New Digital Plug and Imaging Sensor for a Proton Therapy Monitoring System Based on Positron Emission Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
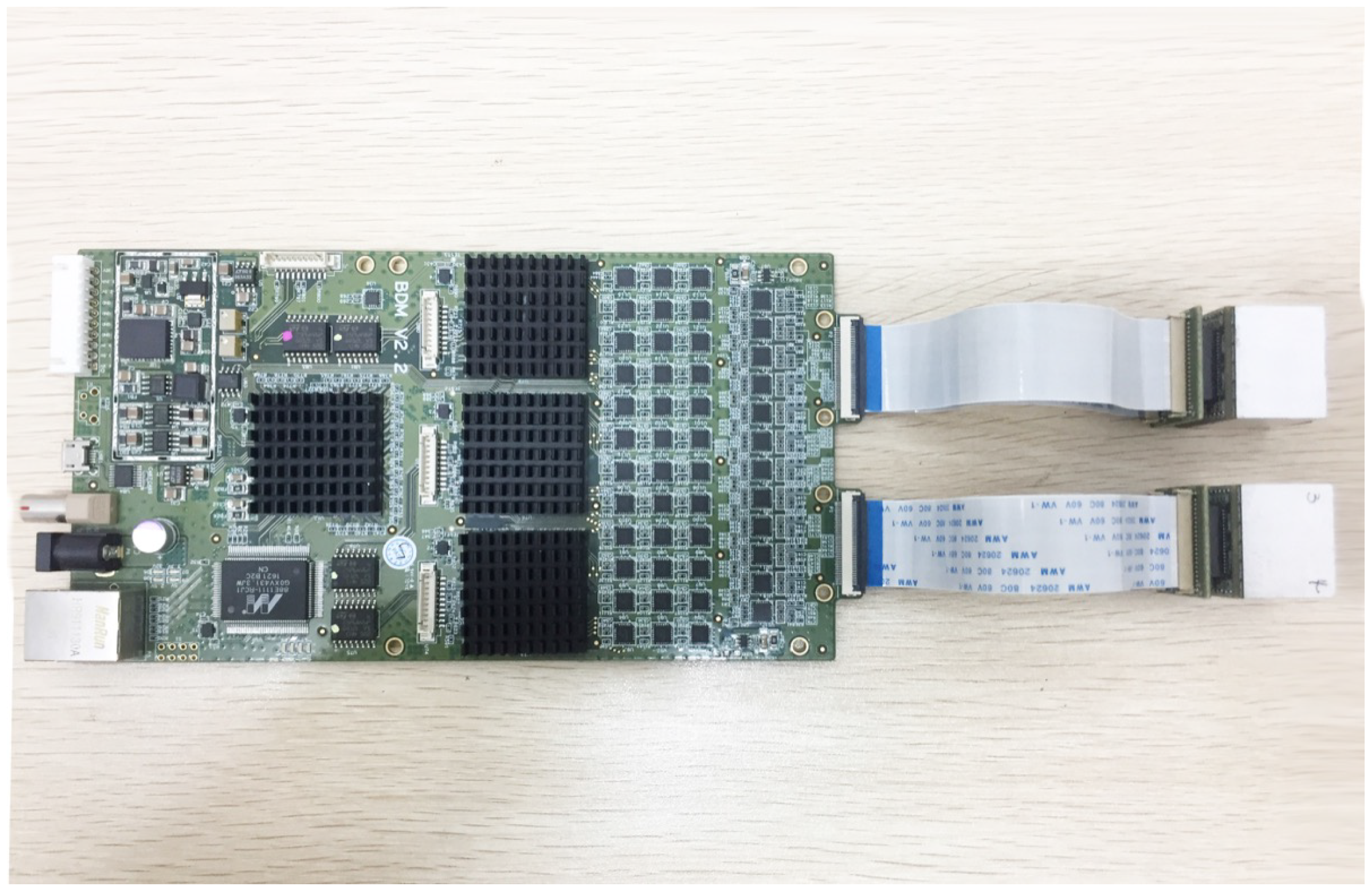
2.1. The Plug and Imaging Sensor System
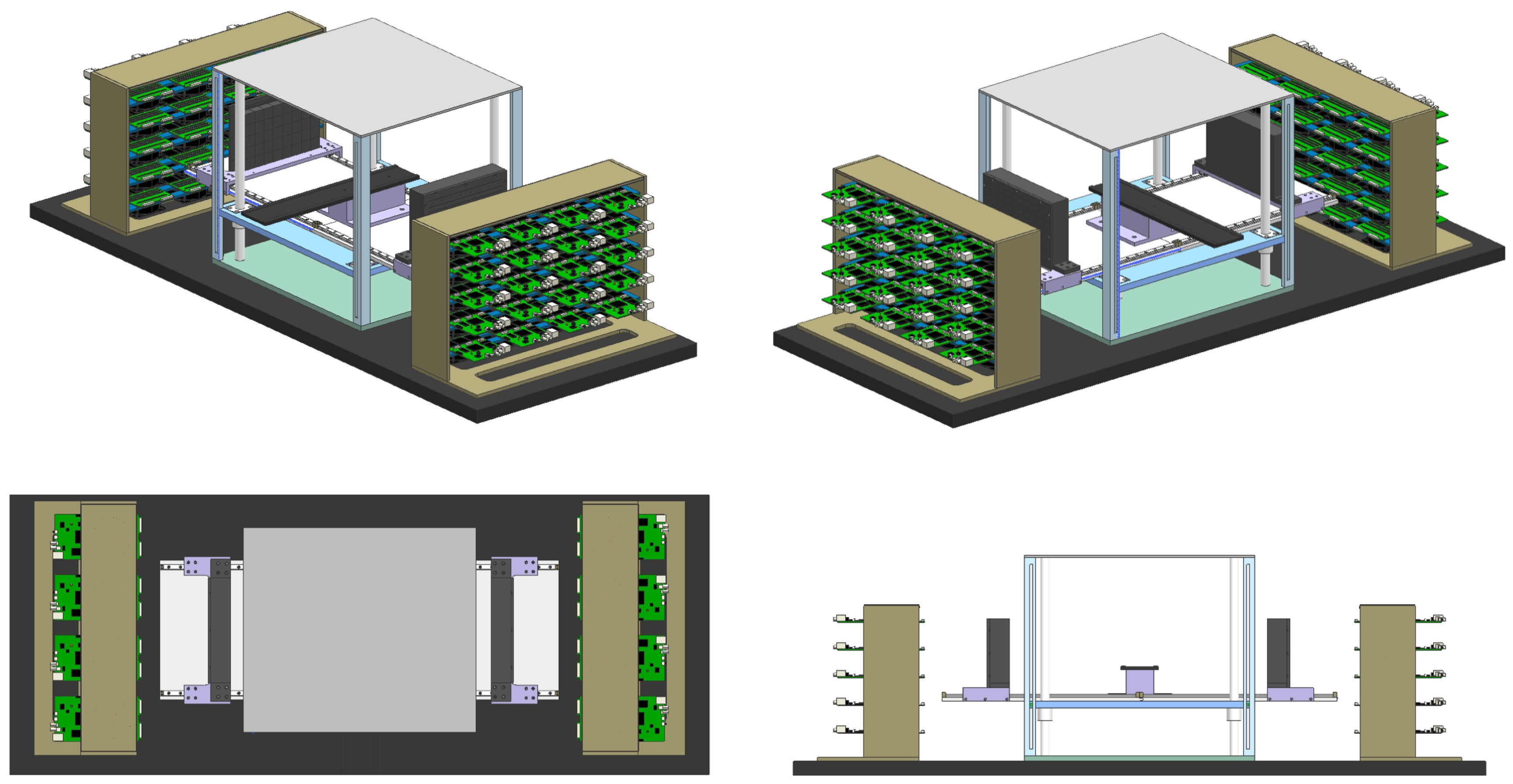
2.2. The Prototype of P&I PET for Proton Therapy Monitoring
2.3. Phantom Irradiation
2.4. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Performance of the P&I Sensor System
3.2. Lateral Profile of the Positron-Emitting Nuclei
3.3. Time Distribution of the Coincidence Rate
3.4. Prototype Performance in Beam-On Operation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| P&I | Plug&Imaging |
| DCR | Dark Count Rate |
| SiPM | Silicon Photomultiplier |
| CMOS | Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor |
| LYSO | Lutetium Yttrium Orthosilicate |
| MVT | Multi Voltage Threshold |
| TDC | Time to Digital Converter |
| LVDS | Low Voltage Differential Signaling |
| FPGA | Field Programmable Gate Array |
| FOV | Field Of View |
| PMMA | Polymethylmethacrylat |
| AU | Arbitrary Units |
| OSEM | Ordered subset expectation maximization |
References
- Colletti, P.M. 2017 SNMM: Highlights Lecture: General Nuclear Medicine. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 11N–15N. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- D’Ascenzo, N.; Xie, Q. Silicon Photomultiplier: Physics, Technological Challenges and Application to Modern Nuclear Medicine, in Photon Counting; Britun, N., Nikiforov, A., Eds.; INTECH: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018; ISBN 978-953-51-5775-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pawelke, J.; Haberer, T.; Hasch, B.G.; Hinz, R.; Kramer, M.; Lauckner, E.; Sobiella, M. In-beam PET imaging for the control of heavy-ion tumour therapy. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1997, 44, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enghardt, W.; Debus, J.; Haberer, T.; Hasch, B.G.; Hinz, R.; Jäkel, M.; Krämer, O.; Lauckner, K.; Pawelke, J.; Pönisch, F. Positron emission tomography for quality assurance of cancer therapy with light ion beams. Nucl. Phys. A 1999, 654, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enghardt, W.; Fromm, W.D.; Geissel, H. The spatial distribution of positron-emitting nuclei generated by relativistic light ion beams in organic matter. Phys. Med. Biol. 1992, 37, 2127–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.; Archambeau, J.; Archambeau, B.; Meltzer, J.; Wingate, C. Visualization and transport of positron emission from proton activation in vivo. Science 1978, 200, 1151–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, C.H.; Zhu, X.; Winey, B.A.; Grogg, K.; Testa, M.; El Fakhri, G.; Bortfeld, T.R.; Paganetti, H.; Shih, H.A. Clinical application of in-room positron emission tomography for in vivo treatment monitoring in proton radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 86, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moehrs, S.; Defrise, M.; Belcari, N.; Del Guerra, A.; Bartoli, A.; Fabbri, S.; Zanetti, G. Multi-ray-based system matrix generation for 3D PET reconstruction. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, 6925–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, T.; Miyatake, A.; Ogino, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Saijo, N.; Esumi, H. The development and clinical use of a beam on-line PET system mounted on a rotating gantry port in proton therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 76, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oelfke, U.; Lam, G.K.; Atkins, M.S. Proton dose monitoring with PET: Quantitative studies in Lucite. Phys. Med. Biol. 1995, 41, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganetti, H. Range uncertainties in proton therapy and the role of Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, K.; Bortfeld, T. A filtering approach based on Gaussian-powerlaw convolutions for local PET verification of proton radiotherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. A 2006, 51, 1991–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, K.; Crespo, P.; Eickhoff, H.; Haberer, T.; Pawelke, J.; Schardt, D.; Enghardt, W. Random coincidences during in-beam PET measurements at microbunched therapeutic ion beams. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2005, 545, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, K.; Enghardt, W. Potential application of PET in quality assurance of proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2000, 45, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendooven, P.; Buitenhuis, H.J.T.; Diblen, F.; Heeres, P.N.; Biegun, A.K.; Fiedler, F.; van Goethem, M.-J.; van der Graaf, E.R.; Brandenburg, S. Short-lived positron emitters in beam-on PET imaging during proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 8923–8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sportelli, G.; Belcari, N.; Camarlinghi, N.; Cirrone, G.A.P.; Cuttone, G.; Ferretti, S.; Kraan, A.; Ortuno, J.E.; Romano, F.; Santos, A.; et al. First full-beam PET acquisitions in proton therapy with a modular dual-head dedicated system. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, J.; Durante, M. Charged particle therapy-optimization, challenges and future directions. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Dedes, G.; Battistoni, G.; Boehlen, T.T.; Buvat, I.; Cerutti, F. Distributions of secondary particles in proton and carbon-ion therapy: A comparison between GATE/Geant4 and FLUKA Monte Carlo codes. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Espallardo, I.; Gillam, J.E.; Solevi, P.; Ortega, P.G.; Rohling, H.; Botas, P.; Oliver, J.F.; Llosa, G.; Solaz, C.; Trovato, M.; et al. Optimizing secondary radiation imaging systems for range verification in hadron therapy. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (2013 NSS/MIC, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Knopf, A.C.; Parodi, K.; Paganetti, H.; Bortfeld, T.; Daartz, J.; Engelsman, M.; Liebsch, N.; Shih, H. Accuracy of proton beam range verification using post-treatment positron emission tomography/computed tomography as function of treatment site. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashima, H.; Yamaya, T.; Yoshida, E.; Kinouchi, S.; Watanabe, M.; Tanaka, E. A single-ring OpenPET enabling PET imaging during radiotherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 4705–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Espana, S.; Daartz, J.; Liebsch, N.; Ouyang, J.; Paganetti, H.; Bortfeld, T.R.; El Fakhri, G. Monitoring proton radiation therapy with in-room PET imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 4041–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, P.; Shakirin, G.; Fiedler, F.; Enghardt, W.; Wagner, A. Direct time-of-flight for quantitative real-time in-beam PET: A concept and feasibility study. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 6795–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, P.; Shakirin, G.; Enghardt, W. On the detector arrangement for in-beam PET for hadron therapy monitoring. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, 2143–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, K.; Enghardt, W.; Haberer, T. In-beam PET measurements of beta+ radioactivity induced by proton beams. Phys. Med. Biol. 2001, 47, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, K. Vision 20/20: Positron emission tomography in radiation therapy planning, delivery, and monitoring. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 7153–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganetti, H.; Jiang, H.; Parodi, K.; Slopsema, R.; Engelsman, M. Clinical implementation of full Monte Carlo dose calculation in proton beam therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, 4825–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, K.; Pönish, F.; Enghardt, W. Experimental Study on the Feasibility of In-Beam PET for Accurate Monitoring of Proton Therapy. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2005, 52, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, T.; Infantino, A.; Lindsay, C.; Barlow, R.; Hoehr, C. Modelling PET radionuclide production in tissue and external targets using Geant4. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 874, 012109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraro, S.; Battistoni, G.; Belcari, N.; Bisogni, M.G.; Camarlinghi, N.; Cristoforetti, L.; Del Guerra, A.; Ferrari, A.; Fracchiolla, F.; Morrocchi, M.; et al. Proton therapy treatment monitoring with the DoPET system: Activity range, positron emitters evaluation and comparison with Monte Carlo predictions. JINST 2017, 12, C12026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brombal, L.; Barbosa, D.; Belcari, N.; Bisogni, M.G.; Camarlinghi, N.; Cristoforetti, L.; Del Guerra, A.; Fracchiolla, F.; Morrocchi, M.; Sportelli, G.; et al. Proton therapy treatment monitoring with in-beam PET: Investigating space and time activity distributions. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2017, 861, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HAMAMATSU. Available online: www.hamamatsu.com (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- SENSL. Available online: www.sensl.com (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- Haemisch, Y.; Frach, T.; Degenhardt, C.; Thon, A. Fully digital arrays of silicon photomultipliers (dSiPM) a scalable alternative to vacuum photomultiplier tubes (PMT). Phys. Procedia 2010, 37, 1546–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diblen, F.; Buitenhuis, T.; Solf, T.; Rodrigues, P.; van der Graaf, E.; van Goethem, M.-J.; Brandenburg, S.; Dendooven, P. Radiation hardness of dsipm sensors in a proton therapy radiation environment. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2017, 64, 1891–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitenhuis, H.J.T.; Diblen, F.; Brzezinski, K.W.; Brandenburg, S.; Dendooven, P. Beam-on imaging of short-lived positron emitters during proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 4654–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, V. The INSIDE project: In-beam PET scanner system features and characterization. J. Instrum. 2017, 12, C03051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piliero, M.A.; Pennazio, F.; Bisogni, M.G.; Camarlinghi, N.; Cerello, P.G.; Del Guerra, A.; Ferrero, V.; Fiorina, E.; Giraudo, G.; Morrocchi, M.; et al. Full-beam performances of a PET detector with synchrotron therapeutic proton beams. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, N650–N666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petzoldt, J.; Roemer, K.E.; Enghardt, W.; Fiedler, F.; Golnik, C.; Hueso-Gonzalez, F.; Helmbrecht, S.; Kormoll, T.; Rohling, H.; Smeets, J.; et al. Characterization of the microbunch time structure of proton pencil beams at a clinical treatment facility. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 2432–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, F.H.; Pausch, G.; Petzoldt, J.; Römer, K.E.; Enghardt, W. Prompt Gamma rays detected with a BGO block Compton camera reveal range deviations of therapeutic proton beams. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2017, 1, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoene, S.; Enghardt, W.; Fiedler, F.; Golnik, C.; Pausch, G.; Rohling, H.; Kormoll, T. An Image Reconstruction Framework and Camera Prototype Aimed for Compton Imaging for In-vivo Dosimetry of Therapeutic Ion Beams. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2017, 1, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Toshito, T.; Komori, M.; Morishita, Y.; Okumura, S.; Yamaguchi, M.; Saito, Y.; Kawachi, N.; Fujimaki, S. Monitoring of positron using high-energy gamma camera for proton therapy. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2015, 29, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCleskey, M.; Kaye, W.; Mackin, D.S.; Beddar, S.; He, Z.; Polf, J.C. Evaluation of a multistage CdZnTe Compton camera for prompt γ imaging for proton therapy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2015, 785, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohling, H.; Golnik, C.; Enghardt, W.; Hueso-González, F.; Kormoll, T.; Pausch, G.; Schumann, A.; Fiedler, F. Simulation study of a combined pair production—Compton camera for in-vivo dosimetry during therapeutic proton irradiation. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2015, 62, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bom, V.; Joulaeizadeh, L.; Beekman, F. Real-time prompt gamma monitoring in spot-scanning proton therapy using imaging through a knife-edge-shaped slit. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, J.; Roellinghoff, F.; Prieels, D.; Stichelbaut, F.; Benilov, A.; Busca, P.; Fiorini, C.; Peloso, R.; Basilavecchia, M.; Frizzi, T.; et al. Prompt gamma imaging with a slit camera for real-time range control in proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 3371–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, M.