Fast and Accurate 3D Measurement Based on Light-Field Camera and Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Our Method
3.1. Measurement System Configuration
3.2. Depth Estimation Neural Network
3.2.1. Network Design
3.2.2. Loss Function
3.2.3. Training Details
4. Experiments
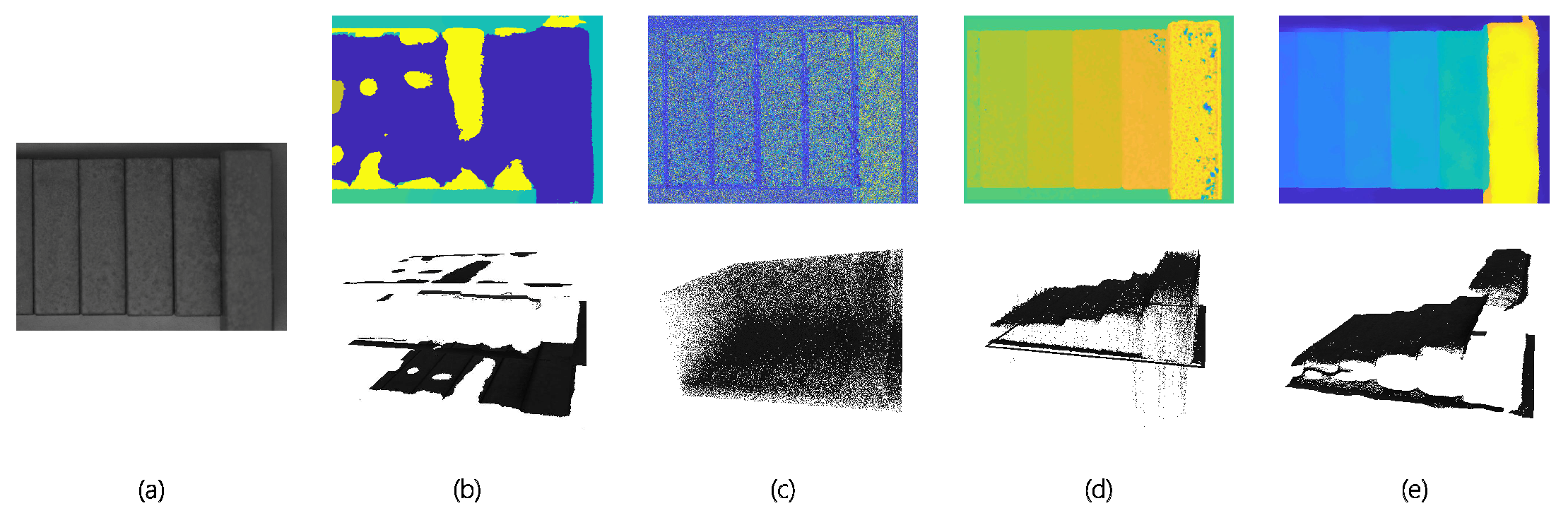
4.1. Qualitative Evaluation on Depth Estimation Algorithms
4.2. Quantitative Evaluation on Benchmark Data
4.3. 3D Geometry Reconsecration Accuracy Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, R.; Levoy, M.; Brédif, M.; Duval, G.; Horowitz, M.; Hanrahan, P. Light field photography with a hand-held plenoptic camera. Comput. Sci. Tech. Rep. CSTR 2005, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lytro Illum. Available online: https://illum.lytro.com/illum (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- Raytrix 3D Light Field Camera Technology. Available online: http://www.raytrix.de/ (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- Levoy, M. Light fields and computational imaging. Computer 2006, 8, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, R.; Hanrahan, P. Digital Light Field Photography; Stanford University Stanford: Stanford, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, H.G.; Park, J.; Choe, G.; Park, J.; Bok, Y.; Tai, Y.W.; So Kweon, I. Accurate depth map estimation from a lenslet light field camera. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1547–1555. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, H.G.; Park, J.; Choe, G.; Park, J.; Bok, Y.; Tai, Y.W.; Kweon, I.S. Depth from a light field image with learning-based matching costs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Sheng, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Z. Robust depth estimation for light field via spinning parallelogram operator. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2016, 145, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, C.; Spyropoulos, S.; Hussmann, S.; Perwass, C. Automated robust metric calibration algorithm for multifocus plenoptic cameras. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2016, 65, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok, Y.; Jeon, H.G.; Kweon, I.S. Geometric calibration of micro-lens-based light field cameras using line features. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, D. Occlusion-aware depth estimation for light field using multi-orientation EPIs. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 74, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, H.; Diebold, M.; Rother, C.; Jähne, B. Trust your model: Light field depth estimation with inline occlusion handling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–21 June 2018; pp. 4530–4538. [Google Scholar]
- Alperovich, A.; Johannsen, O.; Strecke, M.; Goldluecke, B. Light field intrinsics with a deep encoder-decoder network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–21 June 2018; pp. 9145–9154. [Google Scholar]
- Johannsen, O.; Honauer, K.; Goldluecke, B.; Alperovich, A.; Battisti, F.; Bok, Y.; Brizzi, M.; Carli, M.; Choe, G.; Diebold, M.; et al. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense light field depth estimation algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 82–99. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Wilburn, B.; Matsushita, Y.; Theobalt, C. High-quality shape from multi-view stereo and shading under general illumination. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 969–976. [Google Scholar]
- Langguth, F.; Sunkavalli, K.; Hadap, S.; Goesele, M. Shading-aware multi-view stereo. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 469–485. [Google Scholar]
- Oxholm, G.; Nishino, K. Multiview shape and reflectance from natural illumination. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2155–2162. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Gu, J.; Shi, B.; Tan, P.; Kautz, J. Polarimetric multi-view stereo. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1558–1567. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Q.; Yu, J. Light field imaging: models, calibrations, reconstructions, and applications. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2017, 18, 1236–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelson, E.H.; Bergen, J.R. The plenoptic function and the elements of early vision. Computational Models of Visual Processing. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1991, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Levoy, M.; Hanrahan, P. Light field rendering. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Siggraph, New Orleans, LA, USA, 4–9 August 1996; pp. 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gortler, S.J.; Grzeszczuk, R.; Szeliski, R.; Cohen, M.F. The lumigraph. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Siggraph, New Orleans, LA, USA, 4–9 August 1996; Volume 96, pp. 