AFRP Influence on Parallel Bamboo Strand Lumber Beams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Specimens
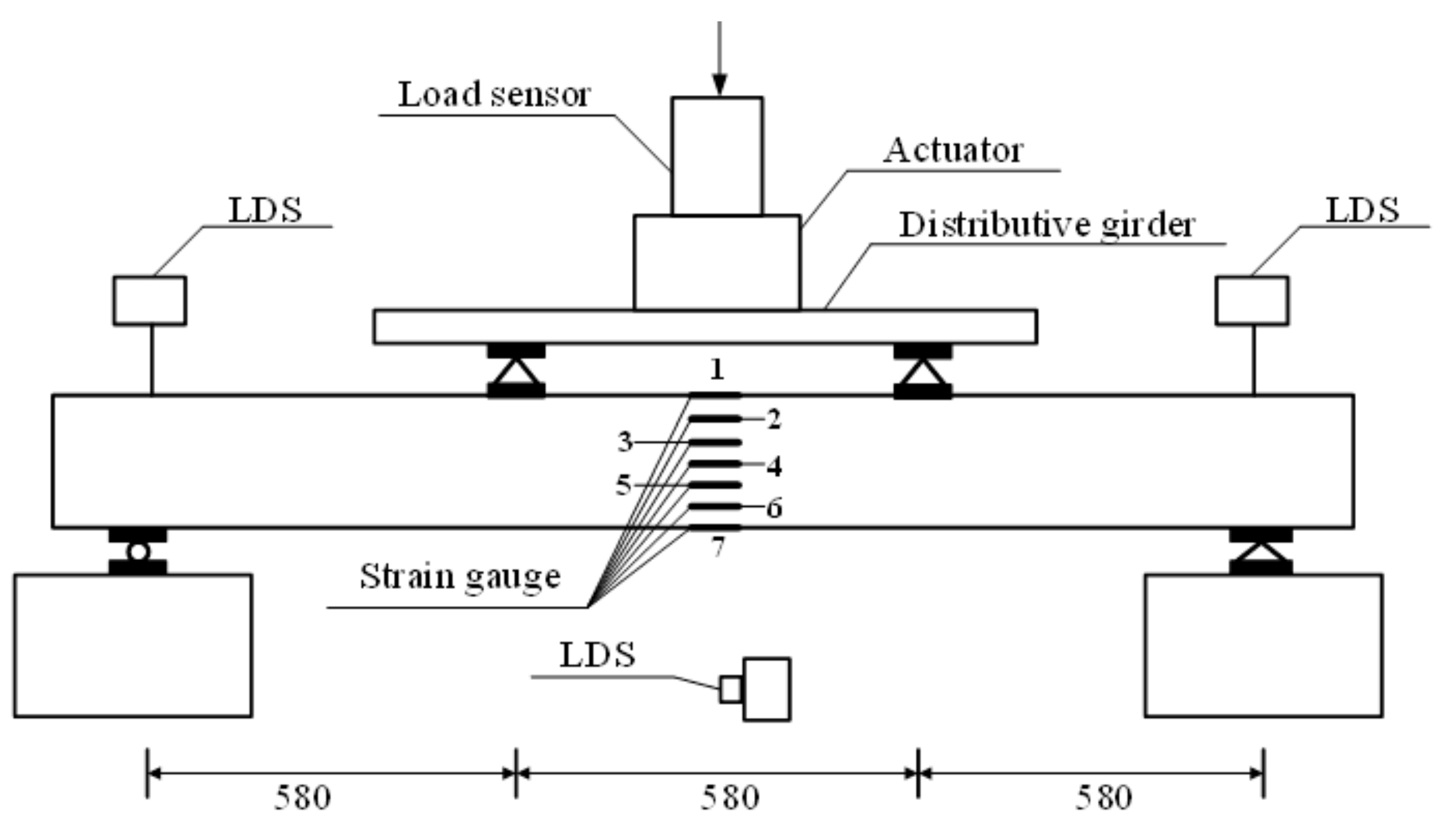
2.2. Test Design
3. Test Results and Analysis
3.1. Damage Patterns and Analysis
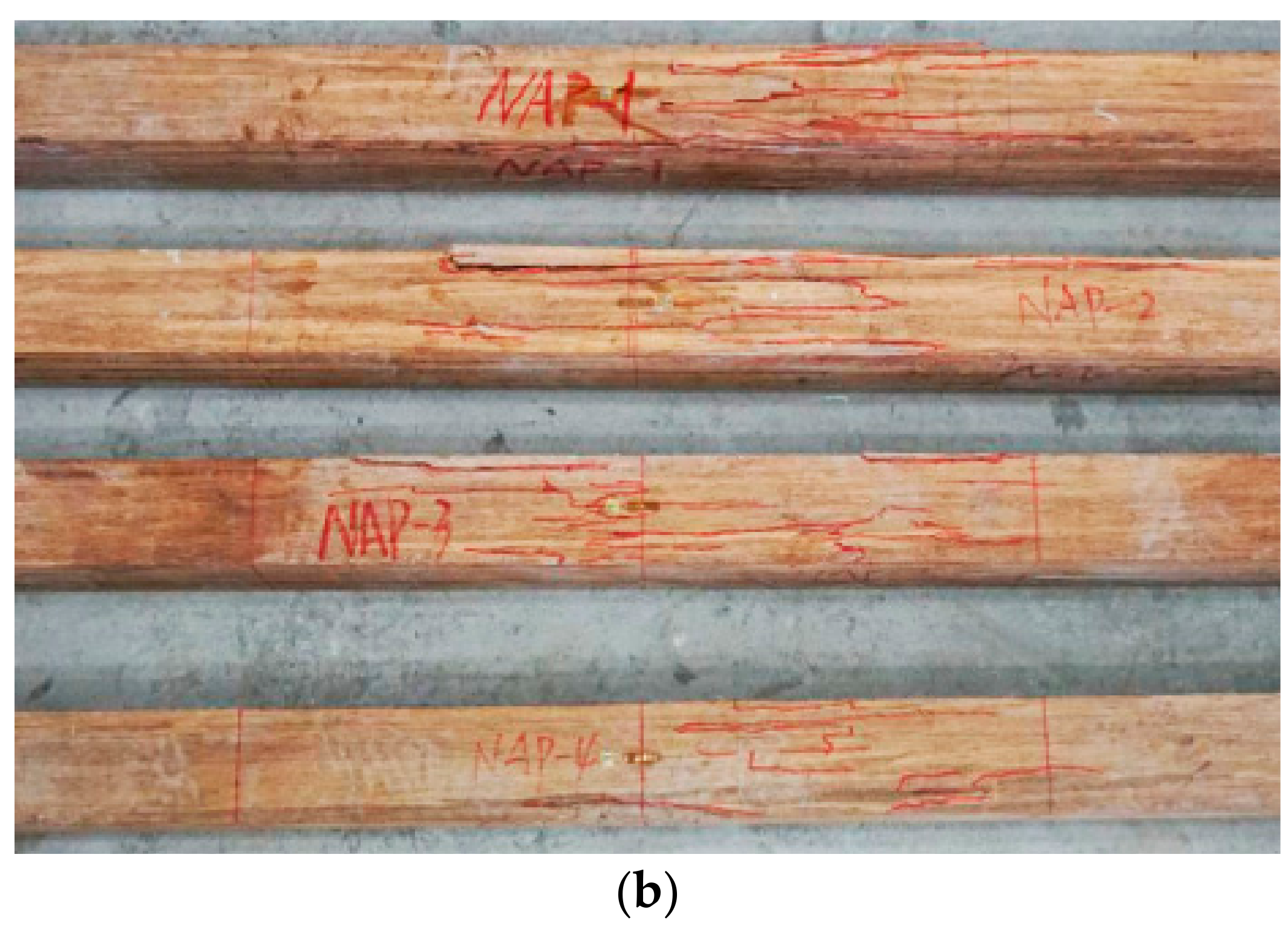
3.1.1. PBSL Beams
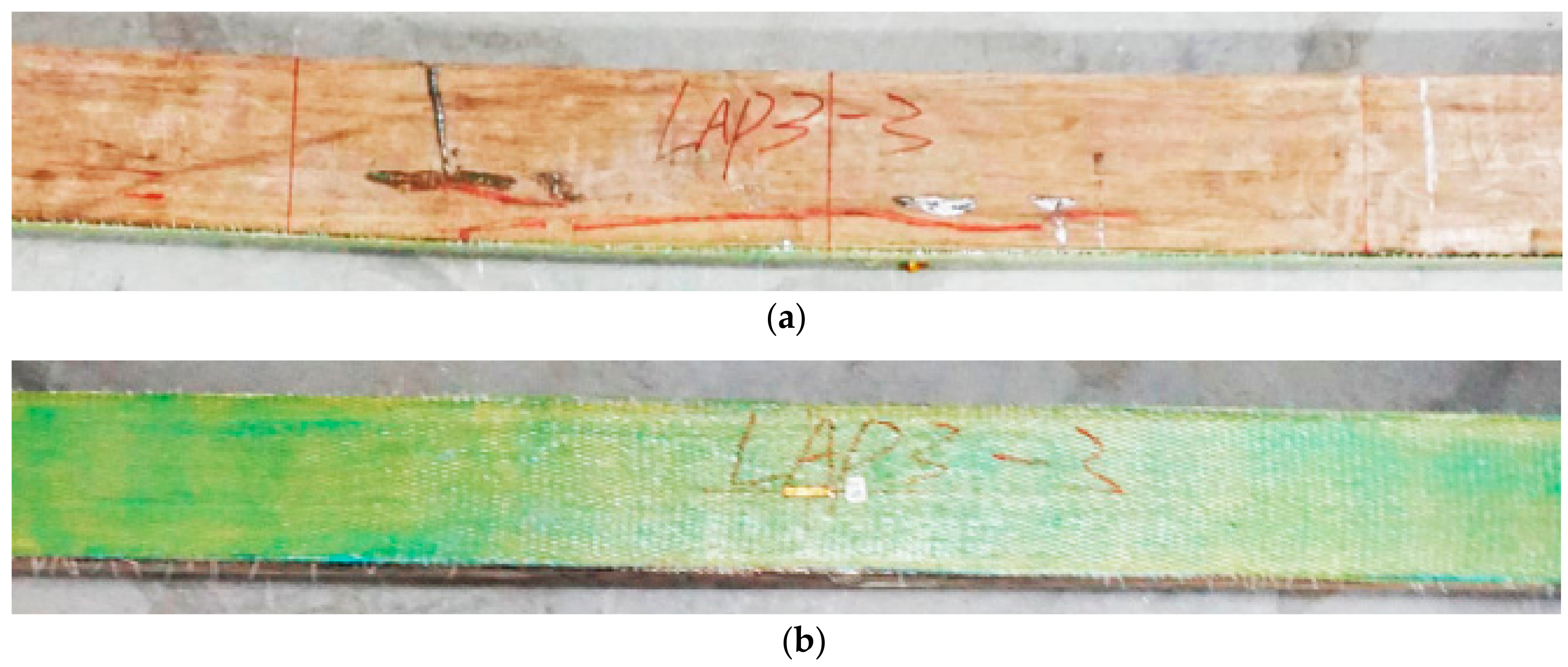
