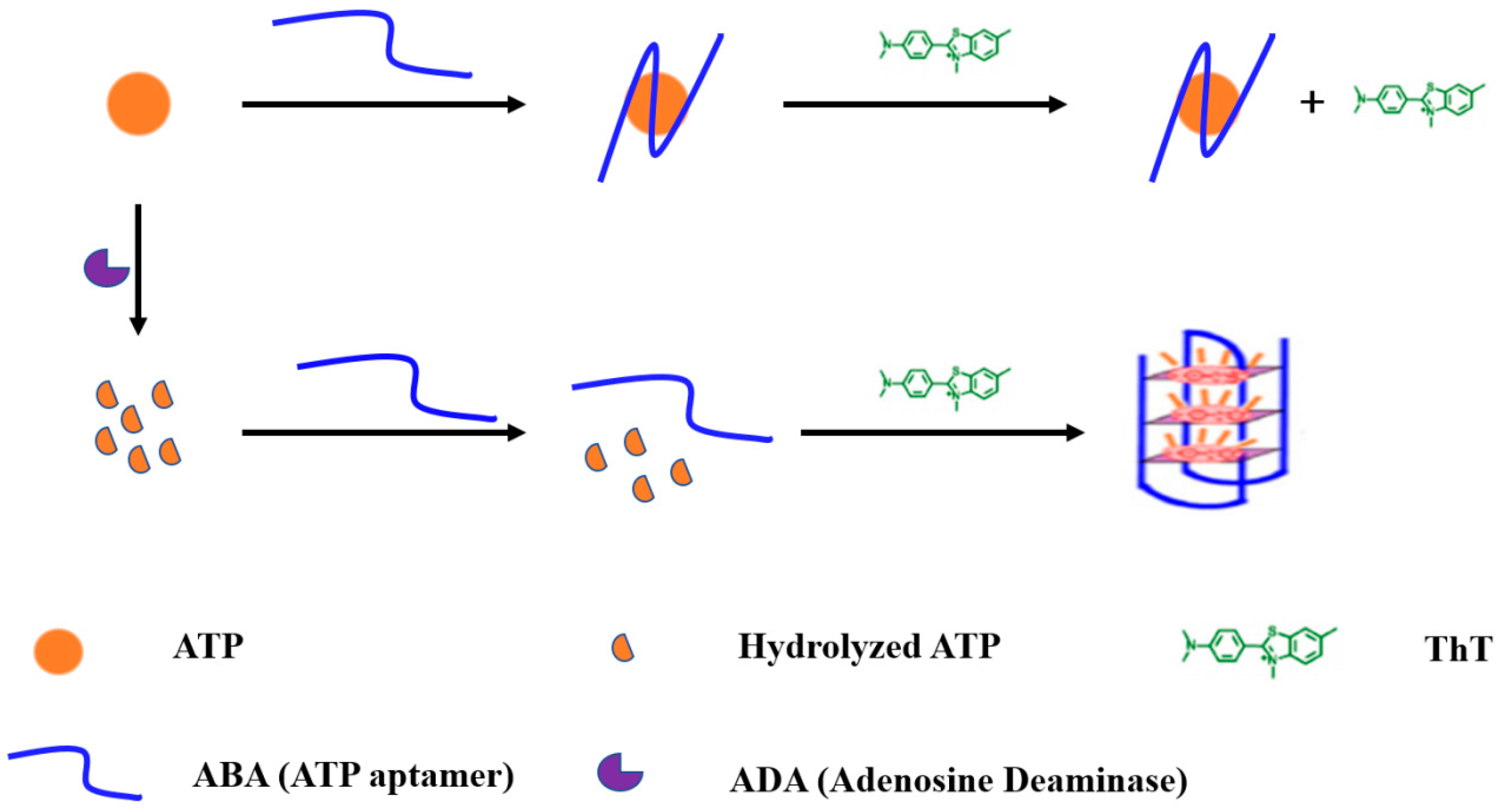
3.1. Principle of ADA Assay
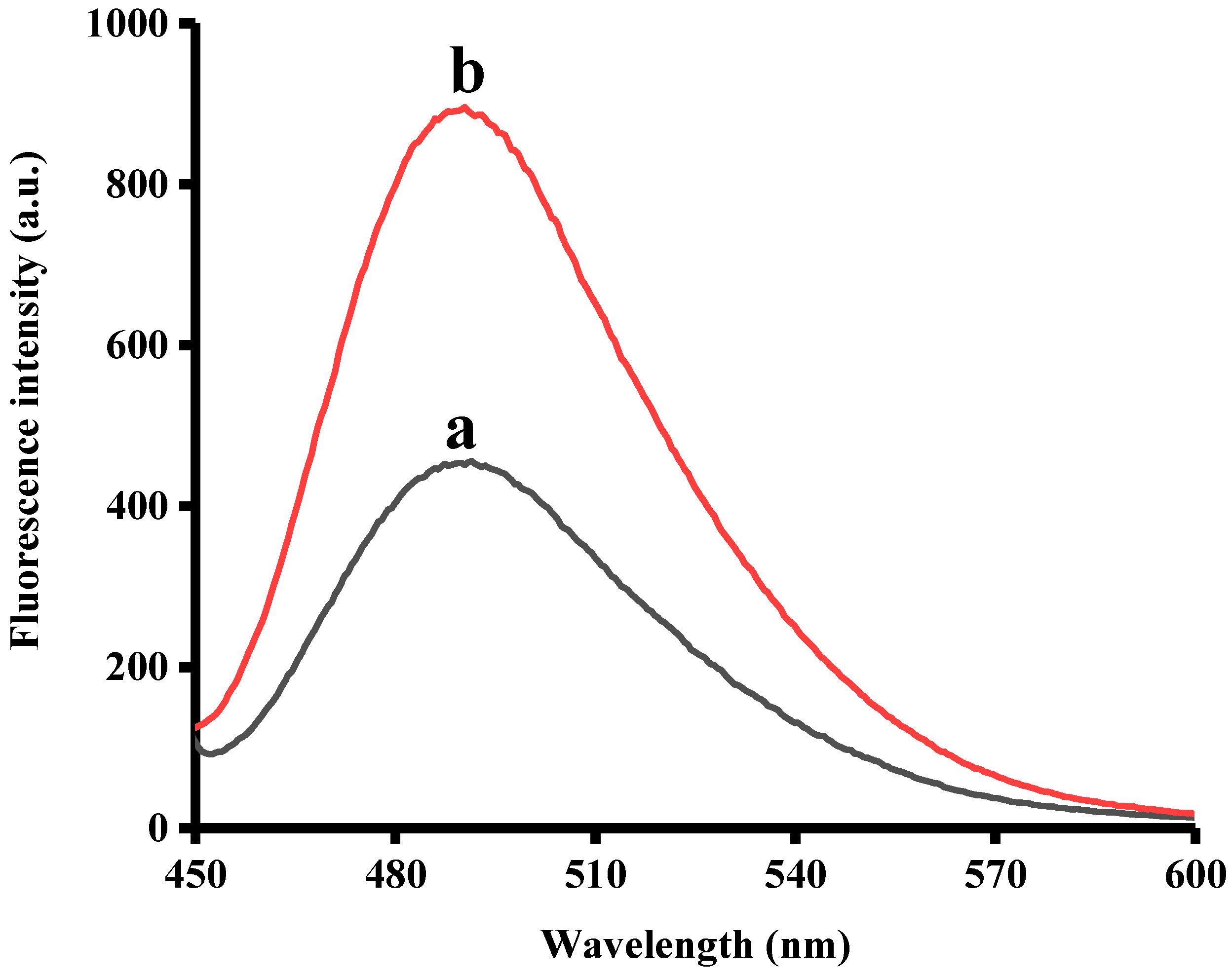
3.2. Strategy Feasibility
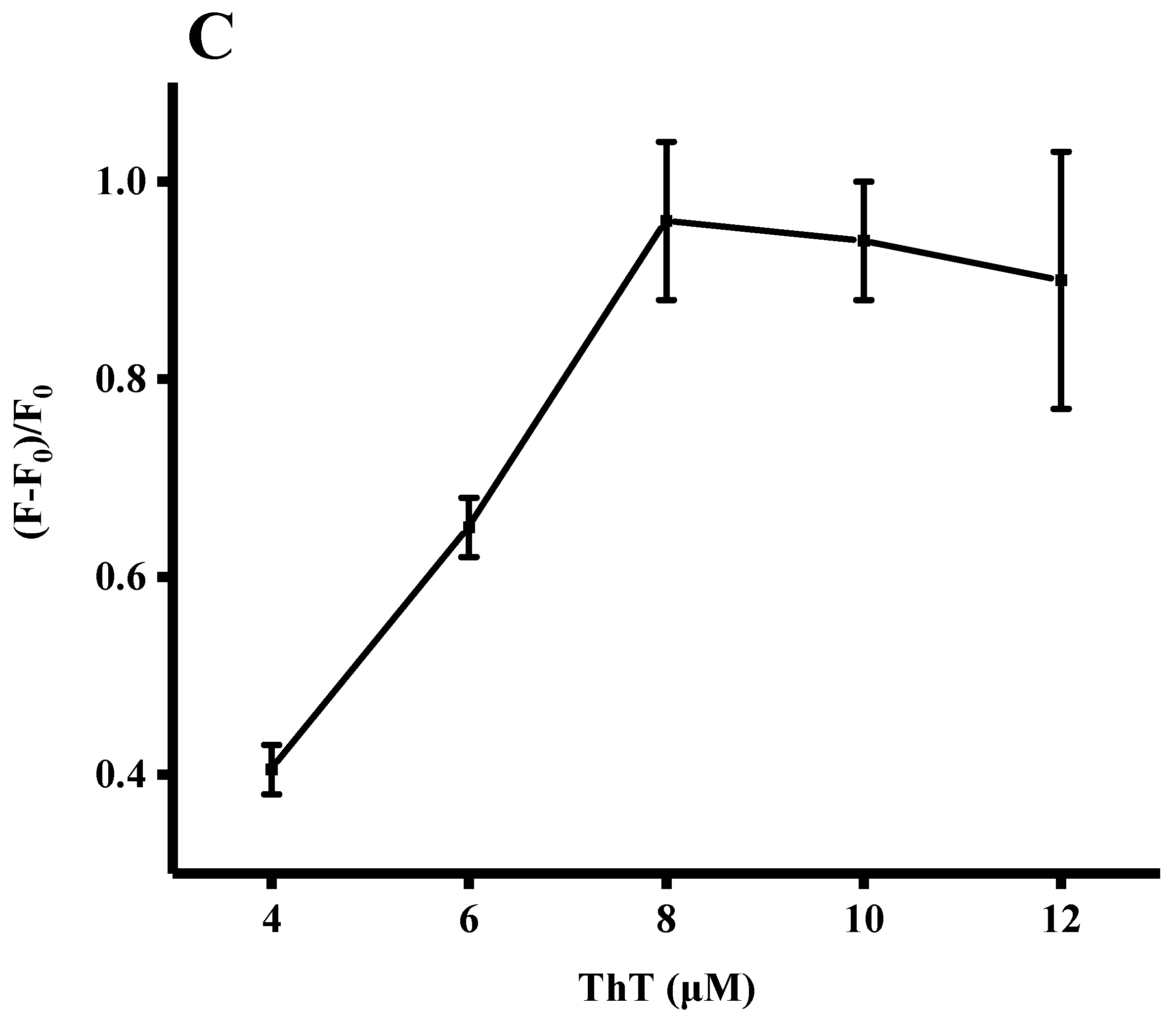
3.3. Optimization of Assay Conditions
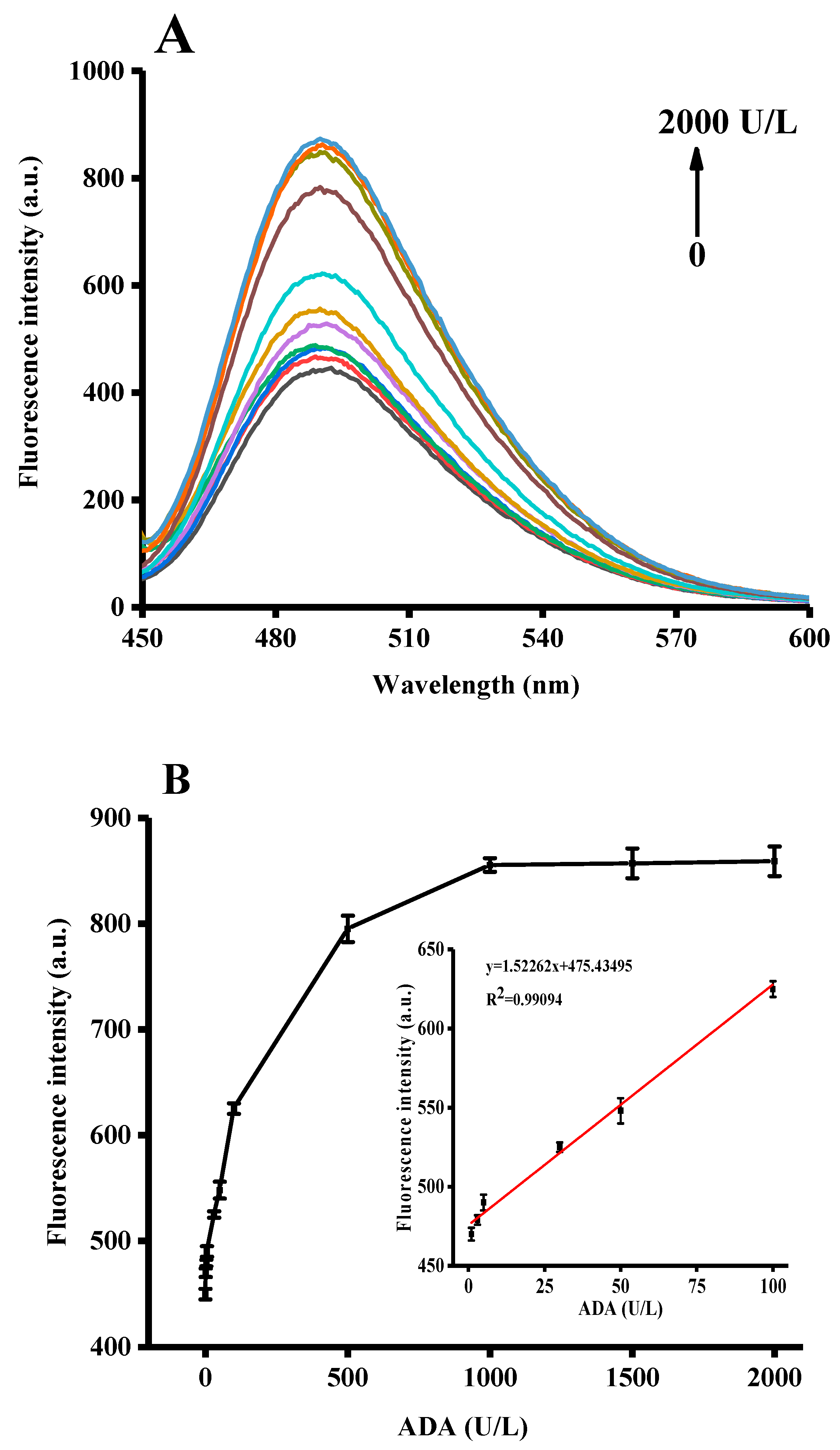
3.4. Quantitative Detection of ADA
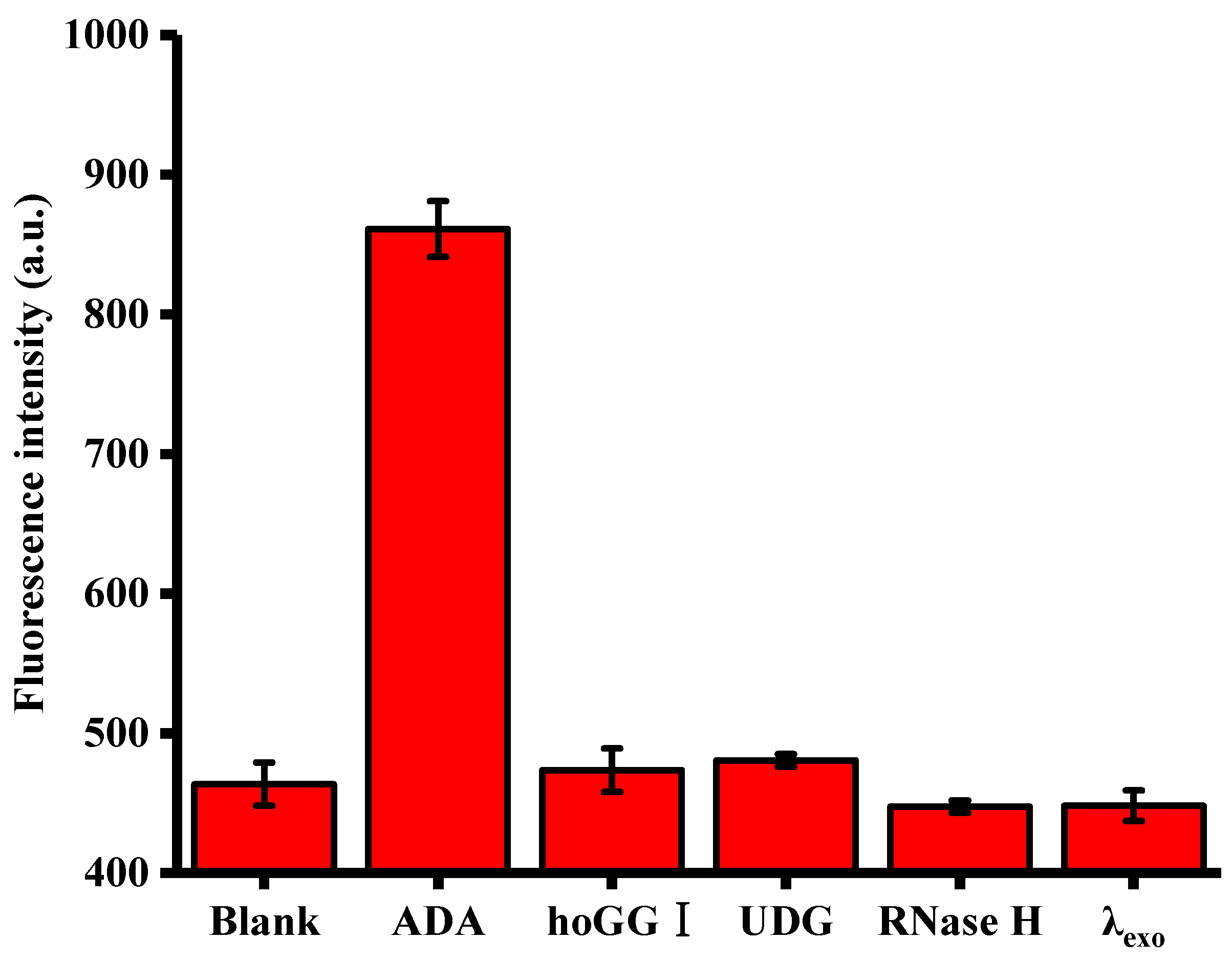
3.5. Selectivity of ADA Assay
3.6. Detection of the ADA Inhibitor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van der Weyden, M.B.; Kelley, W.N. Human adenosine deaminase. J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 251, 5448–5456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Conway, E.J.; Cooke, R. The deaminase of adenosine and adenylic acid in blood and tissues. Biochem. J. 1939, 33, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Gil, M.; Tozzi, M.G.; Allegrini, S.; Folcarelli, S.; Della Sala, G.; Voccoli, V.; Colombaioni, L.; Camici, M. Novel metabolic aspects related to adenosine deaminase inhibition in a human astrocytoma cell line. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, B.K.; Bharat, V.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Role of adenosine deaminase estimation in differentiation of tuberculous and non-tuberculous exudative pleural effusions. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2010, 2, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofbrand, A.V.; Janossy, G.J. Enzyme and membrane markers in leukaemia: Recent developments. J. Clin. Pathol. 