Parameter Estimation Based on Sigmoid Transform in Wideband Bistatic MIMO Radar System under Impulsive Noise Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
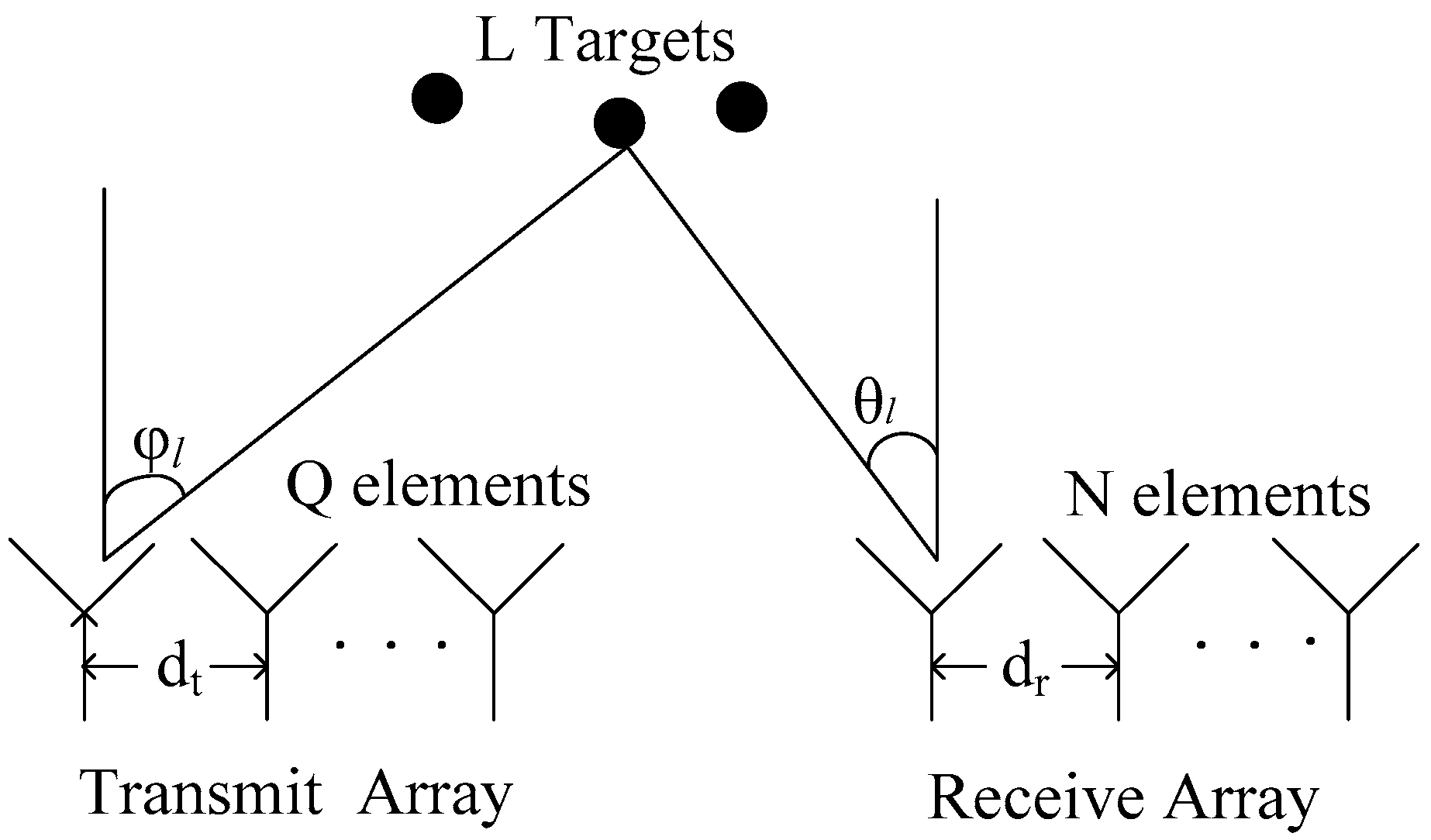
2. Signal Model and Noise Model
2.1. Signal Model and Bandpass Matched Filter
2.1.1. Signal Model
2.1.2. Bandpass Matched Filter
2.2. Distribution Noise Model
3. Sigmoid Wideband Ambiguity Function and Sigmoid Correlation
3.1. Wideband Ambiguity Function
3.2. Sigmoid Transform
3.3. Sigmoid Wideband Ambiguity Function
3.4. Sigmoid Correlation
3.5. Sigmoid-MUSIC Algorithm
- Step 1.