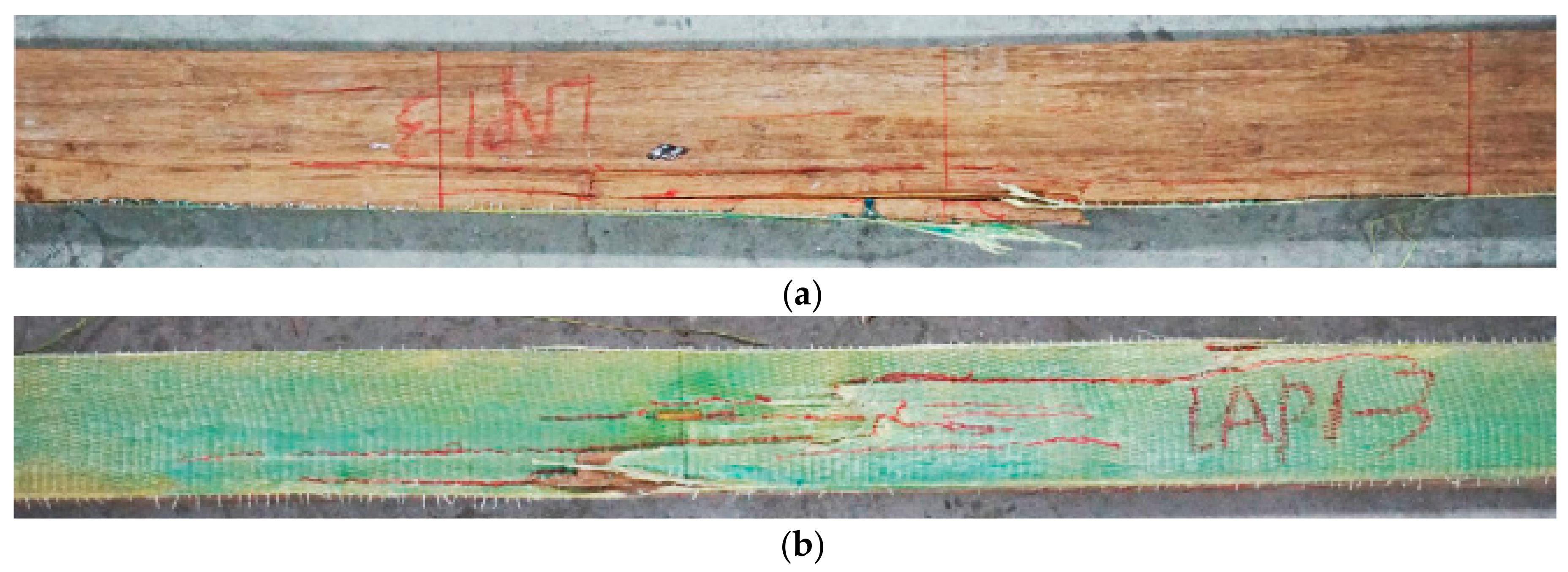
3.1.2. AFRP Strengthened PBSL Beams
3.2. Results of the Test
3.3. Load-Strain Curves Comparison
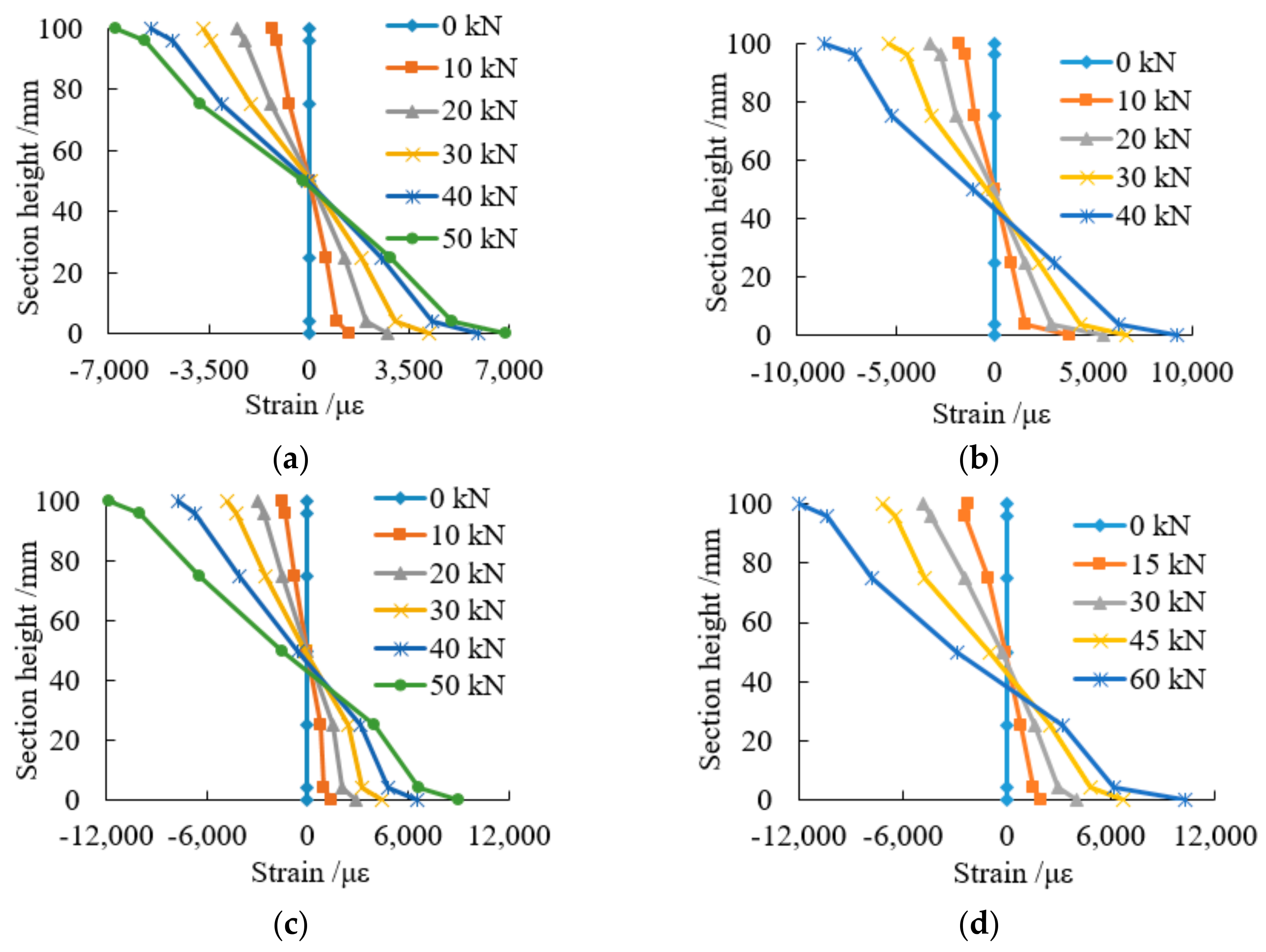
3.4. Plane Cross Section Strain
4. Conclusions
- Typical bending failure happened for all four PBSL beam specimens without AFRP. The first crack always appeared on