A Mobile Anchor Node Assisted RSSI Localization Scheme in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To improve location accuracy, we design an SVR based interpolation method to estimate the projection of sensor nodes on the linear trajectory of the mobile anchor node. This method increases the accuracy of the nonlinear regression model of noisy measured data and synchronously decreases the estimation error caused by the discreteness of measured data.
- To shorten location time, we develop a curve matching method to obtain the perpendicular distance from sensor nodes to the linear trajectory of the mobile anchor node. Compared with existing schemes, the proposed scheme only needs one trajectory of the mobile anchor node to locate sensor nodes, which significantly shortens the location time.
2. Related Works
2.1. Overview of Localization Approaches
2.2. Localization Approaches Related to the Mobile Anchor Node
2.3. Localization Approaches Jointly Using the RSSI and the Mobile Anchor Node
3. Detailed Description of the Proposed Localization Scheme
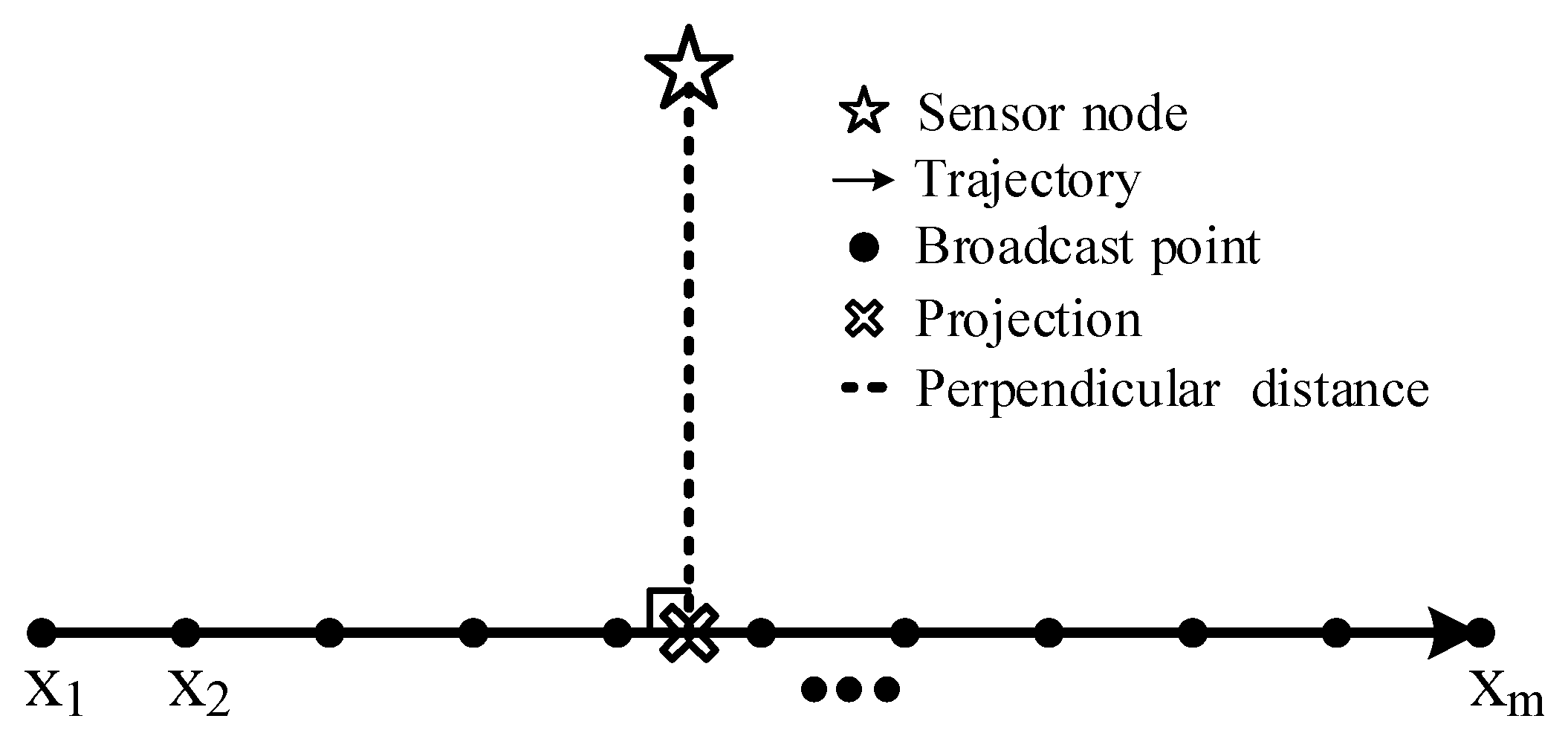
3.1. Network System Architecture, Mobile Anchor Node Trajectory, and Obtaining a Set of Measured RSSI Values
3.1.1. Network System Architecture
3.1.2. The Trajectory of the Mobile Anchor Node
3.1.3. Obtaining a Set of Measured RSSI Values
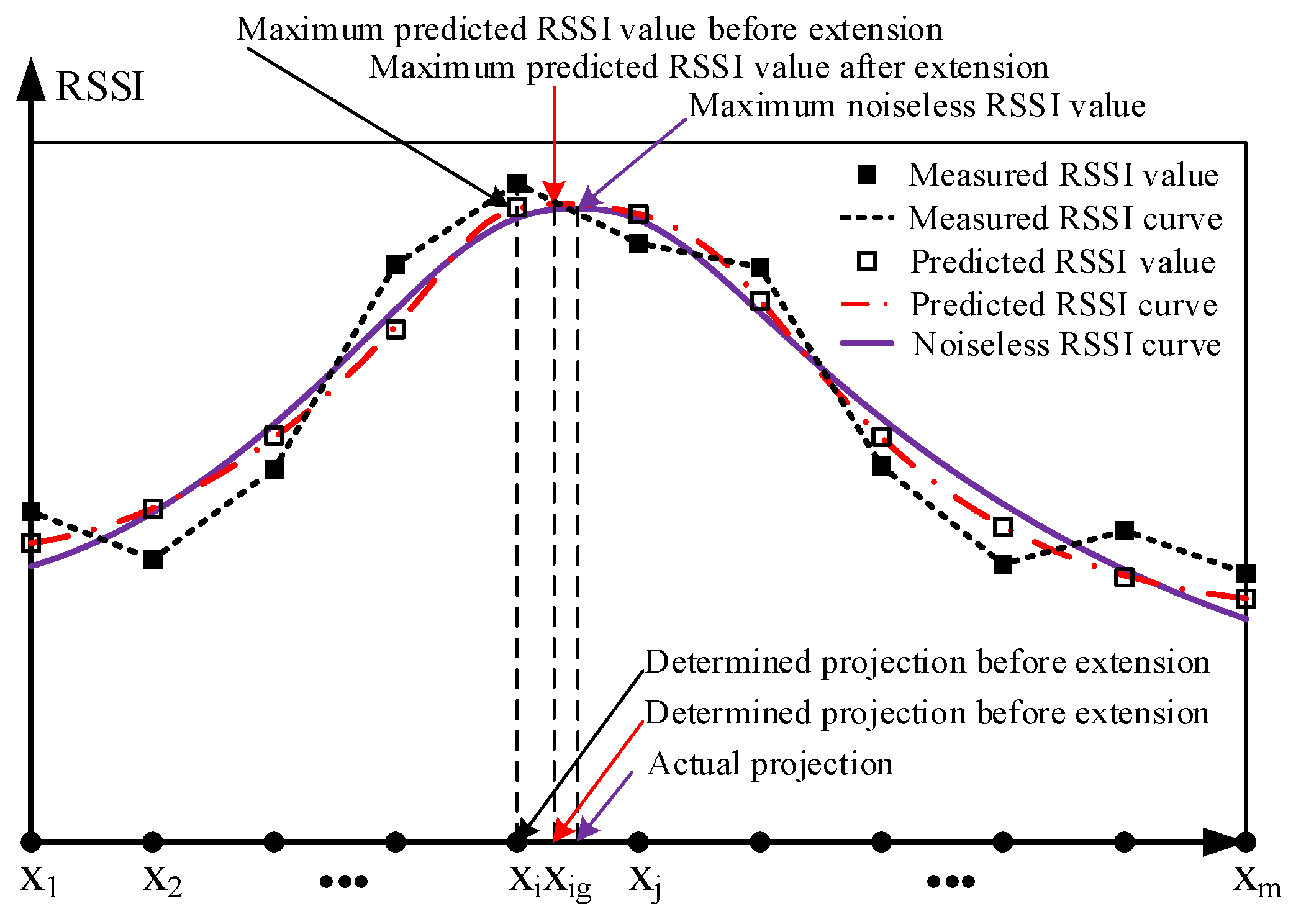
3.2. Determining the Projection of a Node on the Trajectory
3.2.1. Modeling the Nonlinear Relationship Using SVR
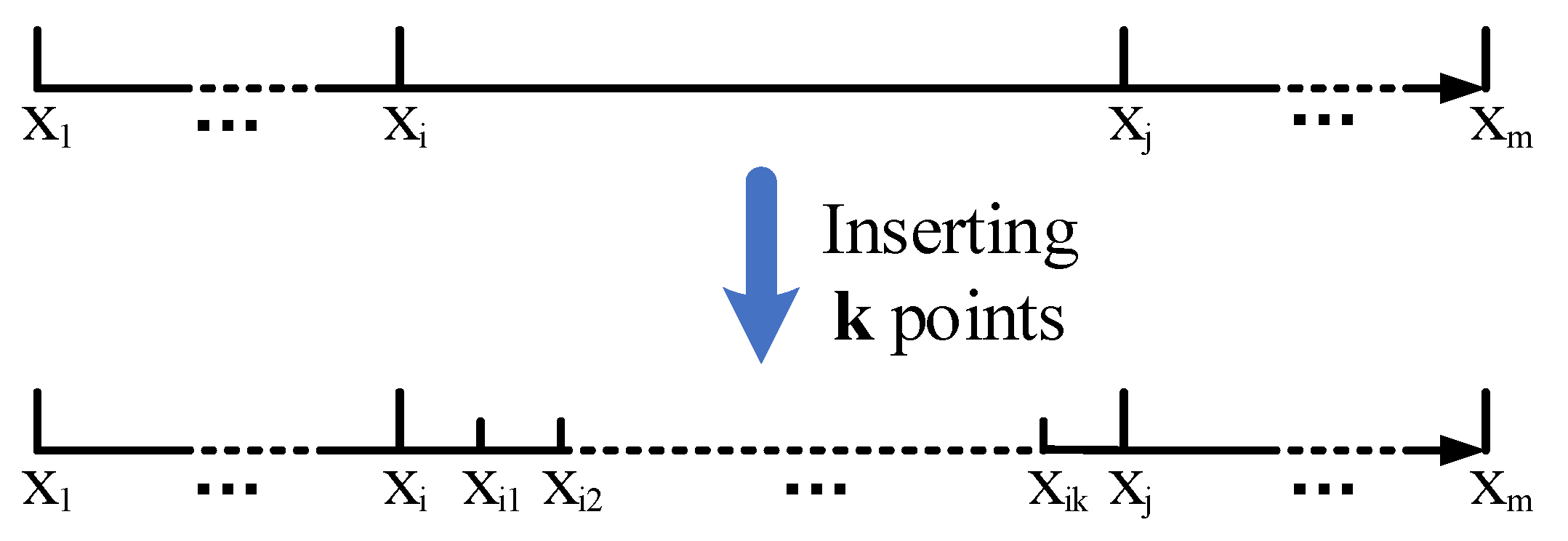
3.2.2. Extending Vectors
3.2.3. Determining the Projection
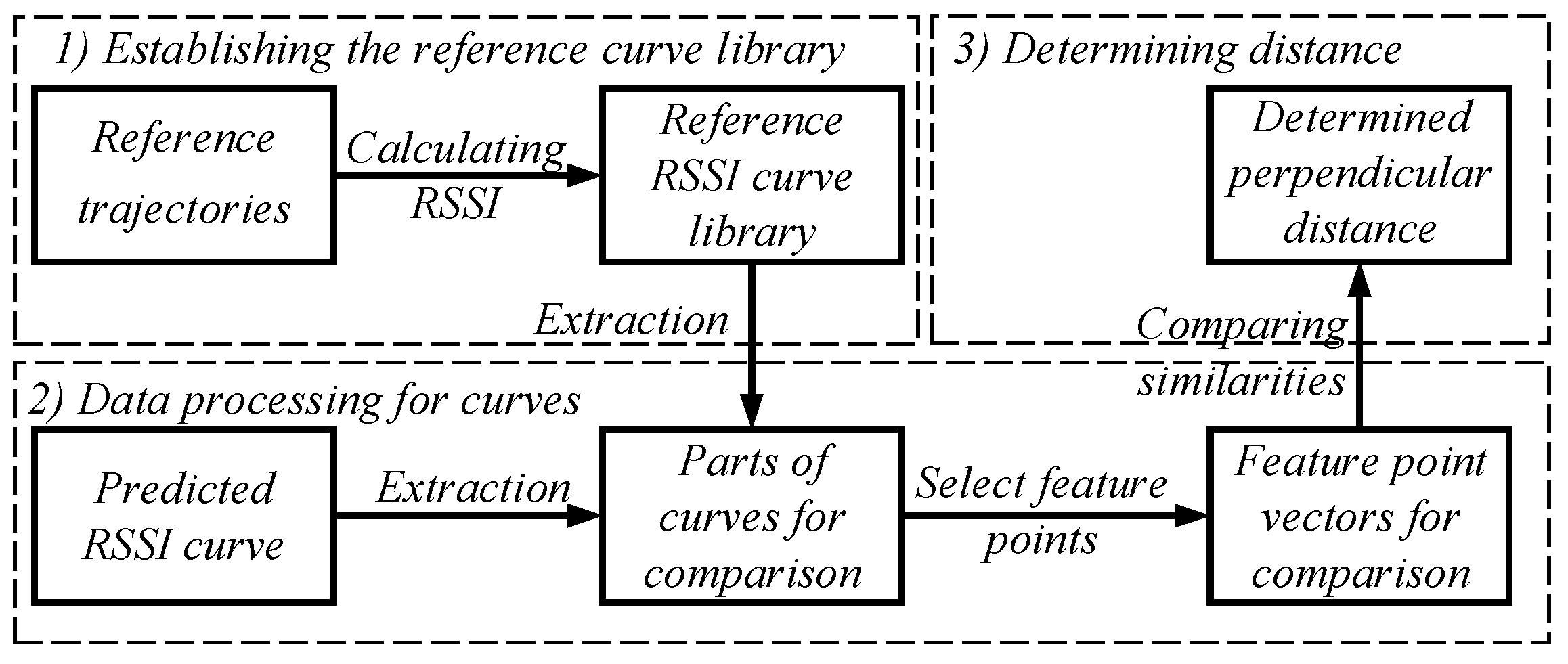
3.3. Determining the Perpendicular Distance from a Node to the Trajectory
3.3.1. Establishing the Reference RSSI Curve Library
3.3.2. Data Processing for Curves Used for Comparison
3.3.3. Determining the Perpendicular Distance by Comparing Curve Similarities
3.4. Calculating the Node Location
3.4.1. Transforming 3D Localization into 2D Localization
3.4.2. The Calculation Process of Localization
