High Precision Compensation for a Total Reflection Prism Laser Gyro Bias in Consideration of High Frequency Oscillator Voltage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model and Algorithm of TRPLG Bias Compensation
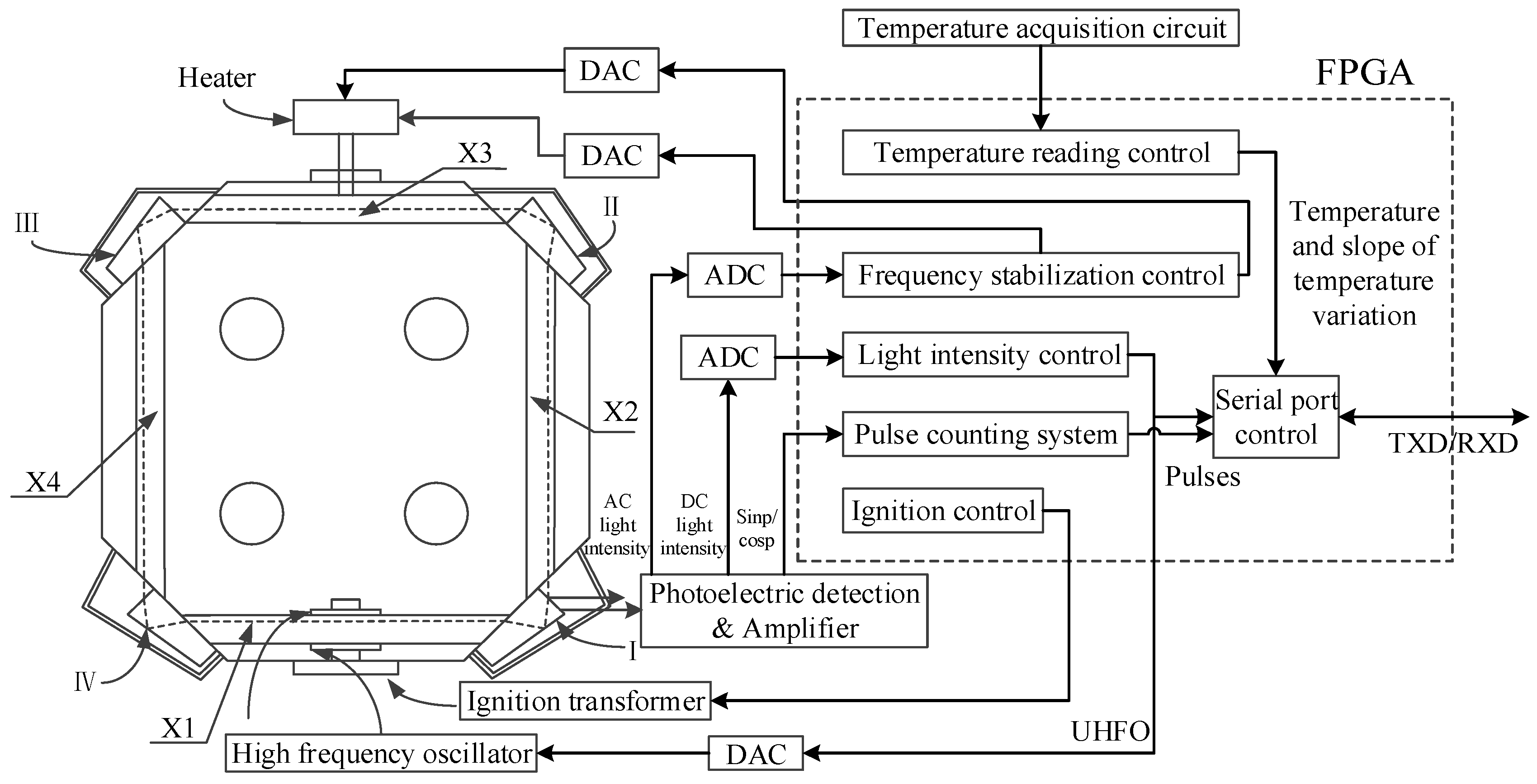
2.1. TRPLG Parameters Used for Bias Compensation
2.2. LSSVM for Nonlinear Function Regression
2.3. Regression by IR-LSSVM
- Given training data , find an optimal combination (by ten-fold cross-validation or generalization bounds) by solving systems (8).
- For the optimal combination one computers from (8).
- Computer from the distribution.
- Determine the weights based on , , besides, a suitable weight function is selected from (15) to (18).
- Solve the weighted LSSVM (14), giving the model .
