putEMG—A Surface Electromyography Hand Gesture Recognition Dataset
Abstract
1. Introduction
Contribution
2. putEMG Data Collection
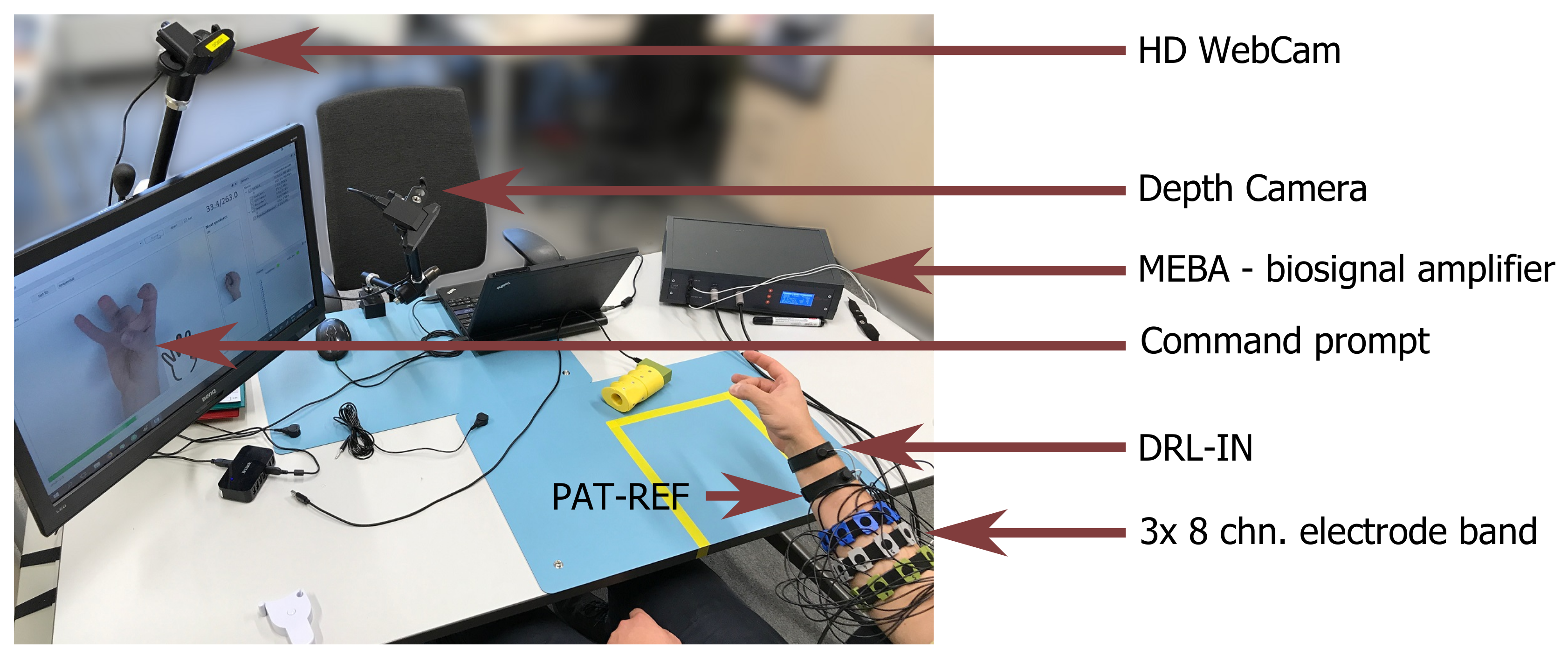
2.1. Experimental Setup
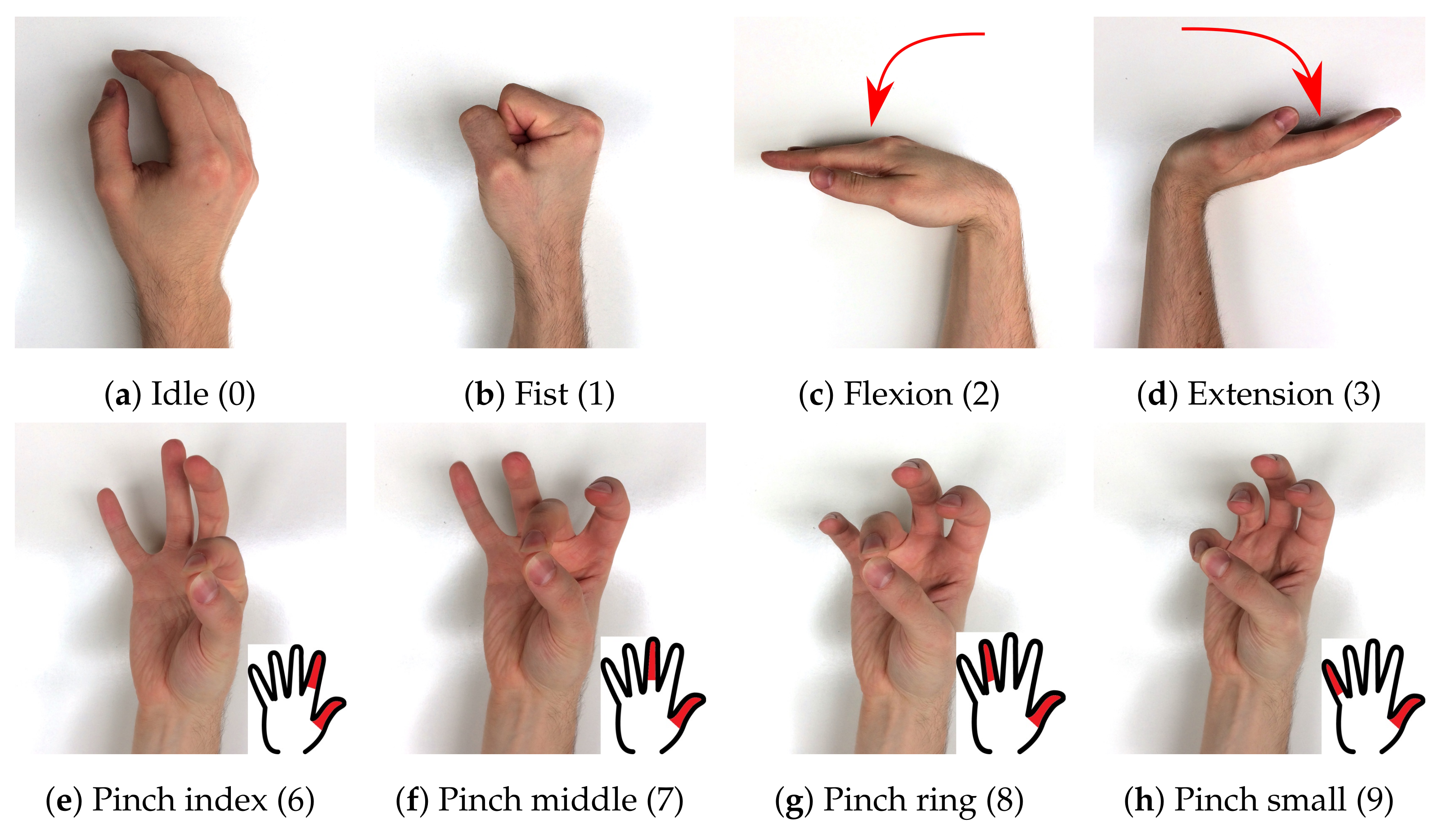
2.2. Procedure
- repeats_long - 7 action blocks, each block contains 8 repetitions of each active gesture:[relax] 0-1-0-1-0-1-0-1-0-1-0-1-0-1-0-1-0 [relax] 0-2-0-2-0-2-0-2-0-2-0-2-0-2-0-2-0 [relax] 0-3-0… ,
- sequential - 6 action blocks, each block is a subsequent execution of all active gestures:[relax] 0-1-0-2-0-3-0-6-0-7-0-8-0-9-0 [relax] 0-1-0-2-0-3-0-6-0-7-0-8-0-9-0 [relax] 0-1-0-2-0… ,
- repeats_short - 7 action blocks, each block contains 6 repetitions of each active gesture:[relax] 0-1-0-1-0-1-0-1-0-1-0-1-0 [relax] 0-2-0-2-0-2-0-2-0-2-0-2-0 [relax] 0-3-0… .
