Fatigue Detection during Sit-To-Stand Test Based on Surface Electromyography and Acceleration: A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subject
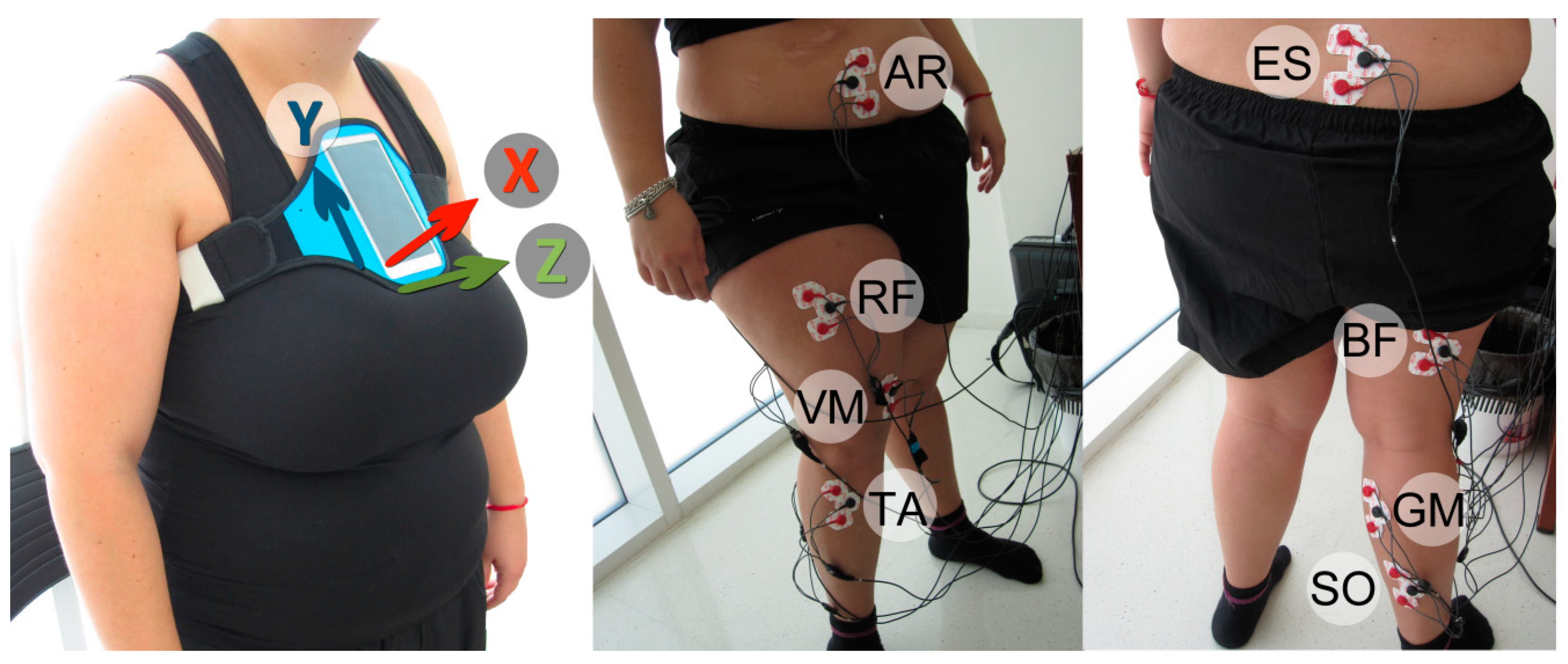
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Preprocessing
2.5. Data Processing
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riley, P.O.; Schenkman, M.L.; Mann, R.W.; Hodge, W.A. Mechanics of a constrained chair-rise. J. Biomech. 1991, 24, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.J.; Rikli, R.E.; Beam, W.C. A 30-s chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community-residing older adults. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1999, 70, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukadida, A.; Piotte, F.; Dehail, P.; Nadeau, S. Determinants of sit-to-stand tasks in individuals with hemiparesis post stroke: A review. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 58, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploutz-Snyder, L.L.; Manini, T.; Ploutz-Snyder, R.J.; Wolf, D.A. Functionally relevant thresholds of quadriceps femoris strength. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2002, 57, B144–B152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, G.D.; Ashburn, A.M. Trunk movements in older subjects during sit-to-stand. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1995, 76, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, K.; White, J.; Barr, D.; Mollan, R. Standardization and definitions of the sit-stand-sit movement cycle. Gait Posture 1994, 2, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, K.; White, J.; Barr, D.; Mollan, R. Analysis of the sit-stand-sit movement cycle: Development of a measurement system. Gait Posture 1994, 2, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveter, A.T.; Dagfinrud, H.; Moseng, T.; Holm, I. Health-related physical fitness measures: Reference values and reference equations for use in clinical practice. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyland, J.; Frost, K.; Quesada, P.; Angeli, C.; Swank, A.; Topp, R.; Malkani, A.L. Self-reported chair-rise ability relates to stair-climbing readiness of total knee arthroplasty patients: A pilot study. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2007, 44, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millor, N.; Lecumberri, P.; Gomez, M.; Martinez-Ramirez, A.; Izquierdo, M. Kinematic parameters to evaluate functional performance of sit-to-stand and stand-to-sit transitions using motion sensor devices: A systematic review. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giansanti, D.; Maccioni, G.; Benvenuti, F.; Macellari, V. Inertial measurement units furnish accurate trunk trajectory reconstruction of the sit-to-stand manoeuvre in healthy subjects. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2007, 45, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, W.G.M.; Bussmann, J.B.J.; Horemans, H.L.D.; Stam, H.J. Validity of accelerometry in assessing the duration of the sit-to-stand movement. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2008, 46, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millor, N.; Lecumberri, P.; Gómez, M.; Martínez-Ramírez, A.; Izquierdo, M. An evaluation of the 30-s chair stand test in older adults: Frailty detection based on kinematic parameters from a single inertial unit. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2013, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doheny, E.P.; Fan, C.W.; Foran, T.; Greene, B.R.; Cunningham, C.; Kenny, R.A. An instrumented sit-to-stand test used to examine differences between older fallers and non-fallers. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2011, 2011, 3063–3066. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Lummel, R.C.; Ainsworth, E.; Lindemann, U.; Zijlstra, W.; Chiari, L.; Van Campen, P.; Hausdorff, J.M. Automated approach for quantifying the repeated sit-to-stand using one body fixed sensor in young and older adults. