D-Shaped POF Sensors for Refractive Index Sensing—The Importance of Surface Roughness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
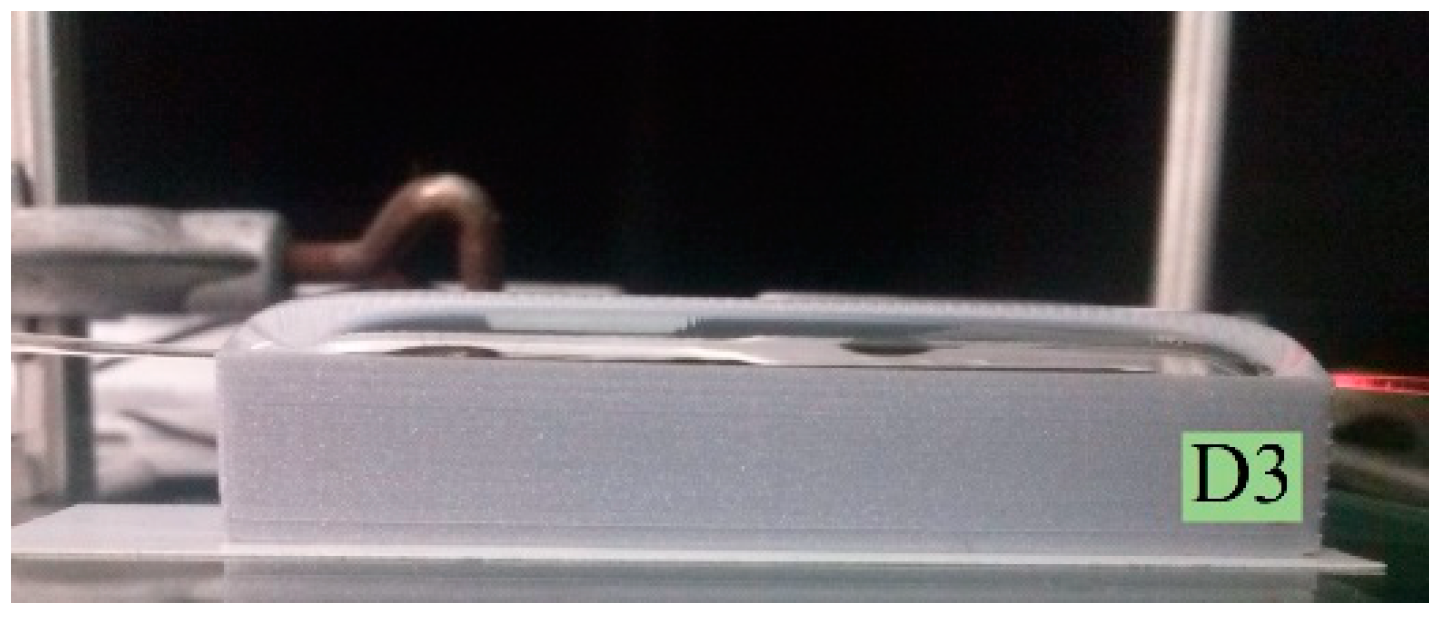
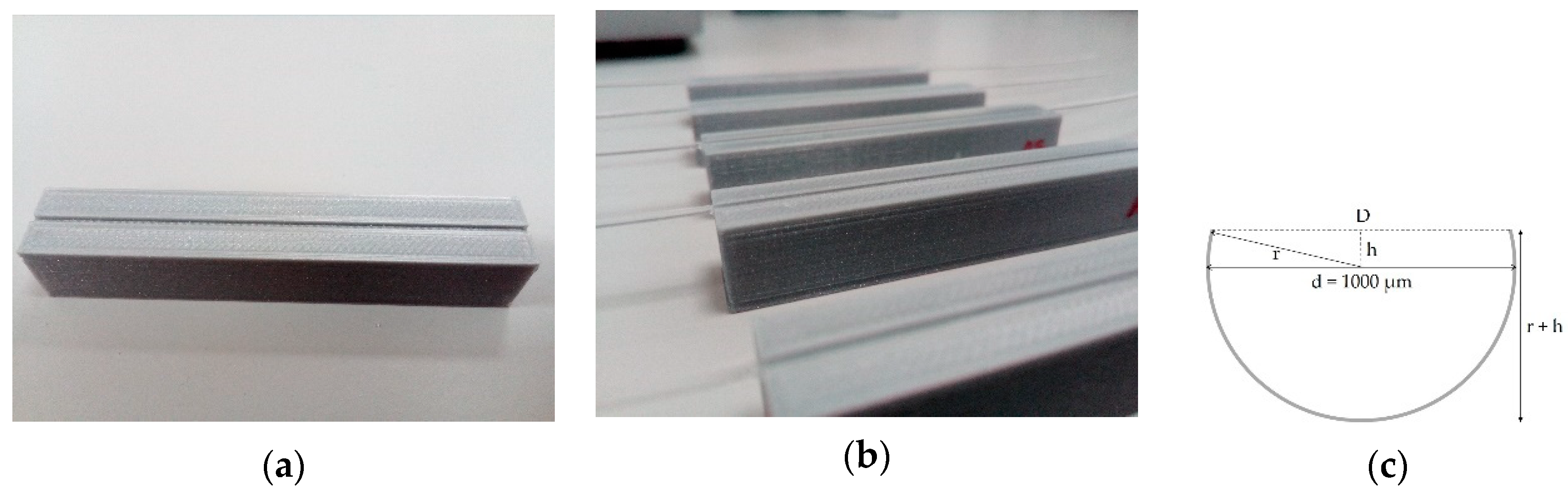
2.1. D-Shaped POF Sensors
2.2. Refractive Index Sensing—Experimental Setup and Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. D-Shaped POF Sensors—Losses Due to the Polishing Procedures
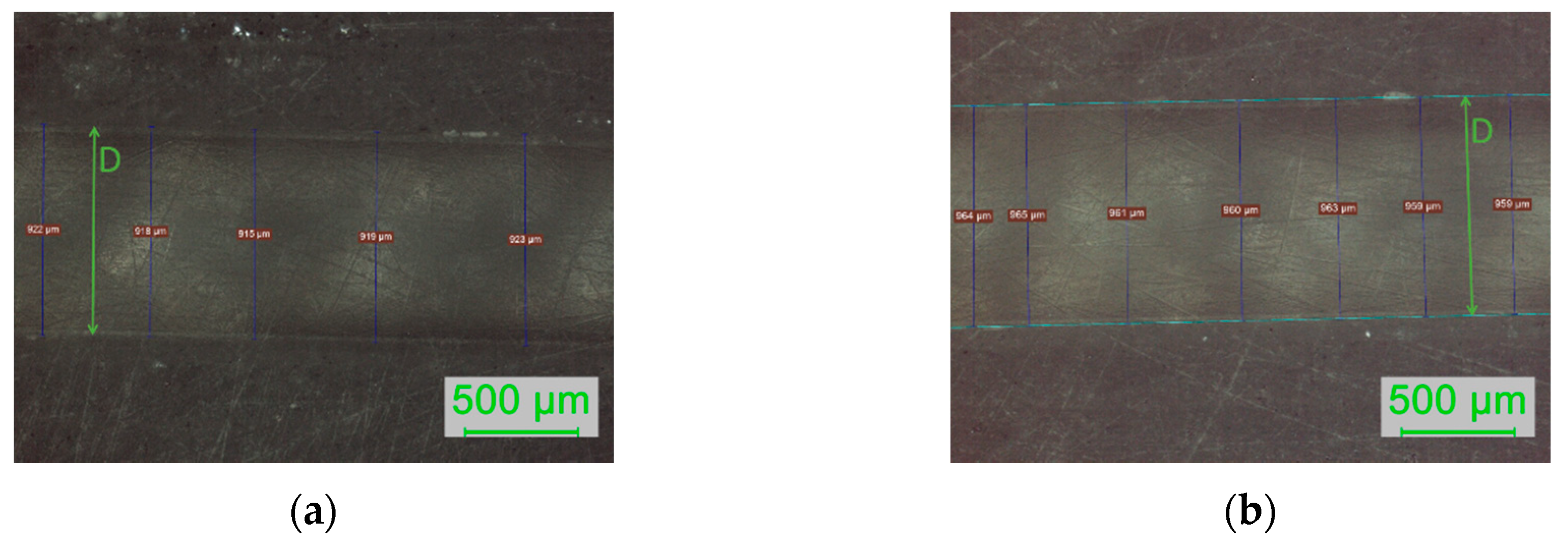
3.2. D-Shaped POF Sensors—Morphology of the Sensing Region
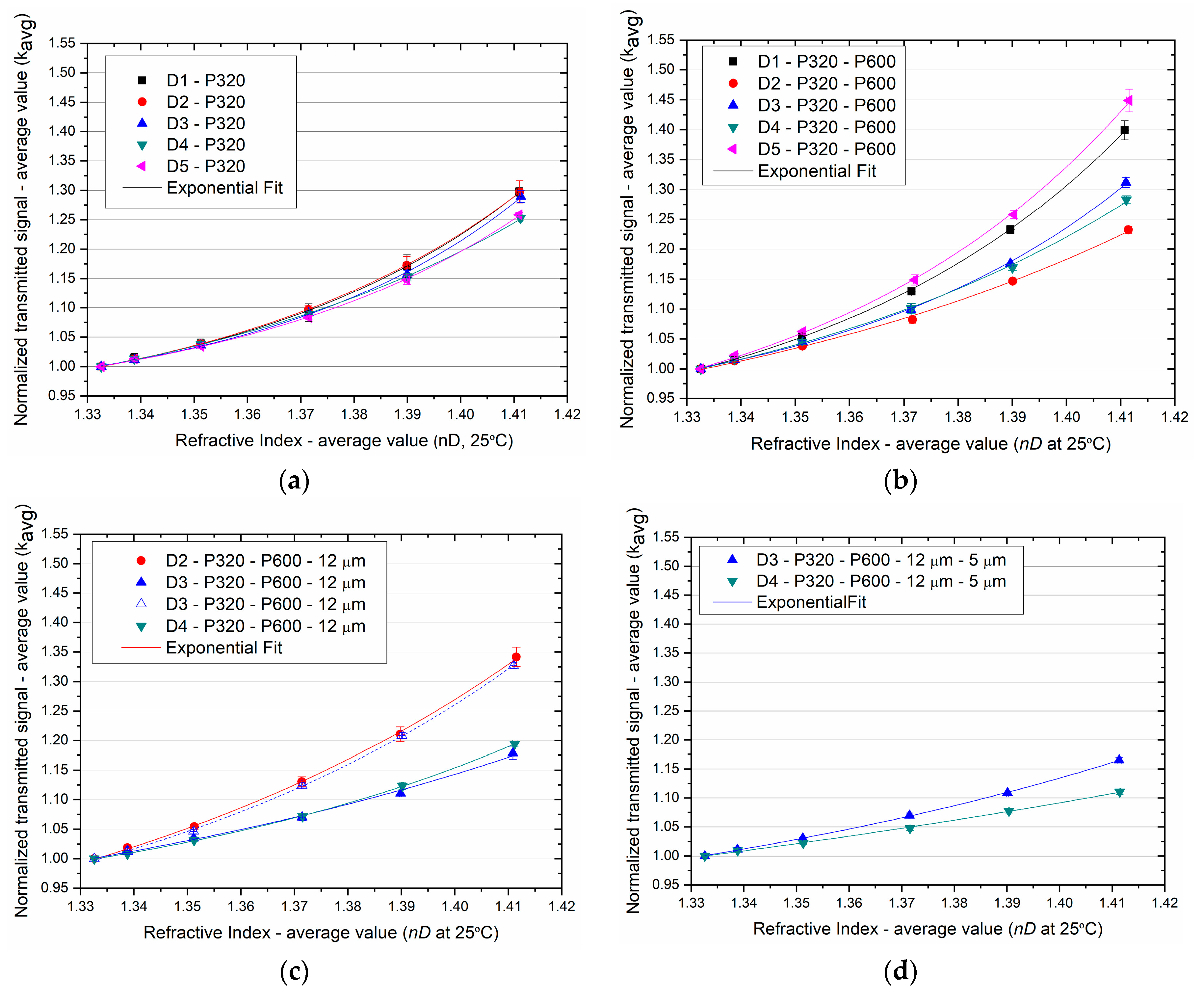
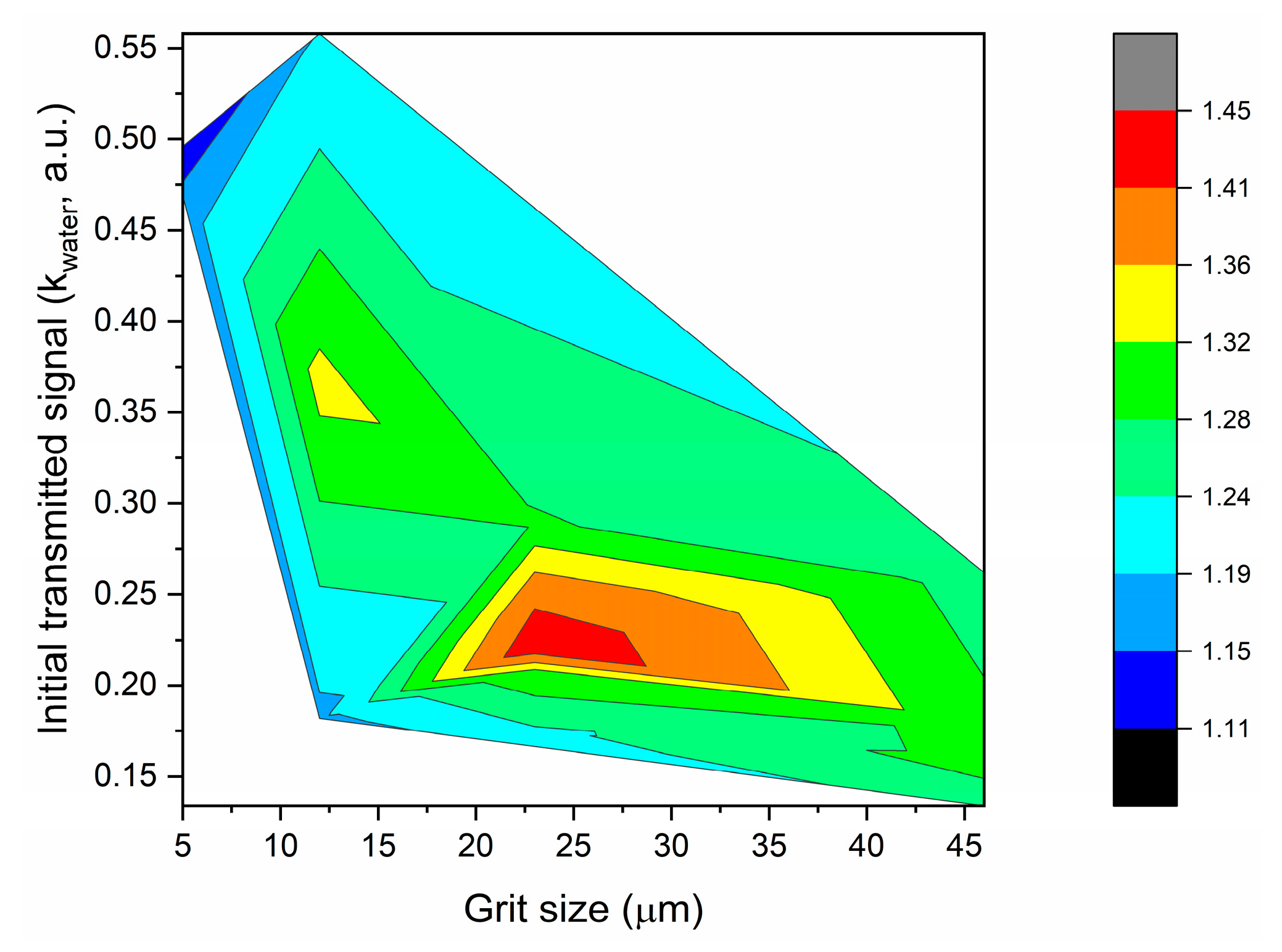
3.3. Refractive Index Sensing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le, T.D.H.; Scharmüller, A.; Kattwinkel, M.; Kühne, R.; Schüürmann, G.; Schäfer, R.B. Contribution of waste water treatment plants to pesticide toxicity in agriculture catchments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ivars, J.; Martella, L.; Massella, M.; Carbonell-Alcaina, C.; Alcaina-Miranda, M.I.; Iborra-Clar, M.I. Nanofiltration as tertiary treatment method for removing trace pharmaceutically active compounds in wastewater from wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2017, 125, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sheng, G.P.; Lu, Y.Z.; Zeng, R.J.; Yu, H.Q. Removal of antibiotic resistance genes from wastewater treatment plant effluent by coagulation. Water Res. 2017, 111, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. A Comprehensive Review on Water Quality Parameters Estimation Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.D.; Ternes, T.A. Water Analysis: Emerging Contaminants and Current Issues. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 398–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-D.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Biosensors (2013–2015). Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pospíšilová, M.; Kuncová, G.; Trögl, J. Fiber-optic chemical sensors and fiber-optic bio-sensors. Sensors 2015, 15, 25208–25259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elosua, C.; Arregui, F.J.; Villar, I.D.; Ruiz-Zamarreño, C.; Corres, J.M.; Bariain, C.; Goicoechea, J.; Hernaez, M.; Rivero, P.J.; Socorro, A.B.; et al. Micro and Nanostructured Materials for the Development of Optical Fibre Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilro, L.; Alberto, N.; Pinto, J.L.; Nogueira, R. Optical sensors based on plastic fibers. Sensors 2012, 12, 12184–12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Granville, A.M. Polymer Fiber Optic Sensors—A Mini Review of their Synthesis and Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 7, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Testa, G.; Marchetti, S.; De Maria, L.; Bernini, R.; Zeni, L.; Pesavento, M. Intensity-based plastic optical fiber sensor with molecularly imprinted polymer sensitive layer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.N.; Rodrigues, D.M.C.; Allil, R.C.S.B.; Werneck, M.M. Plastic optical fiber immunosensor for fast detection of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2018, 125, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foguel, M.V.; Ton, X.A.; Zanoni, M.V.B.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T.; Haupt, K.; Bui, B.T.S. A molecularly imprinted polymer-based evanescent wave fiber optic sensor for the detection of basic red 9 dye. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 218, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalaf, A.L.; Mohamad, F.S.; Rahman, N.A.; Lim, H.N.; Paiman, S.; Yusof, N.A.; Mahdi, M.A.; Yaacob, M.H. Room temperature ammonia sensor using side-polished optical fiber coated with graphene/polyaniline nanocomposite. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 1858–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azkune, M.; Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Aldabaldetreku, G.; Arrospide, E.; Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Bikandi, I.; Zubia, J.; Vilas-Vilela, J. U-Shaped and Surface Functionalized Polymer Optical Fiber Probe for Glucose Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, L.; Izquierdo, D.; Garcés, I.; Salinas, I.; Alonso, J.; Puyol, M. Simple dip-probe fluorescence setup sensor for in situ environmental determinations. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 137, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, X.A.; Acha, V.; Bonomi, P.; Bui, B.T.S.; Haupt, K. A disposable evanescent wave fiber optic sensor coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer as a selective fluorescence probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; D’Agostino, G.; Porto, G.; Biasiolo, A.; Perri, C.; Arcadio, F.; Zeni, L. A molecularly imprinted polymer on a plasmonic plastic optical fiber to detect perfluorinated compounds in water. Sensors 2018, 18, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; D’Agostino, G.; Sequeira, F.; Mattiello, F.; Porto, G.; Biasiolo, A.; Nogueira, R.; Bilro, L.; Zeni, L. A simple and low-cost optical fiber intensity-based configuration for perfluorinated compounds in water solution. Sensors 2018, 18, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, F.; Duarte, D.; Bilro, L.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Pesavento, M.; Zeni, L.; Cennamo, N. Refractive Index Sensing with D-Shaped Plastic Optical Fibers for Chemical and Biochemical Applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.-J.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Jiang, M.; Sui, Q. Refractive index sensor based on plastic optical fiber with tapered structure. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 2007–2011. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.-J.; Zhang, M.-S.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.-L.; Dong-Fang, J. D-Shaped Plastic Optical Fiber Sensor for Testing Refractive Index. IEEE Sens. 2014, 14, 1673–1676. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Feng, D.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, S.; Ye, Z. Side-Hole Plastic Optical Fiber for Testing Liquid’s Refractive Index. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 2902–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowri, A.; Sai, V.V.R. Development of LSPR based U-bent plastic optical fiber sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 230, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Singh, M.K.; Pandey, P.C. Refractive index sensor based on a multi-notched plastic optical fiber. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 1692–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Yu, F.; Jing, N.; Ding, Y.; Si, Z.; Zheng, J. Investigation of refractive index sensors based on side-polished plastic optical fibers. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2017, 36, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, F.; Duarte, D.; Nogueira, R.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Cennamo, N.; Zeni, L.; Bilro, L. Analysis of the roughness in a sensing region on D-shaped POFs. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Plastic Optical Fibers, Birmingham, UK, 13–15 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Frizera, A.; Pontes, M.J. Sensitive zone parameters and curvature radius evaluation for polymer optical fiber curvature sensors. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 100, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Pesavento, M.; Marchetti, S.; de Maria, L.; Zuppella, P.; Zeni, L. Polishing Process Analysis for Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors in D-Shaped Plastic Optical Fibers. In Sensors. CNS 2018. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 539, pp. 253–257. [Google Scholar]