4. Simulation
4.1. Simulation Parameter Setting
4.2. Simulation Results and Discussion
4.2.1. The Network System Architecture in the Simulation
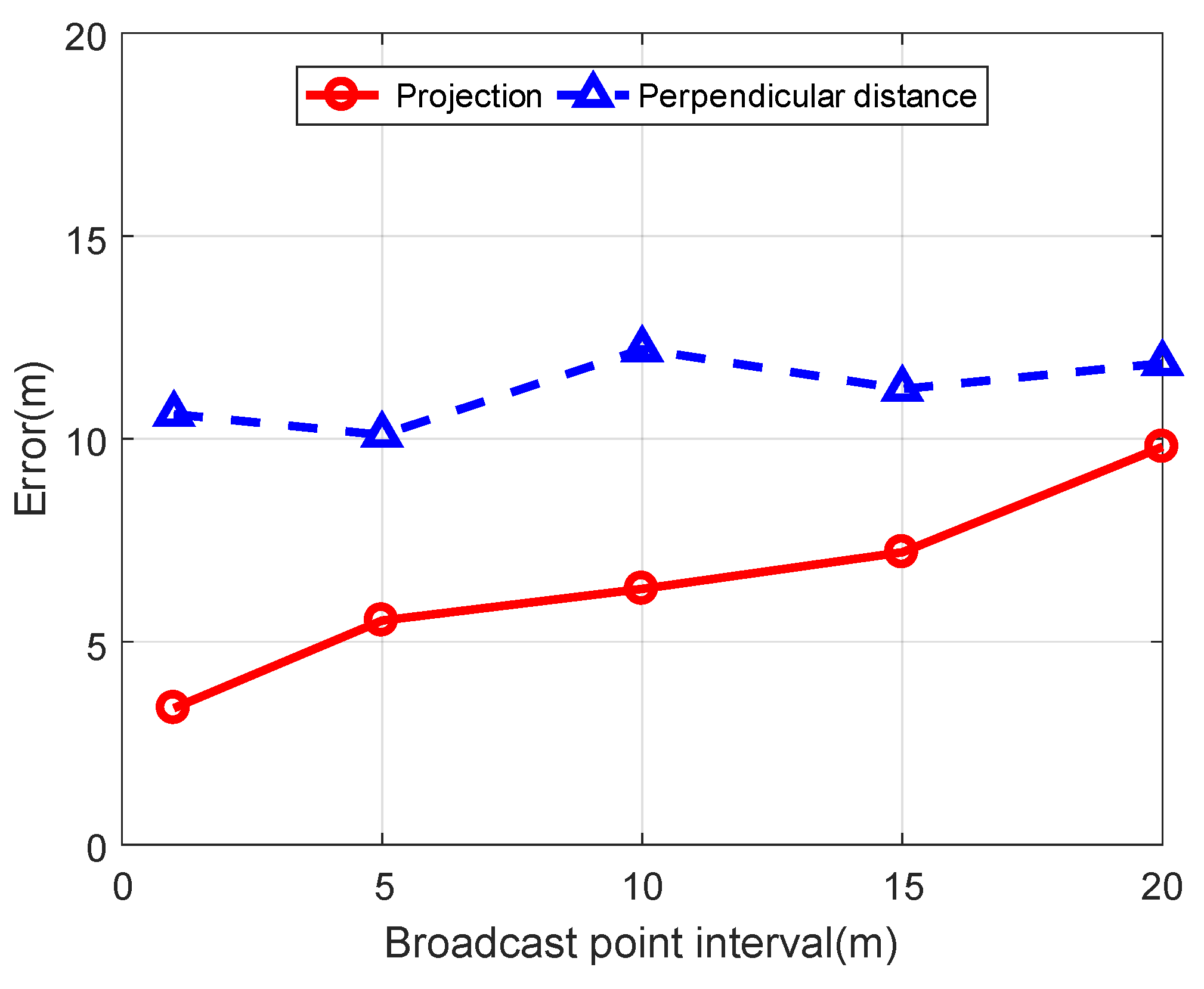
4.2.2. The Error of a Node Projection on the Trajectory
4.2.3. The Error of the Perpendicular Distance from the Node to the Trajectory
4.2.4. The Error of the Node Location
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghoreyshi, S.M.; Shahrabi, A.; Boutaleb, T. Void-handling techniques for routing protocols in underwater sensor networks: Survey and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 800–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, Q.; Guan, X. An adaptive sampling algorithm for target tracking in underwater wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 68324–68336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felemban, E.; Shaikh, F.K.; Qureshi, U.M.; Sheikh, A.A.; Qaisar, S.B. Underwater Sensor Network Applications: A Comprehensive Survey. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2015, 11, 896832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Noh, Y.; Kim, K. RAR: Real-time Acoustic Ranging in Underwater Sensor Networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 2328–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol-Kantarci, M.; Mouftah, H.; Oktug, S. A survey of architectures and localization techniques for underwater acoustic sensor networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 13, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Xu, Z.; Wan, Y. Consensus estimation-based target localization in underwater acoustic sensor networks. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2017, 27, 1607–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, X. Asynchronous Localization with Mobility Prediction for Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 67, 2543–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, R.; Boukerche, A.; Vieira, L.; Loureiro, A.A.F. Geographic and opportunistic routing for underwater sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2016, 65, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Leus, G. RSS-based sensor localization in underwater acoustic sensor networks. In Proceedings of the ICASSP, Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 3906–3910. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Guizani, M.; Zhang, W. A Disaster Management-Oriented Path Planning for Mobile Anchor Node-Based Localization in Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Ghosal, A. A survey on mobility-assisted localization techniques in wireless sensor networks. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 60, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, J.; Yang, X.; Guizani, M. Mobile anchor nodes path planning algorithms using network-density-based clustering in wireless sensor networks. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 85, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Guo, Y.; Hong, F.; Yang, X.; He, F.; Liu, Y. Perpendicular Intersection: Locating Wireless Sensors With Mobile Beacon. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2010, 59, 3501–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pratap, K.S.; Wu, E.H.K.; Jagruti, S. DuRT: Dual RSSI Trend Based Localization for Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3115–3123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Jiang, J.; Leus, G. RSSI Based Localization with Mobile Anchor for Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the GSKI 2018, Wuhan, China, 23–29 September 2018; pp. 176–187. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Fan, L.; Wu, S.; Yan, L. Research on Localization Algorithms Based on Acoustic Communication for Underwater Sensor Networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, C.; Duong, T.Q. A survey on mobile anchor node assisted localization in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 2220–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, V.; Seah, W. An area localization scheme for underwater sensor networks. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2006, Singapore, 16–19 May 2006; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Cui, J.-H.; Zhou, S. Efficient Localization for Large-Scale Underwater Sensor Networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2010, 3, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Jiang, J.; Shu, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F. Localization algorithms of Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks: A survey. Ad Hoc Netw. 2012, 12, 2026–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvenc, I.; Chong, C.-C. A survey on TOA based wireless localization and NLOS mitigation techniques. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2009, 11, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Molisch, A.F.; Salmi, J. Accurate passive location estimation using TOA measurements. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2011, 11, 2182–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zheng, L.; Wu, J.; Zhuang, Z. Joint Synchronization and Localization for Underwater Sensor Networks Considering Stratification Effect. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 26932–26943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Ansari, N. NLOS error mitigation for TOA-based localization via convex relaxation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 4119–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Jackson, D.R.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Z.; Williams, J.T. A TDOA Localization Method for Non-Line-of-Sight Scenarios. IEEE Trans. Antenn. Propag. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.-K.; Ono, N. Closed-form and near closed-form solutions for TDOA-based joint source and sensor localization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 1207–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; So, A.M.-C.; Li, Y. Robust convex approximation methods for TDOA-based localization under NLOS conditions. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 3281–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wu, H.-C. Novel robust Direction-of-Arrival-Based source localization algorithm for wideband signals. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2012, 11, 3850–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yin, Q.; Chen, H.; Gao, F.; Ansari, N. Distributed angle estimation for localization in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ho, D. Unified Near-Field and Far-Field Localization for AOA and Hybrid AOA-TDOA Positionings. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 2017, 17, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.N.; Shin, Y. An Efficient RSS Localization for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Leus, G. Robust differential received signal strength-based localization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 3261–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, R.; Yue, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, C.; Fang, S.H. FaceME: Face-to-Machine Proximity Estimation Based on RSSI Difference for Mobile Industrial Human–Machine Interaction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 2018, 14, 3547–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.P.; Gabor, A.F.; Eu, Z.A.; Seah, W.K. A wide coverage positioning system (WPS) for underwater localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, Cape Town, South Africa, 23–27 May 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, A. GPS-less localization protocol for underwater acoustic networks. In Proceedings of the 15th IFIP International Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications Networks, Surabaya, Indonesia, 5–7 May 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, D.; Schurgers, C. Motion-aware self-localization for underwater networks. In Proceedings of the WuWNeT ’08, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15 September 2008; pp. 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Teymorian, A.Y.; Cheng, W.; Ma, L.; Cheng, X.; Lu, X.; Lu, Z. 3D underwater sensor network localization. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 2009, 8, 1610–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, M.T.; Akan, O.B. A three dimensional localization algorithm for underwater acoustic sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2009, 8, 4457–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, M.; Vieira, L.F.M.; Gerla, M. Localization with Dive’N’Rise (DNR) Beacons for Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Underwater Networks, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14 September 2007; pp. 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Xu, T.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Q. Received signal strength-based underwater acoustic localization considering stratification effect. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2016, Shanghai, China, 10–13 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ban, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, P.; Xiong, J.; Wang, Q. Ship Track Regression Based on Support Vector Machine. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18836–18846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantz, B. Black Box Methods—Neural Networks and Support Vector Machines. In Machine Learning with R; Jones, J., Sheikh, A., Eds.; Packt Publishing: Birmingham, UK, 2013; pp. 205–242. [Google Scholar]











| Notation | Definition |
|---|---|
| L | The length of the trajectory |
| The interval between adjacent broadcast points | |
| m | The number of broadcast points on the trajectory |
| The x-coordinate of the ith broadcast point | |
| The location vector consisting of x-coordinates of all broadcast points | |
| The noiseless RSSI value of the message from the ith broadcast point | |
| The noiseless RSSI value vector | |
| The measured RSSI value of the message from the ith broadcast point | |
| The measured RSSI value vector | |
