Digital Approach to Rotational Speed Measurement Using an Electrostatic Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Measurement Principle and Finite Element Simulation
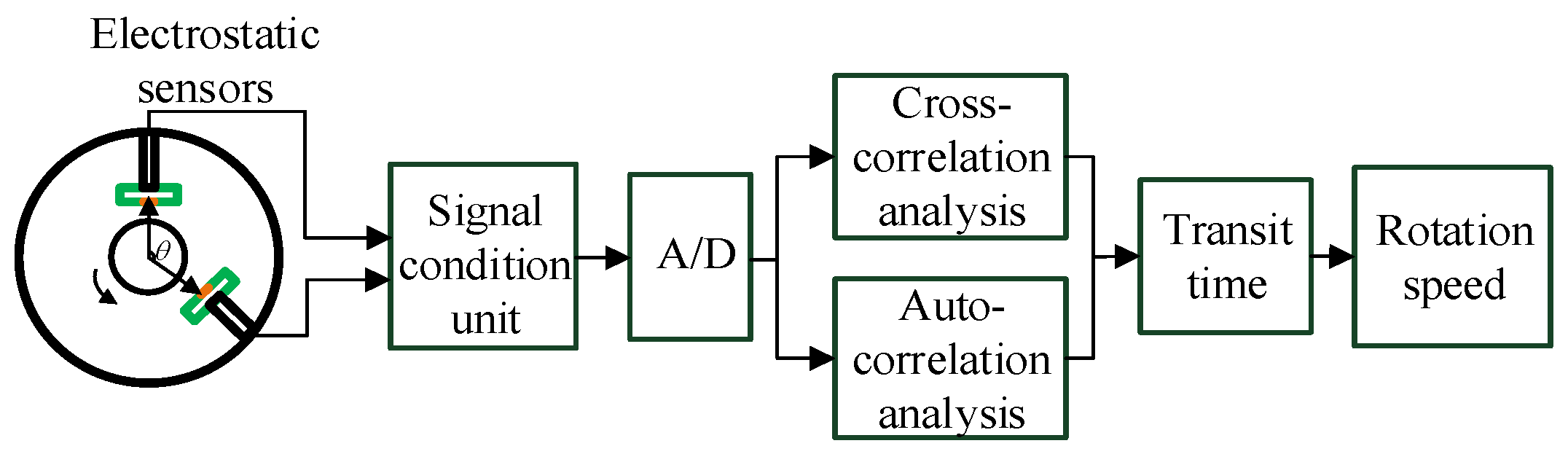
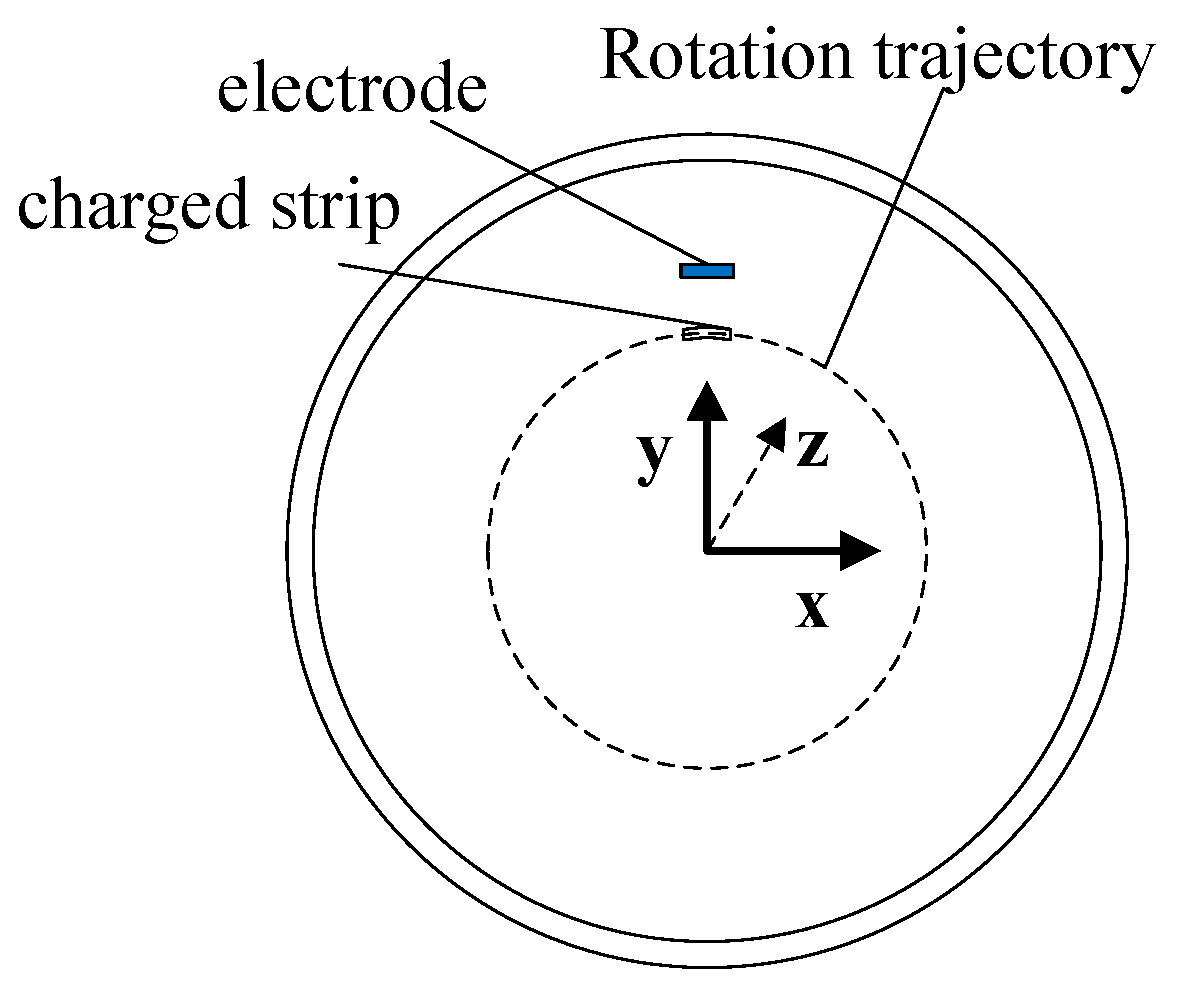
2.1. Measurement Principle
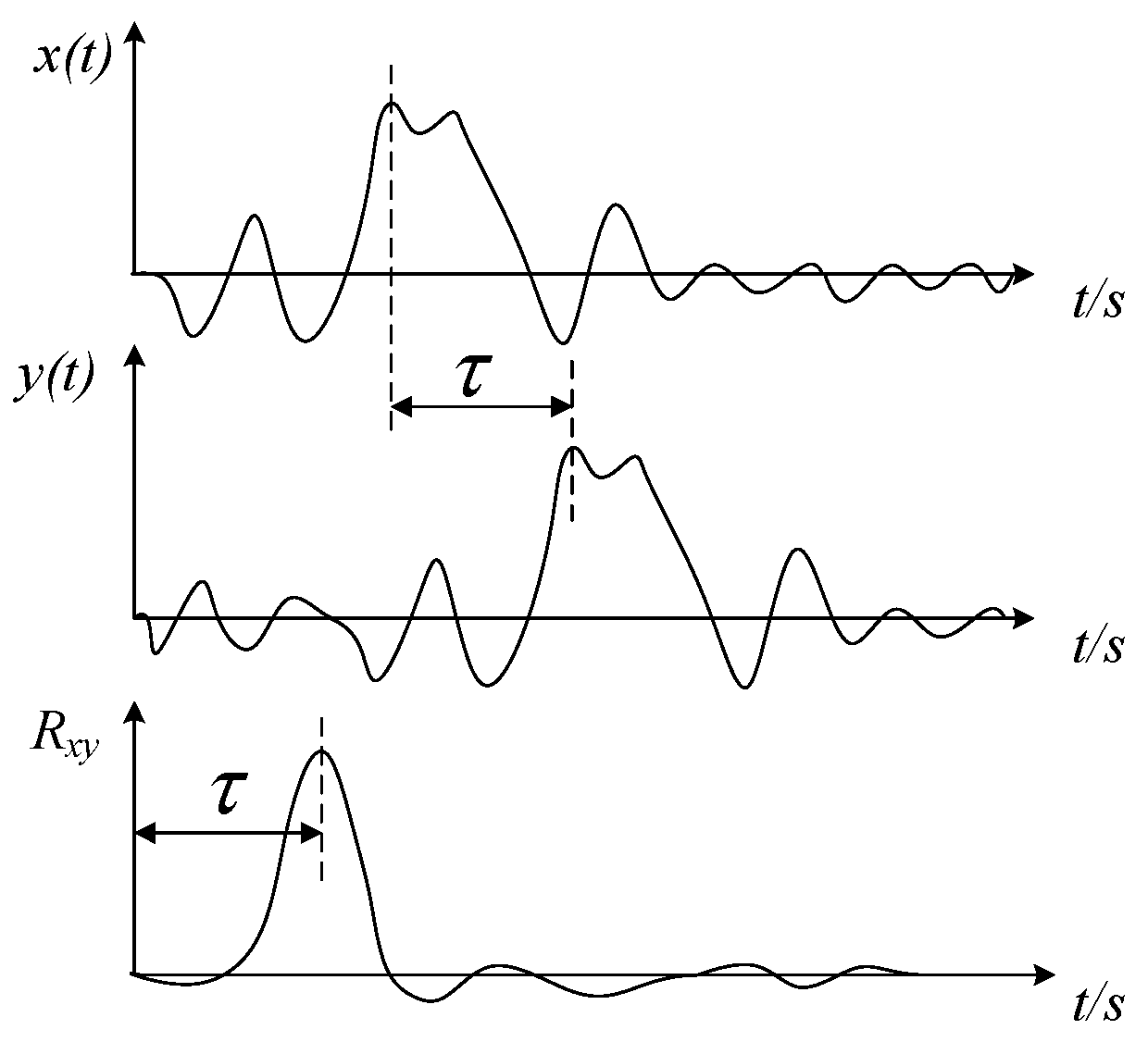
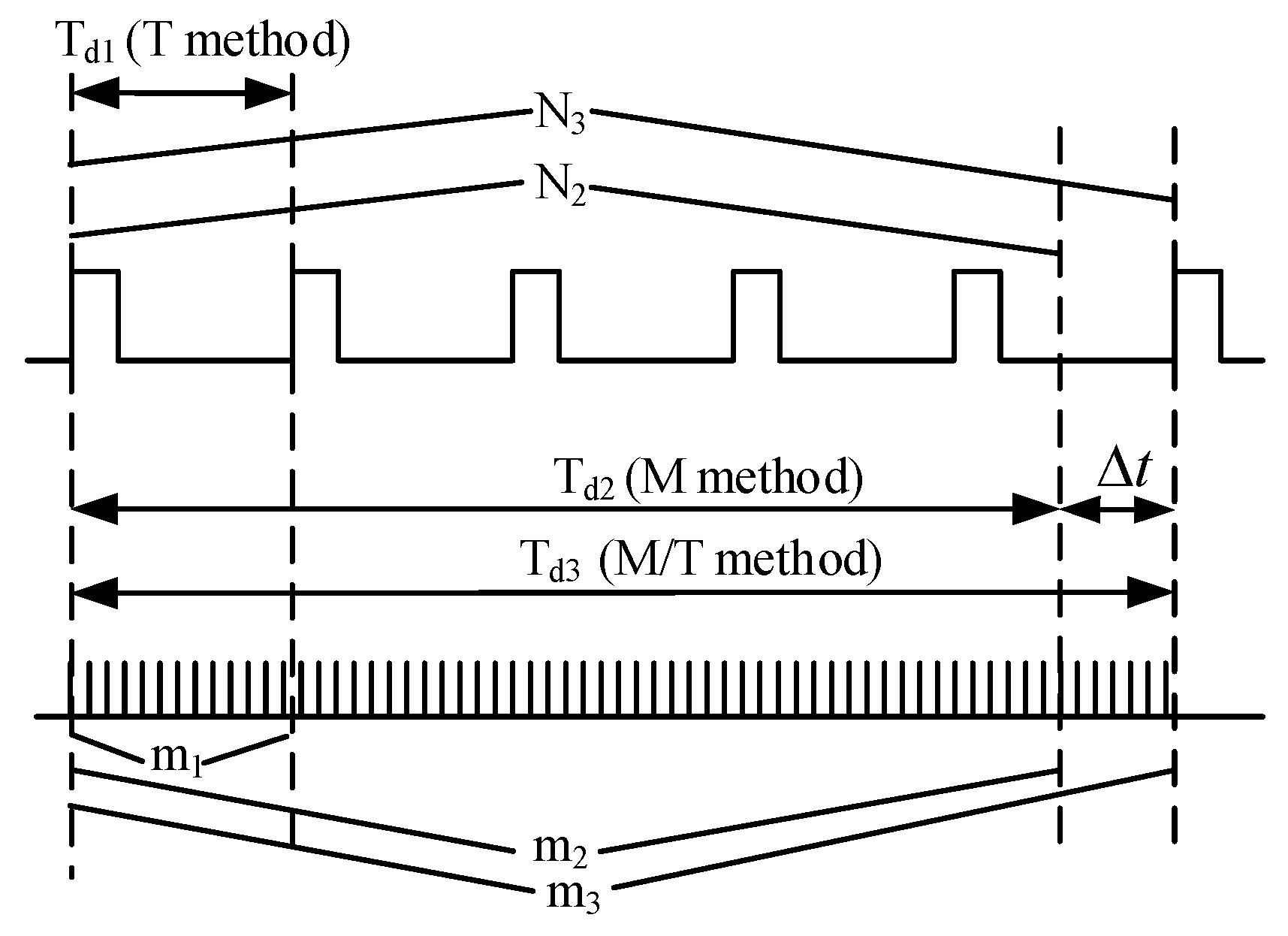
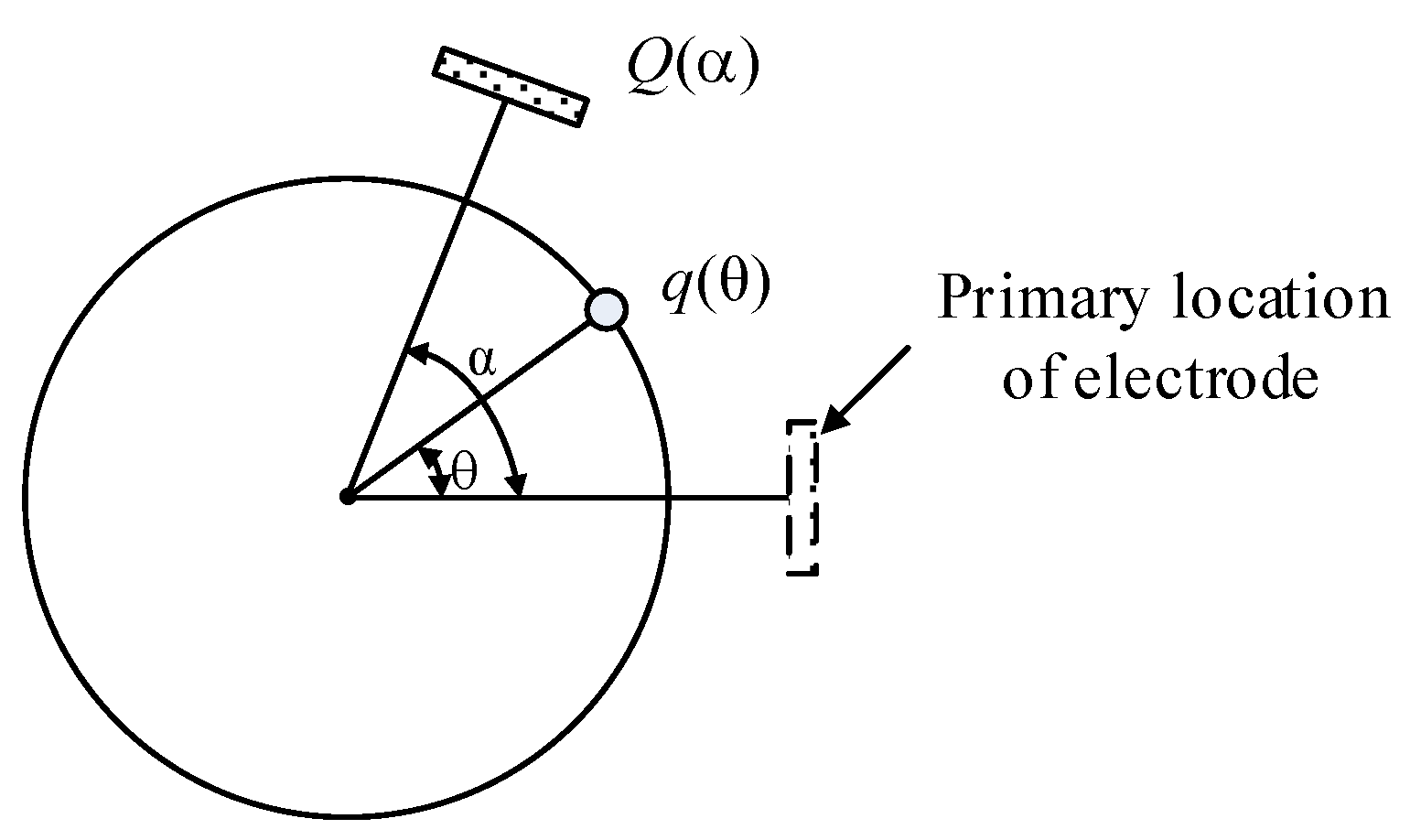
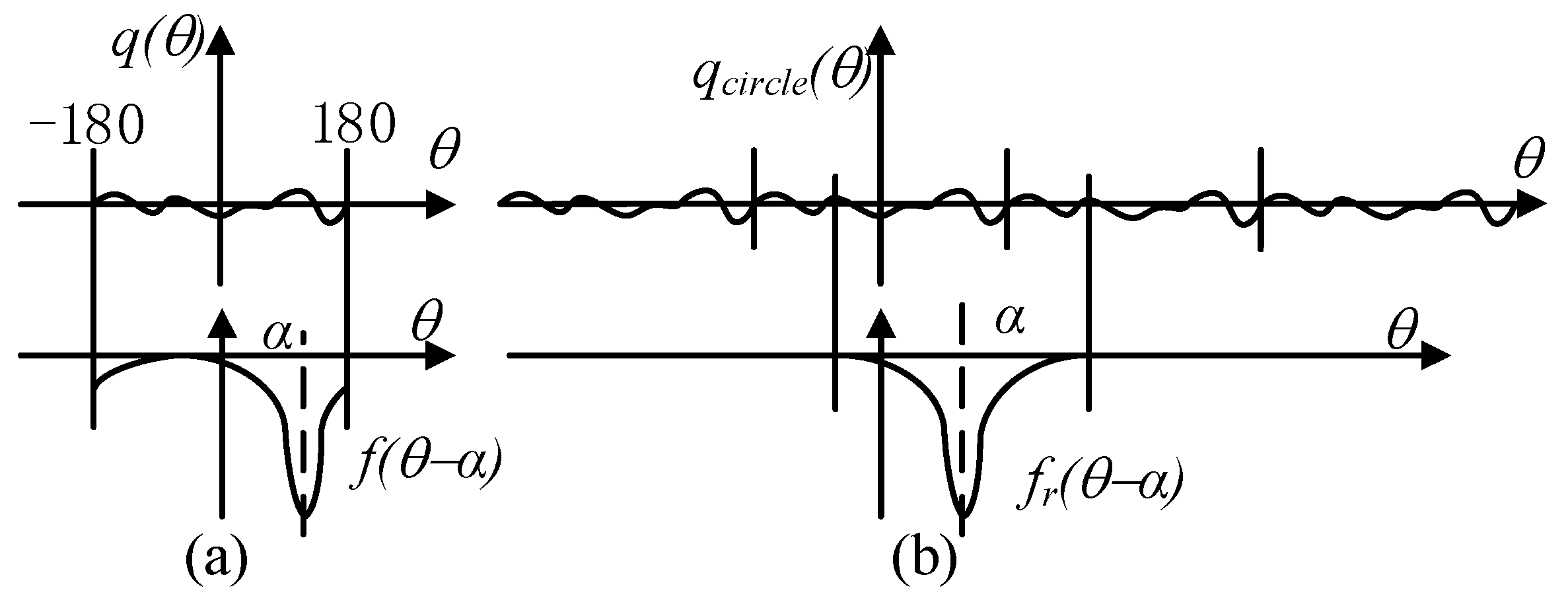
2.2. Rotation Speed Computation Algorithm
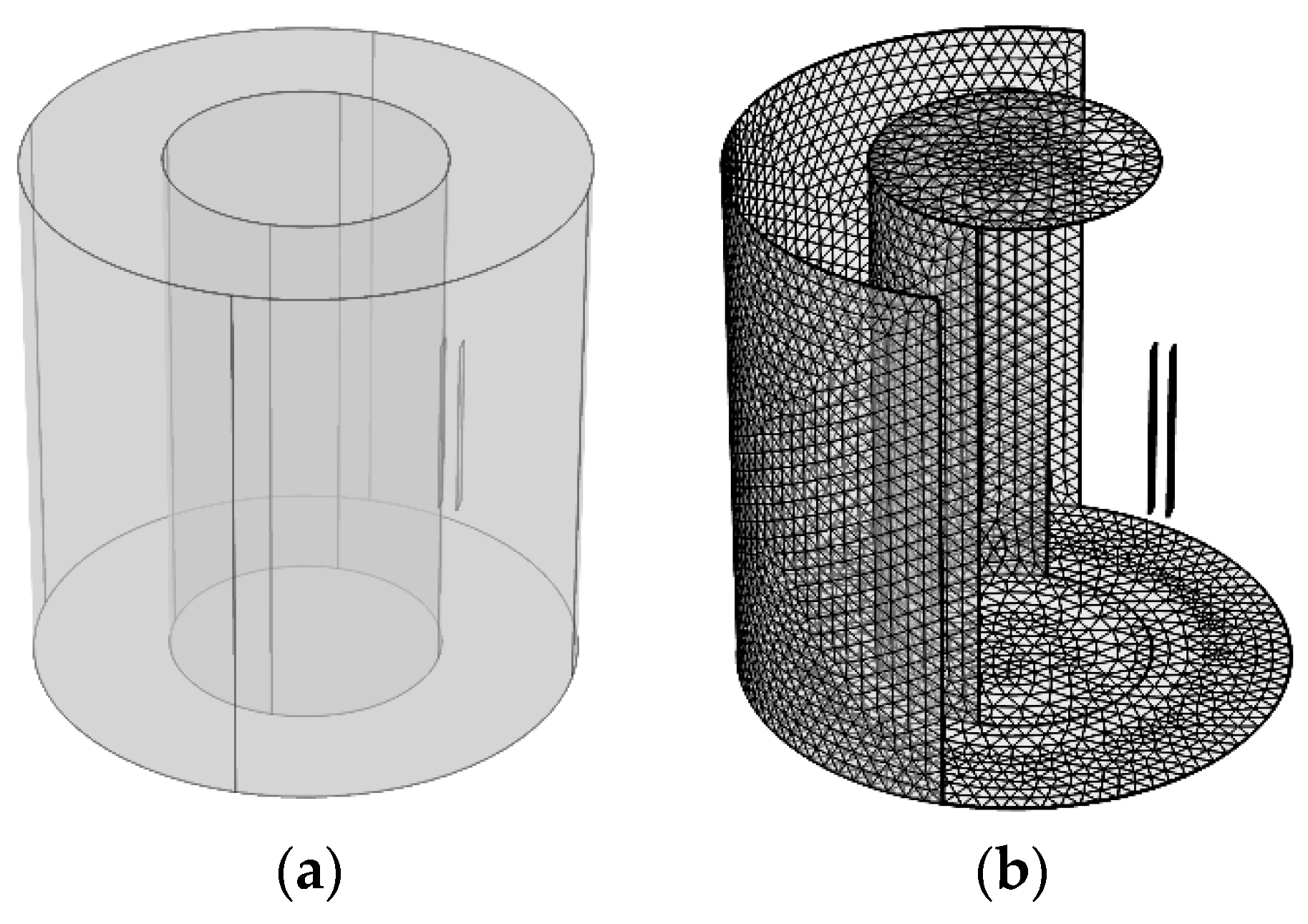
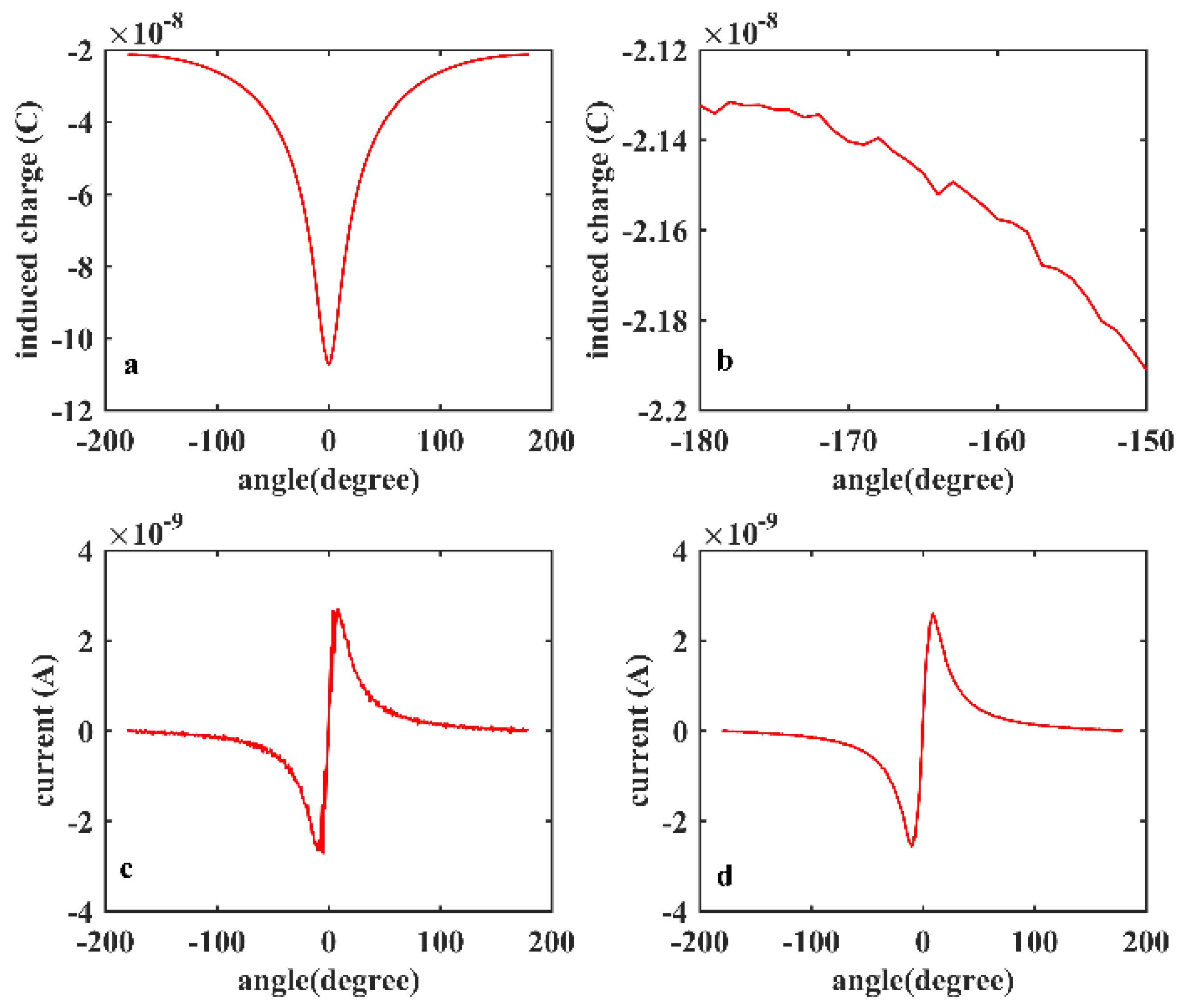
2.3. Finite Element Simulation
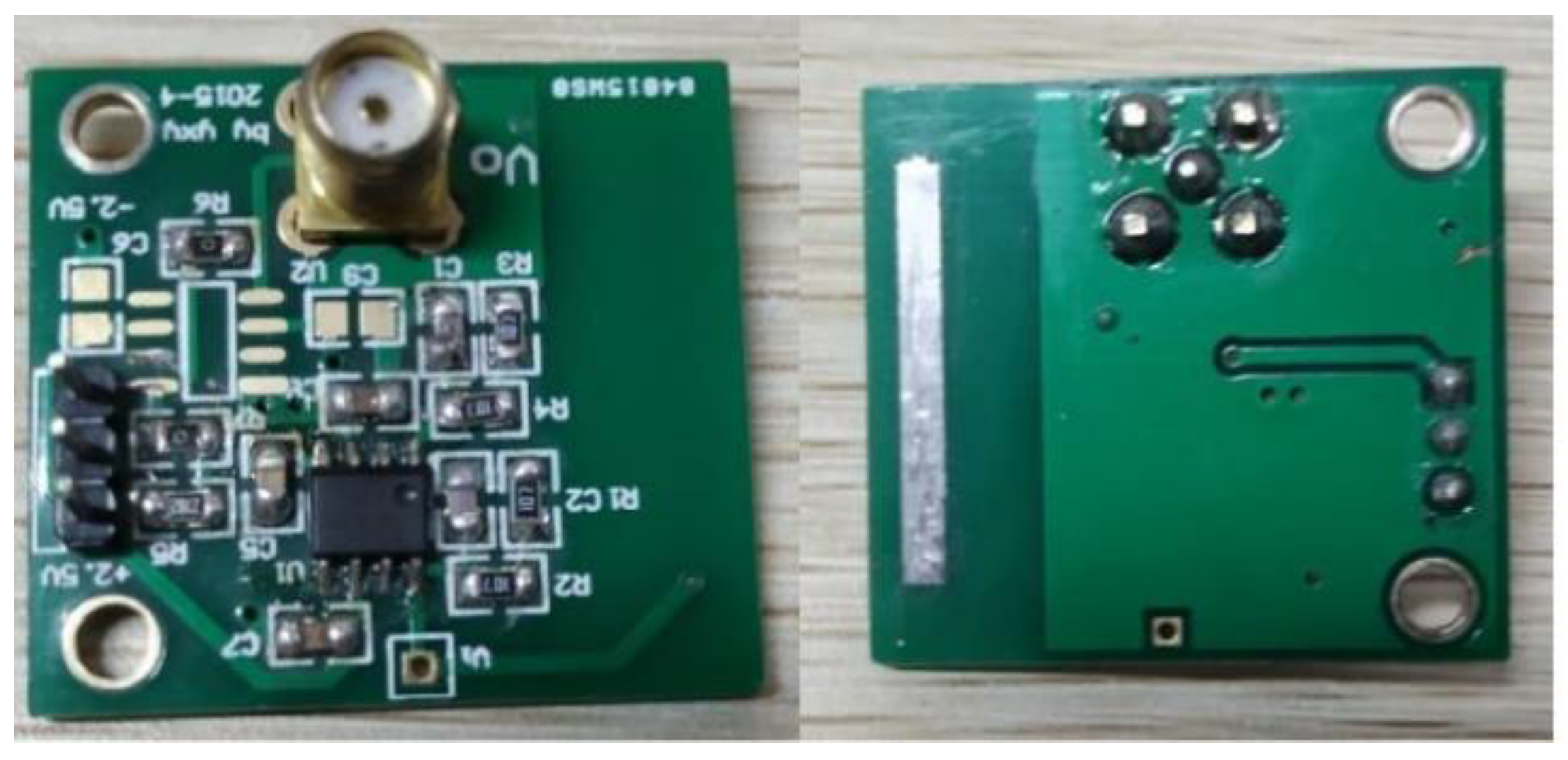
3. Hardware Design
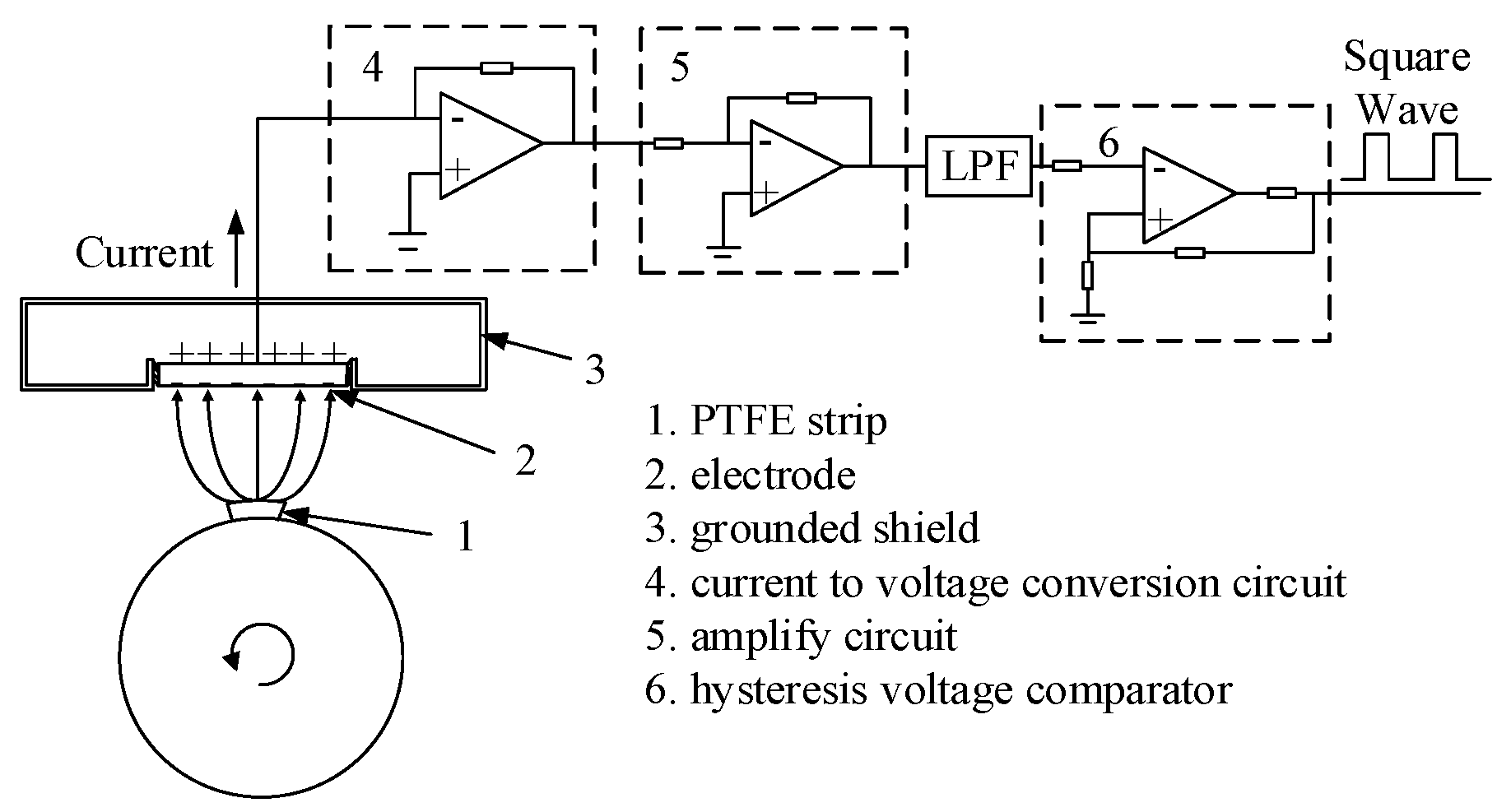
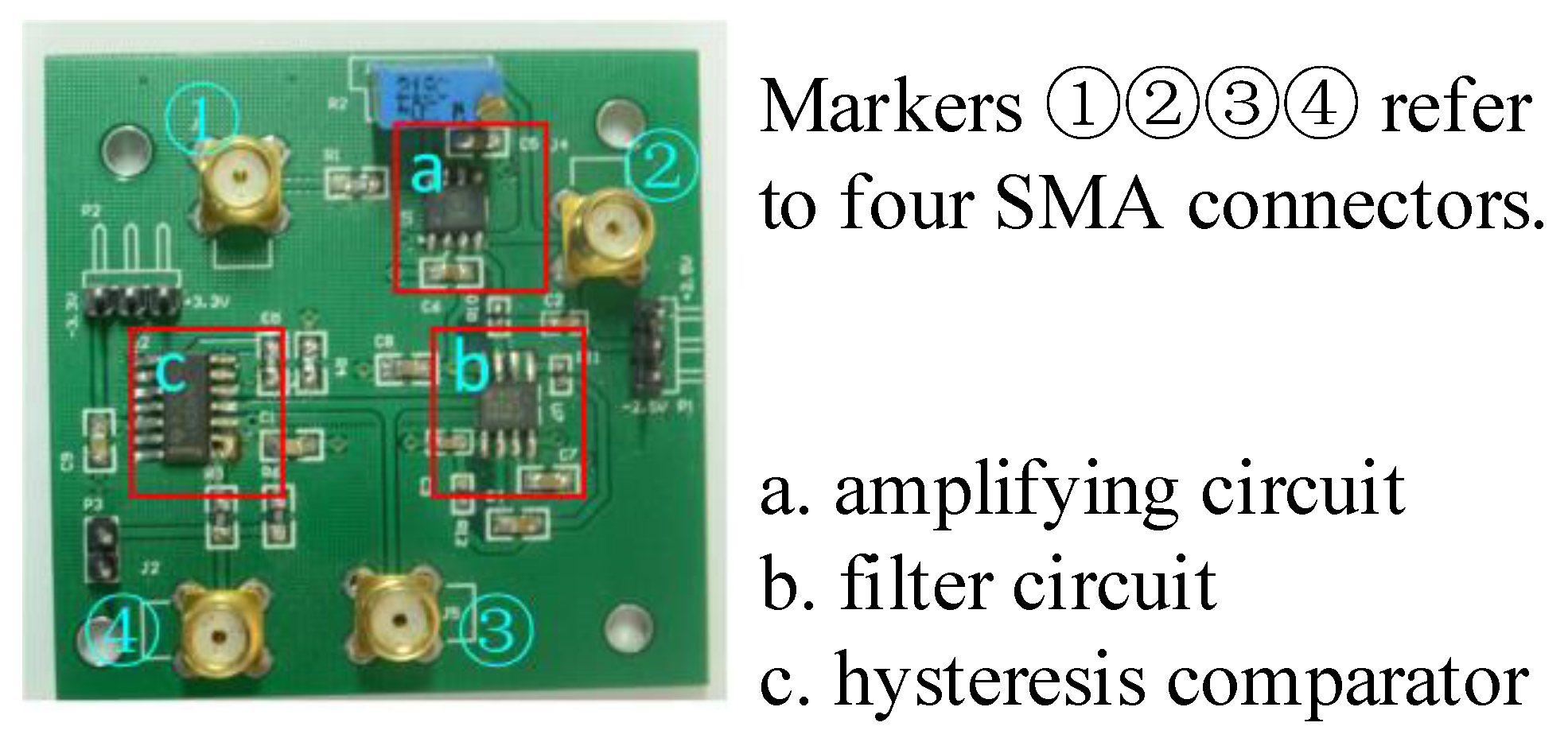
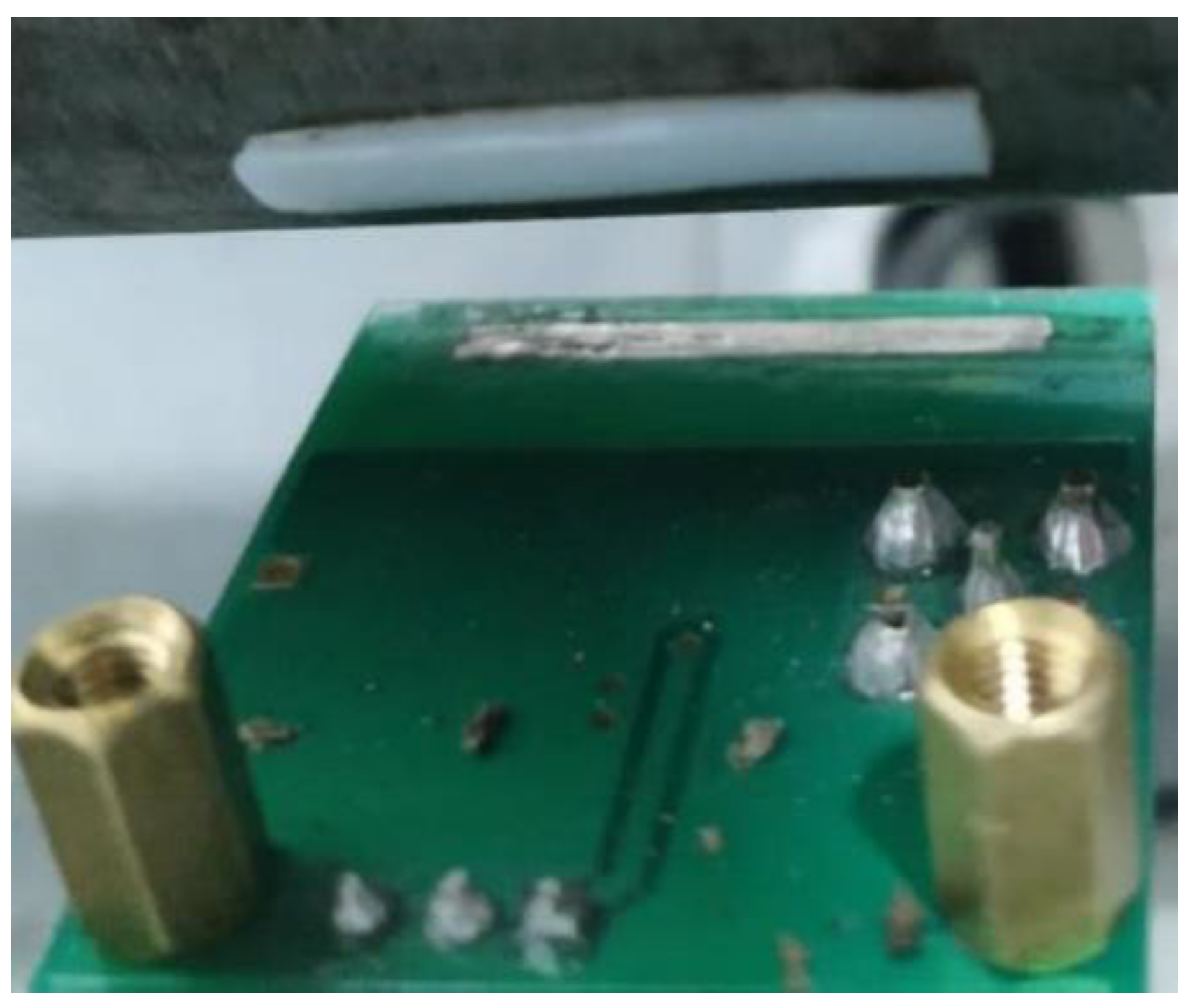
3.1. Sensor Board
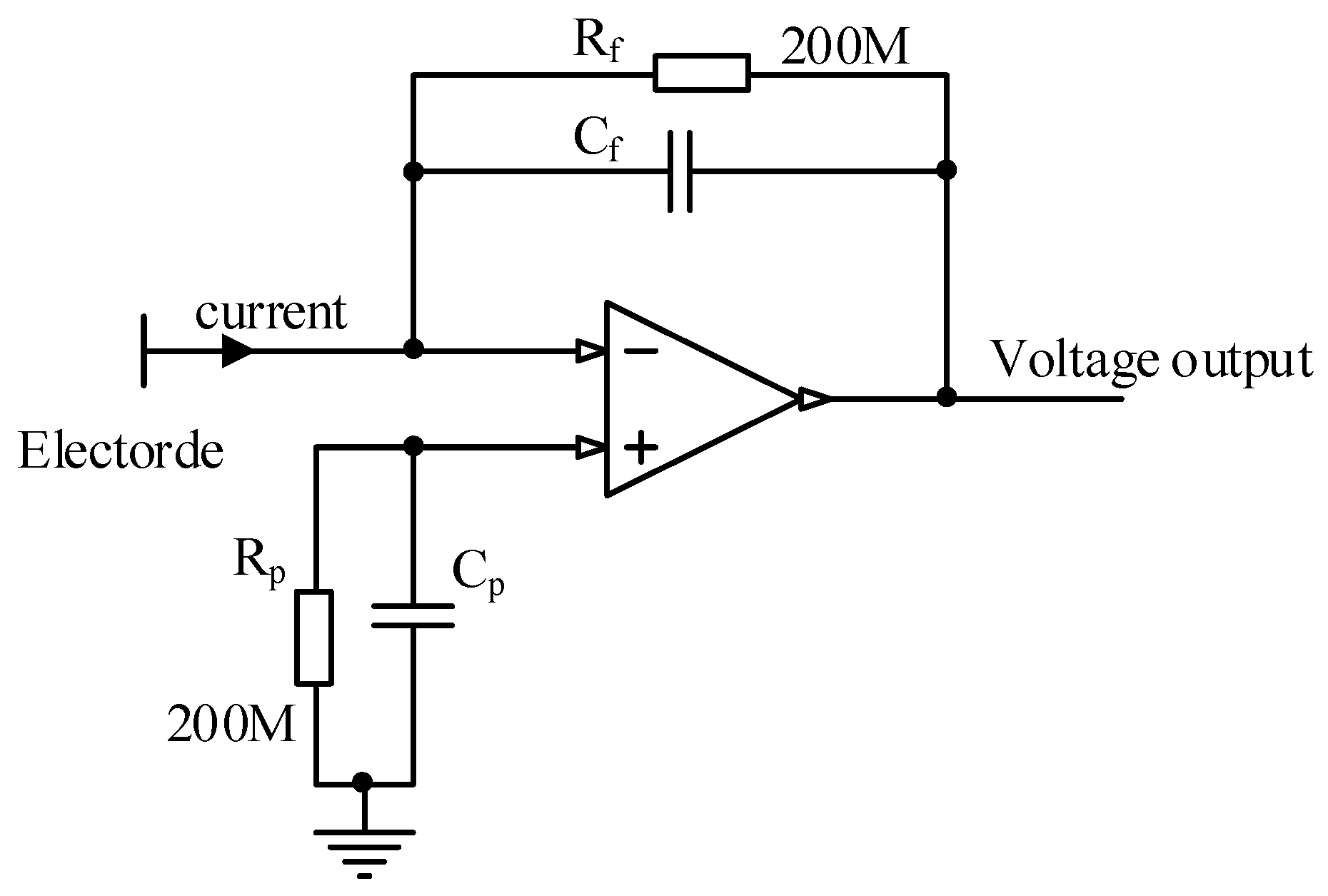
3.2. Signal Condition Unit
4. Experiment Results and Discussion
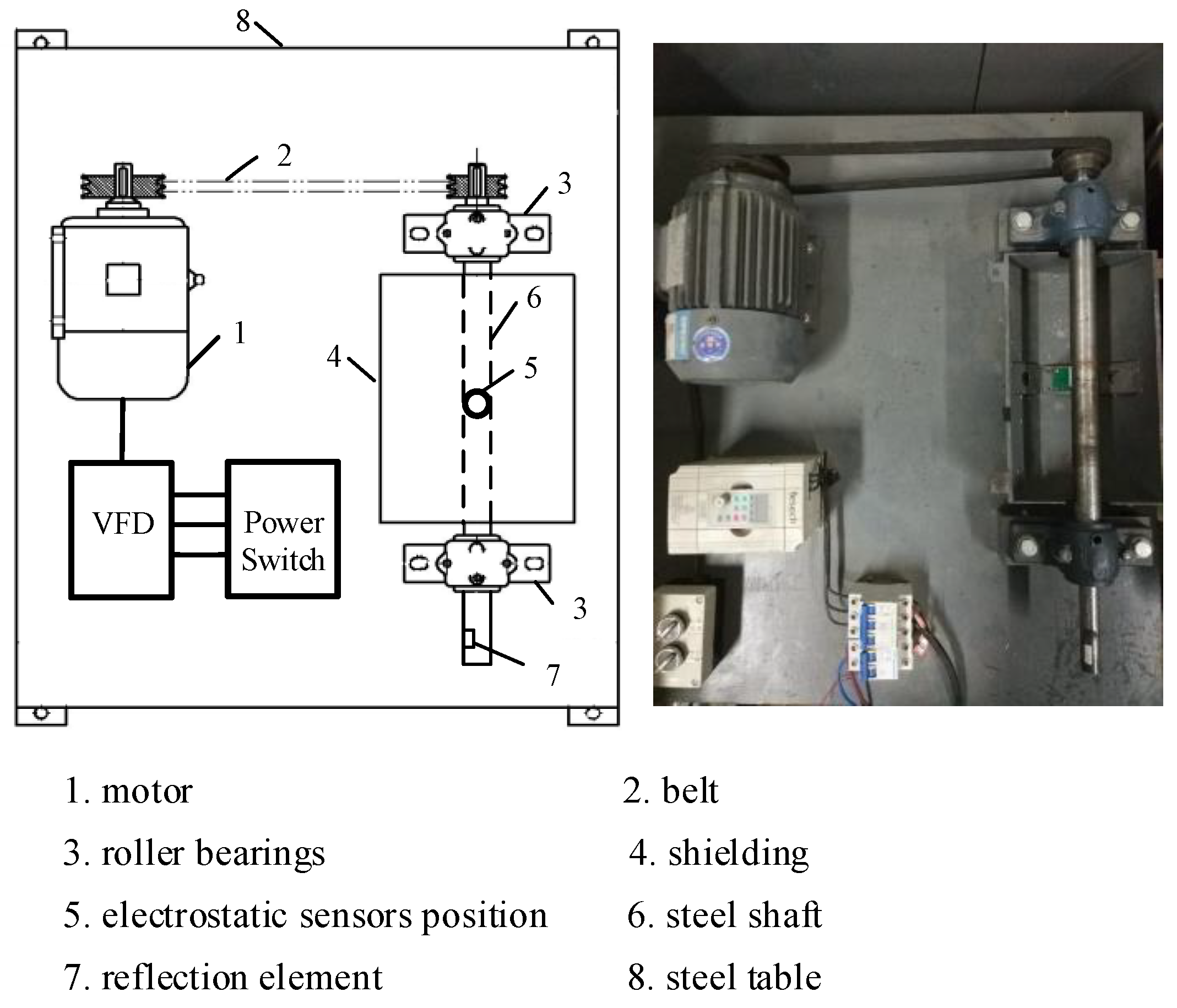
4.1. Experiment Conditions
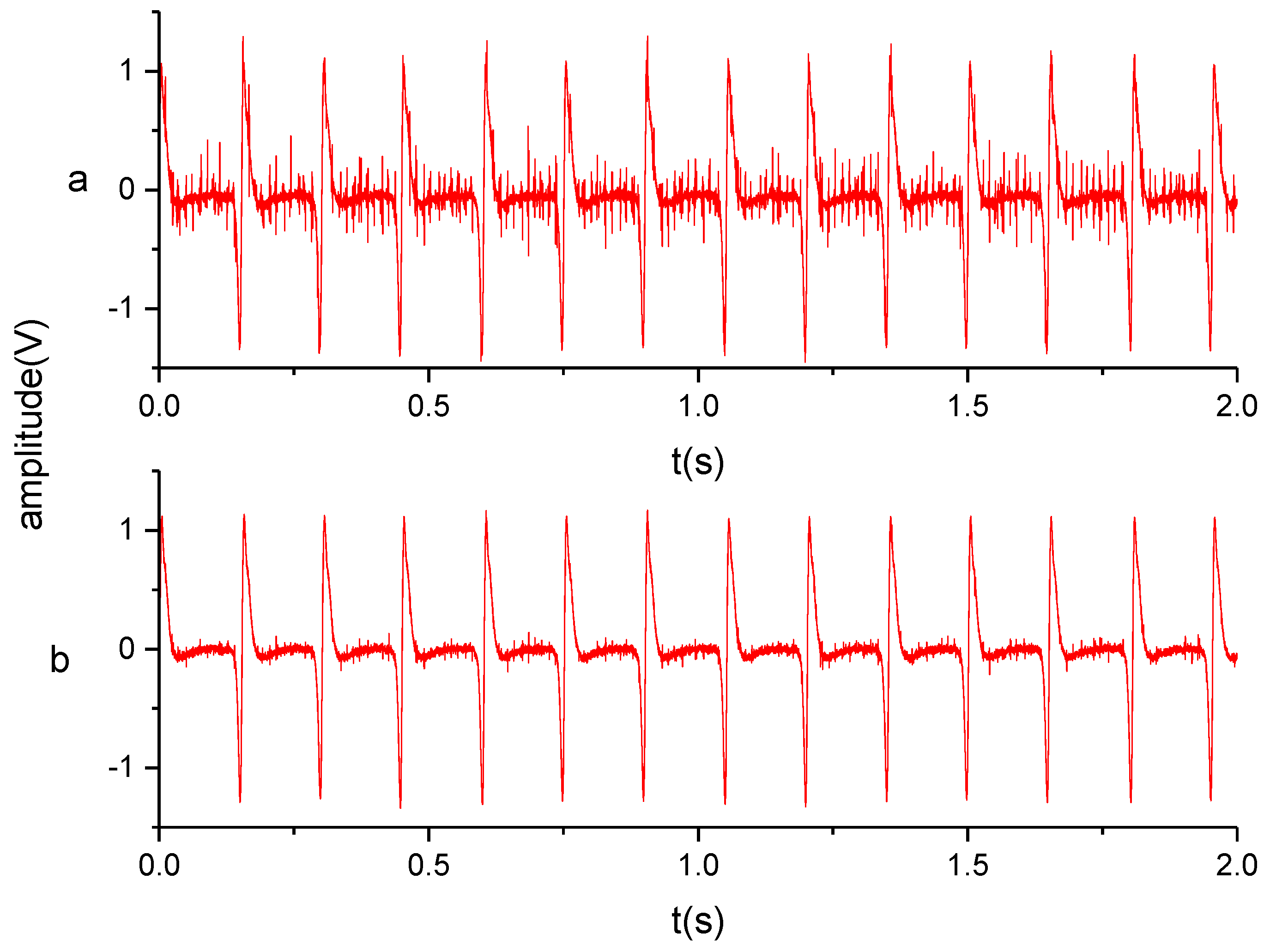
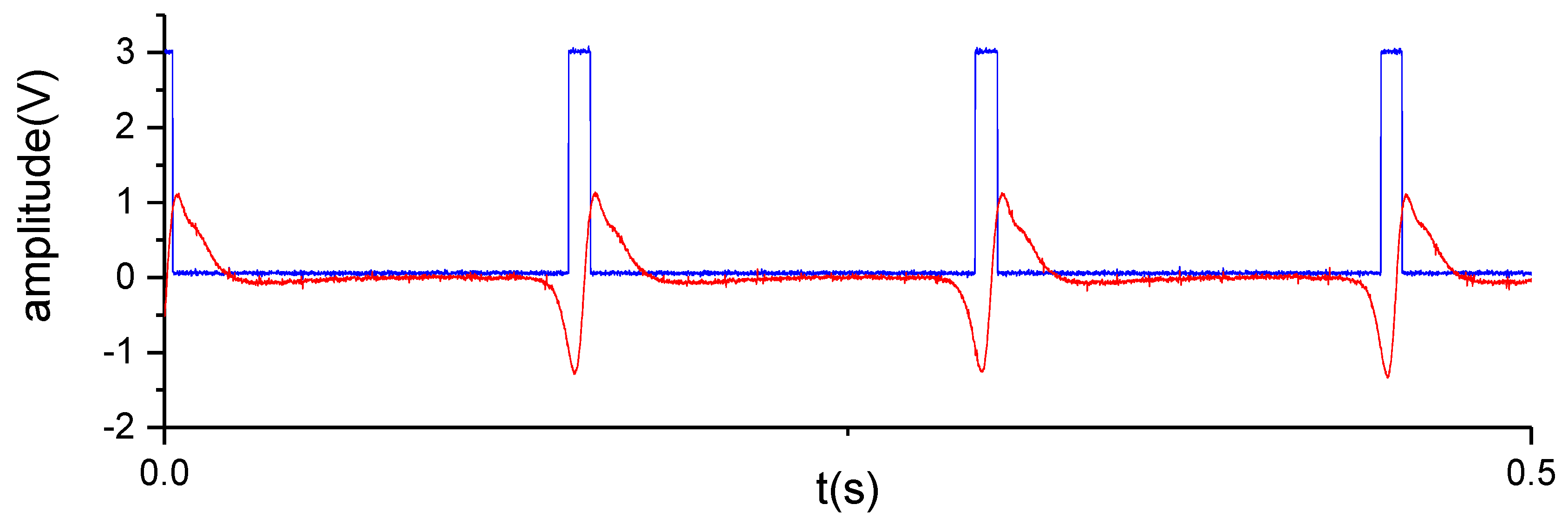
4.2. Signals
4.3. Accuracy
4.4. Standard Deviation