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millor, N.; Lecumberri, P.; Gomez, M.; Martinez-Ramirez, A.; Rodriguez-Manas, L.; Garcia-Garcia, F.J.; Izquierdo, M. Automatic evaluation of the 30-s chair stand test using inertial/magnetic-based technology in an older prefrail population. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2013, 17, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Heijden, M.M.P.; Meijer, K.; Willems, P.J.B.; Savelberg, H.H.C.M. Muscles limiting the sit-to-stand movement: An experimental simulation of muscle weakness. Gait Posture 2009, 30, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnfield, J.M.; Shu, Y.; Buster, T.W.; Taylor, A.P.; McBride, M.M.; Krause, M.E. Kinematic and electromyographic analyses of normal and device-assisted sit-to-stand transfers. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cuesta-Vargas, A.I.; Cano-Herrera, C.L.; Heywood, S. Analysis of the neuromuscular activity during rising from a chair in water and on dry land. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2013, 23, 1446–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonato, P.; Roy, S.H.; Knaflitz, M.; De Luca, C.J. Time-frequency parameters of the surface myoelectric signal for assessing muscle fatigue during cyclic dynamic contractions. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, D.; Pozzo, M.; Merlo, E.; Bottin, A.; Merletti, R. Assessment of average muscle fiber conduction velocity from surface EMG signals during fatiguing dynamic contractions. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mulla, M.R.; Sepulveda, F.; Colley, M. A review of non-invasive techniques to detect and predict localised muscle fatigue. Sensors 2011, 11, 3545–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Mao, J.F.; Wei, C.F.; Fu, S.; Law, R.; Ding, L.; Yu, B.T.; Jia, B.; Yang, C.H. Hybrid BF–PSO and fuzzy support vector machine for diagnosis of fatigue status using EMG signal features. Neurocomputing 2016, 173, 483–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merletti, R.; Rainoldi, A.; Farina, D. Surface electromyography for noninvasive characterization of muscle. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2001, 29, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwarts, M.J.; Bleijenberg, G.; van Engelen, B.G.M. Clinical neurophysiology of fatigue. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluger, B.M.; Krupp, L.B.; Enoka, R.M. Fatigue and fatigability in neurologic illnesses: Proposal for a unified taxonomy. Neurology 2013, 80, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, S.; Dures, E.; Almeida, C. Measures of fatigue: Bristol Rheumatoid Arthritis Fatigue Multi-Dimensional Questionnaire (BRAF MDQ), Bristol Rheumatoid Arthritis Fatigue Numerical Rating Scales (BRAF NRS) for severity, effect, and coping, Chalder Fatigue Questionnaire (CFQ), Checklist Individual Strength (CIS20R and CIS8R), Fatigue Severity Scale (FSS), Functional Assessment Chronic Illness Therapy (Fatigue) (FACIT-F), Multi-Dimensional Assessment of Fatigue (MAF), Multi-Dimensional Fatigue Inventory (MFI), Pediatric Quality Of Life (PedsQL) Multi-Dimensional Fatigue Scale, Profile of Fatigue (ProF), Short Form 36 Vitality Subscale (SF-36 VT), and Visual Analog Scales (VAS). Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2011, 63, S263–S286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Viitasalo, J.H.; Komi, P.V. Signal characteristics of EMG during fatigue. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1977, 37, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H. Functional characteristics of human skeletal muscle revealed by spectral analysis of the surface electromyogram. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1982, 22, 459–516. [Google Scholar]
