Integrating Gaze Tracking and Head-Motion Prediction for Mobile Device Authentication: A Proof of Concept
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Authentication Procedure
3.1. Generating Interactive Visual Stimulus
3.2. Preprocessing Head-Moving Frames
3.3. Extracting Static Features
3.4. Extracting Dynamic Features
3.5. Classifying User’s Identity
4. Results
- Accuracy is the most intuitive performance measure and it is simply a ratio of correctly predicted observation to the total observations. Based on Equation (5), accuracy of our classifier is 0.986:
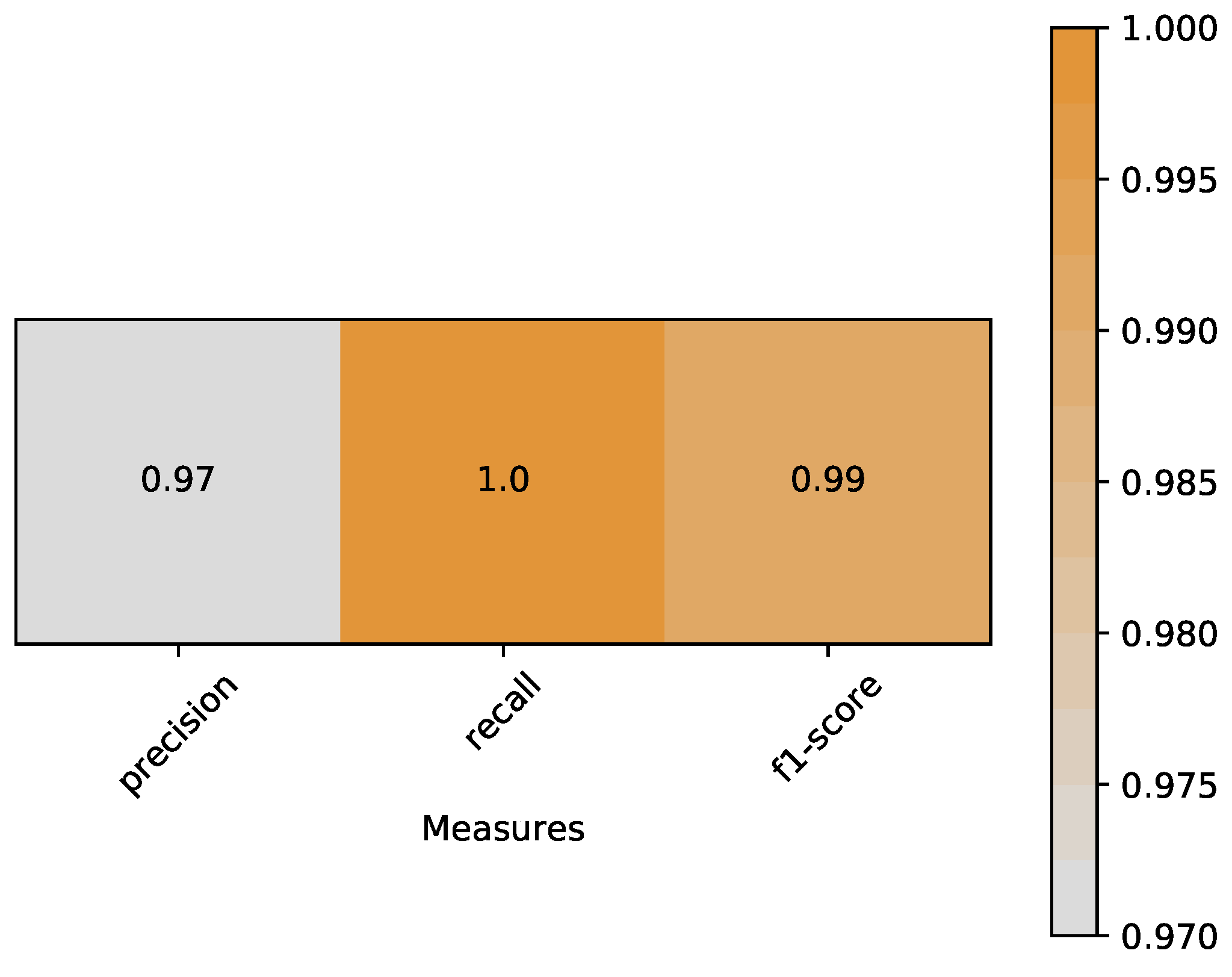
- Precision is the ratio of correctly predicted positive observations to the total predicted positive observations. Based on Equation (6), precision of our classifier is 0.97:Recall is the ratio of correctly predicted positive observations to the all observations in true class. Based on Equation (7), recall of our classifier is 1.0:F1-score is the weighted average of Precision and Recall. Therefore, this score takes both false positives and false negatives into account. Based on Equations (8) and (9), f1-score of our classifier is 0.99:A heat map is plotted in Figure 11 to represent the above measures clearly.