2.3. Participants
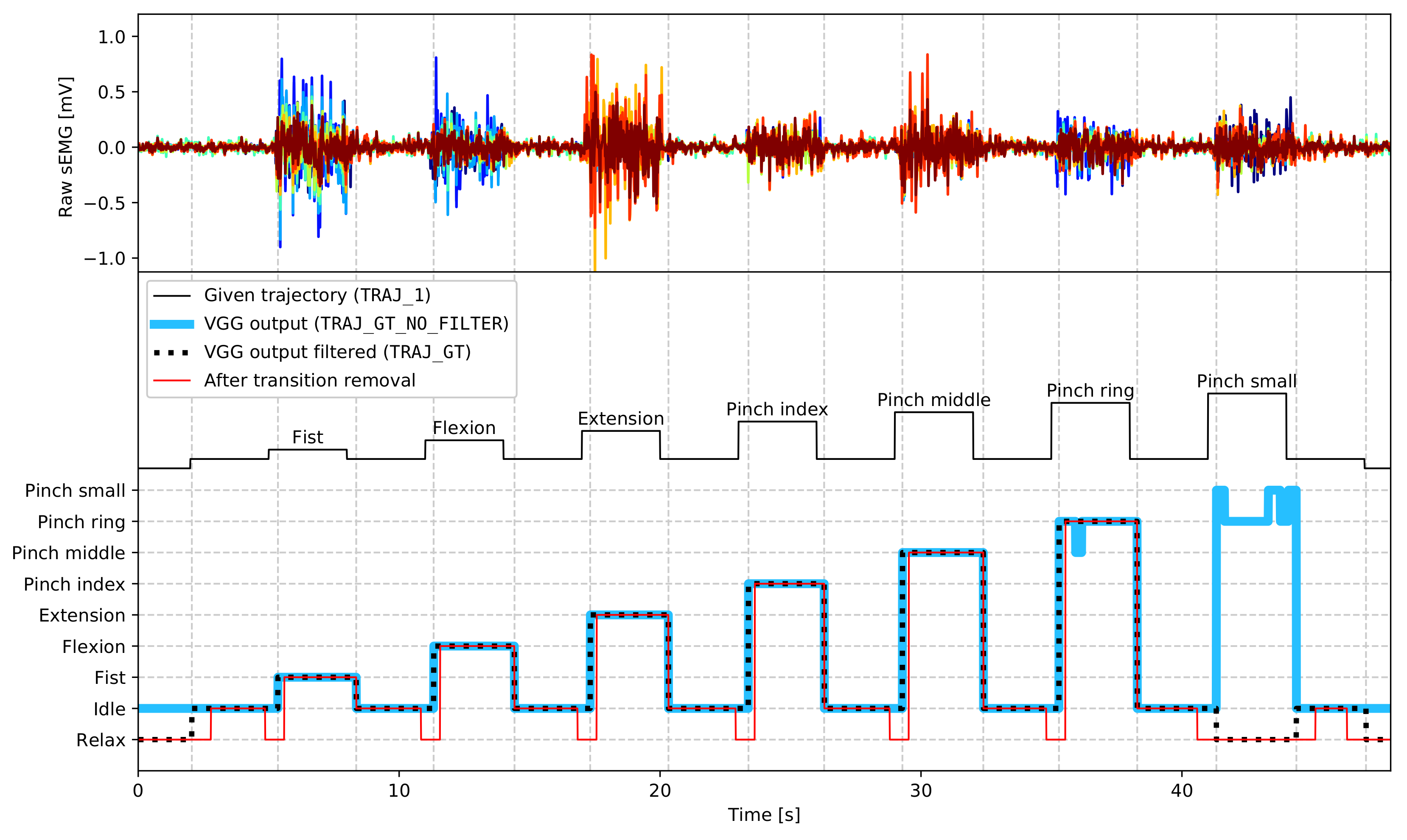
2.4. Pre-Processing and Labelling
3. Technical Validation
3.1. Amplitudes Assessment
3.2. Feature Extraction and Classification Benchmark
3.2.1. Used Feature Sets and Classifiers
3.2.2. Classification Pre-Processing and Data Split
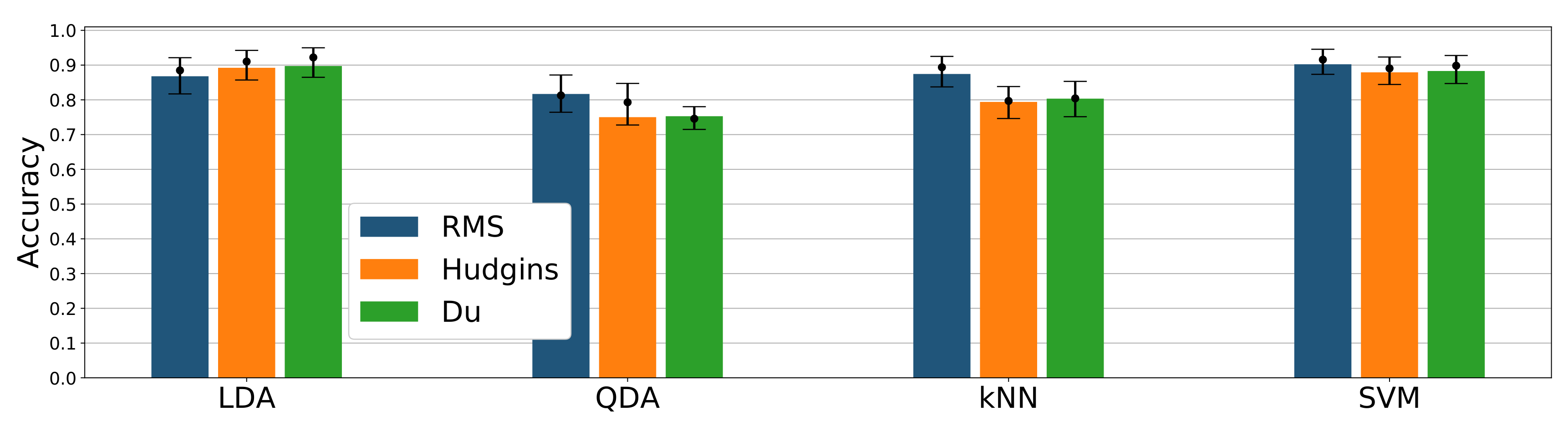
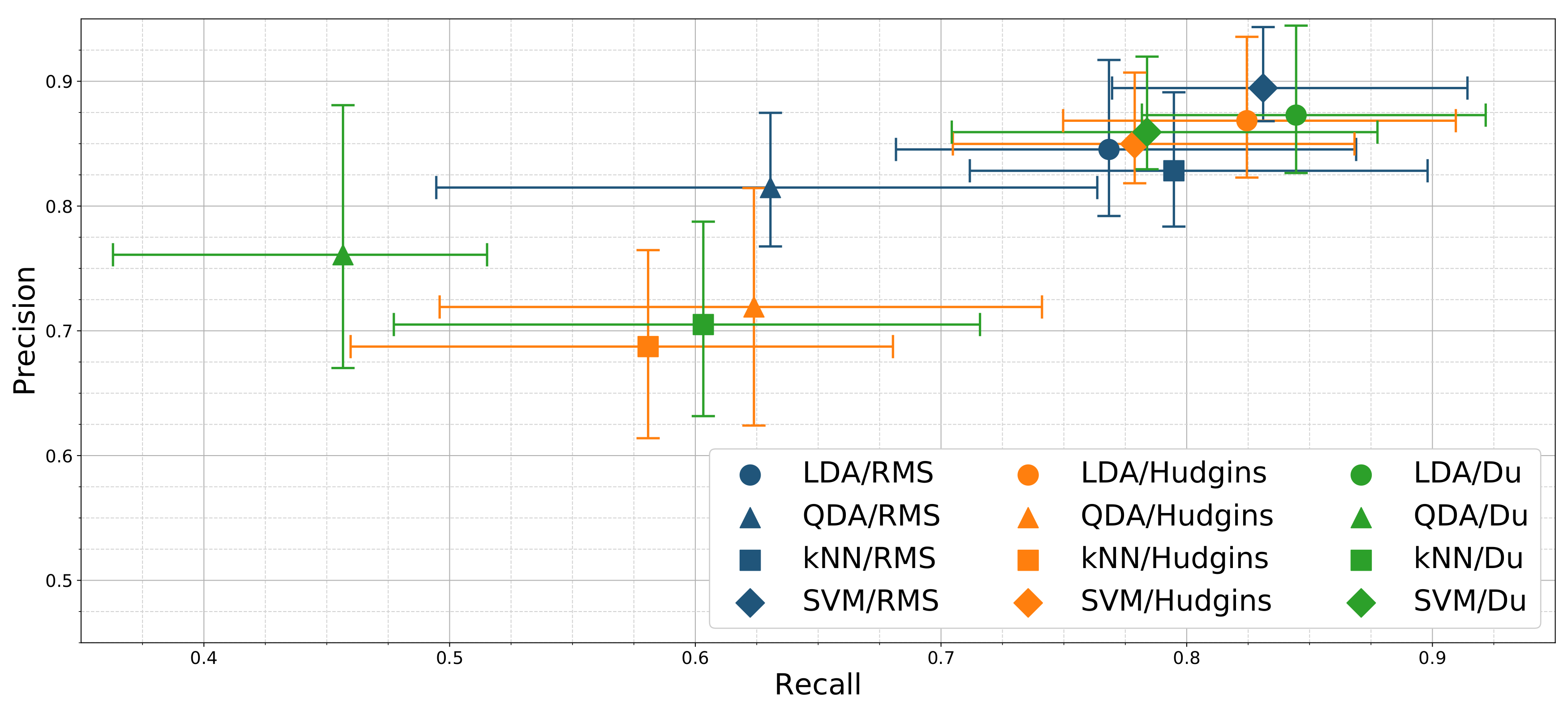
3.2.3. Classification Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | analog to digital converter |
| CSV | comma-separated values |
| DNN | deep neural-network |
| EMG | electromyography |
| HDF5 | Hierarchical Data Format 5 |
| HMI | human machine-interface |
| IAV | Integral Absolute Value |
| iEMG | integrated Electromyogram |
| kNN | k-nearest Neighbours Algorithm |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| MAV | Mean Absolute Value |
| MVC | Maximum Voluntary Contraction |
| OFNDA | Orthogonal Fuzzy Neighbourhood Discriminant Analysis |
| QDA | Quadratic Discriminant Analysis |
| RBF | radial basis function |
| RMS | Root Mean Square |
| sEMG | surface electromyography |
| SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
| SSC | Slope Sign Change |
| SVM | Support-Vector Machine |
| VAR | variance |
| WAMP | Willison Amplitude |
| WL | Waveform Length |
| ZC | Zero Crossing |
Appendix A. putEMG Dataset Structure and Handling
- <subject>—two-digit participant identifier,
- <trajectory>—trajectory type: repeats_long, sequential, repeats_short,
- <YYYY-MM-DD-hh-mm-ss-millisec> - time of experiment start in stated format.