3. Experimental Configuration
4. Analysis and Discussion of Results
4.1. Bias Compensation Using LS(least squares) Model
4.2. Bias Compensation Using Stepwise Regression Model
4.3. Bias Compensation Using IR-LSSVM Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, Q.; Wu, W.; Jiang, M.; Li, Y. A new filtering and smoothing algorithm for railway track surveying based on landmark and IMU/Odometer. Sensors 2017, 17, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakin, Y.V.; Ziouzev, G.N.; Lioudomirski, M.B. Laser Gyros with Total Reflection Prisms; Moscow Bauman State Technical University: Moscow, Russia, 2003; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, W.W. The ring laser gyro. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1985, 57, 61–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonel, N.; Menegozzi Willis, E.; Lamb, J. Theory of a ring lase. Phys. Rev. A 1973, 8, 2103–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, D.A.; Roden, S.; King, T.A. A model for lock-in growth in ring laser gyroscopes. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1995, 31, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Luo, H.; Lu, G.; Hu, S. Online effective backscattering estimation for ring laser gyro. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2012, 10, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, R.B.; Rabeendran, N.; Schreiber, K.U.; Wells, J.R. Correction of backscatter-induced systematic errors in ring laser gyroscopes. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 7610–7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Wu, W.; Wu, M.; Feng, G.; Hao, M. Systematic angle random walk estimation of the constant rate biased ring laser gyro. Sensors 2013, 13, 2750–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Luo, H.; Lu, G.; Hu, S. Dynamic lock-in compensation for mechanically dithered ring laser gyros. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2012, 10, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.W.; Lee, J.C.; Hong, S.K.; Chwa, D. New random walk reduction algorithm in ring laser gyroscopes. J. Opt. 2010, 12, 115501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Luo, H.; Hu, S. Instantaneous phase method for readout signal processing of body dithered ring laser gyro. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 3455–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronowitz, F.; Killpatrick, J.E.; Gallaghan, S.P. Power-dependent correction to the scale factor in the laser gyro. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1974, 10, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, R.B.; Mayerbacher, M.; Gebauer, A.; Schreiber, K.U.; Wells, J.R. High-accuracy absolute rotation rate measurements with a large ring laser gyro: Establishing the scale factor. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Wei, G.; Tang, J. Effect of temperature characteristic of light path on RLG’s bias. Infrared Laser Eng. 2011, 40, 2393–2397. [Google Scholar]
- Beghi, A.; Belfi, J.; Beverini, N.; Bouhadef, B.; Cuccato, D.; Virgilio, A.D.; Ortolan, A. Compensation of the laser parameter fluctuations in large ring-laser gyros: A Kalman filter approach. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 7518–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchler, R.J.; Moeller, R.; Fann, S.W.; Tazartes, D.A.; Mark, J.G. Temperature Compensation Method for Strapdown Inertial Navigation System. U.S. Patent 6,175,807 B1, 16 January 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X. Investigation on the temperature compensation model for ring laser gyroscope. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2006, 4, 100576. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, G.; Zhang, P.; Long, X. Novel temperature modeling and compensation method for bias of ring laser gyroscope based on least-squares support vector machine. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2011, 9, 051201. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, S. Laser gyro temperature compensation using modified RBFNN. Sensors 2014, 14, 18711–18727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vapnik, V.N. An overview of statistical learning theory. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1999, 10, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.N. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Spring: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 988–999. [Google Scholar]
- Suykens, J.A.K.; Gestel, T.V.; Brabanter, J.D.; Moor, B.D.; Vandewalle, J. Least Squares Support Vector Machines; World Scientific: Singapore, 2002; pp. 29–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, G.; Li, G.; W, Y.; Long, X. Application of least squares-support vector machine in system-level temperature compensation of ring laser gyroscope. Measurement 2011, 44, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, F.; Xiao, G.; Wei, G.; Zhang, P.; Long, X. Temperature compensation method using readout signals of ring laser gyroscope. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 13320–13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suykens, J.A.K.; Brabanter, J.D.; Lukas, L.; Vandewalle, J. Weighted least squares support vector machines: Robustness and sparse approximation. Neurocomputing 2002, 48, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Dai, L. Robust iterative algorithm of weighted least squares support vector machine and its application in spectral analysis. Acta Chim. Sin. 2009, 67, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Yan, C.; Li, Y. A robust weighted least squares support vector regression based on least trimmed squares. Neurocomputing 2015, 168, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tan, L.; He, L. A robust least squares support vector machine for regression and classification with noise. Neurocomputing 2014, 140, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhong, P. Robust non-convex least squares loss function for regression with outliers. Knowl. Based Syst. 2014, 71, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashrouz, S.; Mirshekar, H.; Mohaddespour, A. A robust modeling approach to predict the surface tension of ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 236, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Yuan, C. A robust outlier control framework for classification designed with family of homotopy loss function. Neural Netw. 2019, 112, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S. Sparse algorithm for robust LSSVM in primal space. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 2880–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, C.; Zeng, X.; Cao, C. Intensity properties of output light in prism laser gyro with mechanical dither bias. Acta Phys. Sin. 2012, 61, 094216. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, C.; Zeng, X.; Cao, C. Polarization properties in a prism laser gyro with mechanical dither bias. Chin. Phys. B 2012, 21, 124206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Temperature | Slope of Temperature Variation | UHFO | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient with TRPLG output | 0.71 | −0.43 | −0.82 |
| Parameters Based on LS Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Slope of Temperature Variation | UHFO | ||
| TRPLG bias stability () | Before compensation | 0.01850 | 0.01850 | 0.01850 |
| After compensation | 0.01194 | 0.01702 | 0.01100 | |
| Improvement | 35.46% | 8.00% | 40.54% | |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TRPLG bias stability () | Before compensation | 0.01850 | 0.01850 |
| After compensation | 0.00942 | 0.00842 | |
| Improvement | 49.08% | 54.49% | |
| No. | Parameters | Weight Function | Improvement | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Huber | 0.0356 | 8.5410 | 0.01105 | 40.27% | ||
| Hampel | 78.6103 | 0.4086 | 8.5280 | 0.01123 | 39.30% | ||
| Logistic | 0.2138 | 8.4047 | 0.01089 | 41.14% | |||
| Myriad | 0.0742 | 8.4990 | 0.01090 | 41.08% | |||
| 2 | Huber | 7.2794 | 13.1121 | 0.01712 | 7.46% | ||
| Hampel | 1.0207 | 0.0003 | 12.6074 | 0.01357 | 26.65% | ||
| Logistic | 1.4421 | 0.0003 | 12.7182 | 0.01356 | 26.70% | ||
| Myriad | 1.0537 | 3.8071 | 13.1177 | 0.01714 | 7.35% | ||
| 3 | Huber | 0.2718 | 0.0044 | 8.1178 | 0.01009 | 45.46% | |
| Hampel | 0.1643 | 0.0065 | 8.1610 | 0.01024 | 44.65% | ||
| Logistic | 0.2691 | 0.0070 | 8.1394 | 0.01021 | 44.81% | ||
| Myriad | 0.1955 | 0.0060 | 8.1437 | 0.01015 | 45.14% |
| No. | Parameters | Weight Function | Improvement | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Huber | 0.2065 | 6.5456 | 0.00755 | 59.19% | ||
| Hampel | 1.1991 | 0.0930 | 6.6019 | 0.00794 | 57.08% | ||
| Logistic | 0.1399 | 6.5949 | 0.00757 | 59.08% | |||
| Myriad | 0.2041 | 6.5080 | 0.00752 | 59.35% | |||
| 2 | Huber | 0.0390 | 7.0111 | 0.00789 | 57.35% | ||
| Hampel | 79.8662 | 0.0297 | 7.1130 | 0.00823 | 55.51% | ||
| Logistic | 0.0304 | 7.0946 | 0.00807 | 56.38% | |||
| Myriad | 8.4177 | 0.0045 | 7.1402 | 0.00743 | 59.84% | ||
| 3 | Huber | 1.6025 | 6.7729 | 0.00818 | 55.78% | ||
| Hampel | 0.7546 | 0.2386 | 6.8129 | 0.00837 | 54.76% | ||
| Logistic | 1.9995 | 0.2144 | 6.8975 | 0.00832 | 55.03% | ||
| Myriad | 1.4267 | 0.3799 | 6.9093 | 0.00838 | 54.70% | ||
| 4 | Huber | 2.2799 | 6.4217 | 0.00740 | 60.00% | ||
| Hampel | 26.3212 | 0.1263 | 6.4479 | 0.00733 | 60.38% | ||
| Logistic | 1.0623 | 6.4218 | 0.00740 | 60.00% | |||
| Myriad | 76.0796 | 0.1458 | 6.3711 | 0.00718 | 61.19% | ||
| Unweighted | 0.9771 | 6.6791 | 0.00758 | 59.03% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, Y.; Li, S.; Zheng, J.; Wu, F.; Fu, Q. High Precision Compensation for a Total Reflection Prism Laser Gyro Bias in Consideration of High Frequency Oscillator Voltage. Sensors 2019, 19, 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19132986
Tao Y, Li S, Zheng J, Wu F, Fu Q. High Precision Compensation for a Total Reflection Prism Laser Gyro Bias in Consideration of High Frequency Oscillator Voltage. Sensors. 2019; 19(13):2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19132986
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Yuanbo, Sihai Li, Jiangtao Zheng, Feng Wu, and Qiangwen Fu. 2019. "High Precision Compensation for a Total Reflection Prism Laser Gyro Bias in Consideration of High Frequency Oscillator Voltage" Sensors 19, no. 13: 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19132986
APA StyleTao, Y., Li, S., Zheng, J., Wu, F., & Fu, Q. (2019). High Precision Compensation for a Total Reflection Prism Laser Gyro Bias in Consideration of High Frequency Oscillator Voltage. Sensors, 19(13), 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19132986