- ROC curves typically feature a true positive rate (Equation (10)) on the y-axis, and the false positive rate (Equation (11)) on the x-axis. This means that the top left corner of the plot is the ideal point where a false positive rate of zero and a true positive rate of one. It does mean that a larger area under the curve (AUC) is usually better. We plot the ROC curve of our classifier in Figure 12. The area of AUC is labelled in the bottom right corner:
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| PINs | Personal Identification Numbers |
| TP | True Positive |
| FP | False Positive |
| FN | False Negative |
| TN | True Negative |
| AUC | Area Under Curve |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve |
| TPR | True Positive Rate |
| FPR | False Positive Rate |
| FNR | False Negative Rate |
Appendix A


References
- Wu, D.; Yan, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, R. Social Attribute aware Incentive Mechanisms for Video Distribution in Device-to-Device Communications. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2017, 8, 1908–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, R. Socially Aware Energy Efficient Mobile Edge Collaboration for Video Distribution. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2017, 10, 2197–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Si, S.; Wu, S.; Wang, R. Dynamic Trust Relationships Aware Data Privacy Protection in Mobile Crowd-Sensing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 5, 2958–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Li, B.; Shen, J.; Yang, L.; Ma, J. Security analysis and improvement of bio-hashing based three-factor authentication scheme for telecare medical information systems. J. Am. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2017, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zeadally, S.; Ma, J.; He, D. Lightweight three-factor authentication and key agreement protocol for internet-integrated wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 3376–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Ma, J.; Yang, C.; Ma, X.; Shen, J.; Chaudhry, S.A. Efficient end-to-end authentication protocol for wearable health monitoring systems. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2017, 63, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Iqbal, M.; Sharif, M.; Haider, W. A survey of password attacks and comparative analysis on methods for secure authentication. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 19, 439–444. [Google Scholar]
- Sin, S.W.; Zhou, R.; Li, D.; Isshiki, T.; Kunieda, H. Narrow fingerprint sensor verification with template updating technique. IEICE Trans. Fundam. 2012, 95, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Kumar, A. Matching Contactless and Contact-Based Conventional Fingerprint Images for Biometrics Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 4, 2008–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkhi, O.M.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Deep Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Swansea, UK, 10 September 2015; pp. 41.1–41.12. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, X.; Li, W.; Tang, B.; He, H. BULDP: Biomimetic Uncorrelated Locality Discriminant Projection for Feature Extraction in Face Recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2575–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delac, K.; Grgic, M. A survey of biometric recognition methods. In Proceedings of the Elmar 2004. 46th International Symposium Electronics in Marine, Zadar, Croatia, 16–18 June 2004; pp. 184–193. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, R.J.; Karn, K.S. Eye tracking in human–computer interaction and usability research: Ready to deliver the promises. Mind Eye 2003, 573–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majaranta, P.; Bulling, A. Eye tracking and eye-based human–computer interaction. In Advances in Physiological Computing; Springer: London, UK, 2014; pp. 39–65. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, C.H.; Mimica, M.R. Eye gaze tracking techniques for interactive applications. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2005, 98, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, B.; Gao, X.; Wu, X. Design and implementation of an eye gesture perception system based on electrooculography. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 91, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Jagadeesh, V.; Shenoy, R.; Ecksteinz, M.; Manjunath, B.S. From where and how to what we see. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; Volume 10, pp. 625–632. [Google Scholar]