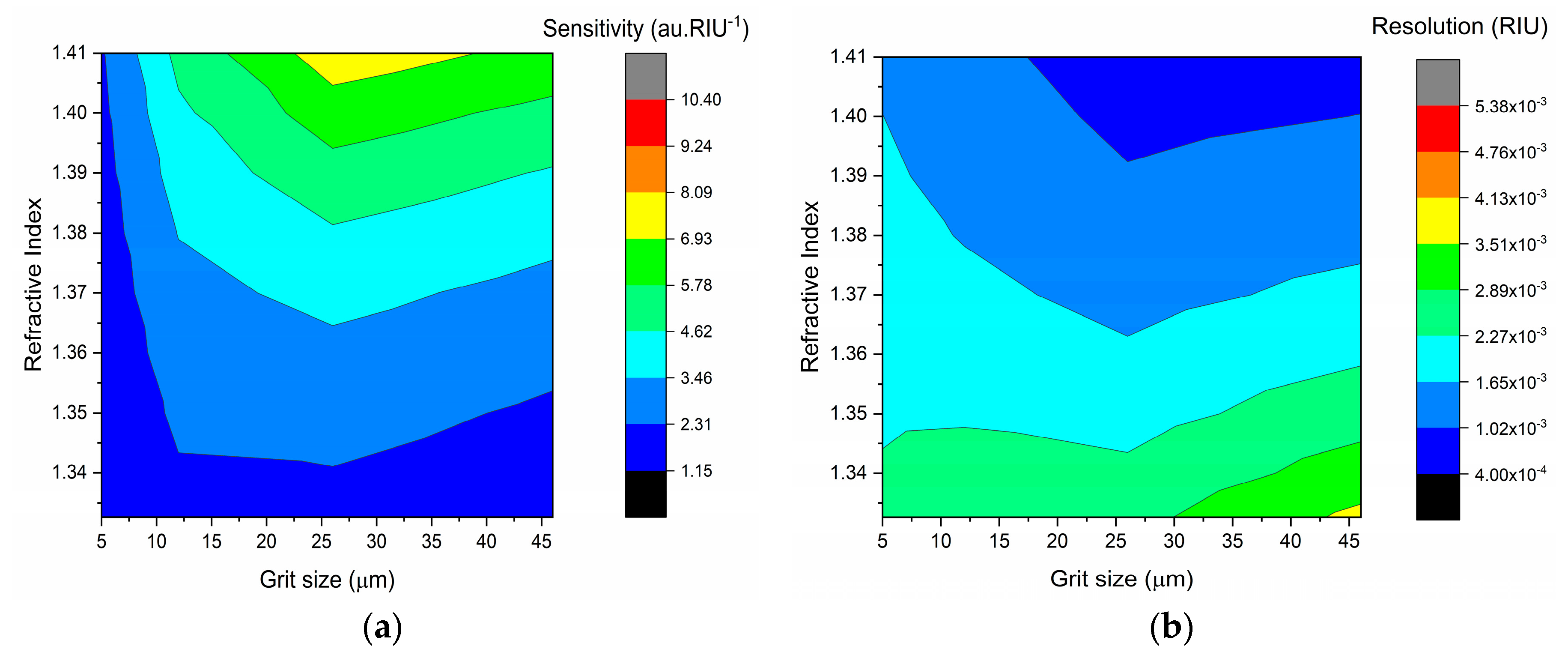
| Light Loss (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensors | Unpolished POF | D-Shaped POF (Polished, Grit Size) | |||
| Embedded | P320 (~46 µm) | P600 (~26 µm) | 12 µm | 5 µm | |
| D1 | <−0.1 | 93.8 | 93.3 | ||
| D2 | 93.3 | - | (88.8–88.2) | ||
| D3 | 94.4 | - | - | (87.1–86.6) | |
| D4 | 90.5 | - | - | (86.0–85.4) | |
| D5 | (93.3–92.7) | 92.2 | |||
| Sensors | Polishing Procedures (Sandpaper Grit Size) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P320 (~46 µm) | P600 (~26 µm) | 12 µm | 5 µm | |
| D1 | 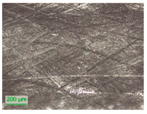 |  | ||
| D2 |  |  |  | |
| D3 |  |  | 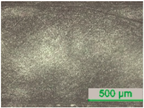 | 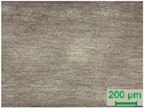 |
| D4 |  | 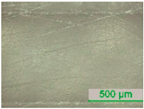 | 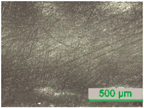 | 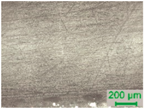 |
| D5 |  |  | ||
| Sensor | Thickness of the Sensing Region (D, µm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P320 (~46 µm) | P600 (~26 µm) | 12 µm | 5 µm | |
| D1 | x | 875 ± 12 (n = 33) | -- | -- |
| D2 | x | 912 ± 07 (n = 29) | 896 ± 05 (n = 14) | -- |
| D3 | 934 ± 08 (n = 13) | 952 ± 10 (n = 14) | 947 ± 10 (n = 11) | 944 ± 06 (n = 12) |
| D4 | x | 888 ± 08 (n = 13) | 893 ± 11 (n = 14) | 868 ± 06 (n = 20) |
| D5 | x | 936 ± 19 (n = 13) | -- | -- |
| Sensor | max(δknorm) (a.u.) | R0 | A | Reduced χ2 | Adj. R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polishing 1—P320 (~46 µm) | |||||