- Compute Sigmoid correlation matrices of the matrix , according to Equation (21).
- Step 2.
- Execute singular value decomposition (SVD) on , where the column vector describes the eigenvectors spanning the noise subspace.
- Step 3.
- Compute the corresponding Sigmoid-MUSIC spectrum as
- Step 4.
- The estimator of can be obtained by searching for peaks of the Sigmoid-MUSIC spectrum .
4. Joint Estimation Parameter Based on Sigmoid-WBAF and Sigmoid-MUSIC
4.1. Estimation of TD and DS Based on Sigmoid-WBAF
- Step 1.
- Present the extracted signal .
- Step 2.
- Compute the Sigmoid-WBAF function from Equation (25).
- Step 3.
- Search for the peaks of and obtain the locations of these peaks , for .
- Step 4.
- Estimate the DS and TD according to Equation (26).
4.2. Estimation of DOD and DOA Based on Sigmoid-MUSIC
- Step 1.
- Construct two matrices and .
- Step 2.
- Substitute the time average with the statistic average, two Sigmoid correlation matrices and are then constructed according to Equation (21).
- Step 3.
- Apply the singular value decomposition (SVD) to and , where the column vectors and are formed from the eigenvectors spanning the noise subspace.
- Step 4.
- Compute the corresponding Sigmoid-MUSIC spectra and from Equations (36) and (37).
- Step 5.
- The DOA and DOD estimates can be obtained by identifying the peaks of the spatial spectra and .
5. Analysis of Sigmoid-WBAF and Sigmoid-MUSIC
5.1. Boundness of Sigmoid-WBAF
5.2. Feasibility Analysis of Sigmoid-WBAF
5.3. The Cramer–Rao Bound
5.4. Complexity Analysis
5.4.1. Doppler Stretch and Time Delay
5.4.2. DOD and DOA
6. Simulation Results
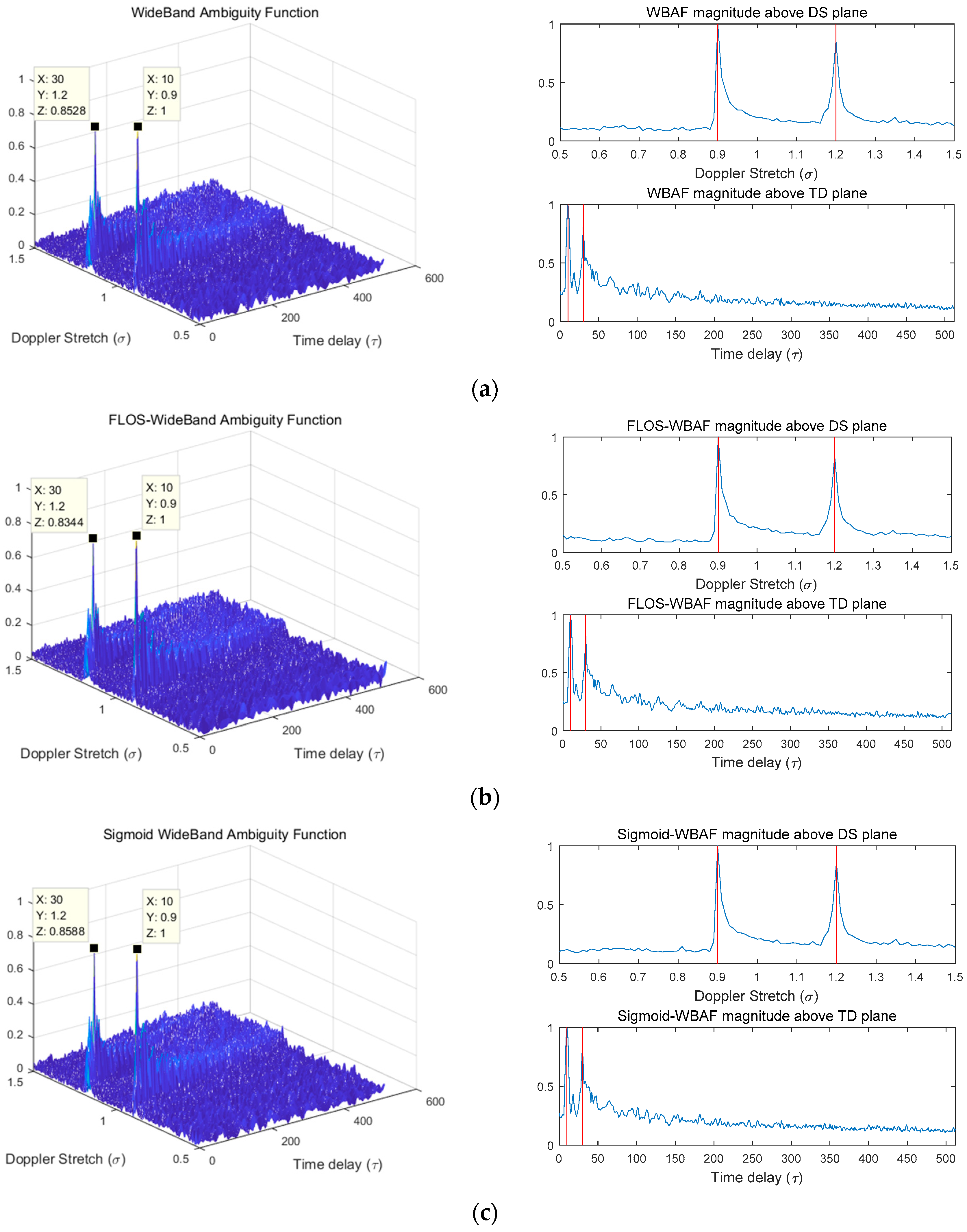
6.1. Simulation 1: Spectra of WBAF, FLOS-WBAF, and Sigmoid-WBAF for a Single Estimation for Two Targets
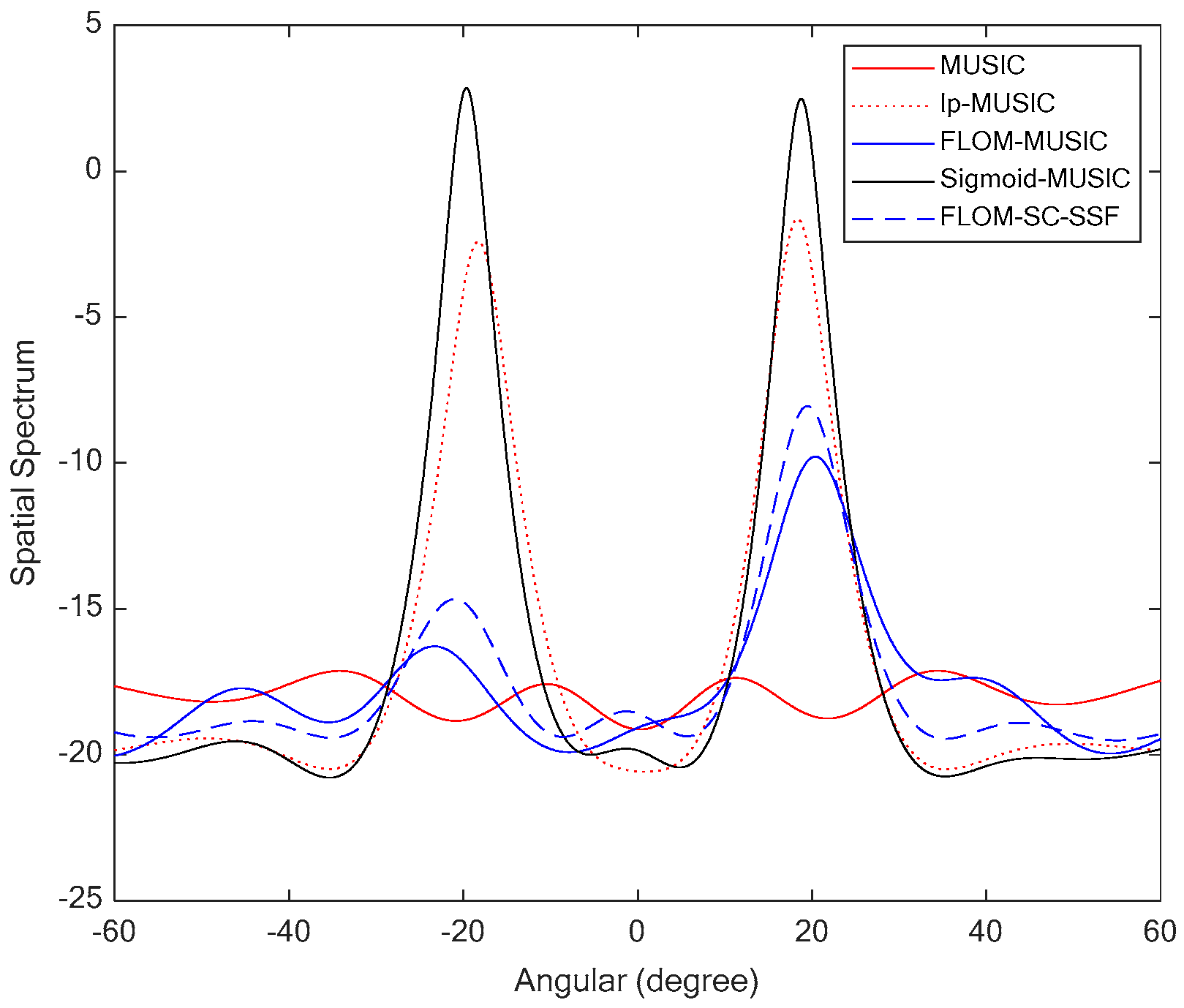
6.2. Simulation 2: Spectrum Performances of the Four Algorithms
6.3. Simulation 3: Generalized Signal-to-Noise Ratio (GSNR)
6.4. Simulation 4: Characteristic Exponent
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Stoica, P. MIMO radar with colocated antennas: Review of some recent work. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2007, 24, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.; So, H.; Huang, L.; Huang, L. Parameter estimation and identifiability in bistatic multiple-input multiple-output radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Stoica, P. MIMO Radar Signal Processing; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, K.; Chung, Y.; Yang, H.; Kim, J.; Chung, W. Reduced-dimension DOD and DOA estimation through projection filtering in bistatic MIMO radar with jammer discrimination. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunhe, C. Joint estimation of angle and Doppler frequency for bistatic MIMO radar. Electron. Lett. 2010, 46, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Wang, W.; Yin, Q. DOD and DOA estimation in bistatic non-uniform multiple-input multiple-output radar systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2012, 16, 1796–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wong, K. Joint DOD and DOA estimation for bistatic MIMO radar in unknown correlated noise. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 5113–5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencheikh, M.; Wang, Y. Joint DOD-DOA estimation using combined ESPRIT-MUSIC approach in MIMO radar. Electron. Lett. 2010, 46, 1081–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Jiang, D.F.; Zhang, X.F. DOA estimation based on combined unitary ESPRIT for coprime MIMO radar. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Liu, Z. Multi-target localization based on polynomial rooting for bistatic MIMO radar. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2010, 32, 2197–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.F.; Wang, K.R. Joint estimation of Doppler and multipath time delay of wideband echoes for LFM pulse radar based on cyclic correlation. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2008, 30, 1736–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Kon, M.W.; Luo, Z.Q. The estimation of time delay and Doppler stretch of wideband signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1995, 43, 904–916. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Goh, J.T. Ambiguity-function-based techniques to estimate DOA of broadband chirp signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 1826–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Kailath, T. Direction-of-arrival estimation via exploitation of cyclostationary a combination of temporal and spatial processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1992, 40, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, G.H.; Qiu, T.S.; Lan, T. DOA estimation algorithm of wideband cyclostationary signals in impulsive noise environment. J. Data Acquis. Process. 2012, 27, 399–403. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.W.; Zhao, J.W. Wideband MVDR beamforming for acoustic vector sensor linear array. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2004, 151, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.S.; Kaplan, L.M.; McClellan, J.H. Tops: New DOA estimator for wideband signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 1977–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qiu, T. A novel method for parameter estimation based on wide-band ambiguity function in bistatic MIMO radar system in impulsive noise environment. Acta Electron. Sin. 2016, 44, 2842–2848. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shao, M.; Nikias, C.L. Signal processing with fractional lower order moments: Stable processes and their applications. Proc. IEEE 1993, 81, 986–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakalides, P.; Nikias, C.L. The robust covariation-based MUSIC (ROC-MUSIC) algorithm for bearing estimation in impulsive noise environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1996, 44, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Arye, N. MUSIC maximum likelihood, and cramer-rao bound. