Wireless Sensor Networks for Long-Term Monitoring of Urban Noise
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. State of the Art of Wireless Acoustic Sensor Networks
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Background: Sound Level
3.2. System Prototyping
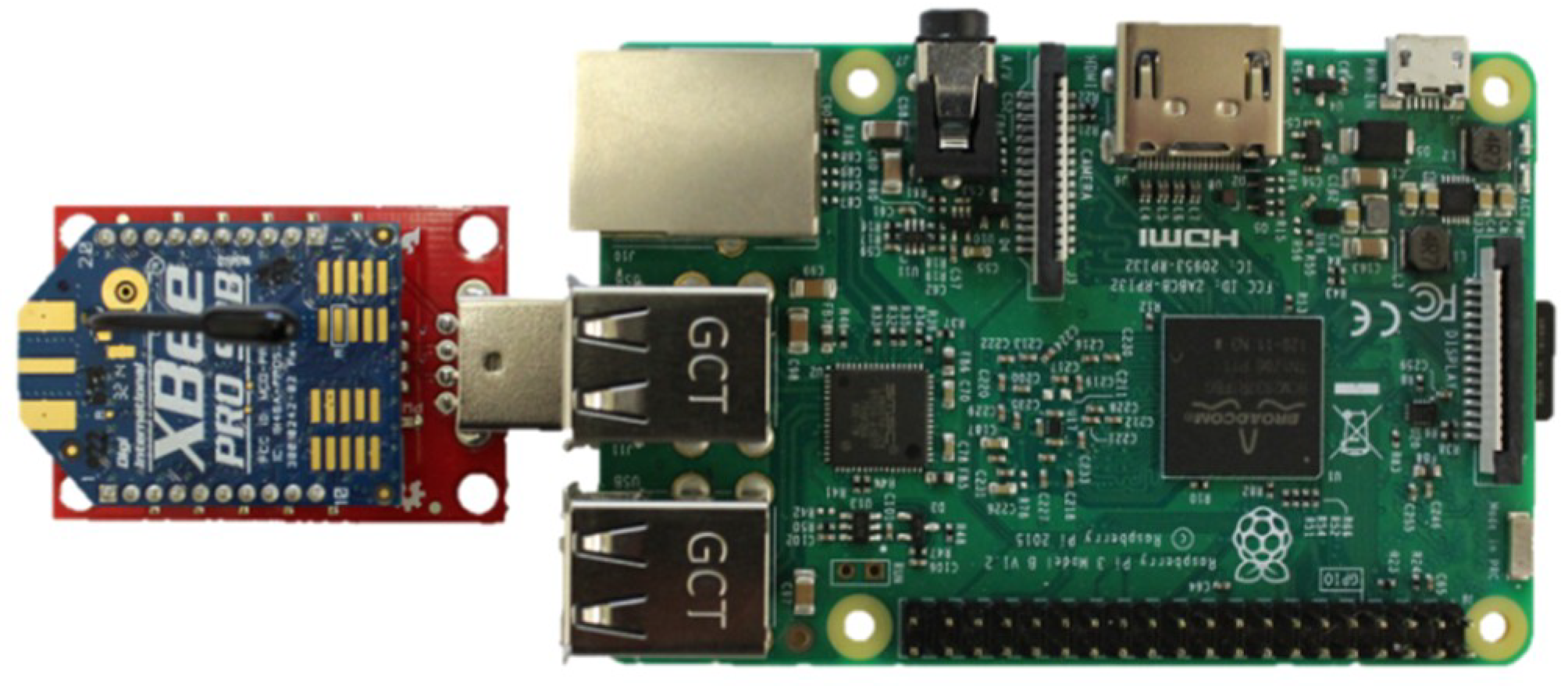
3.2.1. Hardware Design
3.2.2. Software Implementation
3.2.3. Centralized Repository
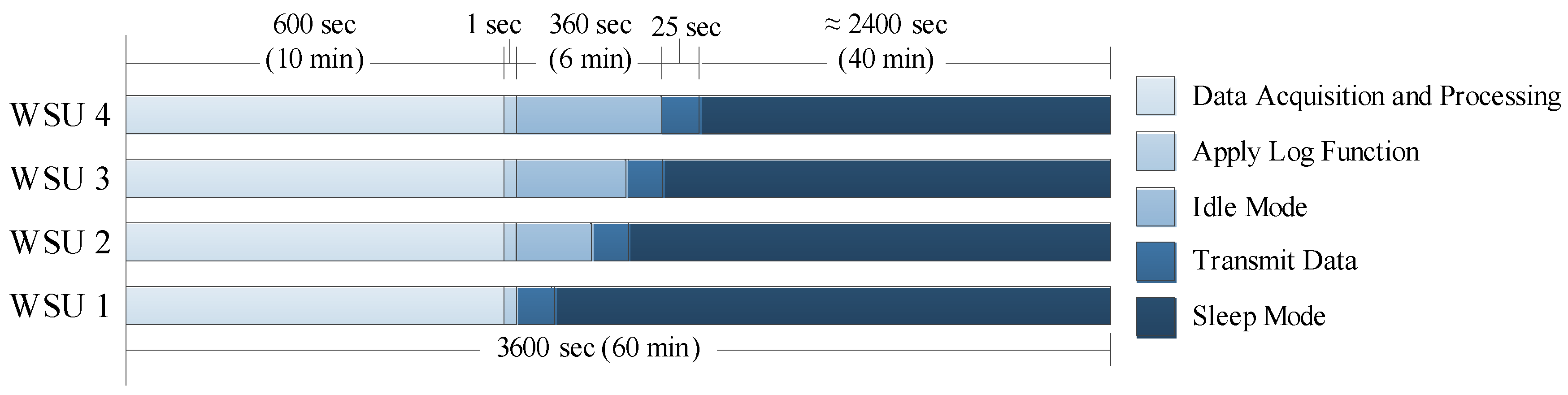
3.2.4. Data Acquisition and Transmission
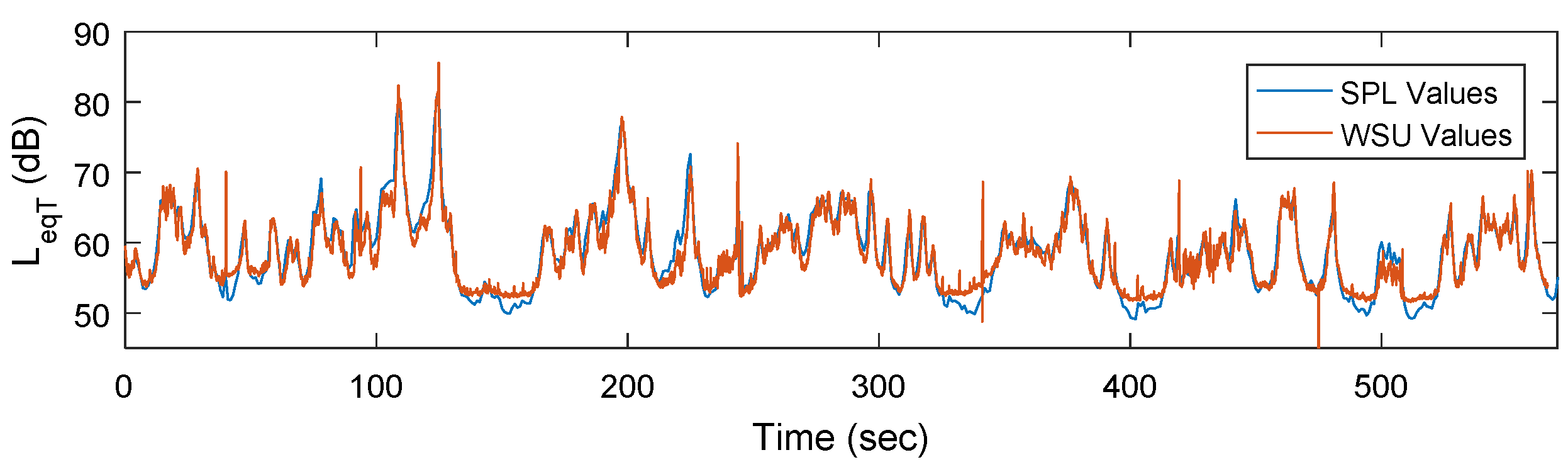
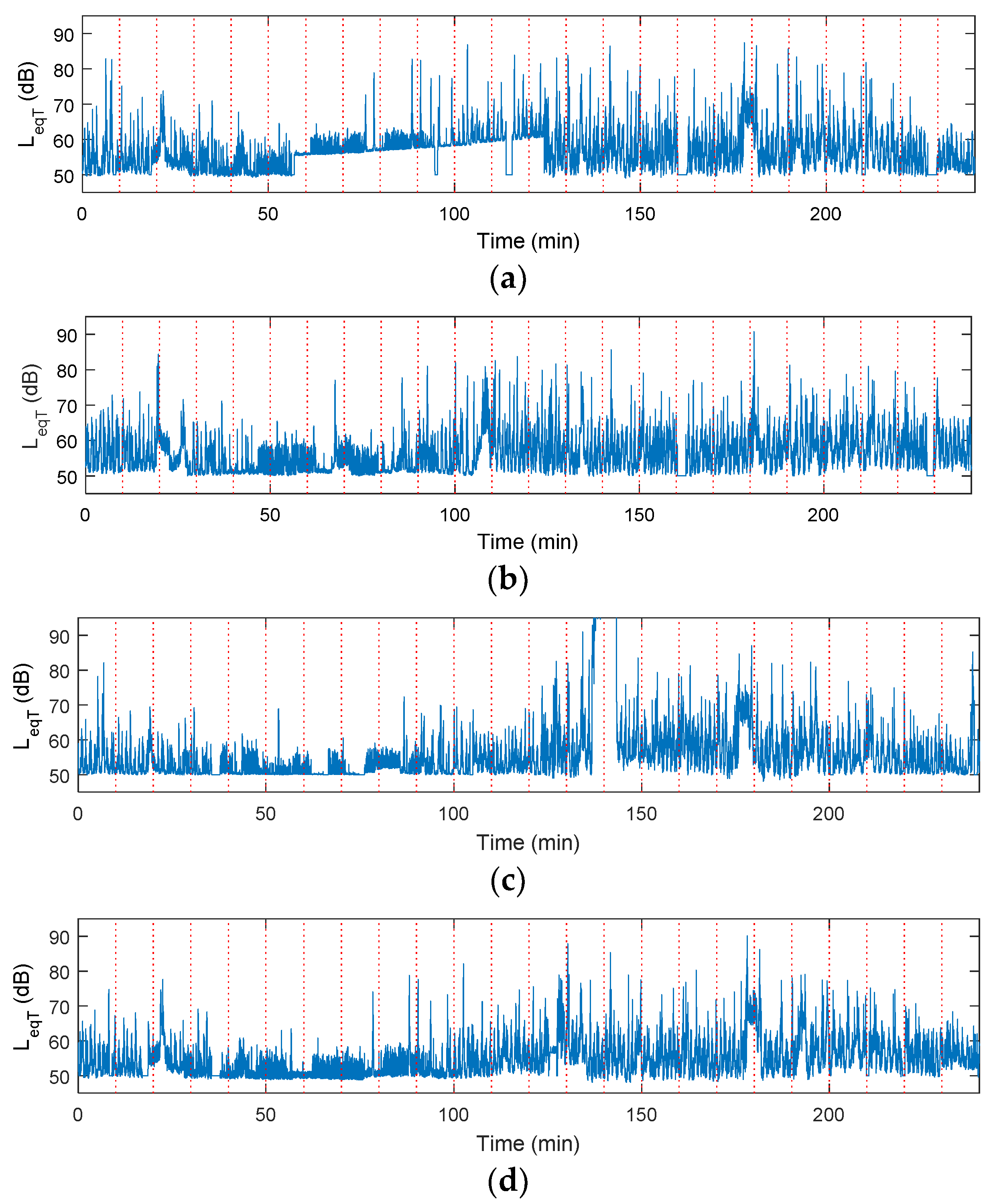
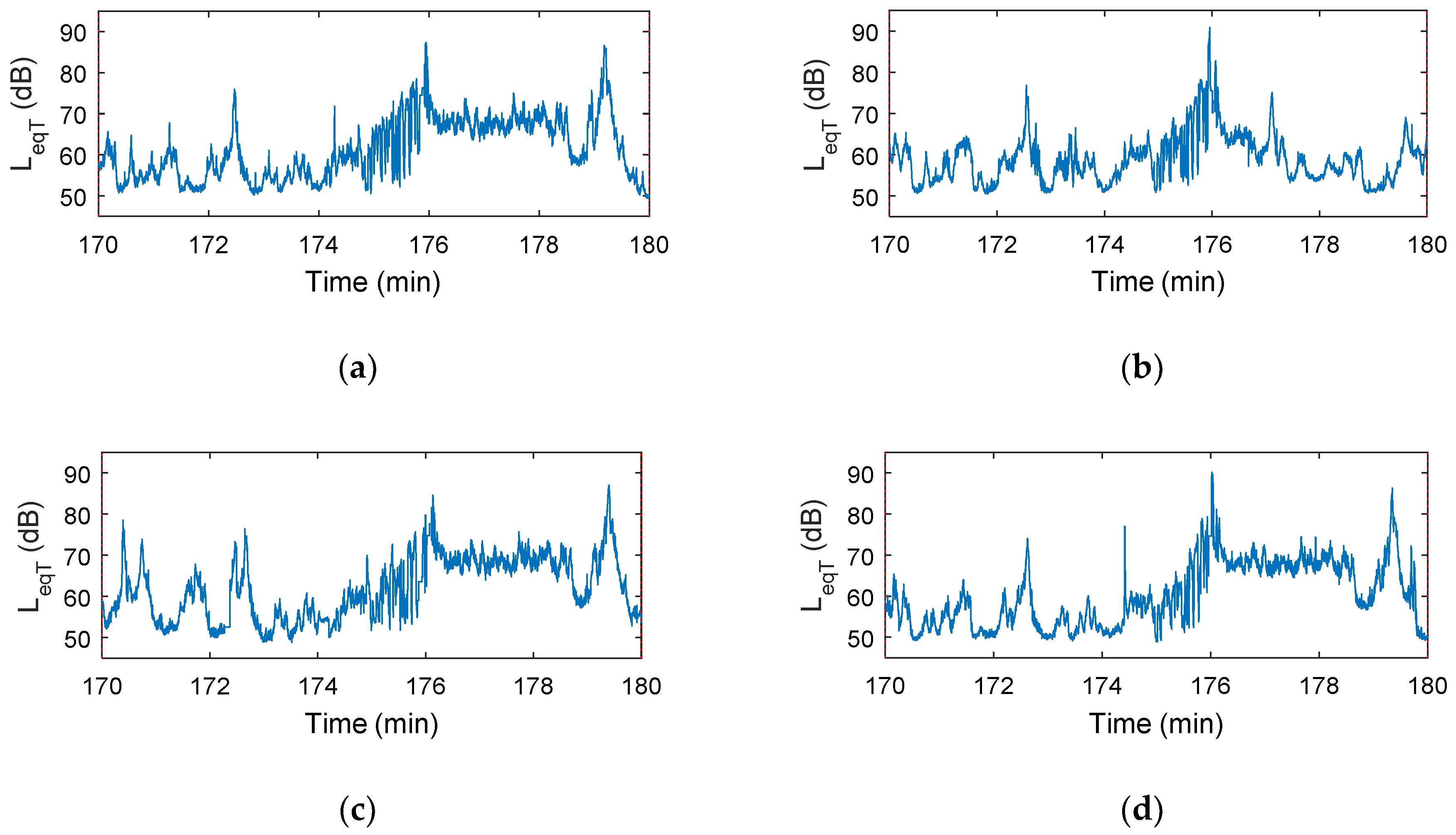
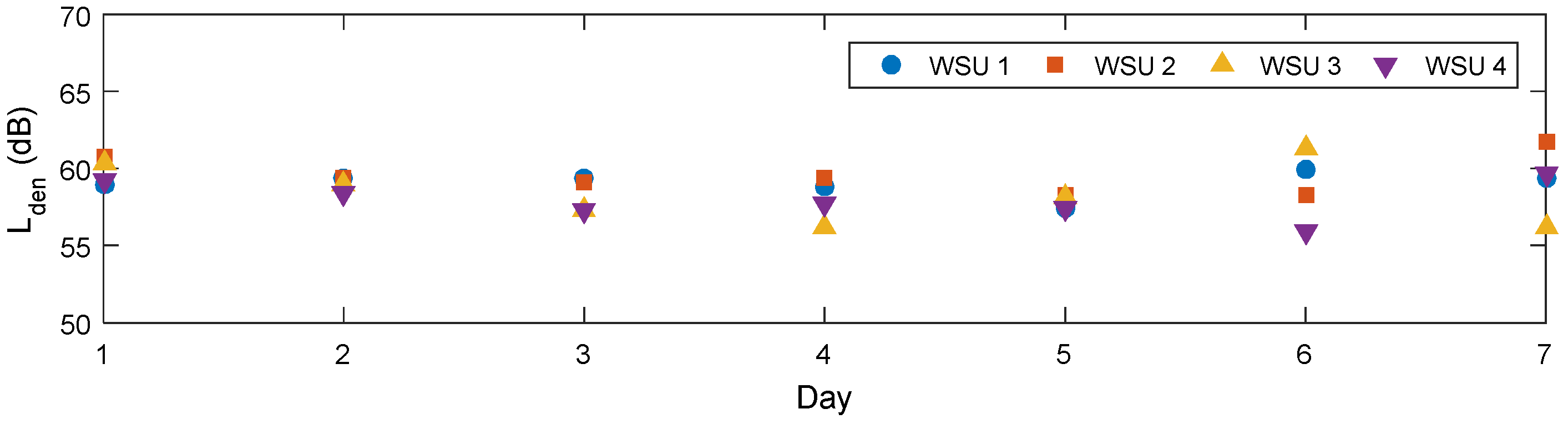