| D1 | 5.67 × 10−3 | 19.7380 ± 0.9183 | (3.0147 ± 3.9643) × 10−13 | 5.7387 × 10−6 | 0.99956 |
| D2 | 5.67 × 10−3 | 17.6686 ± 0.9552 | (5.8028 ± 7.9641) × 10−12 | 6.2849 × 10−6 | 0.99951 |
| D3 | 5.23 × 10−3 | 20.8698 ± 1.3336 | (0.5741 ± 1.0948) × 10−13 | 1.1250 × 10−5 | 0.99908 |
| D4 | 3.86 × 10−3 | 15.5884 ± 0.6314 | (9.9297 ± 9.0497) × 10−11 | 2.0756 × 10−6 | 0.99978 |
| D5 | 7.54 × 10−3 | 19.1898 ± 0.6959 | (5.7353 ± 5.7199) × 10−13 | 2.5028 × 10−6 | 0.99974 |
| Polishing 2—P320 (~46 µm)—P600 (~26 µm) | |||||
| D1 | 4.61 × 10−3 | 18.1293 ± 0.6274 | (4.0916 ± 3.6850) × 10−12 | 4.9376 × 10−6 | 0.99979 |
| D2 | 7.07 × 10−3 | 12.9652 ± 1.3225 | (4.0754 ± 7.8431) × 10−9 | 8.0058 × 10−6 | 0.99900 |
| D3 | 5.94 × 10−3 | 19.5214 ± 1.2709 | (4.2817± 7.7950) × 10−13 | 1.1990 × 10−5 | 0.99915 |
| D4 | 3.72 × 10−3 | 15.4351± 1.1793 | (1.3817± 2.3529) × 10−10 | 8.9359 × 10−6 | 0.99923 |
| D5 | 4.25 × 10−3 | 18.4696 ± 0.8383 | (2.7554 ± 3.3151) × 10−12 | 1.1189 × 10−5 | 0.99962 |
| Polishing 3—P320 (~46 µm)—P600 (~26 µm)—12 µm | |||||
| D2 | 3.44 × 10−3 | 12.1647 ± 0.6685 | (1.9225 ± 1.8762) × 10−8 | 4.4856 × 10−6 | 0.99974 |
| D3 | 6.48 × 10−3 | 8.1991 ± 3.0627 | (0.3456 ± 1.5845) × 10−5 | 2.4399 × 10−5 | 0.99461 |
| 7.32 × 10−3 | 12.0327 ± 0.9656 | (2.2928 ± 3.2333) × 10−8 | 8.6735 × 10−6 | 0.99947 | |
| D4 | 3.77 × 10−3 | 12.3319 ± 0.6847 | (8.6758 ± 8.6656) × 10−9 | 1.5171 × 10−6 | 0.99973 |
| Polishing 4—P320 (~46 µm)—P600 (~26 µm)—12 µm—5 µm | |||||
| D3 | 3.19 × 10−3 | 8.0865 ± 0.6820 | (3.8485 ± 3.9345) × 10−6 | 1.1013 × 10−6 | 0.99973 |