the bottom surfaces in the pure bending area for the beams. Natural bamboo joints are the main reason for the first cracks.
- There are three typical failure modes for AFRP parallel bamboo strand lumber beams. The first failure mode is that both the bamboo fiber and AFRP cloth were pulled off at the bottom of the bamboo beam. As for the failure mode II, besides the split of bamboo fiber, cracks appeared longitudinally along the length of AFRP cloth without pulling off. But, for failure mode III, bamboo fibers split firstly and then the glue between the beam and AFRP lose effectiveness but AFRP cloth didn’t damage.
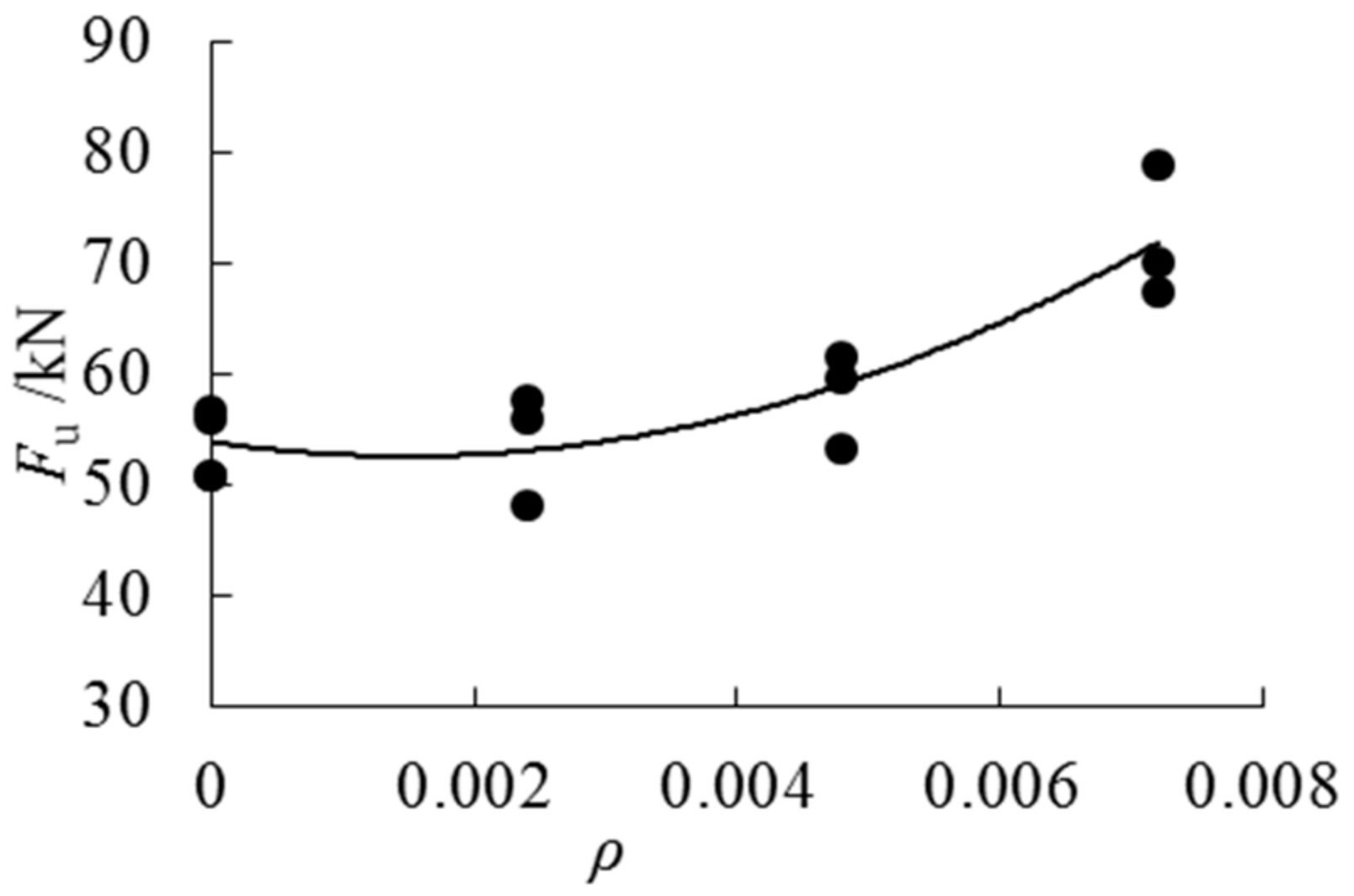