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Population Division World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision. Available online: https://esa.un.org/unpd/wup/Download/ (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- Morandi, C.; Rolando, A.; Di Vita, S. From Smart City to Smart Region: Digital Services for an Internet of Places; SpringerBriefs: Zurich, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fira de Barcelona Smart City Expo World Congress, Report 2017. Available online: http://media.firabcn.es/content/S078018/docs/SCEWC17_Report.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- Anthopoulos, L.G.; Valaki, A. Urban planning and smart cities: Interrelations and reciprocitites. Future Internet 2012, 7281, 178–189. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Hancock, M.G.; Hu, M.-C. Towards an effective framework for building smart cities: Lessons from Seoul and San Francisco. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2014, 89, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency Managing Exposure to Noise in Europe. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/managing-exposure-to-noise-in-europe (accessed on 15 August, 2018).
- Stansfeld, S.A.; Matheson, M.P. Noise pollution: Non-auditory effects on health. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, M.S.; Swinburn, T.K.; Neitzel, R.L. Environmental Noise pollution in the United States: Developing an effective public health response. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goines, L.; Hagler, L. Noise pollution: A modern plague. South. Med. J. 2007, 100, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Night Noise Guidelines for Europe; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Federal Aviation Administration Fundamentals of Noise and Sound. Available online: https://www.faa.gov/regulations_policies/policy_guidance/noise/basics/ (accessed on 16 August 2018).