1981, 34, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierek, T.; Drada, M.; Pilc, J.; Piekarska, J. Adenosine deaminase and purine phosphorylase activities in lymphocytes and red blood cells of patients with carcinoma of the larynx. Auris Nasus Larynx 1987, 14, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocmen, E.; Tez, M.; Ozturk, S.; Koc, M.; Demirci, S. Activities of adenosine deaminase and 5′-nucleotidase in cancereous and non-cancereous human gastric tissues. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2009, 110, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.J.; Monaghan, G.; Borsting, C.; Norbury, G.; Morling, N.; Gaspar, H.B. Carrier frequency of a nonsense mutation in the adenosine deaminase (ADA) gene implies a high incidence of ADA-deficient severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) in Somalia and a single, common haplotype indicates common ancestry. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2007, 71, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resta, R.; Thompson, L.F. SCID: The role of adenosine deaminase deficienc. Immunol. Today 1997, 18, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristalli, G.; Costanzi, S.; Lambertucci, C.; Lupidi, G.; Vittori, S.; Volpini, R.; Camaioni, E. Adenosine deaminase: Functional implications and different classes of inhibitors. Med. Res. Rev. 2001, 21, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacarne, F. Gene Therapy for Immunodeficiency due to Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 447–458. [Google Scholar]