- Petrofsky, J.S.; Lind, A.R. The influence of temperature on the amplitude and frequency components of the EMG during brief and sustained isometric contractions. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 1980, 44, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinyomark, A.; Thongpanja, S.; Hu, H.; Phukpattaranont, P.; Limsakul, C. The Usefulness of Mean and Median Frequencies in Electromyography Analysis. In Computational Intelligence in Electromyography Analysis—A Perspective on Current Applications and Future Challenges; Intech: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-953-51-0805-4. [Google Scholar]
- Roldán-Jiménez, C.; Bennett, P.; Cuesta-Vargas, A.I. Muscular Activity and Fatigue in Lower-Limb and Trunk Muscles during Different Sit-To-Stand Tests. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, J. Electrodiagnosis in Diseases of Nerve and Muscle: Principles and Practice; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-0-19-973868-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lucci, S.; Cortes, N.; Van Lunen, B.; Ringleb, S.; Onate, J. Knee and hip sagittal and transverse plane changes after two fatigue protocols. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2011, 14, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, N.; Quammen, D.; Lucci, S.; Greska, E.; Onate, J. A functional agility short-term fatigue protocol changes lower extremity mechanics. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karg, M.; Venture, G.; Hoey, J.; Kulić, D. Human movement analysis as a measure for fatigue: A hidden Markov-based approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, N.; Onate, J.; Morrison, S. Differential effects of fatigue on movement variability. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonato, P.; Cheng, M.S.; Gonzalez-Cueto, J.; Leardini, A.; O’Connor, J.; Roy, S.H. EMG-based measures of fatigue during a repetitive squat exercise. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2001, 20, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijlstra, W.; Bisseling, R.W.; Schlumbohm, S.; Baldus, H. A body-fixed-sensor-based analysis of power during sit-to-stand movements. Gait Posture 2010, 31, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Medina, L.; González-Badillo, J.J. Velocity loss as an indicator of neuromuscular fatigue during resistance training. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.; Bichler, S.; Fiedler, M.; Alt, W. Fatigue detection in strength training using three-dimensional accelerometry and principal component analysis. Sports Biomech. 2016, 15, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, U.; Klenk, J.; Becker, C. Assessment of fatigability of older women during sit-to-stand performance. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 28, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, M.; Merletti, R.; Rainoldi, A. Atlas of Muscle Innervation Zones: Understanding Surface Electromyography and Its Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; ISBN 978-88-470-2463-2. [Google Scholar]
- Perotto, A.O.; Delagi, E.F.; Lanzetti, J.; Morrison, D. Anatomical Guide for the Electromyographer: The Limbs and Trunk, 6th ed.; Charles C Thomas Publisher: Springfield, IL, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-398-07577-4. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, L.; Worthingham, C. Muscle Testing: Techniques of Manual Examination; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-0-7216-4305-2. [Google Scholar]
- Galán-Mercant, A.; Barón-López, F.J.; Labajos-Manzanares, M.T.; Cuesta-Vargas, A.I. Reliability and criterion-related validity with a smartphone used in timed-up-and-go test. Biomed. Eng. Online 2014, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicharro, J.L.; Vaquero, A.F. Fisiologia del Ejercicio; Ed. Médica Panamericana: Madrid, Spain, 2006; ISBN 978-950-06-8247-3. [Google Scholar]
