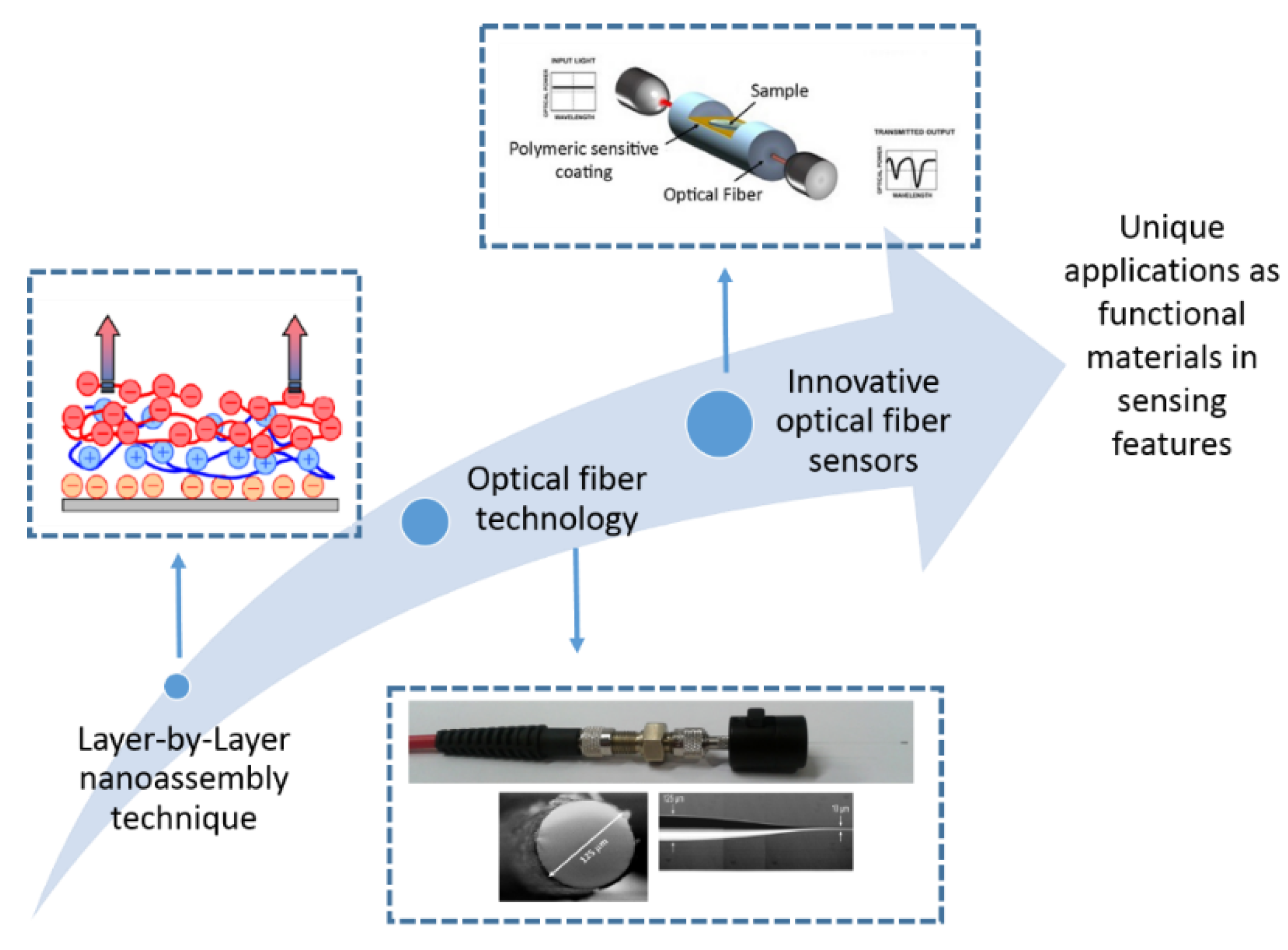
Layer-by-Layer Nano-assembly: A Powerful Tool for Optical Fiber Sensing Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Optical Fiber Configurations
2. Fundamentals of the Layer-by-Layer Technique
2.1. Polyelectrolytes
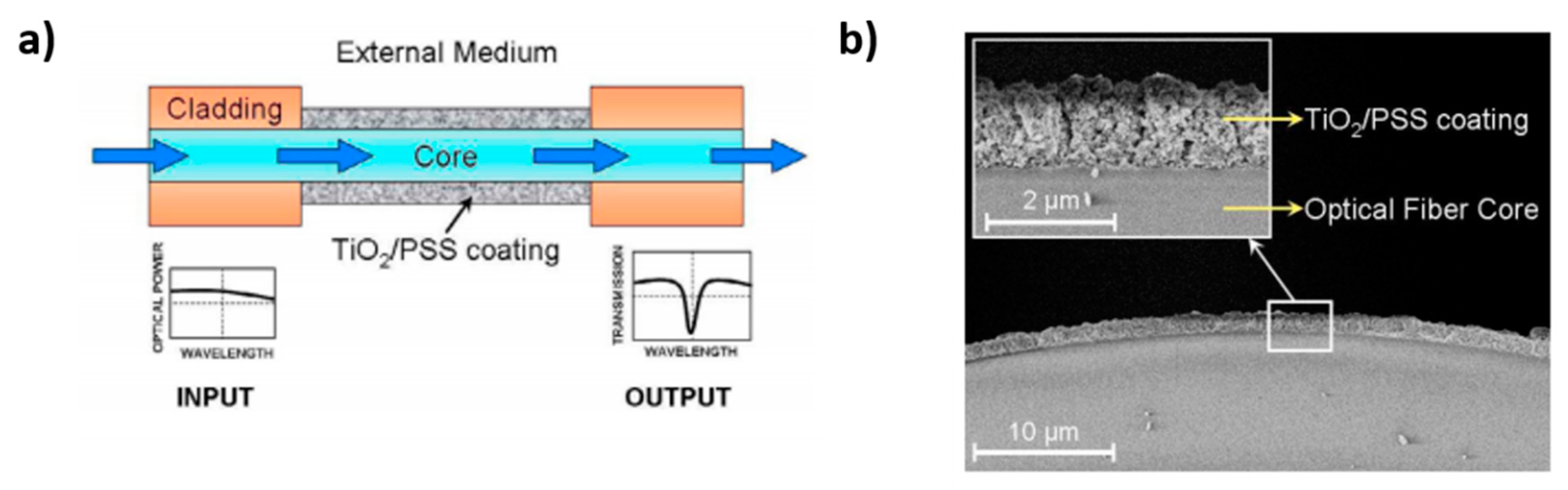
2.2. Implementation of the Layer-by-Layer Technique in Optical Fiber Sensors
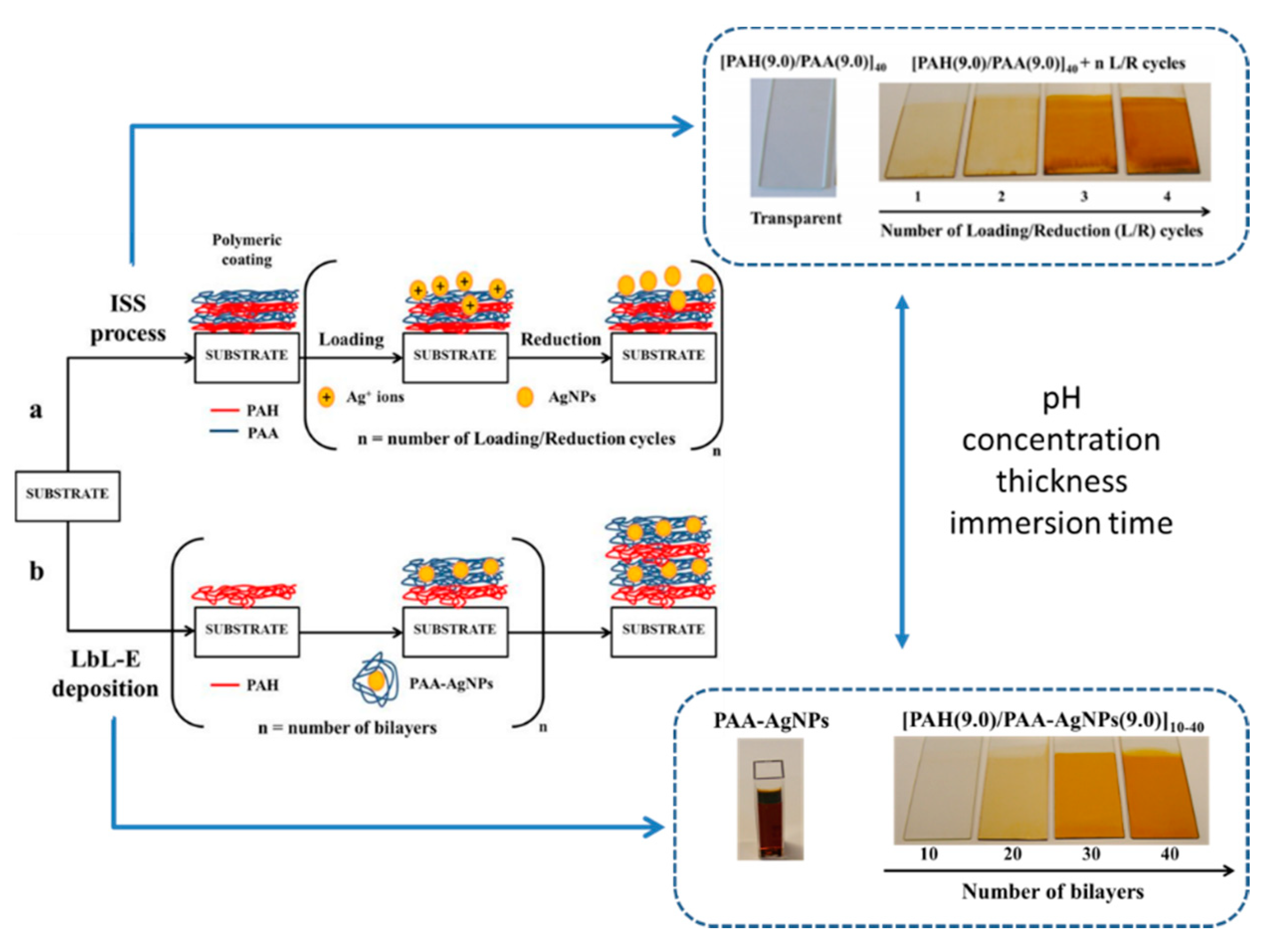
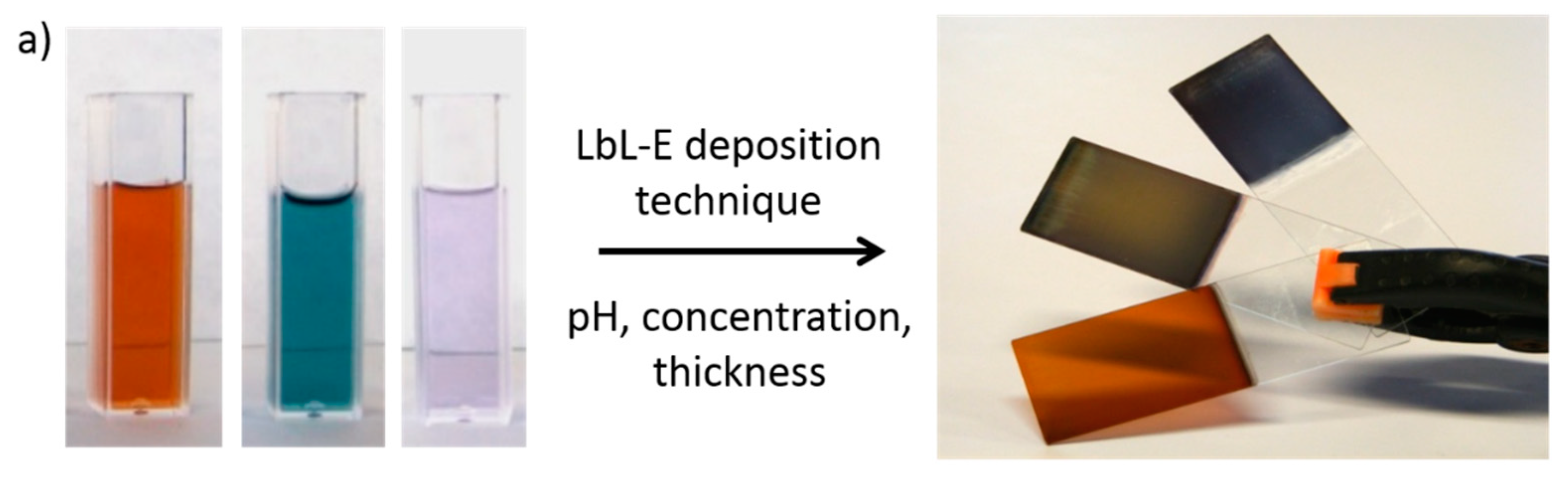
2.3. Examples of Advanced Layer-by-Layer Coatings
3. Applications of the Optical Fiber Sensors Based on Layer-by-Layer Coatings
3.1. Chemical Sensing Applications
3.1.1. pH Sensing Applications
3.1.2. Gas and Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Sensing Applications
3.2. Biological and Biochemical Sensing Applications
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kapany, N.S.; Simms, R.J. Recent Developments in Infrared Fiber Optics. Infrared Phys. 1965, 5, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vali, V.; Shorthill, R.W. Fiber laser gyroscopes. In Fibers and integrated optics; The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1976; Volume 77, pp. 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb, M.; Brandt, G.B. Measurement of Temperature with Optical Fibers Using Transmission Intensity Effects. In Proceedings of the Electro-Optics/Laser 79 Conference and Exposition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 23–25 October 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Bucaro, J.A.; Dardy, H.D. Fiber-optic hydrophone. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1977, 62, 1302–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandridge, A.; Tveten, A.B.; Giallorenzi, T.G. Interferometric current sensors using optical fibres. Electron. Lett. 1981, 17, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petuchowskl, S.J.; Giallorenzi, T.G.; Sheem, S.K. A Sensitive Fiber-Optic Fabry-Perot Interferometer. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1981, 17, 2168–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwis, L.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K.T.V. Fibre optic long period grating-based humidity sensor probe using a Michelson interferometric arrangement. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1970, 178, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebele, E.J.; Askins, C.G.; Putnam, M.A.; Fosha, A.A.; Florio, J.; Donti, R.P.; Blosser, R.G. Distributed strain sensing with fibre Bragg grating arrays embedded in CRTMTM composites. Electron. Lett. 1994, 30, 1783–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltz, G.; Morey, W.W.; Glenn, W.H.; Farina, J.D. In-Fiber Bragg-Grating Sensors; OSA Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, P.M.; Burnett, J.G.; Erry, G.R.G.; Greenaway, A.H.; Harrison, P.; Mangan, B.; Jones, J.D.C. Two-dimensional bend sensing with a single, multi-core optical fibre. Smart Mater. Struct. 2000, 9, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoo, Y.L.; Jin, W.; Ho, H.L.; Wang, D.N.; Windeler, R.S. Evanescent-wave gas sensing using microstructure fiber. Opt. Eng. 2002, 41, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendler, J.H. Self-assembled nanostructured materials. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M.; Grzybowski, B. Self-assembly at all scales. Science 2002, 295, 2418–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matko, V. Next generation AT-cut quartz crystal sensing devices. Sensors 2011, 5, 4474–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, V. Direct electro-optic effect in langasites and α-quartz. Optical Materials 2018, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matko, V.; Jezernik, K. Greatly improved small inductance measurement using quartz crystal parasitic capacitance compensation. Sensors 2010, 10, 3954–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, T.; Su, H.; Cui, X. An approach on a new variable amplitude waveform sensor. Optik- Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 2017, 132, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, P.T. Form and function in multilayer assembly: New applications at the nanoscale. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1271–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.O.; Fujii, Y.; Johnson, D.C.; Kawasaki, B.S. Photosensitivity in optical fiber waveguides: Application to reflection fiber fabrication. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1978, 32, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decher, G. Fuzzy Nanoassemblies: Toward Layered Polymeric Multicomposites. Science 1997, 277, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, P.; Jonas, A.; Laschewsky, A.; Legras, R. Ultrathin Polymer Coatings by Complexation of Polyelectrolytes at Interfaces: Suitable Materials, Structure and Properties. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 319–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decher, G.; Hong, J.D.; Schmitt, J. Buildup of Ultrathin Multilayer Films by a Self-Assembly Process: III. Consecutively Alternating Adsorption of Anionic and Cationic Polyelectrolytes on Charged Surfaces. Thin Solid Films 1992, 210–211, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.J.; Björnmalm, M.; Caruso, F. Technology-Driven Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Nanofilms. Science 2015, 348, aaa2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, J.; Mano, J.F. Molecular Interactions Driving the Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Multilayers. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8883–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Rubner, M.F. Influence of the Degree of Ionization on Weak Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Assembly. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovskaya, V.; Kharlampieva, E.; Mansfield, M.L.; Sukhishvili, S.A. Poly(Methacrylie Acid) Hydrogel Films and Capsules: Response to pH and Ionic Strength, and Encapsulation of Macromolecules. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharlampieva, E.; Koziovskaya, V.; Sukhishvili, S.A. Layer-by-Layer Hydrogen-Bonded Polymer Films: From Fundamentals to Applications. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3053–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Caruso, F. Polymeric Multilayer Films Comprising Deconstructible Hydrogen-Bonded Stacks Confined between Electrostatically Assembled Layers. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 2845–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharlampieva, E.; Sukhishvili, S.A. Hydrogen-Bonded Layer-by-Layer Polymer Films. J. Macromol. Sci. Polym. Rev. 2006, 46, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Such, G.K.; Johnston, A.P.R.; Caruso, F. Engineered Hydrogen-Bonded Polymer Multilayers: From Assembly to Biomedical Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, P.T. Building Biomedical Materials Layer-by-Layer. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Lee, S.; Park, Y.T. Note: Automatic Layer-by-Layer Spraying System for Functional Thin Film Coatings. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 036110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusano, A.; López-Higuera, J.M.; Matias, I.R.; Culshaw, B. Editorial Optical Fiber Sensor Technology and Applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2008, 8, 1052–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.; Shiratori, S.S.; Rubner, M.F. Controlling Bilayer Composition and Surface Wettability of Sequentially Adsorbed Multilayers of Weak Polyelectrolytes. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 4309–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, S.S.; Rubner, M.F. pH-Dependent Thickness Behavior of Sequentially Adsorbed Layers of Weak Polyelectrolytes. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 4213–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharlampieva, E.; Sukhishvili, S.A. Ionization and pH Stability of Multilayers Formed by Self-Assembly of Weak Polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 2003, 19, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itano, K.; Choi, J.; Rubner, M.F. Mechanism of the pH-Induced Discontinuous swelling/deswelling Transitions of Poly(Allylamine Hydrochloride)-Containing Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Films. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 3450–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamarreno, C.R.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Nanofabrication Techniques Applied to the Development of Novel Optical Fiber Sensors Based on Nanostructured Coatings. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 2699–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R.; Corres, J.M.; Del Villar, I.; Goicoechea, J.; Zamarrenoa, C.R.; Hernáez, M.; Claus, R.O. Optical fiber sensors based on layer-by-layer nanostructured films. Procedia Eng. 2010, 5, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Garcia, J.A.; Quintana, I.; Rodriguez, R. Design of Nanostructured Functional Coatings by Using wet-Chemistry Methods. Coatings 2018, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Villar, I.; Arregui, F.J.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Corres, J.M.; Bariain, C.; Goicoechea, J.; Elosua, C.; Hernaez, M.; Rivero, P.J.; Socorro, A.B.; et al. Optical Sensors Based on Lossy-Mode Resonances. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Goicoechea, J.; Arregui, F.J. Optical Fiber Sensors Based on Polymeric Sensitive Coatings. Polymer 2018, 10, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Heflin, J.R.; Stolen, R.H.; Ramachandran, S. Highly Sensitive Optical Response of Optical Fiber Long Period Gratings to Nanometer-Thick Ionic Self-Assembled Multilayers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elosua, C.; Arregui, F.J.; Villar, I.D.; Ruiz-Zamarreño, C.; Corres, J.M.; Bariain, C.; Goicoechea, J.; Hernaez, M.; Rivero, P.J.; Socorro, A.B.; et al. Micro and Nanostructured Materials for the Development of Optical Fibre Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B. Review of the Present Status of Optical Fiber Sensors. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2003, 9, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfbeis, O.S. Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 3269–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, P.J.; Urrutia, A.; Goicoechea, J.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. A Lossy Mode Resonance optical sensor using silver nanoparticles-loaded films for monitoring human breathing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 187, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J.; Corres, J.M.; Bravo, J. Evanescent Field Fiber-Optic Sensors for Humidity Monitoring Based on Nanocoatings. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, P.S.; McShane, M.J. Development of Multilayer Fluorescent Thin Film Chemical Sensors Using Electrostatic Self-Assembly. IEEE Sens. J. 2003, 3, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Yin, M.; Zhang, A.P.; Qian, J.; He, S. Optical Fiber Relative Humidity Sensor Based on FBG Incorporated Thin-Core Fiber Modal Interferometer. Opt. Express. 2011, 19, 4140–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budy, S.M.; Hamilton, D.J.; Cai, Y.; Knowles, M.K.; Reed, S.M. Polymer Mediated Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Different Shaped Gold Nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 487, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.C.; Rubner, M.F.; Cohen, R.E. Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Nanoreactors for Preparing Silver Nanoparticle Composites: Controlling Metal Concentration and Nanoparticle Size. Langmuir 2002, 18, 3370–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, A.; Rivero, P.J.; Ruete, L.; Goicoechea, J.; Matías, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Single-Stage in Situ Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles in Antibacterial Self-Assembled Overlays. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, A.; Goicoechea, J.; Rivero, P.J.; Pildain, A.; Arregui, F.J. Optical Fiber Sensors Based on Gold Nanorods Embedded in Polymeric Thin Films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-López, C.; Pérez-Balado, C.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; De Lera, Á.R.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. A General LbL Strategy for the Growth of pNIPAM Microgels on Au Nanoparticles with Arbitrary Shapes. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 4165–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olek, M.; Ostrander, J.; Jurga, S.; Möhwald, H.; Kotov, N.; Kempa, K.; Giersig, M. Layer-by-Layer Assembled Composites from Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes with Different Morphologies. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1889–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Kim, B.S.; Chen, S.; Shao-Horn, Y.; Hammond, P.T. Layer-by-Layer Assembly of all Carbon Nanotube Ultrathin Films for Electrochemical Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Kotov, N.A. Composite Layer-by-Layer (LBL) Assembly with Inorganic Nanoparticles and Nanowires. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Kotov, N.A. Layer-by-layer (LBL) assembly with semiconductor nanoparticles and nanowires. In Semiconductor Nanocrystal Quantum Dots; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2008; pp. 197–216. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, T.; Ebina, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Harada, M.; Watanabe, M.; Decher, G. Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Titania nanosheet/polycation Composite Films. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 4661–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Omolade, D.; Cohen, R.E.; Rubner, M.F. pH-Dependent Structure and Properties of TiO2/SiO2 Nanoparticle Multilayer Thin Films. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, A.; Rivero, P.J.; Ruete, L.; Goicoechea, J.; Fernández-Valdivieso, C.; Arregui, F.J.; Matías, I.R. An Antibacterial Surface Coating Composed of PAH/SiO2 nanostructurated Films by Layer by Layer. Phys. Status Solidi C. 2010, 7, 2774–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharlampieva, E.; Erel-Unal, I.; Sukhishvili, S.A. Amphoteric Surface Hydrogels Derived from Hydrogen-Bonded Multilayers: Reversible Loading of Dyes and Macromolecules. Langmuir 2007, 23, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chluba, J.; Voegel, J.C.; Decher, G.; Erbacher, P.; Schaaf, P.; Ogier, J. Peptide Hormone Covalently Bound to Polyelectrolytes and Embedded into Multilayer Architectures Conserving Full Biological Activity. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leguen, E.; Chassepot, A.; Decher, G.; Schaaf, P.; Voegel, J.C.; Jessel, N. Bioactive Coatings Based on Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Architectures Functionalized by Embedded Proteins, Peptides Or Drugs. Biomol. Eng. 2007, 24, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lvov, Y.; Ariga, K.; Kunitake, T.; Ichinose, I. Assembly of Multicomponent Protein Films by Means of Electrostatic Layer-by-Layer Adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 6117–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.; Decher, G.; Sukhorukov, G. Assembly of Thin Films by Means of Successive Deposition of Alternate Layers of DNA and Poly(Allylamine). Macromolecules 1993, 26, 5396–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasteva, N.; Besnard, I.; Guse, B.; Bauer, R.E.; Müllen, K.; Yasuda, A.; Vossmeyer, T. Self-Assembled Gold Nanoparticle/Dendrimer Composite Films for Vapor Sensing Applications. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattoussi, H.; Radzilowski, L.H.; Dabbousi, B.O.; Thomas, E.L.; Bawendi, M.G.; Rubner, M.F. Electroluminescence from Heterostructures of Poly(Phenylene Vinylene) and Inorganic CdSe Nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 7965–7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bastida, G.; Arregui, F.J.; Goicoechea, J.; Matias, I.R. Quantum Dots-Based Optical Fiber Temperature Sensors Fabricated by Layer-by-Layer. IEEE Sens. J. 2006, 6, 1378–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Goicoechea, J.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. A Comparative Study of Two Different Approaches for the Incorporation of Silver Nanoparticles into Layer-by-Layer Films. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, P.J.; Goicoechea, J.; Urrutia, A.; Arregui, F.J. Effect of both Protective and Reducing Agents in the Synthesis of Multicolor Silver Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Goicoechea, J.; Urrutia, A.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Multicolor Layer-by-Layer Films using Weak Polyelectrolyte Assisted Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernaez, M.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Del Villar, I.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Lossy mode resonances supported by TiO2-coated optical fibers. Procedia Eng. 2010, 5, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamarreño, C.R.; Bravo, J.; Goicoechea, J.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Response Time Enhancement of pH Sensing Films by Means of Hydrophilic Nanostructured Coatings. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 128, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
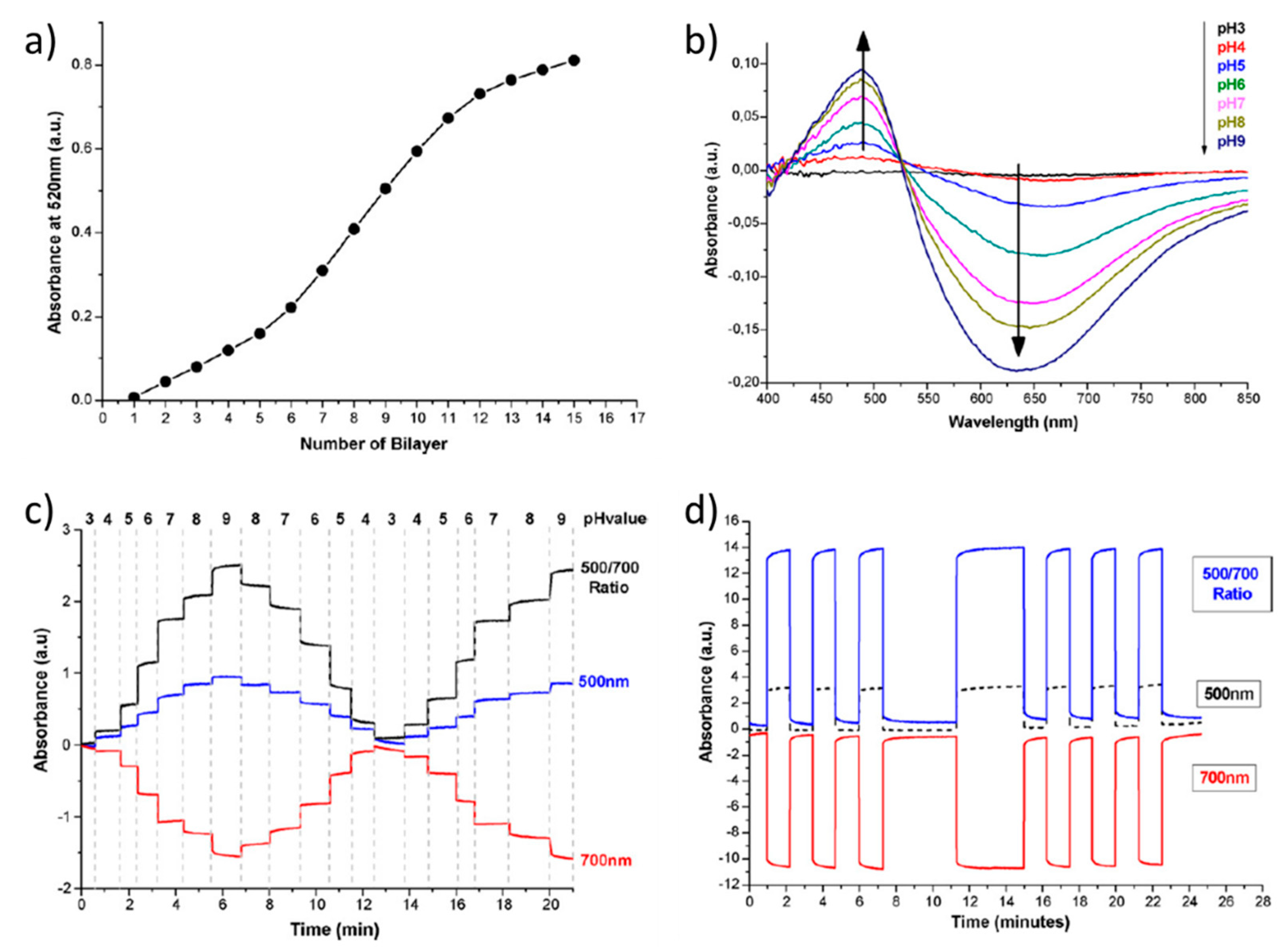
- Goicoechea, J.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Matías, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Optical Fiber pH Sensors Based on Layer-by-Layer Electrostatic Self-Assembled Neutral Red. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 132, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arregui, F.J.; Del Villar, I.