- Chottiner, E.G.; Cloft, H.J.; Tartaglia, A.P.; Mitchell, B.S. Elevated adenosine deaminase activity and hereditary hemolytic anemia. Evidence for abnormal translational control of protein synthesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1987, 79, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, X.J.; Liu, X.G.; He, Y.; Luo, Q.Y.; Tang, H.W.; Pang, D.W. Graphene oxide based fluorescent aptasensor for adenosine deaminase detection using adenosine as the substrate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 37, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, J. Molecular Approach to Adenosine Receptors: Receptor-Mediated Mechanisms of Tissue Protection. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, M.K.; Grover, V.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K. Merits of HPLC-based method over spectrophotometric method for assessing the kinetics and inhibition of mammalian adenosine deaminase. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 822, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vielh, P.; Castellazzi, M.J. A colorimetric assay for serial determination of adenosine deaminase activity in small lymphocyte populations. J. Immunol. Methods 1984, 73, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Li, G. Strategy to Fabricate an Electrochemical Aptasensor: Application to the Assay of Adenosine Deaminase Activity. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3207–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.N.; Wei, C.Y. The aptamer DNA-templated fluorescence silver nanoclusters: ATP detection and preliminary mechanism investigation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; He, Y.; Xing, X.J.; Tan, D.D.; Pang, D.W.; Tang, H.W. A gold nanoparticle-based label