Spatial Reorganization of Myoelectric Activities in Extensor Digitorum for Sustained Finger Force Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Signal Acquisition
2.4. Data Processing
2.4.1. Visualization of 2D Myoelectric Activities of ED
2.4.2. Quantification of the Myoelectric Activities in sEMG TM
2.4.3. Changes of Myoelectric Activities Distribution in ED
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
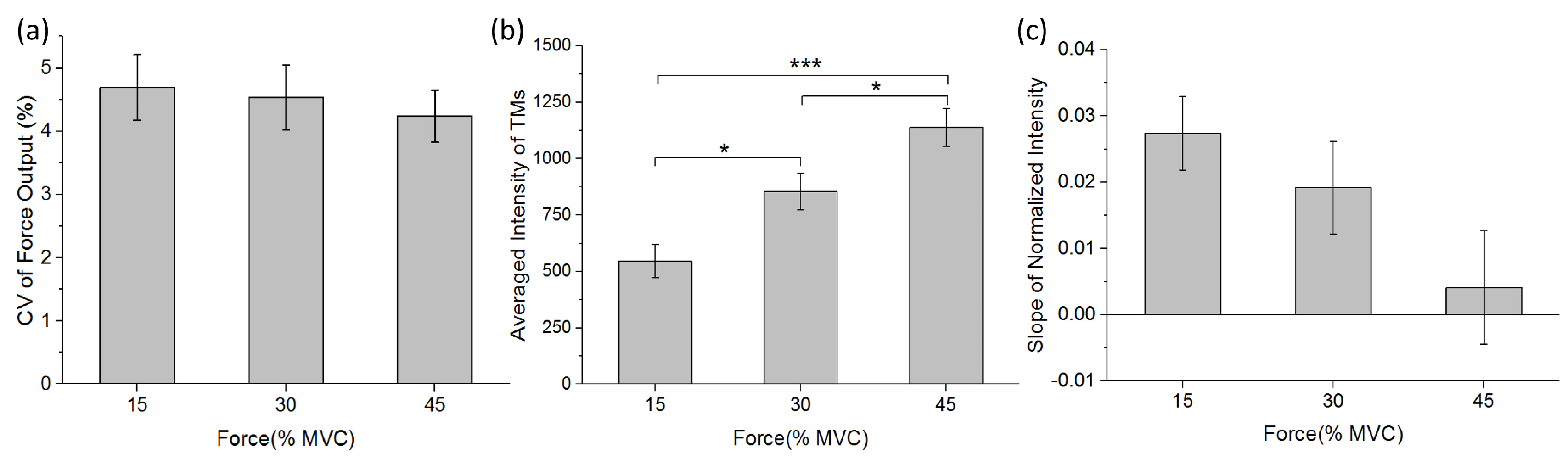
3.1. Performance of Force Output and Changes of TM during Sustained Contraction
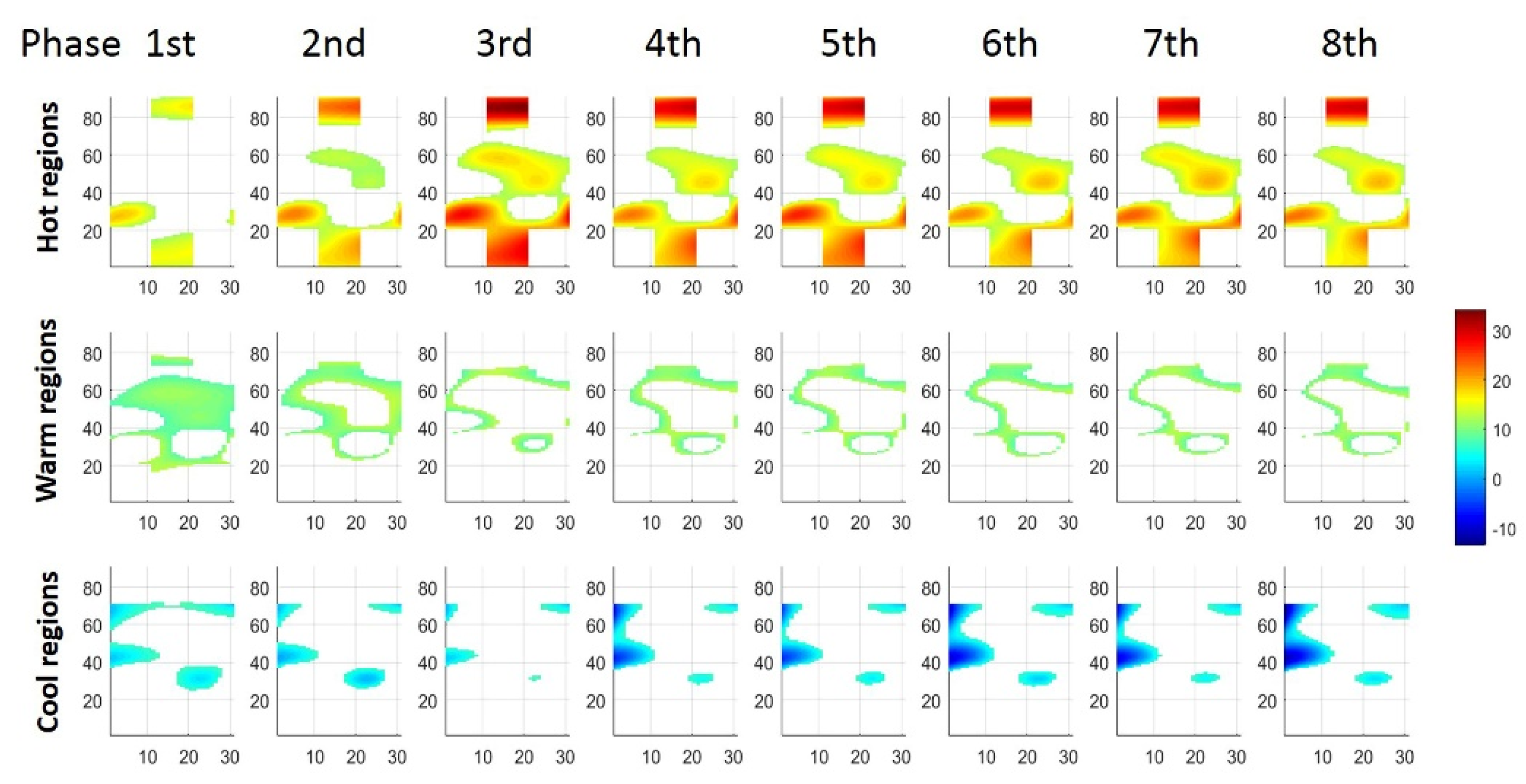
3.2. Distribution Variation of STMs at Three Force Levels during Sustained Contraction
3.3. Regionalization Distribution of STMs at Three Force Levels during Sustained Contraction
4. Discussions
4.1. Regionalization of ED Activity
4.2. Reorganization in ED to Maintain Sustained Constant Force Output of Index Finger
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonio, J. Skeletal Muscle: Form and Function. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1996, 28, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Kouzaki, M.; Moritani, T. Task-dependent spatial distribution of neural activation pattern in human rectus femoris muscle. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2012, 22, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylie, T.; Jane, B.; Thomas, G.N.; Stephan, R.; Paul, H. Motor unit recruitment strategies are altered during deep-tissue pain. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 10820–10826. [Google Scholar]
- Contessa, P.; Adam, A.; De Luca, C.J. Motor unit control and force fluctuation during fatigue. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farina, D.; Leclerc, F.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Buttelli, O.; Madeleine, P. The change in spatial distribution of upper trapezius muscle activity is correlated to contraction duration. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2008, 18, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mista, C.A.; Salomoni, S.E.; Thomas, G.N. Spatial reorganisation of muscle activity correlates with change in tangential force variability during isometric contractions. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2014, 24, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Chen, X.; Cao, S.; Qiu, B.; Zhang, X. An isometric muscle force estimation framework based on a high-density surface EMG array and an NMF algorithm. J. Neural Eng. 2017, 14, 046005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Chen, X.; Cao, S.; Zhang, X. Muscle-tendon units localization and activation level analysis based on high-density surface EMG array and NMF algorithm. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 066001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ison, M.; Vujaklija, I.; Whitsell, B.; Farina, D.; Artemiadis, P. High-Density Electromyography and Motor Skill Learning for Robust Long-Term Control of a 7-DoF Robot Arm. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranceta-Garza, A.; Lakany, H.; Conway, B.A. An Investigation into Thumb Rotation Using High Density Surface Electromyography of Extrinsic Hand Muscles. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Manchester, UK, 13–16 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Castroflorio, T.; Falla, D.; Wang, K.; Svensson, P.; Farina, D. Effect of experimental jaw-muscle pain on the spatial distribution of surface EMG activity of the human masseter muscle during tooth clenching. J. Oral Rehabil. 2012, 39, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, Y.K.; Armando, M.; Glaser, K.J.; Amrami, K.K.; Ehman, R.L. Vibration imaging for localization of functional compartments of the extrinsic flexor muscles of the hand. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 31, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brorsson, S.; Nilsdotter, A.; Hilliges, M.; Sollerman, C.; Aurell, Y. Ultrasound evaluation in combination with finger extension force measurements of the forearm musculus extensor digitorum communis in healthy subjects. BMC Med. Imaging 2008, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, P.; Pengel, L.; Herbert, R.; Gandevia, S.; Gandevia, S. Measurement of muscle contraction with ultrasound imaging. Muscle Nerve 2003, 27, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yuan, Y.; Cao, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X. A SEMG-Force Estimation Framework Based on a Fast Orthogonal Search Method Coupled with Factorization Algorithms. Sensors 2018, 18, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Suresh, N.L.; Xue, C.; Rymer, W.Z. Extracting extensor digitorum communis activation patterns using high-density surface electromyography. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Cao, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X. HD-sEMG-based research on activation heterogeneity of skeletal muscles and the joint force estimation during elbow flexion. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 056027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.D.; Hou, W.S.; Wu, X.-Y.; Zheng, X.L. Design of Electrode Array for Multichannel sEMG Recording of Multitendoned Forearm Muscles. Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2012, 10, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Leijnse, J.N.; Carter, S.; Gupta, A.; Mccabe, S. Anatomic basis for individuated surface EMG and homogeneous electrostimulation with neuroprostheses of the extensor digitorum communis. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 100, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifrek, M.; Medved, V.; Tonković, S.; Ostojić, S. Surface EMG based muscle fatigue evaluation in biomechanics. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallentin, N.; Jørgensen, K.; Simonsen, E.B. Motor unit recruitment during prolonged isometric contractions. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1993, 67, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westad, C.; Westgaard, R.H.; De Luca, C.J. Motor unit recruitment and derecruitment induced by brief increase in contraction amplitude of the human trapezius muscle. J. Physiol. 2010, 552, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigland-Ritchie, B.; Johansson, R.; Lippold, O.C.; Smith, S.; Woods, J.J. Changes in motoneurone firing rates during sustained maximal voluntary contractions. J. Physiol. 