- Timestamp,
- EMG_1…EMG_24—sEMG raw ADC samples—column numbers explained in Section 2.1 and Figure 2a,
- TRAJ_1—label representing command shown to the subject during the experiment,
- TRAJ_GT_NO_FILTER - gesture recognised from the video stream, not processed,
- TRAJ_GT—ground-truth estimated from the video stream, processed as described in Section 2.4,
- VIDEO_STAMP—frame timestamp in the corresponding video stream.
References
- Roland, T.; Wimberger, K.; Amsuess, S.; Russold, M.F.; Baumgartner, W. An insulated flexible sensor for stable electromyography detection: Application to prosthesis control. Sensors 2019, 19, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagami, M.; Peters, K.; Milovanovic, I.; Kuang, I.; Yang, Z.; Lu, N.; Steele, K. Assessment of dry epidermal electrodes for long-term electromyography measurements. Sensors 2018, 18, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada-Quintero, H.F.; Rood, R.T.; Burnham, K.; Pennace, J.; Chon, K.H. Assessment of carbon/salt/adhesive electrodes for surface electromyography measurements. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2016, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabard-Fougère, A.; Rose-Dulcina, K.; Pittet, V.; Dayer, R.; Vuillerme, N.; Armand, S. EMG normalization method based on grade 3 of manual muscle testing: Within-and between-day reliability of normalization tasks and application to gait analysis. Gait Posture 2018, 60, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, W.; Du, Y.; Jin, W.; Wei, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, J. Gesture recognition by instantaneous surface EMG images. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Takruri, M.; Miro, J.V.; Kodagoda, S. Towards limb position invariant myoelectric pattern recognition using time-dependent spectral features. Neural Netw. 2014, 55, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Al-Timemy, A.; Kodagoda, S.; Nazarpour, K. Combined influence of forearm orientation and muscular contraction on EMG pattern recognition. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 61, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakonen, M.; Piitulainen, H.; Visala, A. Current state of digital signal processing in myoelectric interfaces and related applications. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2015, 18, 334–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyński, J.; Mańkowski, T.; Kaczmarek, P. Localisation method for sEMG electrode array, towards hand gesture recognition HMI development. In Proceedings of the 2017 Signal Processing: Algorithms, Architectures, Arrangements, and Applications (SPA), Poznan, Poland, 20–22 September 2017; pp. 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Palermo, F.; Cognolato, M.; Gijsberts, A.; Müller, H.; Caputo, B.; Atzori, M. Repeatability of grasp recognition for robotic hand prosthesis control based on sEMG data. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1154–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Jelfs, B.; Chan, R.H.; Tin, C. Self-recalibrating surface EMG pattern recognition for neuroprosthesis control based on convolutional neural network. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinyomark, A.; Quaine, F.; Charbonnier, S.; Serviere, C.; Tarpin-Bernard, F.; Laurillau, Y. EMG feature evaluation for improving myoelectric pattern recognition robustness. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 4832–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinyomark, A.; Scheme, E. EMG pattern recognition in the era of big data and deep learning. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2018, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsberts, A.; Atzori, M.; Castellini, C.; Müller, H.; Caputo, B. Movement error rate for evaluation of machine learning methods for sEMG-based hand movement classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzori, M.; Gijsberts, A.; Kuzborskij, I.; Elsig, S.; Hager, A.G.M.; Deriaz, O.; Castellini, C.; Müller, H.; Caputo, B. Characterization of a benchmark database for myoelectric movement classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 23, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzori, M.; Gijsberts, A.; Castellini, C.; Caputo, B.; Hager, A.G.M.; Elsig, S.; Giatsidis, G.; Bassetto, F.; Müller, H. Electromyography data for non-invasive naturally-controlled robotic hand prostheses. Sci. Data 2014, 1, 140053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzolato, S.; Tagliapietra, L.; Cognolato, M.; Reggiani, M.; Müller, H.; Atzori, M. Comparison of six electromyography acquisition setups on hand movement classification tasks. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Feleke, G.; Guan, C. A review on EMG-based motor intention prediction of continuous human upper limb motion for human-robot collaboration. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 51, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cene, V.H.; Tosin, M.; Machado, J.; Balbinot, A. Open database for accurate upper-limb intent detection using electromyography and reliable extreme learning machines. Sensors 2019, 19, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordaniello, F.; Cognolato, M.; Graziani, M.; Gijsberts, A.; Gregori, V.; Saetta, G.; Hager, A.G.M.; Tiengo, C.; Bassetto, F.; Brugger, P.; et al. Megane pro: Myo-electricity, visual and gaze tracking data acquisitions to improve hand prosthetics. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1148–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Jin, W.; Wei, W.; Hu, Y.; Geng, W. Surface EMG-based inter-session gesture recognition enhanced by deep domain adaptation. Sensors 2017, 17, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasoulis, A.; Kyranou, I.; Erden, M.S.; Nazarpour, K.; Vijayakumar, S. Improved prosthetic hand control with concurrent use of myoelectric and inertial measurements. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Kodagoda, S. Electromyogram (EMG) feature reduction using mutual components analysis for multifunction prosthetic fingers control. In Proceedings of the 2012 12th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision (ICARCV), Guangzhou, China, 5–7 December 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1534–1539. [Google Scholar]
- Amma, C.; Krings, T.; Böer, J.; Schultz, T. Advancing muscle-computer interfaces with high-density electromyography. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Seoul, Korea, 18–23 April 2015; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 929–938. [Google Scholar]
- Tomczyński, J.; Kaczmarek, P.; Mańkowski, T. Hand gesture-based interface with multichannel sEMG band enabling unknown gesture discrimination. In Proceedings of the 2015 10th International Workshop on Robot Motion and Control (RoMoCo), Poznan, Poland, 6–8 July 2015; pp. 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyński, J.; Mańkowski, T.; Kaczmarek, P. Influence of sEMG electrode matrix configuration on hand gesture recognition performance. In Proceedings of the 2017 Signal Processing: Algorithms, Architectures, Arrangements and Applications (SPA), Poznan, Poland, 18–20 December 2017; pp. 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Merletti, R.; Di Torino, P. Standards for reporting EMG data. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 1999, 9, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Phinyomark, A.; Nuidod, A.; Phukpattaranont, P.; Limsakul, C. Feature extraction and reduction of wavelet transform coefficients for EMG pattern classification. Elektron. Elektrotech. 2012, 122, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudgins, B.; Parker, P.; Scott, R.N. A new strategy for multifunction myoelectric control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1993, 40, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.C.; Lin, C.H.; Shyu, L.Y.; Chen, T. Portable hand motion classifier for multi-channel surface electromyography recognition using grey relational analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4283–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskoei, M.A.; Hu, H. Support vector machine-based classification scheme for myoelectric control applied to upper limb. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinyomark, A.; Phothisonothai, M.; Suklaead, P.; Phukpattaranont, P.; Limsakul, C. Fractal analysis of surface electromyography (EMG) signal for identify hand movements using critical exponent analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Software Engineering and Computer Systems, Pahang, Malaysia, 27–29 June 2011; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 703–713. [Google Scholar]
