Analysis of Model Mismatch Effects for a Model-Based Gas Source Localization Strategy Incorporating Advection Knowledge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Related Work
1.3. Contributions
2. Model Based Exploration
2.1. Gas Dispersion PDE
2.2. Probabilistic Modeling of a PDE
2.3. Variational Inference
- initialize with a low value
- compute the mean and variance of using Equations (24) and (25).
- update , from Equation (27).
2.4. Uncertainty Map
3. Simulation and Results
3.1. Simulation Setup
3.2. Parameter Evaluation
3.2.1. PDE Relaxation, Sensor Noise and Source Prior
3.2.2. Wind Prior
3.2.3. Time Discretization
3.2.4. Dispersion Model Mismatch
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PDE | Partial Differential Equation |
| POI | Point of Interest |
| Probability Density Function | |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| FVM | Finite Volume Method |
| SBL | Sparse Bayesian Learning |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| EMD | Earth Mover’s Distance |
| EM | Expectation Maximization |
| CBRN | chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear |
| NMSE | Normalized Mean Square Error |
References
- Nicol, C.; Ellery, A.; Lynch, B.; Cloutis, E.; Croon, G.D.; Ellery, A. Martian methane plume models for defining Mars rover methane source search strategies. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2018, 17, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilienthal, A.; Duckett, T. Building gas concentration gridmaps with a mobile robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2004, 48, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lilienthal, A.; Duckett, T. Experimental analysis of gas-sensitive Braitenberg vehicles. Adv. Robot. 2004, 18, 817–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, R.A.; Bab-Hadiashar, A.; Shepherd, R.L.; Wallace, G.G. A comparison of reactive robot chemotaxis algorithms. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2003, 45, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Li, H.; Sun, F. 3D moth-inspired chemical plume tracking. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Zhuhai, China, 6–9 December 2015; Volume 24, pp. 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, L.; De Almeida, A. Electronic nose-based odour source localization. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control Proceedings, Nagoya, Japan, 30 March–1 April 2000; pp. 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimaldi, J.P.; Wiley, M.B.; Koseff, J.R. The relationship between mean and instantaneous structure in turbulent passive scalar plumes. J. Turbul. 2002, 3, N14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjovi, A.; Marques, L. Multi-robot odor distribution mapping in realistic time-variant conditions. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 3720–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilienthal, A.J.; Duckett, T.; Ishida, H.; Werner, F. Indicators of gas source proximity using metal oxide sensors in a turbulent environment. In Proceedings of the First IEEE/RAS-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, BioRob 2006, Pisa, Italy, 20–22 Febuary 2006; pp. 