| The predicted RSSI value of the message from the ith broadcast point | |
| The predicted RSSI value vector | |
| The x-coordinate of the kth point inserted after the ith broadcast point | |
| The extended location vector | |
| The RSSI value of the kth point inserted after the ith broadcast point | |
| The extended RSSI value vector | |
| The reference RSSI value vector of the ith reference trajectory | |
| The perpendicular distance corresponding to the ith reference trajectory | |
| Floor function | |
| The vector formed by the location of all feature points | |
| The vector formed by the RSSI value of all feature points | |
| The vector formed by the location of selected feature points | |
| The vector formed by the RSSI value of selected feature points on the ith reference trajectory |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| L | 600 m | H | 100 m |
| N | 100 | m | |
| m | 1 m | ||
| 100 db | f | 24 KHz | |
| k | 2 | v | 5 m/s |
| 100 m | 600 m |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, Q.; Hua, C.; Guan, X. A Mobile Anchor Node Assisted RSSI Localization Scheme in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 4369. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204369
Sun Y, Yuan Y, Xu Q, Hua C, Guan X. A Mobile Anchor Node Assisted RSSI Localization Scheme in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors. 2019; 19(20):4369. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204369
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yanlong, Yazhou Yuan, Qimin Xu, Changchun Hua, and Xinping Guan. 2019. "A Mobile Anchor Node Assisted RSSI Localization Scheme in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks" Sensors 19, no. 20: 4369. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204369
APA StyleSun, Y., Yuan, Y., Xu, Q., Hua, C., & Guan, X. (2019). A Mobile Anchor Node Assisted RSSI Localization Scheme in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors, 19(20), 4369. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204369