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 720–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Mendel, J.M. A subspace-based direction finding algorithm using fractional lower order statistics. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2001, 49, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, J.G.; Paredes, J.L.; Arce, G.R. Zero-order statistics: A mathematical framework for the processing and characterization of very impulsive signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 3839–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.J.; So, H.C.; Huang, L. lp-MUSIC: Robust direction-of-arrival estimator for impulsive noise environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 4296–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qiu, T.S.; Shi, X.F. Parameter estimation based on fractional power spectrum density in bistatic MIMO radar system under impulsive noise environment. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 35, 3266–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, R.X.; Lin, B.; Sun, F. DOA estimation based on sparse representation of the fractional lower order statistics in impulsive noise. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2017, 99, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qiu, T.S. Parameter dynamic estimation in near-field bistatic MIMO radar system. J. Commun. 2015, 10, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.J.; Tao, R.; Zhang, F. Multiple-parameter discrete fractional transform and its applications. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 3402–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Younan, N.H.; Shi, X. A novel parameter estimation method based on a tuneable sigmoid in alpha-stable distribution noise environments. Sensors 2018, 18, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Qiu, T. A novel phase parameter estimation method of quadratic FM signal based on Sigmoid fractional ambiguity function in impulsive noise environment. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2018, 93, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swick, D.A. An Ambiguity Function Independent of Assumption about Bandwidth and Carrier Frequency; NRL Report 6471; Naval Research Laboratory: Washington DC, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Swick, D.A. A Review of Wide-Band Ambiguity Function; NRL Report 6994; Naval Research Laboratory: Washington, DC, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Brodersen, K.H.; Daunizeau, J.; Mathys, C.; Chumbley, J.R.; Buhmann, J.M.; Stephan, K.E. Variational Bayesian Mixed-Effects Inference for Classification Studies. Neuroimage 2013, 76, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Meng, J. Ship classification in SAR image by joint feature and classifier selection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, H. Non-linear transform-based robust adaptive latency change estimation of evoked potentials. Meth. Inf. Med 2002, 41, 331–336. [Google Scholar]