4.5. Response Time
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, W.H.; Bletscher, W.; Mansuripur, M. High resolution optical shaft encoder for motor speed control based on an optical disk pick-up. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1998, 69, 3068–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lygouras, J.N.; Lalakos, K.A.; Ysalides, P.G. High-performance position detection and velocity adaptive measurement for closed-loop position control. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1998, 47, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, W.; Chatto, R.B. Alternatives to Analog DC Tachogenerators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1975, IA-11, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giebeler, C.; Adelerhof, D.J.; Kuiper, A.E.T.; Van Zon, J.B.A.; Oelgeschläger, D.; Schulz, G. Robust GMR sensors for angle detection and rotation speed sensing. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 91, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Huang, Q.; Wu, G.S.; Xu, Y.H.; Yang, M.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, C.; Ma, J. Design and Development of a Tachometer Using Magnetoelectric Composite as Magnetic Field Sensor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 4000604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.E. Analog Tachometers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Gen. Appl. 1966, IGA-2, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokin, M. Extremely wide-range speed measurement using a double-buffered method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1994, 41, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Qian, X. Rotational Speed Measurement through Electrostatic Sensing and Correlation Signal Processing. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Yan, Y.; Reda, K. Comparison of single and double electrostatic sensors for rotational speed measurement. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 266, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, J.; Rose-Innes, A.C. Contact electrification. Adv. Phys. 1980, 29, 947–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, G.; Xu, Z. Tribo-charging properties of waste plastic granules in process of tribo-electrostatic separation. Waste Manag. 