free colorimetric aptasensor for adenosine deaminase detection and inhibition assay. Analyst 2015, 140, 1572–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.T.; Ma, H.M. Fluorescence sensing of adenosine deaminase based on adenosine induced self-assembly of aptamer structures. Analyst 2013, 138, 2438–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. Selection in vitro of single-stranded DNA molecules that fold into specific ligand-binding structures. Nature 1992, 355, 850–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Ma, C.; Gu, P.; Zhang, G.; Wu, K.; Chen, M.; Wang, K. Colorimetric determination of the activity of alkaline phosphatase based on the use of Cu(II)-modulated G-quadruplex-based DNAzymes. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breaker, R.R. DNA aptamers and DNA enzymes. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1997, 1, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.H.; Donovan, M.J.; Jiang, J.H. Aptamers from cell-based selection for bioanalytical applications. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2842–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Chandra, P.; Song, K.M.; Ban, C.; Shim, Y.B. Label-free detection of kanamycin based on the aptamer-functionalized conducting polymer/gold nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 36, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, T.; Patel, D.J. Adaptive Recognition by Nucleic Acid Aptamers. Science 2000, 287, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abnous, K.; Danesh, N.M.; Alibolandi, M.; Ramezani, M.; Taghdisi, S.M. Amperometric aptasensor for ochratoxin A based on the use of a gold electrode modified with aptamer, complementary DNA, SWCNTs and the redox marker methylene blue. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Ning, L.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Li, G. A colorimetric method for protein assay via exonuclease III-assisted signal attenuation strategy and specific DNA–protein interaction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 788, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.S.; Sekhon, S.S.; Shin, W.R.; Kim, H.C.; Min, J.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Detecting and Discriminating Shigella sonnei Using an Aptamer-Based Fluorescent Biosensor Platform. Molecules 2017, 22, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Wu, K.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, K.; Xia, K. Fluorometric aptasensor of ochratoxin A based on the use of graphene oxide and RNase H-aided amplification. Microchim. Acta 2018, 7, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Ma, C.; Zhao, H.; He, H.; Chen, H. Label-free G-quadruplex aptamer fluorescence assay for Ochratoxin A using a thioflavin T probe. Toxins 2018, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, J.; Zhong, L.; Wu, K. Label-free monitoring of DNA polymerase activity based on a thrombin-binding aptamer G-quadruplex. Mol. Cell. Probe 2017, 32, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.L.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Tang, B. Stable label-free fluorescent sensing of biothiols based on ThT direct inducing conformation-specific G-quadruplex. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.C.; Zhu, L.N.; Kong, D.M. Label-free thioflavin T/G-quadruplex-based real-time strand displacement amplification for biosensing applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, M.; Jin, Y.; Li, B. Label-free fluorescent assay of T4 polynucleotide kinase phosphatase activity based on G-quadruplexe-thioflavin T complex. Talanta 2017, 165, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ma, C.; Ning, F.; Chen, H.; He, H.; Wang, K.; Wang, J. A facile label-free fluorescence aptasensor for rapid detection of ATP based on G-quadruplex formation. Spectrochim. Acta A 2017, 175, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.L.; Guan, H.D.; Deng, G.; Yang, T.; Cheng, X.M.; Liu, W.; Liu, P.; Wang, C.H. Rapid, reliable, and sensitive detection of adenosine deaminase activity by UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS and its application to inhibitory activity evaluation of traditional Chinese medicines. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 153, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.X.; Li, X.X.; Su, Y.Y.; An, J.; Tang, Y.L. Label-free aptasensor for adenosine deaminase sensing based on fluorescence turn-on. Analyst 2015, 140, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, X.B.; Zheng, L. A New Method to Fabricate an Electrochemical Aptasensor to Assay Adenosine Deaminase Concentration using an Assistance DNA. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2014, 35, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Biosensing Principle | LOD (U/L) | Linear Range (U/L) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| GO based fluorescent aptasensor | 12.9 | 0–240 | [13] |