- Borji, A.; Itti, L. State-of-the-art in visual attention modeling. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, D.; Ji, Q. In the eye of the beholder: A survey of models for eyes and gaze. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 3, 478–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krafka, K.; Khosla, A.; Kellnhofer, P.; Kannan, H.; Bhandarkar, S.; Matusik, W.; Torralba, A. Eye tracking for everyone. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1606.05814. [Google Scholar]
- Lotter, W.; Kreiman, G.; Cox, D. Deep predictive coding networks for video prediction and unsupervised learning. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1605.08104. [Google Scholar]
- Komogortsev, O.V.; Karpov, A.; Holland, C.D. Attack of mechanical replicas: Liveness detection with eye movements. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 4, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Deravi, F.; Hoque, S. Spoofing attempt detection using gaze colocation. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference of the BIOSIG Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), Darmstadt, Germany, 5–6 September 2013; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chi, Z.; Feng, D. An Analysis of Eye Movement Based Authentication Systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Technology, London, UK, 24–25 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, U. Eye movements during scene understanding for biometric identification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2016, 82, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bulling, A.; Gellersen, H. Towards pervasive eye tracking using low-level image features. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 28–30 March 2012; pp. 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Bulling, A.; Gellersen, H. SideWays: A gaze interface for spontaneous interaction with situated displays. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Paris, France, 27 April–2 May 2013; pp. 851–860. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Bulling, A.; Gellersen, H. Pupil-canthi-ratio: A calibration-free method for tracking horizontal gaze direction. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Working Conference on Advanced Visual Interfaces, Como, Italy, 27–29 May 2014; pp. 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Garfinkel, T.; Boneh, D.; Winograd, T. Reducing shoulder-surfing by using gaze-based password entry. In Proceedings of the 3rd symposium on Usable privacy and security, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 18–20 July 2007; pp. 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, J.; Mock, K.; Hoanca, B. Gaze-based password authentication through automatic clustering of gaze points. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Anchorage, AK, USA, 9–12 October 2011; pp. 2749–2754. [Google Scholar]
- Bulling, A.; Alt, F.; Schmidt, A. Increasing the security of gaze-based cued-recall graphical passwords using saliency masks. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Austin, TX, USA, 5–10 May 2012; pp. 3011–3020. [Google Scholar]
- Boehm, A.; Chen, D.; Frank, M.; Huang, L.; Kuo, C.; Lolic, T.; Martinovic, I.; Song, D. Safe: Secure authentication with face and eyes. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Privacy and Security in Mobile Systems, Atlantic City, NJ, USA, 24–27 June 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- De Luca, A.; Denzel, M.; Hussmann, H. Look into my eyes!: Can you guess my password? In Proceedings of the 5th Symposium on Usable Privacy and Security, Mountain View, CA, USA, 15–17 July 2009; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kocejko, T.; Wtorek, J. Gaze pattern lock for elders and disabled. In Information Technologies in Biomedicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 589–602. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hedgpeth, T. EyeTell: Video-Assisted Touchscreen Keystroke Inference from Eye Movements. In Proceedings of the EyeTell: Video-Assisted Touchscreen Keystroke Inference from Eye Movements, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–24 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sluganovic, I.; Roeschlin, M.; Rasmussen, K.B.; Martinovic, I. Using reflexive eye movements for fast challenge-response authentication. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 October 2016; Volume 10, pp. 1056–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 568–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Lin, D.; Tang, X.; Van Gool, L. Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 10, pp. 20–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.Y.; Chen, M.H.; Kira, Z.; AlRegib, G. TS-LSTM and Temporal-Inception: Exploiting Spatiotemporal Dynamics for Activity Recognition. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1703.10667. [Google Scholar]