- Van Beek, N.; Stegeman, D.F.; Van Den Noort, J.C.; Veeger, D.H.; Maas, H. Activity patterns of extrinsic finger flexors and extensors during movements of instructed and non-instructed fingers. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 38, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Timemy, A.H.; Bugmann, G.; Escudero, J.; Outram, N. Classification of finger movements for the dexterous hand prosthesis control with surface electromyography. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 2013, 17, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Jin, D. A method of recognizing finger motion using wavelet transform of surface EMG signal. Procedings of the 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference, Shanghai, China, 1–4 September 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 2672–2674. [Google Scholar]
- Tenore, F.V.; Ramos, A.; Fahmy, A.; Acharya, S.; Etienne-Cummings, R.; Thakor, N.V. Decoding of individuated finger movements using surface electromyography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 56, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dataset Name | EMG Recording Setup | Gesture Tracking System | No. of Participants | No. of Gestures | Repetitions per Session | Session Count | Session Organisation and Intervals | Trials Organisation | Gesture Durations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NinaPro DB1 [15] | 10 sEMG | yes | 27 | 52 | 10 | 1 | - | random | gesture: 5 s idle: 3 s |
| NinaPro DB2 [16] | 12 sEMG | yes | 40 | 49 | 6 | 1 | - | repetitive | gesture: 5 s idle: 3 s |
| NinaPro DB4 [17] | 12 sEMG | - | 10 | 52 | 6 | 1 | - | repetitive | gesture: 5 s idle: 3 s |
| NinaPro DB5 [17] | 16 sEMG | yes | 10 | 52 | 6 | 1 | - | repetitive | gesture: 5 s idle: 3 s |
| NinaPro DB6 [10] | 14 sEMG e | yes | 10 | 7 | 12 | 10 | 2 per day, 5 days | repetitive | gesture: 4 s idle: 4 s |
| NinaPro DB7 [22] | 12 sEMG e, 9DoF IMU | - | 20 | 40 | 6 | 1 | - | sequential | gesture: 5 s idle: 5 s |
| IEE EMG [19] | 12 sEMG | - | 4 | 17 | 32 | 1 | - | sequential (4 varying) | no idle phase |
| Megane Pro [20] | 14 sEMG e | yes | 10 | 15 | 12 | 10 | 2 per day, 5 days | repetitive | gesture: 8 s idle: 4 s |
| EMG Dataset 2 [23] | 8 sEMG | - | 8 | 15 | 12 | 3 | - | sequential | gesture: 20 s |
| EMG Dataset 6 [6] | 7 sEMG | - | 11 | 8 | 12 | 6 | 5 poses | sequential | gesture: 5 s idle: 3-5s |
| CapgMyo(DB-a) [21] | 128 HD-sEMG | - | 18 | 8 | 10 | 1 | - | repetitive | gesture: 3–10 s idle: 7 s |
| CapgMyo(DB-b) [21] | 128 HD-sEMG | - | 10 | 8 | 10 | 2 | 1 day | sequential | gesture: 3 s idle: 7 s |
| CapgMyo(DB-c) [21] | 128 HD-sEMG | - | 10 | 12 | 10 | 1 | - | repetitive | gesture: 3 s idle: 7 s |
| CSL-HDEMG [24] | 192 HD-sEMG | yes | 5 | 27 | 10 | 5 | different days | sequential | gesture: 3 s idle: 3 s |
| putEMG (this work) | 24 sEMG | yes | 44 | 8 | 20 | 2 | 1 week | sequential repetitive | gesture: 1 s or 3 s idle: 3 s |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaczmarek, P.; Mańkowski, T.; Tomczyński, J. putEMG—A Surface Electromyography Hand Gesture Recognition Dataset. Sensors 2019, 19, 3548. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163548
Kaczmarek P, Mańkowski T, Tomczyński J. putEMG—A Surface Electromyography Hand Gesture Recognition Dataset. Sensors. 2019; 19(16):3548. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163548
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaczmarek, Piotr, Tomasz Mańkowski, and Jakub Tomczyński. 2019. "putEMG—A Surface Electromyography Hand Gesture Recognition Dataset" Sensors 19, no. 16: 3548. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163548
APA StyleKaczmarek, P., Mańkowski, T., & Tomczyński, J. (2019). putEMG—A Surface Electromyography Hand Gesture Recognition Dataset. Sensors, 19(16), 3548. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163548