2015, 35, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.H.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Y.; Wang, L.J.; Qian, X.; Yang, L. A Smart Electrostatic Sensor for Online Condition Monitoring of Power Transmission Belts. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7313–7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Qian, X.C. Rotational Speed Measurement Using Electrostatic Sensors and Correlation Signal Processing Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 6–9 May 2013; pp. 224–227. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Xiaoxin, W.; Hongli, H.; Xiao, L. Use of double correlation techniques for the improvement of rotation speed measurement based on electrostatic sensors. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2016, 27, 025004. [Google Scholar]
- Ohmae, T.; Matsuda, T.; Kamiyama, K.; Tachikawa, M. A Microprocessor-Controlled High-Accuracy Wide-Range Speed Regulator for Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1982, IE-29, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachiya, K.; Ohmae, T. Digital speed control system for a motor using two speed detection methods of an incremental encoder. In Proceedings of the 2007 European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Aalborg, Denmark, 2–5 September 2007; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hace, A. The Improved Division-Less MT-Type Velocity Estimation Algorithm for Low-Cost FPGAs. Electronics 2019, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Yan, Y. Mathematical modelling and experimental validation of electrostatic sensors for rotational speed measurement. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


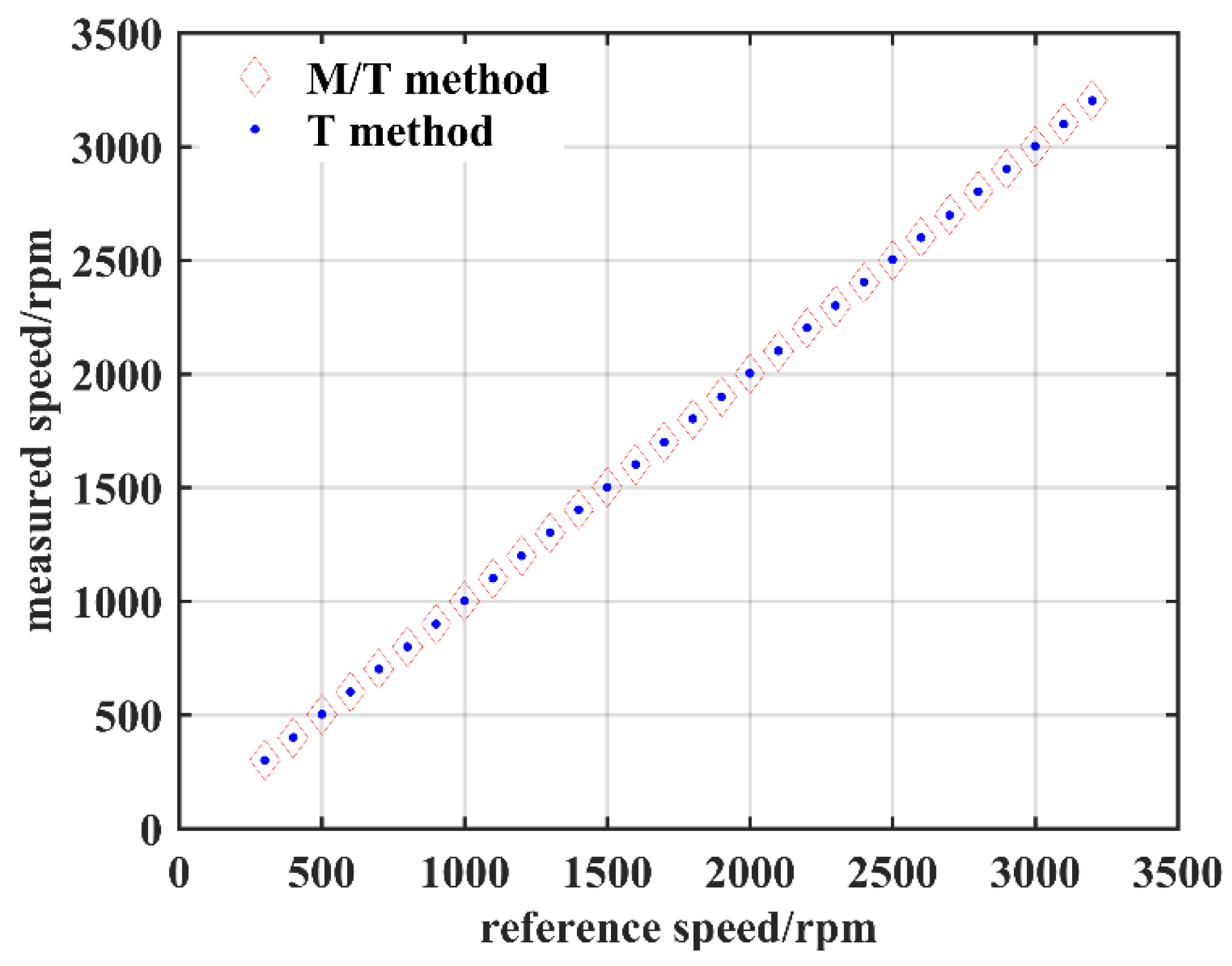
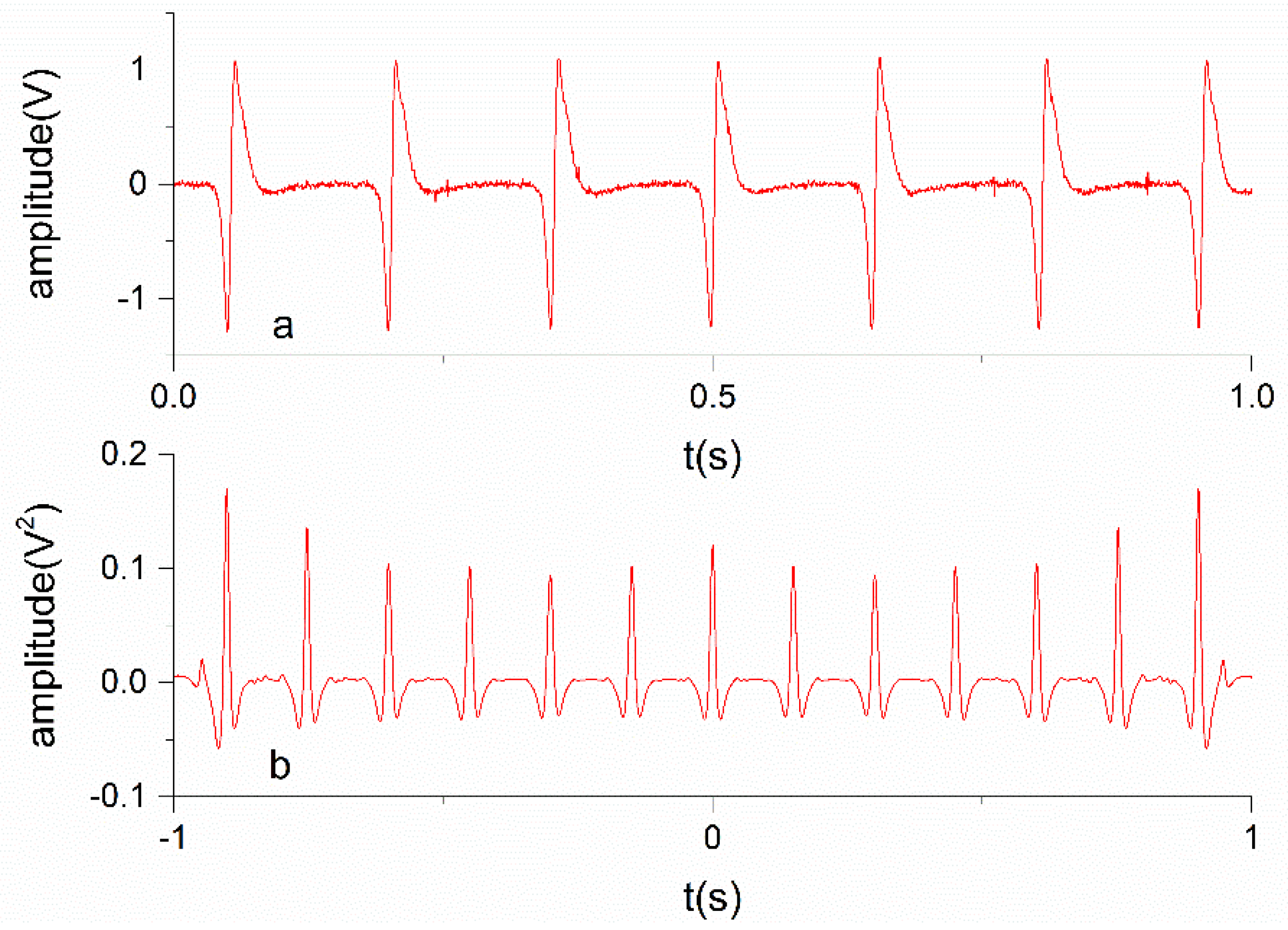
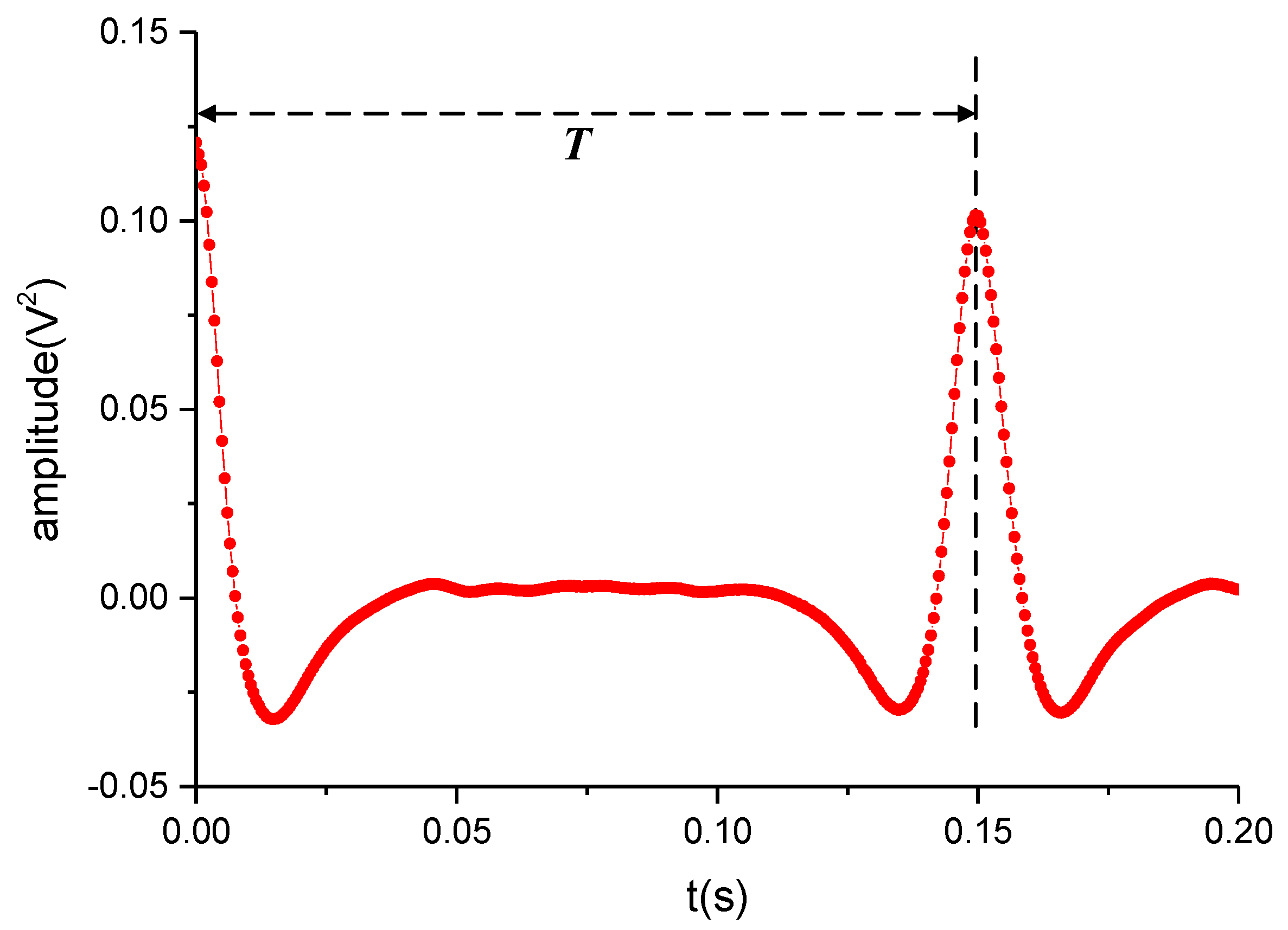
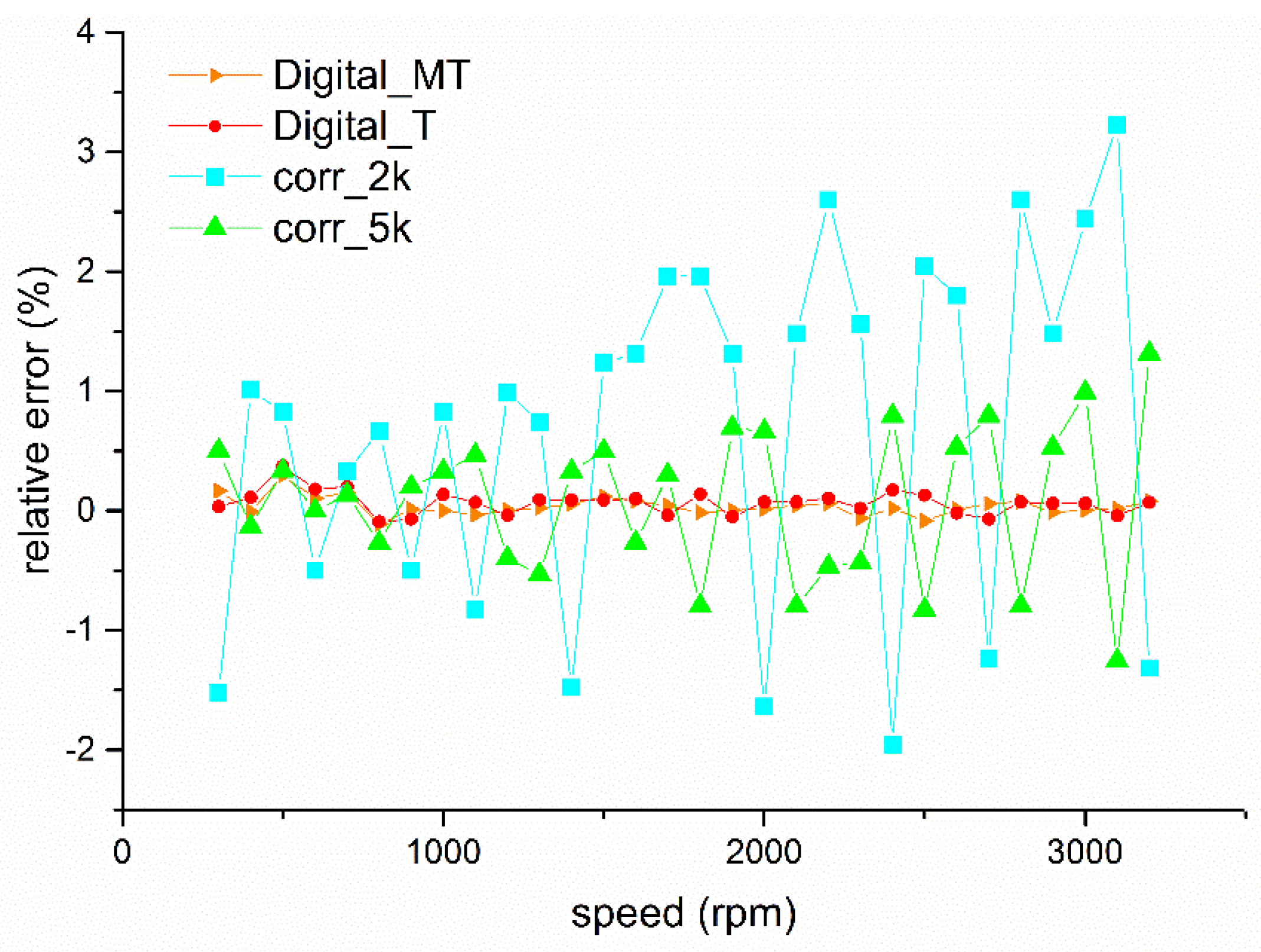
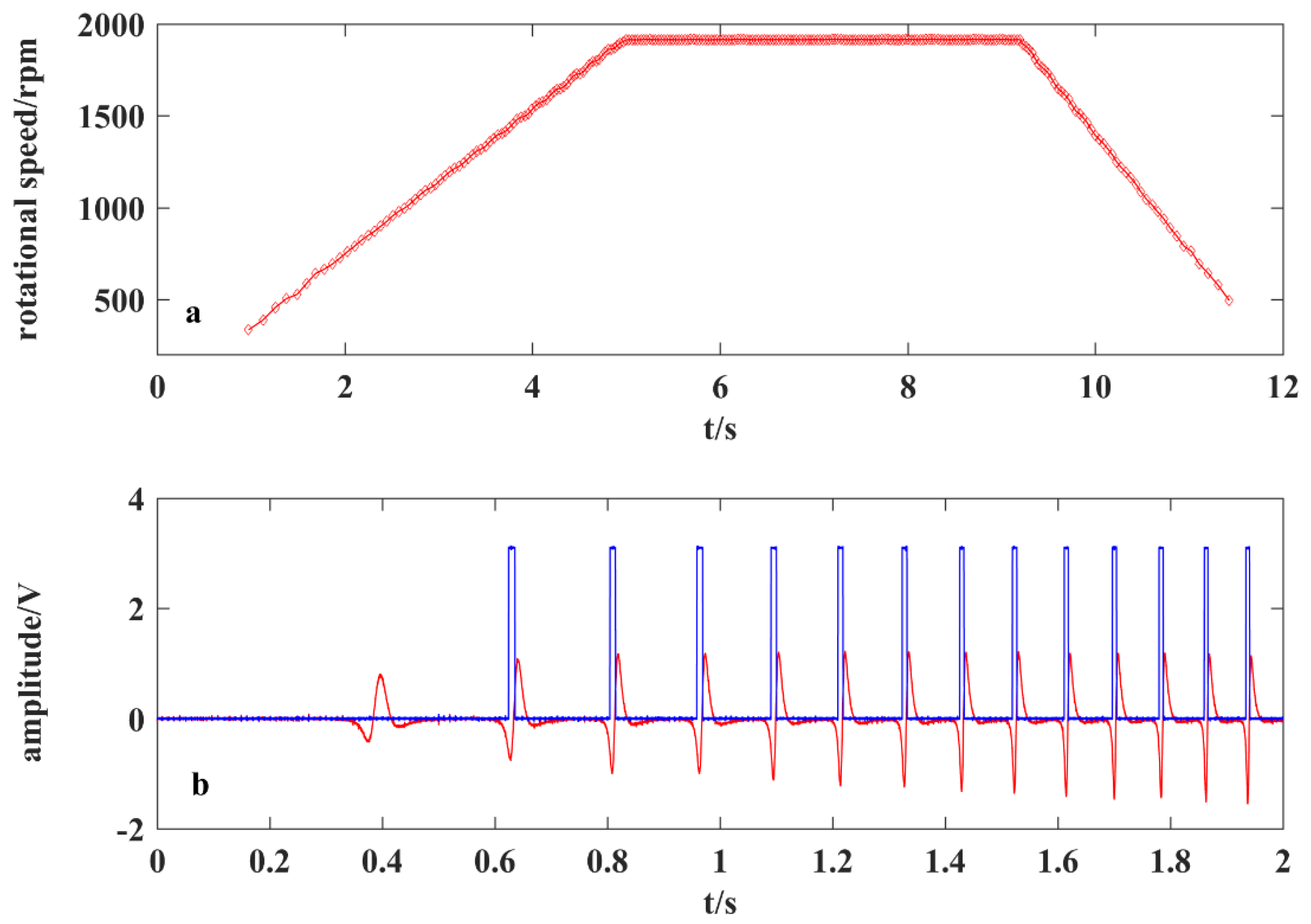
| Reference Speed (rpm) | Measured Speed (rpm) | Relative Error (‰) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M/T | T | M/T | T | |
| 300 | 300.50 | 300.11 | 1.67 | 0.36 |