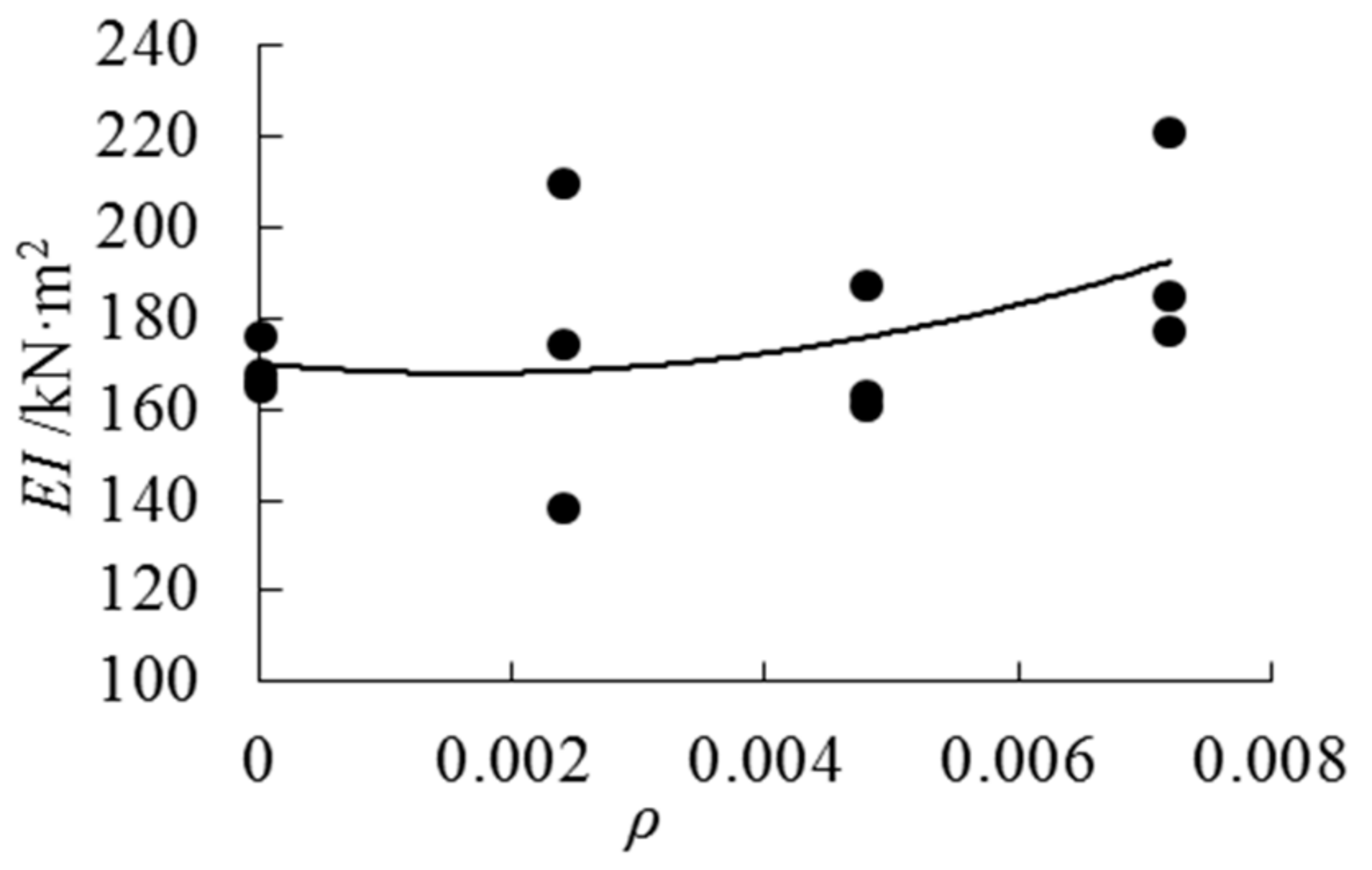
- AFRP can improve the flexural properties of parallel bamboo strand lumber beams effectively. With the increase of the cloth ratio, the ultimate bearing capacity, the stiffness, and the ductility for AFRP PBSL beams increased. When the cloth ratio reaches 0.72%, the stiffness of the beam can be increased by 15%.