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, S. Dense ray tracing based reconstruction algorithm for light-field volumetric particle image velocimetry. In Proceedings of the 7th Australian Conference on Laser Diagnostics in Fluid Mechanics and Combustion, Melbourne, Australia, 9–11 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fahringer, T.W.; Lynch, K.P.; Thurow, B.S. Volumetric particle image velocimetry with a single plenoptic camera. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 115201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Ding, J.; New, T.; Soria, J. Light-field camera-based 3D volumetric particle image velocimetry with dense ray tracing reconstruction technique. Exp. Fluids 2017, 58, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Niu, X.; Quinn, M.K. 3D surface pressure measurement with single light-field camera and pressure-sensitive paint. Exp. Fluids 2018, 59, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hane, C.; Ladicky, L.; Pollefeys, M. Direction matters: Depth estimation with a surface normal classifier. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 381–389. [Google Scholar]
- Bolles, R.C.; Baker, H.H.; Marimont, D.H. Epipolar-plane image analysis: An approach to determining structure from motion. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1987, 1, 7–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, S.; Goldluecke, B. Reconstructing reflective and transparent surfaces from epipolar plane images. In Proceedings of the German Conference on Pattern Recognition, Saarbrücken, Germany, 3–6 September 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Johannsen, O.; Sulc, A.; Goldluecke, B. What sparse light field coding reveals about scene structure. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3262–3270. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, C.; Jeon, H.G.; Yoon, Y.; So Kweon, I.; Joo Kim, S. Epinet: A fully-convolutional neural network using epipolar geometry for depth from light field images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–21 June 2018; pp. 4748–4757. [Google Scholar]
- Heber, S.; Pock, T. Convolutional networks for shape from light field. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3746–3754. [Google Scholar]
- Heber, S.; Yu, W.; Pock, T. Neural epi-volume networks for shape from light field. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2252–2260. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, M.; Zulqarnain Gilani, S.; Wang, Y.; Mian, A. 3D face reconstruction from light field images: A model-free approach. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 501–518. [Google Scholar]
- Wanner, S.; Goldluecke, B. Variational light field analysis for disparity estimation and super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.W.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Hadap, S.; Rusinkiewicz, S.; Malik, J.; Ramamoorthi, R. Shape estimation from shading, defocus, and correspondence using light-field angular coherence. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.03167. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Ozay, M.; Zhang, Y.; Okatani, T. Revisiting single image depth estimation: Toward higher resolution maps with accurate object boundaries. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.08673. [Google Scholar]
- Honauer, K.; Johannsen, O.; Kondermann, D.; Goldluecke, B. A dataset and evaluation methodology for depth estimation on 4D light fields. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 November 2016; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Ding, J.; New, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H. Volumetric calibration enhancements for single-camera light-field PIV. Exp. Fluids 2019, 60, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, C.B.; Xu, D.; Gwak, J.; Chen, K.; Savarese, S. 3D-R2N2: A unified approach for single and multi-view 3D object reconstruction. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 628–644. [Google Scholar]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Qian, Z.; Mu, T.; Shi, S. Fast and Accurate 3D Measurement Based on Light-Field Camera and Deep Learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 4399. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204399
Ma H, Qian Z, Mu T, Shi S. Fast and Accurate 3D Measurement Based on Light-Field Camera and Deep Learning. Sensors. 2019; 19(20):4399. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204399
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Haoxin, Zhiwen Qian, Tingting Mu, and Shengxian Shi. 2019. "Fast and Accurate 3D Measurement Based on Light-Field Camera and Deep Learning" Sensors 19, no. 20: 4399. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204399
APA StyleMa, H., Qian, Z., Mu, T., & Shi, S. (2019). Fast and Accurate 3D Measurement Based on Light-Field Camera and Deep Learning. Sensors, 19(20), 4399. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204399