- European Communities. Directive 2002/49/EC of the European Parliament and the Management of Environmental Noise; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kephalopoulos, S.; Paviotti, M.; Anfosso-Ledee, F. Common Noise Assessment Methods in Europe (CNOSSOS-EU); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- X-NOISE: Dedicated to the Reduction of Aircraft Noise. Available online: https://www.xnoise.eu/home/ (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- FONOMOC—The Main Network for Noise Monitoring. Available online: https://workinggroupnoise.com/fonomoc/ (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- Environmental Protection Agency Clean Air Act Title IV—Noise Pollution. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/clean-air-act-overview/clean-air-act-title-iv-noise-pollution (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- Steele, C. A critical review of some traffic noise prediction models. Appl. Acoust. 2001, 62, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedo, K.K.; Perseedoss, R.; Mungur, A. A wireless sensor network air pollution monitoring system. Int. J. Wirel. Mob. Netw. 2010, 2, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, A.; Yaacoub, E.; Mushtaha, M.; Abu-Dayya, A. Wireless sensor network for real-time air pollution monitoring. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Communication, Signal Processing, and their Applications, Sharjah, UAE, 12–14 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Moltchanov, S.; Levy, I.; Etzion, Y.; Lerner, U.; Broday, D.M.; Fishbain, B. On the feasibility of measuring urban air pollution by wireless distributed sensor networks. Natl. Cent. Biotechnol. Inf. 2015, 502, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idwan, S.; Zubairi, J.A.; Mahmood, I. Smart Solutions for Smart Cities: Using Wireless Sensor Network for Smart Dumpster Management. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Collaboration Technologies and Systems, Orlando, FL, USA, 31 October–4 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bartos, M.; Wong, B.; Kerkez, B. Open storm: A complete framework for sensing and control of urban watersheds. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipponi, L.; Santini, S.; Vitaletti, A. Data collection in wireless sensor networks for noise pollution monitoring. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems, DCOSS 2008, Santorini Island, Greece, 11–14 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hakala, I.; Kivela, I.; Ihalainen, J.; Luomala, J.; Gao, C. Design of low-cost noise measurement sensor network: Sensor function design. In Proceedings of the 2010 First International Conference on Sensor Device Technologies and Applications, Venice, Italy, 18–25 July 2010; pp. 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Noriega-Linares, J.E.; Ruiz, J.M.N. On the application of the Raspberry PI as an advanced acoustic sensor network for noise monitoring. Electronics 2016, 5, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mydlarz, C.; Salamon, J.; Bello, J.P. The implementation of low-cost urban acoustic monitoring devices. J. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 117, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsina-Pages, R.M.; Hernandez-Jayo, U.; Alias, F.; Angulo, I. Design of mobile low-cost sensor network using urban buses for real-time ubiquitous noise monitoring. Sensors 2017, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubbi, J.; Marusic, S.; Rao, A.S.; Law, Y.W.; Palaniswami, M. A pilot study of urban noise monitoring architecture using wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics, Mysore, India, 22–25 August 2013; pp. 1047–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Zappatore, M.; Longo, A.; Bochicchio, M.A. Crowd-sensing our smart cities: A platform for noise monitoring and acoustic urban planning. J. Commun. Softw. Syst. 2017, 13, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspuru, I.; Garcia, I.; Herranz, K.; Santander, A. CITI-SENSE: Methods and tools for empowering citizens to observe acoustic comfort in outdoor public spaces. Noise Mapp. 2016, 3, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardous, C.A.; Shaw, P.B. Evaluation of smartphone sound measurement applications. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nast, D.R.; Speer, W.S.; Le Prell, C.G. Sound level measurements using smartphone “apps”: Userful or inaccurate? Noise Health 2014, 16, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumond, P.; Lavandier, C.; Riberio, C.; Gonzalez Boix, E.; Kambona, K.; D’Hondt, E.; Delaitre, P. A study of the accuracy of mobile technology for measuring urban noise pollution in large scale participatory sensing campaigns. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 117, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, R.; Chou, C.T.; Bulusu, N.; Kanhere, S.; Hu, W. Ear-Phone: A Context-aware noise mapping using smart phones. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2015, 17, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, W.; Calafate, C.T.; Cano, J.-C.; Manzoni, P. Accurate ambient noise assessment using smartphones. Sensors 2017, 17, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivela, I.; Hakala, I. Area-based environmental noise measurements with a wireless sensor network. In Proceedings of the Euronoise 2015, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 31 May–3 June 2015; pp. 218–220. [Google Scholar]
- Mietlicki, F.; Mietlicki, C.; Sineau, M. An innovative approach for long-term envinronmental noise measurement: RUMEUR network in Paris region. In Proceedings of the Euronoise 2015, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 31 May–3 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Maijala, P.; Shuyang, Z.; Heittola, T.; Virtanen, T. Environmental noise monitoring using source classification in sensors. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 129, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acoustical Society of America (ASA). American National Standards Institute Design Response of Weighting Networks for Acoustical Measurement; ASA: Melville, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- PJRC Teensy USB Development Board. Available online: https://www.pjrc.com/teensy/ (accessed on 18 July 2018).
- Digi Zigbee RF Modules: XBEE2, XBEEPRO2, PRO S2B. Available online: https://www.digi.com/resources/documentation/digidocs/pdfs/90000976.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2018).
- NoiseMeters CEL-200 Series: Digital Sound Level Meters. Available online: https://www.noisemeters.com/product/cel/pdf/cel200.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2018).