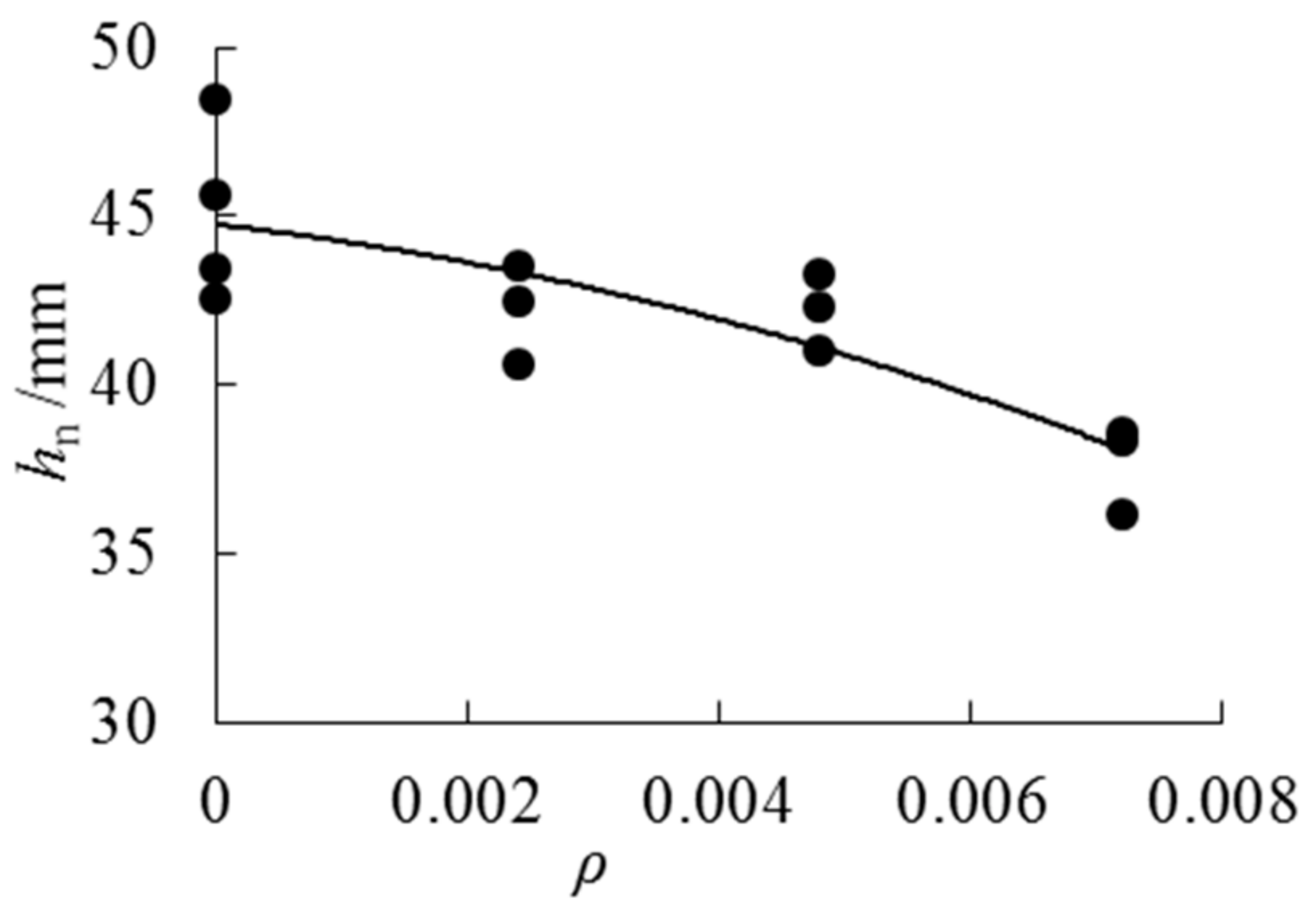
- It can be observed that the uniform strain values for the middle cross section conform to the assumption of the plane section. With the increase of load, the neutral axis for the AFRP PBSL beam moved downwards compared with the PBSL beams. AFRP plays a certain role in bearing tensile force for the beam.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nugroho, N.; Ando, N. Development of structural composite products made from bamboo. II. Fundamental properties of laminated bamboo lumber. J. Wood Sci. 2001, 47, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Wahab, R. Evaluation of shear strength of oil treated laminated bamboo. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 2466–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulastiningsih, I.M. Nurwati Physical and mechanical properties of laminated bamboo board. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2009, 21, 246–251. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, G.; Xiong, X.; Li, Y. Review on laminated bamboo lumber. J. For. Eng. 2016, 1, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.J.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Q.S.; Jiang, S.X. Present situation and the countermeasure analysis of bamboo timber processing industry in China. J. For. Eng. 2016, 1, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, X.; Wenjun, Y.U.; Wenzhu, L.I.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W. Mechanical properties and structure characterization of bamboo softened by high temperature steam. J. For. Eng. 2016, 1, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Zhou, T.; Li, C.L.; Zhang, Q.S.; Li, H.T. Experimental study on the OSB webbed bamboo beams. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2016, 40, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, L.I.; Xiao, Z.; Zhu, N. Bending strength and loading simulation analysis of bamboo scrimber I—Shaped beam. J. For. Eng. 2017, 2, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Su, J. Mechanical evaluation for laminated bamboo lumber along two eccentric compression directions. J. Wood Sci. 2016, 62, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, G. Experimental study on side pressure LBL under tangential eccentric compression. J. Hunan Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2016, 43, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Su, J.; Zhang, Q.; Deeks, A.J.; Hui, D. Mechanical performance of laminated bamboo column under axial compression. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 79, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Li, H.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, G. Mechanical performance study on laminated bamboo lumber column pier under axial compression. China For. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Q.; Ashraf, M.; Xu, B.; Li, Y. Mechanical properties of laminated bamboo lumber column under radial eccentric compression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 121, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Deeks, A.J.; Su, J. Ultimate bending capacity evaluation of laminated bamboo lumber beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Clouston, P.L.; Arwade, S.R. Development of laminated bamboo lumber: Review of processing, performance, and economical considerations. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Chung, M.; Lin, C.; Yang, T. Effects of layered structure on the physical and mechanical properties of laminated moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) flooring. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.S.; Chariar, V.M. Development of layered laminate bamboo composite and their mechanical properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, D.; Deeks, A.J. Compressive performance of laminated bamboo. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 54, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, G. Stress-strain model under compression for side pressure laminated bamboo. J. Southeast Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2015, 45, 1130–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Correal, J.F.; Echeverry, J.S.; Ramírez, F.; Yamín, L.E. Experimental evaluation of physical and mechanical properties of Glued Laminated Guadua angustifolia Kunth. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, M.C.; Lin, Y.L. Finger joint performance of structural laminated bamboo member. J. Wood Sci. 2012, 58, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, R.Z.; Shan, B. Production, environmental impact and mechanical properties of glubam. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lv, Y.; Huang, C.; Ni, Y.H.; Song, J.G.; Ni, Z.J. Design of control system of automatic bamboo scrimber cold pressing unit. J. For. Eng. 2017, 2, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Wu, B.; Hu, Y.; Yu, W. Fabrication, material properties, and application of bamboo scrimber. Wood Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, R.; Xing, X.; Ren, H. Experimental study on tensile and compressive strength of bamboo scrimber. BioResources 2016, 11, 7334–7344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, W.; Zhong, Y.; Xing, X.; Zhao, R.; Ren, H. Strength models of bamboo scrimber for compressive properties. J. Wood Sci. 2015, 61, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, W.; Gong, Y.; Zhao, R.; Ren, H. Effects of heat treatment on the properties of bamboo scrimber. J. Wood Sci. 2016, 62, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Vlach, T.; Laiblova, L.; Hrouda, M.; Kasal, B.; Tywoniak, J. Engineered bamboo scrimber: Influence of density on the mechanical and water absorption properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Cui, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, J. Experimental study on compressive and tensile properties of a bamboo scrimber at elevated temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, R.; Huang, Y.; Meng, F.; Yu, W. Preparation, physical, mechanical, and interfacial morphological properties of engineered bamboo scrimber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 157, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Gatóo, A.; Bock, M.; Ramage, M. Engineered bamboo for structural applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 81, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Shangguan, W.; Ren, H. Design value of the compressive strength for bamboo fiber-reinforced composite based on a reliability analysis. BioResources 2014, 9, 7737–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Su, J.; Deeks, A.J.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, D.; Yuan, C. Eccentric compression performance of parallel bamboo strand lumber column. BioResources 2015, 10, 7065–7080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Wu, G.; Ren, H.; Jiang, Z. Bending properties evaluation of newly designed reinforced bamboo scrimber composite beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 143, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wu, F.; Li, H.; Yang, P. Experimental research on parallel bamboo strand lumber column under axial compression. China Sci. Pap. 2015, 10, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Ren, H.; Jiang, Z. Effects of Temperature on the Compressive Strength Parallel to the Grain of Bamboo Scrimber. Materials 2016, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratta, A.; Corbi, I.; Corbi, O. Bounds on the Elastic Brittle solution in bodies reinforced with FRP/FRCM composite provisions. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 68, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratta, A.; Corbi, I. Topology optimization for reinforcement of no-tension structures. Acta Mech. 2014, 225, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratta, A.; Corbi, O. Closed-form solutions for FRP strengthening of masonry vaults. Comput. Struct. 2015, 147, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratta, A.; Corbi, O. An approach to the positioning of FRP provisions in vaulted masonry structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 53, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Wu, G.; Pang, Y.Y. Theoretical and Numerical Study on Stress Intensity Factors for FRP-Strengthened Steel Plates with Double-Edged Cracks. Sensors 2018, 18, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.P.; Chen, K.; Li, Z.C.; Jiang, X.L. Crack Monitoring Method for an FRP-Strengthened Steel Structure Based on an Antenna Sensor. Sensors 2017, 17, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.S.; Wu, Z.S. Distributed Long-Gauge Optical Fiber Sensors Based Self-Sensing FRP Bar for Concrete Structure. Sensors 2016, 16, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Lin, J.; Huang, L.P. A Modified Lamb Wave Time-Reversal Method for Health Monitoring of Composite Structures. Sensors 2017, 17, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.B.; Peter, J.; Deborah, M. Localized Temperature Variations in Laser-Irradiated Composites with Embedded Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.S.; Sai, Y.Z.; Geng, X.Y.; Sui, Q.M.; Liu, X.H.; Jia, L. Development of an FBG Sensor Array for Multi-Impact Source Localization on CFRP Structures. Sensors 2016, 16, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, F.; Nagaraj, M.; Khosravi, P. Buckling response of glue-laminated columns reinforced with fiber-rein forced plastic sheets. Compos. Struct. 2009, 88, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaludin, A.; Andriani, V. Bolted Bamboo Joints Reinforced with Fibers. Procedia Eng. 2014, 95, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.H. Experimental Study on Bending Behavior of BFRP Composite Bamboo Beams. Master’s Thesis, Southeast University, Nanjing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L. Study on Mechanical Behavior of Wood Beams Strengthened with Carbon Fiber Sheets. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 50329-2012. Standard for Test Method of Timber Structures; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2006.