-H.; Chevallier, M.; Dauvergne, D.; Freud, N.; Henriquet, P.; Le Foulher, F.; Letang, J.M.; Montarou, G.; Ray, C.; Roellinghoff, F.; et al. Design guidelines for a double scattering Compton camera for prompt-γ imaging during ion beam therapy: A Monte Carlo simulation study. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2011, 58, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golnik, C.; Dersch, U.; Fiedler, F.; Kormoll, T.; Rohling, H.; Enghardt, W. A pair production upgrade for a Compton imager for in-vivo dosimetry at therapeutic proton and ion beams. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, Valencia, Spain, 23–29 October 2011; pp. 3323–3326. [Google Scholar]
- Kormoll, T.; Fiedler, F.; Schöne, S.; Wüstemann, J.; Zuber, K.; Enghardt, W. A Compton imager for in-vivo dosimetry of proton beams—A design study. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2011, 626, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Fiedler, F.; Georg, D.; Hopfgartner, J.; Enghardt, W. 118 in-beam SPECT based in vivo dosimetry: From treatment planning to measured dose. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 103, S47–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ascenzo, N.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Q. Application of CMOS Technology to Silicon Photomultiplier Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ascenzo, N.; Brockherde, W.; Dreiner, S.; Schwinger, A.; Schmidt, A.; Xie, Q. Design and Characterization of a Silicon Photomultiplier in 0.35-μm CMOS. J. Electron Dev. Soc. 2018, 6, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Xi, D.; Li, C.; Zeng, C.; Wang, R.; Liang, K.; Yang, R.; Xie, Q.; Han, D. Feasibility Study on Silicon Photomultiplier with Epitaxial Quenching Resistors as the Readout for PET Detectors. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2016, 63, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Xie, Q. Quadratic Programming Time Pickoff Method for Multivoltage Threshold Digitizer in PET. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2015, 62, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Xie, Q.; Duan, Z.; Xiao, P. Scintillation event energy measurement via a pulse model based iterative deconvolution method. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 7815–7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, D.; Kao, C.-M.; Liu, W.; Zeng, C.; Liu, X.; Xie, Q. FPGA-only MVT digitizer for TOF PET. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 3253–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, Q.; Chen, Y.; Niu, M. Advantages of digitally sampling scintillation pulses in pileup processing in PET. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2012, 59, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, D.; Xie, Q.; Zhu, J.; Lin, L.; Niu, M.; Xiao, P.; Chen, C.-T.; Kao, C.-M. Optimization of the SiPM pixel size for a monolithic PET detector. Phys. Proc. 2012, 37, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Kao, C.-M.; Wang, X.; Guo, N.; Zhu, C.; Frisch, H.; Moses, W.W.; Chen, C.T. Potentials of digitally sampling scintillation pulses in timing determination in PET. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2009, 56, 2607–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kao, C.-M.; Xie, Q.; Frisch, H.; Chen, C.-T.; Tang, F. A multi-threshold method for TOF PET signal processing. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 2009, 602, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Kao, C.-M.; Hsiau, Z.; Chen, C.-T. A new approach for pulse processing in Positron Emission Tomography. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2005, 52, 988–995. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, D.; Liu, X.; Zeng, C.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Hua, Y.; Mei, X.; Kim, H.; Xiao, P.; Kao, C.-M.; et al. Modularized compact positron emission tomography detector for rapid system development. J. Med. Imaging 2016, 4, 011006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, X.; Xi, D.; Zeng, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Hua, Y.; Kim, H.; Xiao, P.; Kao, C.-M.; Xie, Q. A 72-channel FPGA-only MVT digitizer board and a micro-system for coincidence detection/imaging. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC), Seattle, WA, USA, 8–15 November 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, D.; Zeng, C.; Mei, X.; Wan, L.; Liang, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Kim, H.; Xiao, P.; et al. A digital PET system based on SiPMs and FPGA-only MVT digitizers. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC), Seattle, WA, USA, 8–15 November 2014; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Xie, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, C.; Wang, S.; Zheng, R.; Wan, L.; Xiao, P. A Panel PET With Window: Design Performance Evaluation and Prototype Development. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2017, 1, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcari, N.; Attanasi, F.; Moehrs, S.; Rosso, V.; Santos, A.; Spinella, F.; Sportelli, G.; Del Guerra, A. A novel random counts estimation method for PET using a symmetrical delayed window technique and random single event acquisition. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record (NSS/MIC), Orlando, FL, USA, 24 October–1 November 2009; pp. 3611–3614. [Google Scholar]
- Beebe-Wang, J.; Vaska, P.; Dilmanian, F.A.; Peggs, S.G.; Schlyer, D.J. Simulation of Proton Therapy Treatment Verificationvia PET Imaging of Induced Positron-Emitters. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Portland, OR, USA, 19–25 October 2003; pp. 2496–2500. [Google Scholar]
- Lestand, L.; Montarou, G.; Force, P.; Joly, B.; Lambert, D.; Martin, F.; Rozes, A.; Vert, P.E.; Chadelas, R. In Beam PET Acquisition on 75 MeV. textu−1 Carbon Beam Using Sampling-Based Read-Out Electronics. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2017, 1, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmbrecht, S.; Enghardt, W.; Fiedler, F.; Iltzsche, M.; Pausch, G.; Tintori, C.; Kormoll, T. In-beam PET at clinical proton beams with pile-up rejection. Z. Med. Phys. 2017, 27, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binet, S.; Bongrand, A.; Busato, E.; Force, P.; Guicheney, C.; Insa, C.; Lambert, D.; Magne, M.; Martin, F.; Perrin, H.; et al. FPGA-based multichannel data acquisition system for prototype in-beam PET. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (2013 NSS/MIC), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ritt, S.; Dinapoli, R.; Hartmann, U. Application of the DRS chip for fast waveform digitizing. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2010, 623, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, B.; Montarou, G.; Lecoq, J.; Bohner, G.; Crouau, M.; Brossard, M.; Vert, P.-E. An optimal filter based algorithm for PET detectors with digital sampling front-end. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2010, 57, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varner, G.; Ruckman, L.; Wong, A. The first version buffered large analog bandwidth (BLAB1) ASIC for high luminosity collider and extensive radio neutrino detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2008, 591, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritt, S. Design and performance of the 6 GHz waveform digitizing chip DRS4. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, Dresden, Germany, 19–25 October 2008; pp. 1512–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Cambraia Lopes, P.; Bauer, J.; Salomon, A.; Rinaldi, I.; Tabacchini, V.; Tessonnier, T.; Crespo, P.; Parodi, K.; Schaart, D.R. First in situ TOF-PET study using digital photon counters for proton range veri cation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 6203–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- (TheCALICE Collaboration). Construction and commissioning of the CALICE analog hadron calorimeter prototype. J. Instrum. 2010, 5, P05004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the P&I system are available from the authors. |











| Isotope | Channel | Threshold [MeV] |
|---|---|---|
| 15O | 16O(p,pn)15O | 16.79 |
| 11C | 12C(p,pn)11C | 20.61 |
| 16O(p,3p3n)11C | 59.64 | |
| 10C | 12C(p,p2n)10C | 35 |
| 16O(p,3p4n)10C | 72 |
| Element | Half life Literature [s] | Half Life Measurement [s] | Abundance Simulation (%) | Abundance Measurement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15O | 122 | 2 | ||
| 11C | 1220 | |||
| 10C | 19.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Ascenzo, N.; Gao, M.; Antonecchia, E.; Gnudi, P.; Chen, H.-H.; Chen, F.-H.; Hong, J.-H.; Hsiao, I.-T.; Yen, T.-C.; Wang, W.; et al. New Digital Plug and Imaging Sensor for a Proton Therapy Monitoring System Based on Positron Emission Tomography. Sensors 2018, 18, 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093006
D’Ascenzo N, Gao M, Antonecchia E, Gnudi P, Chen H-H, Chen F-H, Hong J-H, Hsiao I-T, Yen T-C, Wang W, et al. New Digital Plug and Imaging Sensor for a Proton Therapy Monitoring System Based on Positron Emission Tomography. Sensors. 2018; 18(9):3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093006
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Ascenzo, Nicola, Min Gao, Emanuele Antonecchia, Paolo Gnudi, Hsien-Hsin Chen, Fang-Hsin Chen, Ji-Hong Hong, Ing-Tsung Hsiao, Tzu-Chen Yen, Weidong Wang, and et al. 2018. "New Digital Plug and Imaging Sensor for a Proton Therapy Monitoring System Based on Positron Emission Tomography" Sensors 18, no. 9: 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093006
APA StyleD’Ascenzo, N., Gao, M., Antonecchia, E., Gnudi, P., Chen, H.-H., Chen, F.-H., Hong, J.-H., Hsiao, I.-T., Yen, T.-C., Wang, W., Xi, D., Zhang, B., & Xie, Q. (2018). New Digital Plug and Imaging Sensor for a Proton Therapy Monitoring System Based on Positron Emission Tomography. Sensors, 18(9), 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093006