- Raspberrypi.org Raspberry Pi 3 Model B. Available online: https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-3-model-b/ (accessed on 19 July 2018).
- Pule, M.; Yahya, A.; Chuma, J. Wireless sensor networks: A survey on monitoring water quality. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2017, 15, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
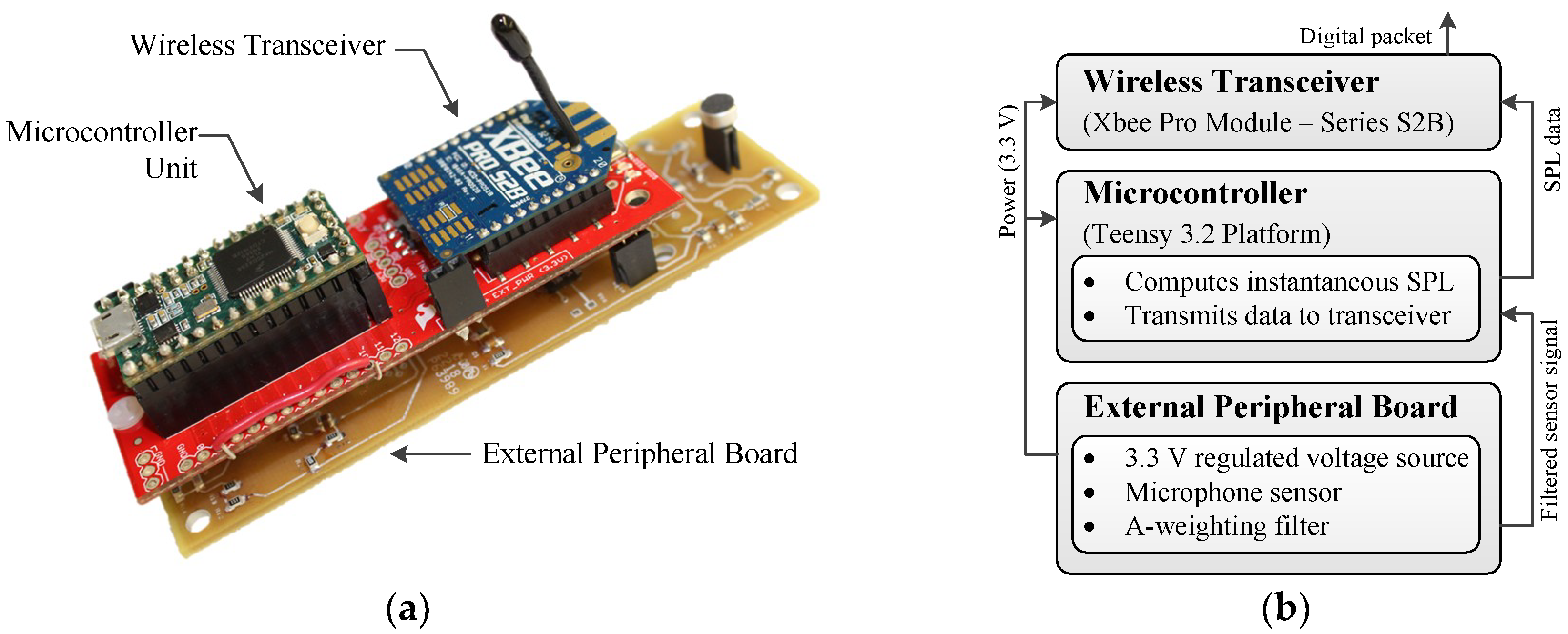


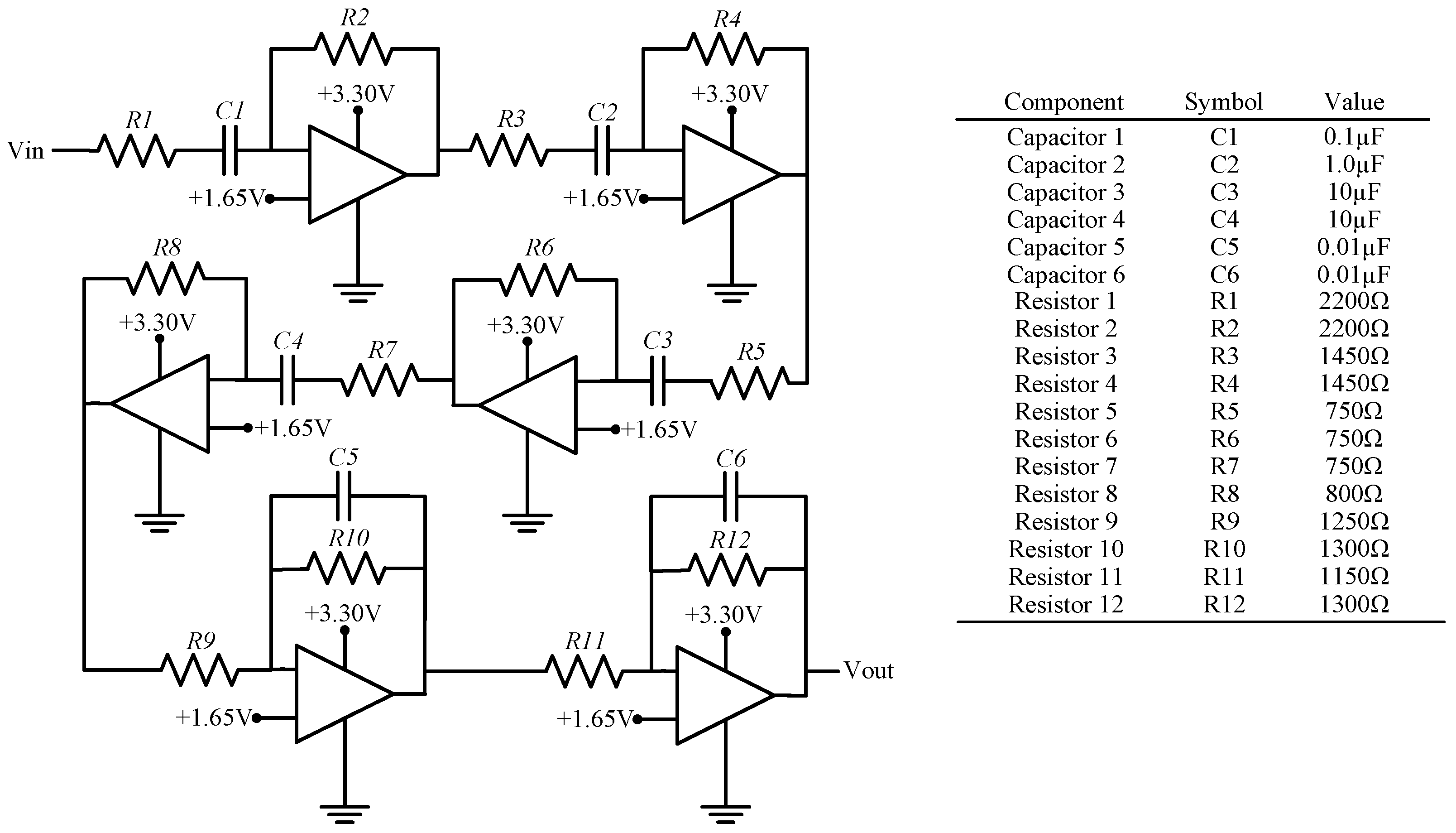
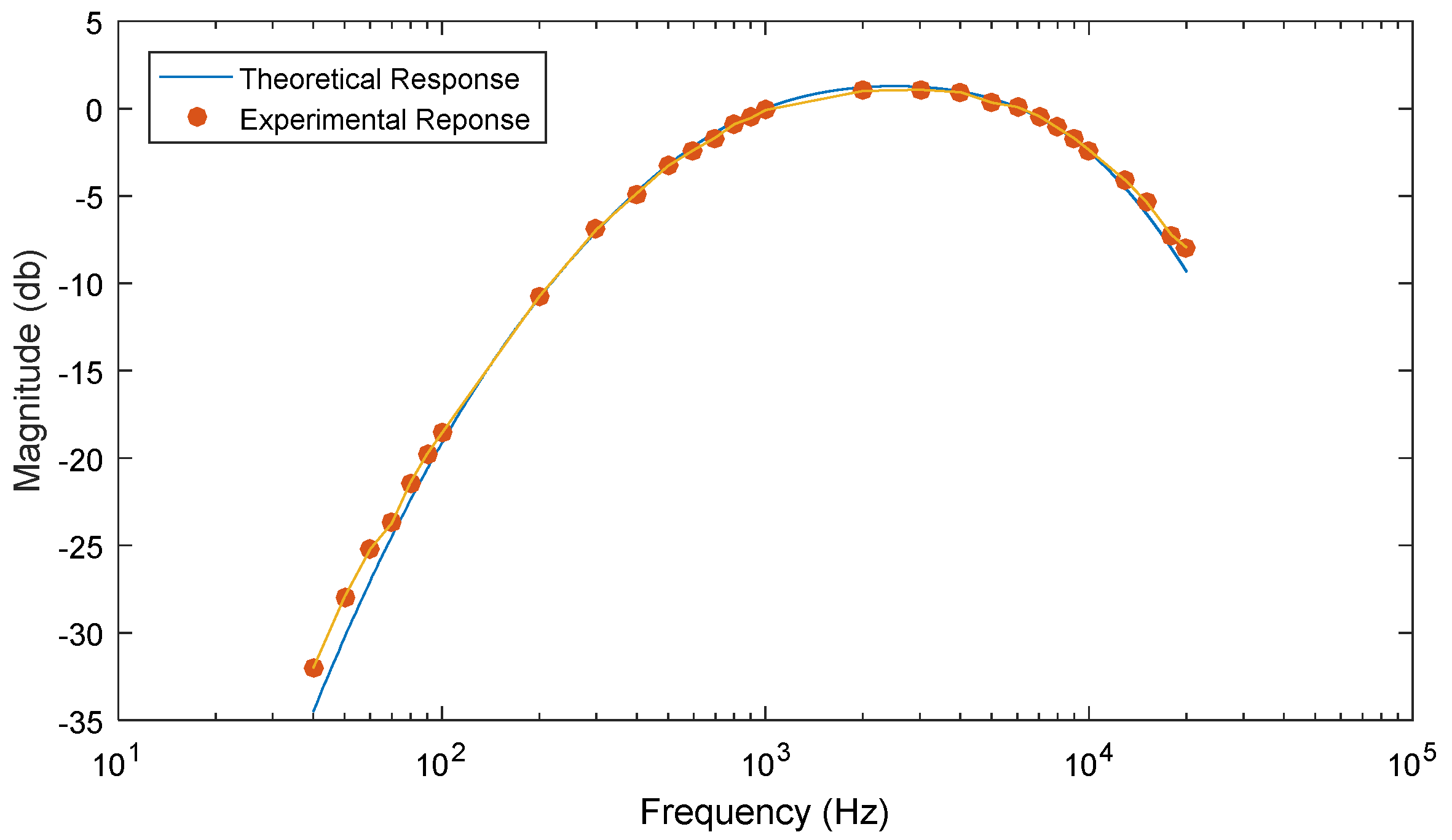

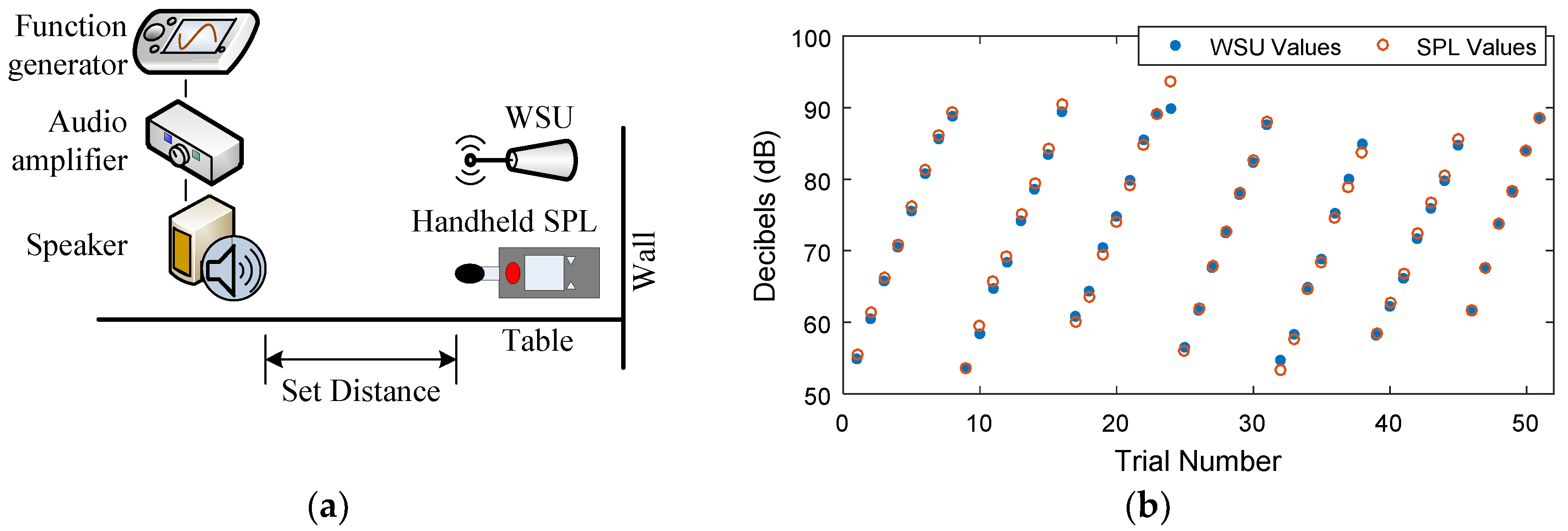


| Part | Commercial Name | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Microcomputer | Teensy 3.2 Platform | $20 |
| Wireless transceiver | XBee Pro Module—Series 2SB | $20 |
| Adapter board | Teensy 3.1 XBee Adapter | $10 |
| Microphone | PUI Audio Microphone | $5 |
| Ext. Peripheral Board and Components | - | $20 |
| Assembly Cost | 3 h @ $20/h | $60 |
| Total Price per Node | $135 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peckens, C.; Porter, C.; Rink, T. Wireless Sensor Networks for Long-Term Monitoring of Urban Noise. Sensors 2018, 18, 3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093161
Peckens C, Porter C, Rink T. Wireless Sensor Networks for Long-Term Monitoring of Urban Noise. Sensors. 2018; 18(9):3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093161
Chicago/Turabian StylePeckens, Courtney, Cédric Porter, and Taylor Rink. 2018. "Wireless Sensor Networks for Long-Term Monitoring of Urban Noise" Sensors 18, no. 9: 3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093161
APA StylePeckens, C., Porter, C., & Rink, T. (2018). Wireless Sensor Networks for Long-Term Monitoring of Urban Noise. Sensors, 18(9), 3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093161