| 400 | 399.97 | 400.45 | −0.08 | 1.12 |
| 500 | 501.04 | 501.87 | 2.08 | 3.74 |
| 600 | 600.63 | 601.08 | 1.05 | 1.80 |
| 700 | 701.09 | 701.39 | 1.56 | 1.98 |
| 800 | 799.12 | 799.26 | −1.10 | −0.92 |
| 900 | 900.10 | 899.38 | 0.11 | −0.69 |
| 1000 | 1000.02 | 1001.35 | 0.02 | 1.35 |
| 1100 | 1099.65 | 1100.79 | −0.32 | 0.72 |
| 1200 | 1200.06 | 1199.55 | 0.05 | −0.38 |
| 1300 | 1300.30 | 1301.22 | 0.23 | 0.94 |
| 1400 | 1400.83 | 1401.27 | 0.59 | 0.91 |
| 1500 | 1501.81 | 1501.34 | 1.21 | 0.89 |
| 1600 | 1601.33 | 1601.60 | 0.83 | 0.99 |
| 1700 | 1700.71 | 1699.35 | 0.42 | −0.38 |
| 1800 | 1799.75 | 1802.47 | −0.14 | 1.37 |
| 1900 | 1900.12 | 1899.11 | 0.06 | −0.47 |
| 2000 | 2000.34 | 2001.50 | 0.17 | 0.75 |
| 2100 | 2100.87 | 2101.57 | 0.41 | 0.75 |
| 2200 | 2201.38 | 2202.34 | 0.63 | 1.06 |
| 2300 | 2298.58 | 2300.50 | −0.62 | 0.21 |
| 2400 | 2400.52 | 2404.21 | 0.22 | 1.75 |
| 2500 | 2497.95 | 2503.25 | −0.82 | 1.30 |
| 2600 | 2600.32 | 2599.51 | 0.12 | 0.19 |
| 2700 | 2701.59 | 2698.14 | 0.59 | −0.69 |
| 2800 | 2802.13 | 2802.10 | 0.76 | 0.75 |
| 2900 | 2899.71 | 2901.81 | −0.10 | 0.62 |