- Gershman, A.B.; Pesavento, M.; Amin, M.G. Estimating parameters of multiple wideband polynomial-phase sources in sensor arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2001, 49, 2924–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swindlehurst, A.L.; Stoica, P. Maximum likelihood methods in radar array signal processing. IEEE Proc. 1998, 86, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkerman, I.; Tabrikian, J. Target detection and localization using MIMO radars and sonars. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 3873–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Guo, F.; Feng, D. Low-complexity methods for joint delay and Doppler estimation of unknown wideband signals. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2018, 12, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Duan, F.; Yan, H.; Hua, B.; Ma, S.; Deng, C.; Bu, L.; Sun, Z.; Li, C. An sufficient algorithm for WBAF estimation absed on linear interpolation and its estimation error. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 142, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubsamen, M.; Gershman, A. Direction-of-arrival estimation for nonuniform sensor arrays: Form manifold separation to Fourier domain MUSIC methods. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Qiu, T.S.; Luan, S.Y. Robust joint estimation for time delay and Doppler frequency shift based on generalized sigmoid cyclic cross-ambiguity function. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 721–728. [Google Scholar]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Younan, N.H.; Shi, X. Parameter Estimation Based on Sigmoid Transform in Wideband Bistatic MIMO Radar System under Impulsive Noise Environment. Sensors 2019, 19, 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020232
Li L, Younan NH, Shi X. Parameter Estimation Based on Sigmoid Transform in Wideband Bistatic MIMO Radar System under Impulsive Noise Environment. Sensors. 2019; 19(2):232. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020232
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Li, Nicolas H. Younan, and Xiaofei Shi. 2019. "Parameter Estimation Based on Sigmoid Transform in Wideband Bistatic MIMO Radar System under Impulsive Noise Environment" Sensors 19, no. 2: 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020232
APA StyleLi, L., Younan, N. H., & Shi, X. (2019). Parameter Estimation Based on Sigmoid Transform in Wideband Bistatic MIMO Radar System under Impulsive Noise Environment. Sensors, 19(2), 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020232