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuker, M.; Bahr, V.; Huerta, R. Exploiting plume structure to decode gas source distance using metal-oxide gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, D.W.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, C.L. Localising odour source using multi-robot and anemotaxis-based particle swarm optimisation. IET Control Theory Appl. 2012, 6, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Kagawa, Y.; Nakamoto, T.; Moriizumi, T. Odor-source Localization In Clean Room By Autonomous Mobile Sensing System. In Proceedings of the TRANSDUCERS ’95 International Solid-State Sensors and Actuators Conference, Stockholm, Sweden, 25–29 June 1995; Volume 1, pp. 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.M.; Aguiar, A.P.; Martinoli, A. An Algorithm for Formation-Based Chemical Plume Tracing Using Robotic Marine Vehicles. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2016 MTS/IEEE Monterey, Monterey, CA, USA, 19–23 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Albertson, J.D.; Harvey, T.; Foderaro, G.; Zhu, P.; Zhou, X.; Ferrari, S.; Amin, M.S.; Modrak, M.; Brantley, H.; Thoma, E.D. A Mobile Sensing Approach for Regional Surveillance of Fugitive Methane Emissions in Oil and Gas Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2487–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayat, B.; Crasta, N.; Li, H.; Ijspeert, A. Optimal search strategies for pollutant source localization. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 1801–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergassola, M.; Villermaux, E.; Shraiman, B.I. ‘Infotaxis’ as a strategy for searching without gradients. Nature 2007, 445, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriou, M.A.; Ucinski, D. State Estimation of Spatially Distributed Processes Using Mobile Sensing Agents. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference (ACC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 1770–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Guo, Y.; Bingham, B. Multi-robot cooperative control for monitoring and tracking dynamic plumes. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uciński, D. Optimal Measurement Methods for Distributed Parameter System Identification; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pukelsheim, F. Optimal Design of Experiments; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Demetriou, M.A.; Hussein, I.I. Estimation of Spatially Distributed Processes Using Mobile Spatially Distributed Sensor Network. SIAM J. Control Opt. 2009, 48, 266–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriou, M.A.; Egorova, T.; Gatsonis, N.A. Estimation of a gaseous release into the atmosphere using a formation of UAVs. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunisch, K.; Pieper, K.; Vexler, B. Measure Valued Directional Sparsity for Parabolic Optimal Control Problems. SIAM J. Control Opt. 2014, 52, 3078–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.H.; Yang, W.X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, M. Collective odor source estimation and search in time-variant airflow environments using mobile robots. Sensors 2011, 11, 10415–10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemerek, J.R.; Ferrari, S.; Albertson, J.D. Fugitive Gas Emission Rate Estimation Using Multiple Heterogeneous Mobile Sensors. In Proceedings of the ISOCS/IEEE International Symposium on Olfaction and Electronic Nose (ISOEN), Montreal, QC, Canada, 28–31 May 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zabaras, N. Using Bayesian statistics in the estimation of heat source in radiation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 48, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexanderian, A.; Petra, N.; Stadler, G.; Ghattas, O. A-optimal design of experiments for infinite-dimensional Bayesian linear inverse problems with regularized l0-sparsification. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2013, 36, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawo, F.; Roberts, K.; Hanebeck, U.D. Bayesian Estimation of Distributed Phenomena using Discretized Representations of Partial Differential Equations. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, Setúbal, Portugal, 1–5 August 2006; pp. 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, L.A.; Krishnamachari, B.; Kuo, C.C. Distributed parameter estimation for monitoring diffusion phenomena using physical models. In Proceedings of the 2004 First Annual IEEE Communications Society Conference on Sensor and Ad Hoc Communications and Networks, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 4–7 October 2004; pp. 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, M.E. Sparse Bayesian Learning and the Relevance Vector Machine. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2001, 1, 211–244. [Google Scholar]
- Wipf, D.P.; Rao, B.D. Sparse Bayesian learning for basis selection. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2004, 52, 2153–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, T.; Manss, C.; Shutin, D. Multi-agent exploration of spatial dynamical processes under sparsity constraints. Auton. Agents Multi-Agent Syst. 2018, 32, 134–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logg, A.; Mardal, K.; Wells, G. (Eds.) Automated Solution of Differential Equations by the Finite Element Method; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bennetts, V.H.; Kucner, T.P.; Schaffernicht, E.; Neumann, P.P.; Fan, H.; Lilienthal, A.J. Probabilistic Air Flow Modelling Using Turbulent and Laminar Characteristics for Ground and Aerial Robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, M.J. Variational Algorithm for Approximate Bayesian Inference. Ph.D. Thesis, University College London, London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.M.; Tipping, M.E.; Cb, C. Variational Relevance Vector Machines. In Proceedings of the Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence Proceedings, Stanford, CA, USA, 30 June–3 July 2000; pp. 