| 3000 | 3000.15 | 3001.87 | 0.05 | 0.62 |
| 3100 | 3100.52 | 3098.77 | 0.17 | −0.40 |
| 3200 | 3202.58 | 3202.23 | 0.81 | 0.70 |
| Reference Speed (rpm) | Standard Deviation (rpm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M/T | T | 2k | 5k | |
| 300 | 0.055 | 0.175 | 1.755 | 2.047 |
| 400 | 0.013 | 0.292 | 2.641 | 2.250 |
| 500 | 0.013 | 0.397 | 4.652 | 1.867 |
| 600 | 0.032 | 0.274 | 1.651 | 2.161 |
| 700 | 0.023 | 0.458 | 3.437 | 1.472 |
| 800 | 0.097 | 0.142 | 2.367 | 2.592 |
| 900 | 0.091 | 0.115 | 3.011 | 1.206 |
| 1000 | 0.068 | 0.378 | 0 | 2.790 |
| 1100 | 0.011 | 0.146 | 0 | 0 |
| 1200 | 0.044 | 0.190 | 0 | 0 |
| 1300 | 0.015 | 0.284 | 0 | 2.525 |
| 1400 | 0.051 | 0.038 | 0 | 0 |
| 1500 | 0.010 | 0.027 | 0 | 0 |
| 1600 | 0.013 | 0.265 | 0 | 4.674 |
| 1700 | 0.017 | 0.190 | 0 | 0 |
| 1800 | 0.019 | 0.467 | 0 | 2.542 |
| 1900 | 0.010 | 0.065 | 0 | 0 |
| 2000 | 0.027 | 0.284 | 0 | 0 |
| 2100 | 0.029 | 0.234 | 0 | 0 |
| 2200 | 0.051 | 0.006 | 18.069 | 0 |
| 2300 | 0.016 | 0.368 | 0 | 7.878 |
| 2400 | 0.051 | 0.281 | 0 | 0 |
| 2500 | 0.050 | 0.415 | 0 | 0 |
| 2600 | 0.048 | 0.155 | 0 | 0 |
| 2700 | 0.018 | 0.364 | 0 | 0 |
| 2800 | 0.069 | 0.082 | 0 | 0 |
| 2900 | 0.039 | 0.301 | 0 | 0 |
| 3000 | 0.052 | 0.131 | 0 | 0 |
| 3100 | 0.012 | 0.327 | 0 | 0 |
| 3200 | 0.094 | 0.345 | 46.747 | 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Hu, H.; Qin, Y.; Tang, K. Digital Approach to Rotational Speed Measurement Using an Electrostatic Sensor. Sensors 2019, 19, 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112540
Li L, Hu H, Qin Y, Tang K. Digital Approach to Rotational Speed Measurement Using an Electrostatic Sensor. Sensors. 2019; 19(11):2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112540
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lin, Hongli Hu, Yong Qin, and Kaihao Tang. 2019. "Digital Approach to Rotational Speed Measurement Using an Electrostatic Sensor" Sensors 19, no. 11: 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112540
APA StyleLi, L., Hu, H., Qin, Y., & Tang, K. (2019). Digital Approach to Rotational Speed Measurement Using an Electrostatic Sensor. Sensors, 19(11), 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112540