1983, 340, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Rymer, W.Z.; Suresh, N.L. Motor unit firing rate patterns during voluntary muscle force generation: a simulation study. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 11, 026015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessio, G.; Roberto, M.; Marco, G. Uneven spatial distribution of surface EMG: what does it mean? Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 113, 887–894. [Google Scholar]
- Merletti, R.; Knaflitz, M.; De Luca, C.J. Myoelectric manifestations of fatigue in voluntary and electrically elicited contractions. J. Appl. Physiol. 1990, 69, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, K.G.; Farina, D.; Maluf, K.S.; Merletti, R.; Enoka, R.M. Influence of amplitude cancellation on the simulated surface electromyogram. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 98, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanson, J.; Persson, A. Changes in the action potential and contraction of isolated frog muscle after repetitive stimulation. Acta Physiol. 2010, 81, 340–348. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrova, N.A.; Dimitrov, G.V. Interpretation of EMG changes with fatigue: Facts, pitfalls, and fallacies. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2003, 13, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.; Cosmos, E.; Brierley, J. Differentiation of muscle fiber types in aneurogenic brachial muscles of the chick embryo. J. Exp. Zool. Part A 1982, 224, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.E.; Levine, D.N.; Rd, Z.F. Mammalian motor units: physiological-histochemical correlation in three types in cat gastrocnemius. Science 1971, 174, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukulka, C.G.; Clamann, H.P. Comparison of the recruitment and discharge properties of motor units in human brachial biceps and adductor pollicis during isometric contractions. Brain Res. 1981, 219, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Tang, S.; Wu, X.; Fu, Q.; Fan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, L.; Chen, L.; Hou, W. Spatial Reorganization of Myoelectric Activities in Extensor Digitorum for Sustained Finger Force Production. Sensors 2019, 19, 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030555
Gao Z, Tang S, Wu X, Fu Q, Fan X, Zhao Y, Hu L, Chen L, Hou W. Spatial Reorganization of Myoelectric Activities in Extensor Digitorum for Sustained Finger Force Production. Sensors. 2019; 19(3):555. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030555
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Zhixian, Shangjie Tang, Xiaoying Wu, Qiang Fu, Xingyu Fan, Yun Zhao, Lintao Hu, Lin Chen, and Wensheng Hou. 2019. "Spatial Reorganization of Myoelectric Activities in Extensor Digitorum for Sustained Finger Force Production" Sensors 19, no. 3: 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030555
APA StyleGao, Z., Tang, S., Wu, X., Fu, Q., Fan, X., Zhao, Y., Hu, L., Chen, L., & Hou, W. (2019). Spatial Reorganization of Myoelectric Activities in Extensor Digitorum for Sustained Finger Force Production. Sensors, 19(3), 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030555