| D4 | 3.19 × 10−3 | 4.0643 ± 1.8767 | (1.2900 ± 3.9300) × 10−3 | 3.7801 × 10−6 | 0.99794 |
| Sensor | Sandpaper | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P320 (~46 µm) | P600 (~26 µm) | 12 µm Grit Size | 5 µm Grit Size | |
| D1 | 0.94575 | 0.95417 | - | - |
| D2 | 0.95513 | 0.97251 | 0.97823 | - |
| D3 | 0.94009 | 0.94718 | 0.97839–0.97865 | 0.99037 |
| D4 | 0.96572 | 0.96648 | 0.97791 | 0.99368 |
| D5 | 0.94895 | 0.95200 | - | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sequeira, F.; Cennamo, N.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Nogueira, R.; Zeni, L.; Bilro, L. D-Shaped POF Sensors for Refractive Index Sensing—The Importance of Surface Roughness. Sensors 2019, 19, 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112476
Sequeira F, Cennamo N, Rudnitskaya A, Nogueira R, Zeni L, Bilro L. D-Shaped POF Sensors for Refractive Index Sensing—The Importance of Surface Roughness. Sensors. 2019; 19(11):2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112476
Chicago/Turabian StyleSequeira, Filipa, Nunzio Cennamo, Alisa Rudnitskaya, Rogério Nogueira, Luigi Zeni, and Lúcia Bilro. 2019. "D-Shaped POF Sensors for Refractive Index Sensing—The Importance of Surface Roughness" Sensors 19, no. 11: 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112476
APA StyleSequeira, F., Cennamo, N., Rudnitskaya, A., Nogueira, R., Zeni, L., & Bilro, L. (2019). D-Shaped POF Sensors for Refractive Index Sensing—The Importance of Surface Roughness. Sensors, 19(11), 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112476