- De Luca, C.J.; Sabbahi, M.A.; Stulen, F.B.; Bilotto, G. Some properties of median nerve frequency of the myoelectric signal during localized muscular fatigue. Biochem. Excercise Hum. Kinet. Inc 1982, 13, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, G.T.; Fujiwara, T. The relationship between EMG median frequency and low frequency band amplitude changes at different levels of muscle capacity. Clin. Biomech. (Bristol Avon) 2002, 17, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.J.; Sabbahi, M.A.; Roy, S.H. Median frequency of the myoelectric signal. Effects of hand dominance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1986, 55, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma’as, M.D.F.; Azmi, A.Z.U. Real-time muscle fatigue monitoring based on median frequency of electromyography signal. In Proceedings of the 2017 5th International Conference on Instrumentation, Control, and Automation (ICA), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 9–11 August 2017; pp. 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, S.; Vankov, E.R.; Yeh, H.J.; Guindani, M.; Vannucci, M.; Haneef, Z.; Stern, J.M. Temporal and spectral characteristics of dynamic functional connectivity between resting-state networks reveal information beyond static connectivity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayrulu-Erdem, B.; Barshan, B. Leg motion classification with artificial neural networks using wavelet-based features of gyroscope signals. Sensors (Basel) 2011, 11, 1721–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruthers, E.J.; Thompson, J.A.; Chaudhari, A.M.; Schmitt, L.C.; Best, T.M.; Saul, K.R.; Siston, R.A. Muscle Forces and Their Contributions to Vertical and Horizontal Acceleration of the Center of Mass during Sit-to-Stand Transfer in Young, Healthy Adults. J. Appl. Biomech. 2016, 32, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari Oskoei, M.; Hu, H.; Gan, J.Q. Manifestation of fatigue in myoelectric signals of dynamic contractions produced during playing PC games. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2008, 2008, 315–318. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mulla, M.R.; Sepulveda, F.; Colley, M.; Al-Mulla, F. Statistical Class Separation Using sEMG Features towards Automated Muscle Fatigue Detection and Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Tianjin, China, 17–19 October 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Basmajian, J.V.; De Luca, C.J. Muscles Alive: Their Functions Revealed by Electromyography, 5 Sub ed.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, ML, USA, 1985; ISBN 978-0-683-00414-4. [Google Scholar]
- Voge, K.; Dingwell, J. Relative timing of changes in muscle fatigue and movement coordination during a repetitive one-hand lifting task. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37439), Cancun, Mexico, 17–21 September 2003; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Behm, D.G. Force maintenance with submaximal fatiguing contractions. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 29, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, D.; Fattorini, L.; Felici, F.; Filligoi, G. Nonlinear surface EMG analysis to detect changes of motor unit conduction velocity and synchronization. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 93, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulart, F.R.; Valls-Solé, J. Patterned electromyographic activity in the sit-to-stand movement. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 110, 1634–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehail, P.; Bestaven, E.; Muller, F.; Mallet, A.; Robert, B.; Bourdel-Marchasson, I.; Petit, J. Kinematic and electromyographic analysis of rising from a chair during a “Sit-to-Walk” task in elderly subjects: Role of strength. Clin. Biomech. (Bristol Avon) 2007, 22, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donatelli, R. Sports-Specific Rehabilitation; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; ISBN 978-0-443-06642-9. [Google Scholar]