| Electrochemical aptasensor | 200 | 0–10,000 | [17] |
| Silver nanocluster | 5 | -- | [18] |
| Gold nanoparticle | 1.5 | 4.2–21 | [19] |
| Mass spectrometry | 0.5 | -- | [38] |
| Label-free aptasensor | 2 | 0–20 | [39] |
| Electrochemical aptasensor | 1 | 0–100 | [40] |
| ThT | 1 | 1–100 | This work |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; Wu, K.; Zhao, H.; Chen, M.; Ma, C. A Label-Free Fluorescent Assay for the Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Adenosine Deaminase Activity and Inhibition. Sensors 2018, 18, 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082441
Tang X, Wu K, Zhao H, Chen M, Ma C. A Label-Free Fluorescent Assay for the Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Adenosine Deaminase Activity and Inhibition. Sensors. 2018; 18(8):2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082441
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xinxing, Kefeng Wu, Han Zhao, Mingjian Chen, and Changbei Ma. 2018. "A Label-Free Fluorescent Assay for the Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Adenosine Deaminase Activity and Inhibition" Sensors 18, no. 8: 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082441
APA StyleTang, X., Wu, K., Zhao, H., Chen, M., & Ma, C. (2018). A Label-Free Fluorescent Assay for the Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Adenosine Deaminase Activity and Inhibition. Sensors, 18(8), 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082441