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- SciPy. 2018. Available online: https://www.scipy.org/ (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Uciński, D. Measurement Optimization for Parameter Estimation in Distributed Systems; Technical University Press: Zielona Gora, Poland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.; Boyd, S. Sensor Selection via Convex Optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacKay, D.J.C. Information-Based Objective Functions for Active Data Selection. Neural Comput. 1992, 4, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thuerey, N.; Pfaff, T. MantaFlow. 2016. Available online: http://mantaflow.com/ (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Rubner, Y.; Tomasi, C.; Guibas, L.J. A Metric for Distributions with Applications to Image Databases. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision, Bombay, India, 7 January 1998; pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, T.; Manss, C.; Shutin, D.; Lilienthal, A.J.; Karolj, V.; Viseras, A. Probabilistic modeling of gas diffusion with partial differential equations for multi-robot exploration and gas source localization. In Proceedings of the ECMR 2017 European Conference on Mobile Robots, Paris, France, 6–8 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

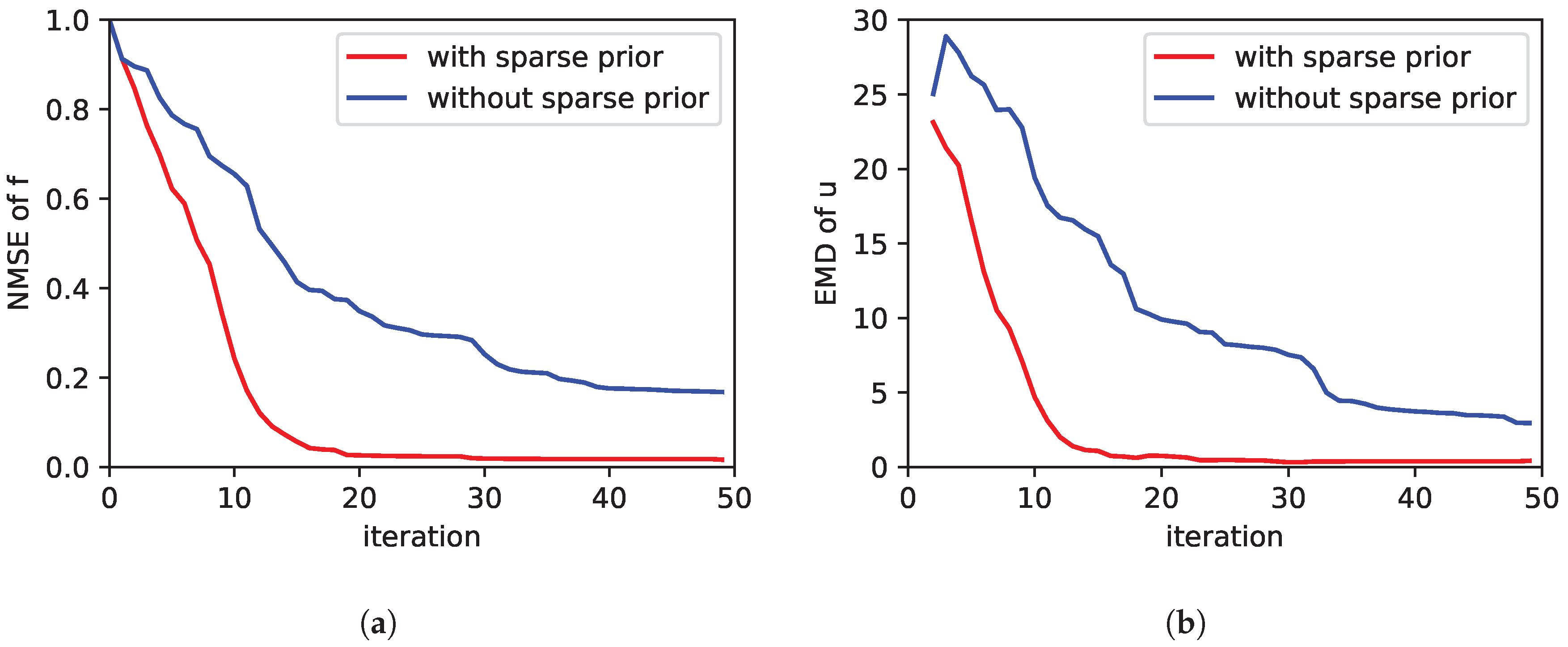
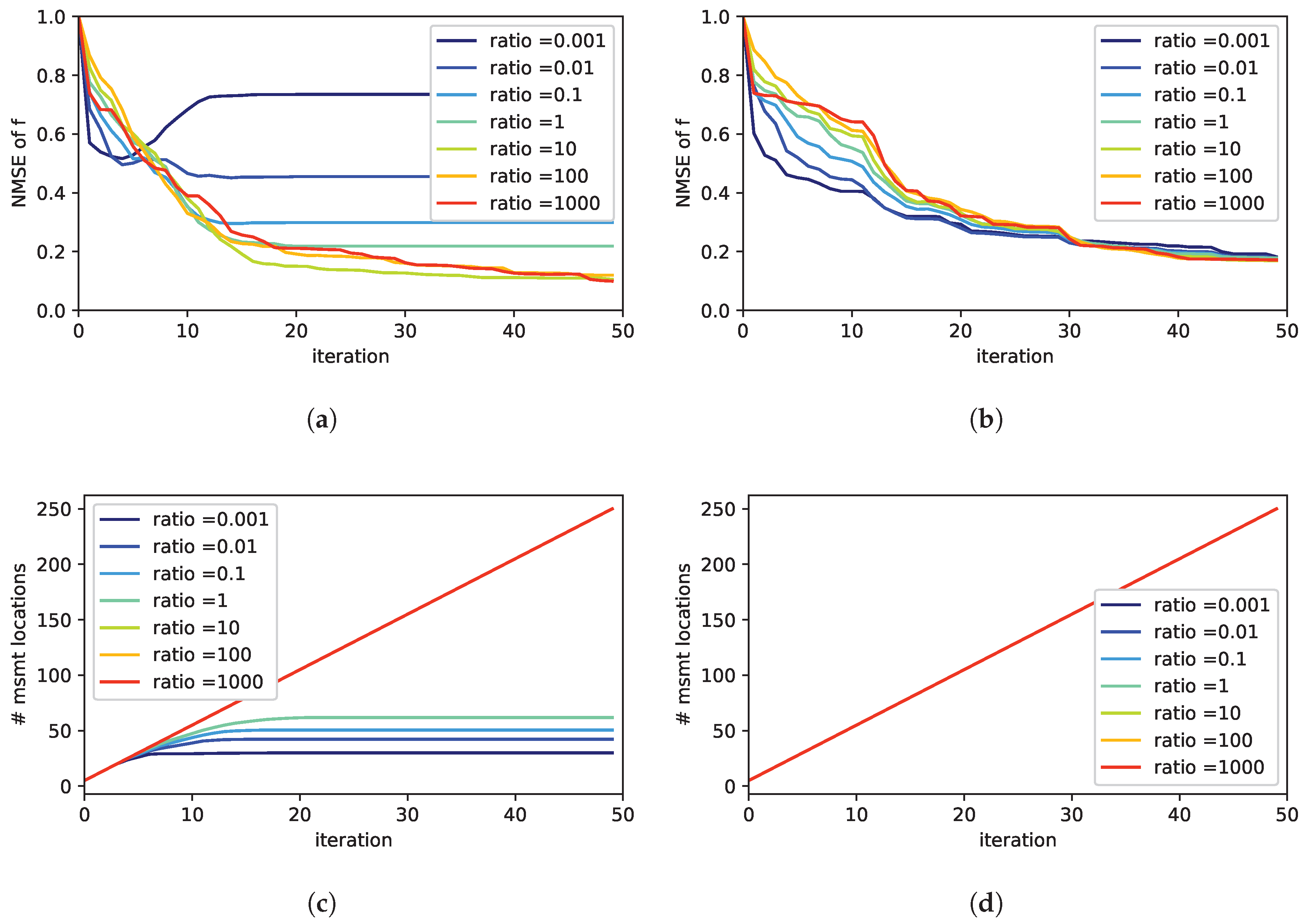






| Source(s) at | (10,10); (15,13); (10,17), (17,7); (8,12), (15,12); (12,17), (5,10), (15,12) |
|---|---|
| ; ; | |
| ; ; |
| Source(s) At | (10,10); (15,13); (10,17), (17,7); (8,12), (15,12); (12,17), (5,10), (15,12) |
|---|---|
| ; ; ; ; | |
| ; ; ; ; |
| prior wind speed | 0 ; 0.5 ; 1 ; 2 |
| prior wind direction | 0 deg ; 5 deg ; 10 deg ; 30 deg ; 60 deg |
| ; ; | |
| ground truth wind speed (direction 0 deg) | 0 ; 0.5 ; 1 ; 2 |
| Source(s) At | (10,10); (15,13); (10,17), (17,7); (8,12), (15,12); (12,17), (5,10), (15,12) |
|---|---|
| ; ; | |
| ; | |
| delta t | 0.2 ; 1.0 ; 5.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiedemann, T.; Lilienthal, A.J.; Shutin, D. Analysis of Model Mismatch Effects for a Model-Based Gas Source Localization Strategy Incorporating Advection Knowledge. Sensors 2019, 19, 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030520
Wiedemann T, Lilienthal AJ, Shutin D. Analysis of Model Mismatch Effects for a Model-Based Gas Source Localization Strategy Incorporating Advection Knowledge. Sensors. 2019; 19(3):520. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030520
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiedemann, Thomas, Achim J. Lilienthal, and Dmitriy Shutin. 2019. "Analysis of Model Mismatch Effects for a Model-Based Gas Source Localization Strategy Incorporating Advection Knowledge" Sensors 19, no. 3: 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030520
APA StyleWiedemann, T., Lilienthal, A. J., & Shutin, D. (2019). Analysis of Model Mismatch Effects for a Model-Based Gas Source Localization Strategy Incorporating Advection Knowledge. Sensors, 19(3), 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030520