- Yiou, E.; Heugas, A.M.; Mezaour, M.; Le Bozec, S. Effect of lower limb muscle fatigue induced by high-level isometric contractions on postural maintenance and postural adjustments associated with bilateral forward-reach task. Gait Posture 2009, 29, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, S.K. Sex Differences in Human Fatigability: Mechanisms and Insight to Physiological Responses. Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 2014, 210, 768–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudry, S.; Klass, M.; Pasquet, B.; Duchateau, J. Age-related fatigability of the ankle dorsiflexor muscles during concentric and eccentric contractions. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibella, F.; Galli, M.; Romei, M.; Montesano, A.; Crivellini, M. Biomechanical analysis of sit-to-stand movement in normal and obese subjects. Clin. Biomech. (Bristol Avon) 2003, 18, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumway-Cook, A.; Woollacott, M.H. Motor Control: Translating Research into Clinical Practice, 4th ed.; Lippincott Raven: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-60831-018-0. [Google Scholar]
- Cuesta-Vargas, A.; Buchan, J.; Pajares, B.; Alba, E.; Roldan-Jiménez, C. Cancer-related fatigue stratification system based on patient-reported outcomes and objective outcomes: A cancer-related fatigue ambulatory index. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta-Vargas, A.; Luciano, J.V.; Peñarrubia-María, M.T.; García-Campayo, J.; Fernández-Vergel, R.; Arroyo-Morales, M.; Serrano-Blanco, A. FibroQoL Study Group Clinical dimensions of fibromyalgia symptoms and development of a combined index of severity: The CODI index. Qual. Life Res. 2013, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Muscles | Real Activation (µV) | Average Activation (µV) | MVC Percentage (%) | Muscle Involvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM | 288 | 128 (24.04) | 42.88 (2.20) | 8.5 (0.70) |
| BF | 474 | 148 (41.01) | 28.05 (4.47) | 9.5 (2.12) |
| VM | 762 | 212.50 (10.60) | 27.46 (0.60) | 14 (1.41) |
| AR | 145 | 106.50 (10.60) | 83.62 (14.38) | 7 (1.41) |
| ES | 81 | 116.50 (7.77) | 14.80 (0.99) | 7.5 (0.70) |
| RF | 493 | 269 (5.65) | 52.53 (2.86) | 17.5 (2.12) |
| SO | 492 | 263 (100.4) | 49.08 (6.18) | 15.5 (3.53) |
| TA | 1098 | 298 (14.14) | 28.64 (2.12) | 21 (0.0) |
| Axis. | Mean (SD) |
|---|---|
| X | 3.88 (0.39) |
| Y | 25.79 (4.16) |
| Z | 20.72 (0.28) |
| Nrv | 28.04 (3.67) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roldán Jiménez, C.; Bennett, P.; Ortiz García, A.; Cuesta Vargas, A.I. Fatigue Detection during Sit-To-Stand Test Based on Surface Electromyography and Acceleration: A Case Study. Sensors 2019, 19, 4202. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194202
Roldán Jiménez C, Bennett P, Ortiz García A, Cuesta Vargas AI. Fatigue Detection during Sit-To-Stand Test Based on Surface Electromyography and Acceleration: A Case Study. Sensors. 2019; 19(19):4202. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194202
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoldán Jiménez, Cristina, Paul Bennett, Andrés Ortiz García, and Antonio I. Cuesta Vargas. 2019. "Fatigue Detection during Sit-To-Stand Test Based on Surface Electromyography and Acceleration: A Case Study" Sensors 19, no. 19: 4202. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194202
APA StyleRoldán Jiménez, C., Bennett, P., Ortiz García, A., & Cuesta Vargas, A. I. (2019). Fatigue Detection during Sit-To-Stand Test Based on Surface Electromyography and Acceleration: A Case Study. Sensors, 19(19), 4202. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194202