- Tesfaldet, M.; Brubaker, M.A.; Derpanis, K.G. Two-stream convolutional networks for dynamic texture synthesis. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1706.06982. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, R.A.; Meyer, D.E.; Kornblum, S. Speed and accuracy of saccadic eye movements: Characteristics of impulse variability in the oculomotor system. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1989, 15, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Krishnan, D.; Taylor, G.W.; Fergus, R. Deconvolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; Volume 6, pp. 2528–2535. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Taylor, G.W.; Fergus, R. Adaptive deconvolutional networks for mid and high level feature learning. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; Volume 11, pp. 2018–2025. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–7 and 12 September 2014; Volume 9, pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1511.06434. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Lars, B.; Gilles, L.; Mathieu, B.; Fabian, P.; Andreas, M.; Olivier, G.; Vlad, N.; Peter, P.; Alexandre, G.; Jaques, G.; et al. API design for machine learning software: Experiences from the scikit-learn project. ECML PKDD Workshop Lang. Data Min. Mach. Learn. 2013, arXiv:1309.0238, 108–122. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: All the experiments data and source code are available from the authors. |













| Distance from head to screen (cm) | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area of black | ≈ | ≈ | ≈ | ≈ |
| Name | Filter Size | Number of Kernel |
|---|---|---|
| CONV-E1 | 11 × 11 | 96 |
| CONV-F1 | 11 × 11 | 96 |
| CONV-E2 | 5 × 5 | 256 |
| CONV-F2 | 5 × 5 | 256 |
| CONV-E3 | 3 × 3 | 384 |
| CONV-F3 | 3 × 3 | 384 |
| CONV-E4 | 1 × 1 | 64 |
| CONV-F4 | 1 × 1 | 64 |
| Name | Number of Neurons |
|---|---|
| FC-E1 | 128 |
| FC-F1 | 128 |
| FC-F2 | 64 |
| FC-FG1 | 256 |
| FC-FG2 | 128 |
| FC1 | 128 |
| FC2 | 2 |
| Hyper-Parameter | Explanation | List of Values |
|---|---|---|
| kernel function | [‘rbf’, ‘linear’] | |
| C | cost parameter | [1 , ..., 1, 10, 100] |
| hyper-parameter of RBF (only if kernel = ‘rbf’) | [1 , ..., 1, 10, 100] |
| Prediction | 1.0 | −1.0 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ground truth | |||
| 1.0 | 37 | 0 | |
| −1.0 | 1 | 34 | |
| Authentication Method | Accuracy | FPR | FNR | Resist Shoulder Surfing? | Resist Impersonation Attacks? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Password | 100.0% | 0.00 | 0.00 | No | No |
| Fingerprint [8] | 98.6% | 0.00 | 0.01 | Yes | No |
| Face recognition [10] | 100.0% | 0.00 | 0.00 | Yes | No |
| Our method | 98.6% | 0.01 | 0.00 | Yes | Yes |
| Authentication Method | Accepted Impersonation | Rejected Impersonation | Error Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deep face recognition [10] | 11 | 5 | 68.75% |
| Our method | 0 | 16 | 0.00% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Ma, R.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J. Integrating Gaze Tracking and Head-Motion Prediction for Mobile Device Authentication: A Proof of Concept. Sensors 2018, 18, 2894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092894
Ma Z, Wang X, Ma R, Wang Z, Ma J. Integrating Gaze Tracking and Head-Motion Prediction for Mobile Device Authentication: A Proof of Concept. Sensors. 2018; 18(9):2894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092894
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Zhuo, Xinglong Wang, Ruijie Ma, Zhuzhu Wang, and Jianfeng Ma. 2018. "Integrating Gaze Tracking and Head-Motion Prediction for Mobile Device Authentication: A Proof of Concept" Sensors 18, no. 9: 2894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092894
APA StyleMa, Z., Wang, X., Ma, R., Wang, Z., & Ma, J. (2018). Integrating Gaze Tracking and Head-Motion Prediction for Mobile Device Authentication: A Proof of Concept. Sensors, 18(9), 2894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092894