| Group | l/mm | FRP | n | Number | b/mm | h/mm | λ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAP | 1860 | — | — | 4 | 80 | 100 | 5.8 |
| LAP1 | 1860 | AFRP | 1 | 3 | 80 | 100 | 5.8 |
| LAP2 | 1860 | AFRP | 2 | 3 | 80 | 100 | 5.8 |
| LAP3 | 1860 | AFRP | 3 | 3 | 80 | 100 | 5.8 |
| Group | ρ | Fu/kN | wu/mm | α | EI/kN·m2 | μΔ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAP-1 | — | 50.8 | 41.56 | — | 166.3 | 0.82 |
| NAP-2 | — | 56.8 | 54.42 | — | 167.6 | 0.93 |
| NAP-3 | — | 56.1 | 48.43 | — | 175.8 | 1.22 |
| NAP-4 | — | 51.0 | 47.72 | — | 164.9 | 1.21 |
| Average | — | 53.7 | 48.03 | — | 168.6 | 1.04 |
| LAP1-1 | 0.24% | 56.0 | 54..89 | 4.2% | 209.3 | 1.14 |
| LAP1-2 | 0.24% | 48.3 | 48.46 | −10.0% | 137.9 | 1.07 |
| LAP1-3 | 0.24% | 57.8 | 55.56 | 7.6% | 174.1 | 1.15 |
| Average | — | 54.0 | 52.97 | 0.6% | 173.8 | 1.12 |
| LAP2-1 | 0.48% | 61.6 | 72.73 | 14.6% | 163.1 | 1.26 |
| LAP2-2 | 0.48% | 59.7 | 64.72 | 11% | 160.6 | 1.12 |
| LAP2-3 | 0.48% | 53.3 | 61.98 | −0.69% | 187.5 | 1.00 |
| Average | — | 59.5 | 66.48 | 10.8% | 170.4 | 1.13 |
| LAP3-1 | 0.72% | 78.9 | 65.10 | 46.9% | 220.8 | 1.18 |
| LAP3-2 | 0.72% | 70.2 | 58.12 | 30.8% | 184.9 | 1.21 |
| LAP3-3 | 0.72% | 67.5 | 70.77 | 25.7% | 177.2 | 1.25 |
| Average | — | 72.2 | 64.66 | 34.5% | 194.3 | 1.22 |
| F/kN | w0/mm | w1/mm | w2/mm | w3/mm | α1 | α2 | α3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 6.28 | 5.51 | 5.24 | 5.28 | 12.1% | 16.4% | 15.8% |
| 20 | 12.02 | 11.18 | 11.17 | 10.21 | 7.0% | 7.1% | 15.0% |
| 30 | 18.21 | 17.51 | 17.77 | 15.52 | 3.8% | 2.4% | 14.8% |
| 40 | 26.29 | 25.99 | 26.21 | 21.60 | 1.1% | 0.68% | 17.8% |
| 50 | 36.50 | 36.31 | 39.2 | 29.46 | 0.53% | −0.073% | 19.3% |
| Group | ρ | hn/mm | β |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAP1 | — | 43.49 | 0.43 |
| NAP2 | — | 45.64 | 0.46 |
| NAP3 | — | 48.47 | 0.48 |
| NAP4 | — | 42.56 | 0.43 |
| Average | — | 45.04 | 0.45 |
| LAP1-1 | 0.24% | 42.5 | 0.43 |
| LAP1-2 | 0.24% | 43.51 | 0.44 |
| LAP1-3 | 0.24% | 40.62 | 0.41 |
| Average | — | 42.21 | 0.42 |
| LAP2-1 | 0.48% | 41.06 | 0.41 |
| LAP2-2 | 0.48% | 43.32 | 0.43 |
| LAP2-3 | 0.48% | 42.32 | 0.42 |
| Average | — | 42.23 | 0.42 |
| LAP3-1 | 0.72% | 36.2 | 0.36 |
| LAP3-2 | 0.72% | 38.6 | 0.39 |
| LAP3-3 | 0.72% | 38.32 | 0.38 |
| Average | — | 37.71 | 0.38 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Corbi, I.; Corbi, O.; Wu, G.; Zhao, C.; Cao, T. AFRP Influence on Parallel Bamboo Strand Lumber Beams. Sensors 2018, 18, 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092854
Zhang H, Li H, Corbi I, Corbi O, Wu G, Zhao C, Cao T. AFRP Influence on Parallel Bamboo Strand Lumber Beams. Sensors. 2018; 18(9):2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092854
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huizhong, Haitao Li, Ileana Corbi, Ottavia Corbi, Gang Wu, Chengjie Zhao, and Tongwei Cao. 2018. "AFRP Influence on Parallel Bamboo Strand Lumber Beams" Sensors 18, no. 9: 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092854
APA StyleZhang, H., Li, H., Corbi, I., Corbi, O., Wu, G., Zhao, C., & Cao, T. (2018). AFRP Influence on Parallel Bamboo Strand Lumber Beams. Sensors, 18(9), 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092854