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Zubiate, P.; Matias, I.R. Giant Sensitivity of Optical Fiber Sensors by Means of Lossy Mode Resonance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 232, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, P.; Zamarreno, C.R.; Hernaez, M.; Del Villar, I.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Considerations for Lossy-Mode Resonance-Based Optical Fiber Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Villar, I.; Hernaez, M.; Zamarreno, C.R.; Sánchez, P.; Fernández-Valdivielso, C.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Design Rules for Lossy Mode Resonance Based Sensors. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 4298–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Villar, I.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Hernaez, M.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Generation of Lossy Mode Resonances with Absorbing Thin-Films. J. Lightwave Technol. 2010, 28, 3351–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamarreño, C.R.; Hernáez, M.; Del Villar, I.; Matías, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Optical Fiber pH Sensor Based on Lossy-Mode Resonances by Means of Thin Polymeric Coatings. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 155, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socorro, A.B.; Del Villar, I.; Corres, J.M.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Sensitivity Enhancement in a Multimode Interference-Based SMS Fibre Structure Coated with a Thin-Film: Theoretical and Experimental Study. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socorro, A.B.; Del Villar, I.; Corres, J.M.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Lossy Mode Resonance-based pH sensor using a tapered single mode optical fiber coated with a polymeric nanostructure. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors, Limerick, Ireland, 28–31 October 2011; pp. 238–241. [Google Scholar]
- Socorro, A.B.; Del Villar, I.; Corres, J.M.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Tapered Single-Mode Optical Fiber pH Sensor Based on Lossy Mode Resonances Generated by a Polymeric Thin-Film. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 2598–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubiate, P.; Zamarreno, C.R.; Del Villar, I.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. D-shape optical fiber pH sensor based on Lossy Mode Resonances (LMRs). In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE SENSORS, Busan, South Korea, 1–4 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
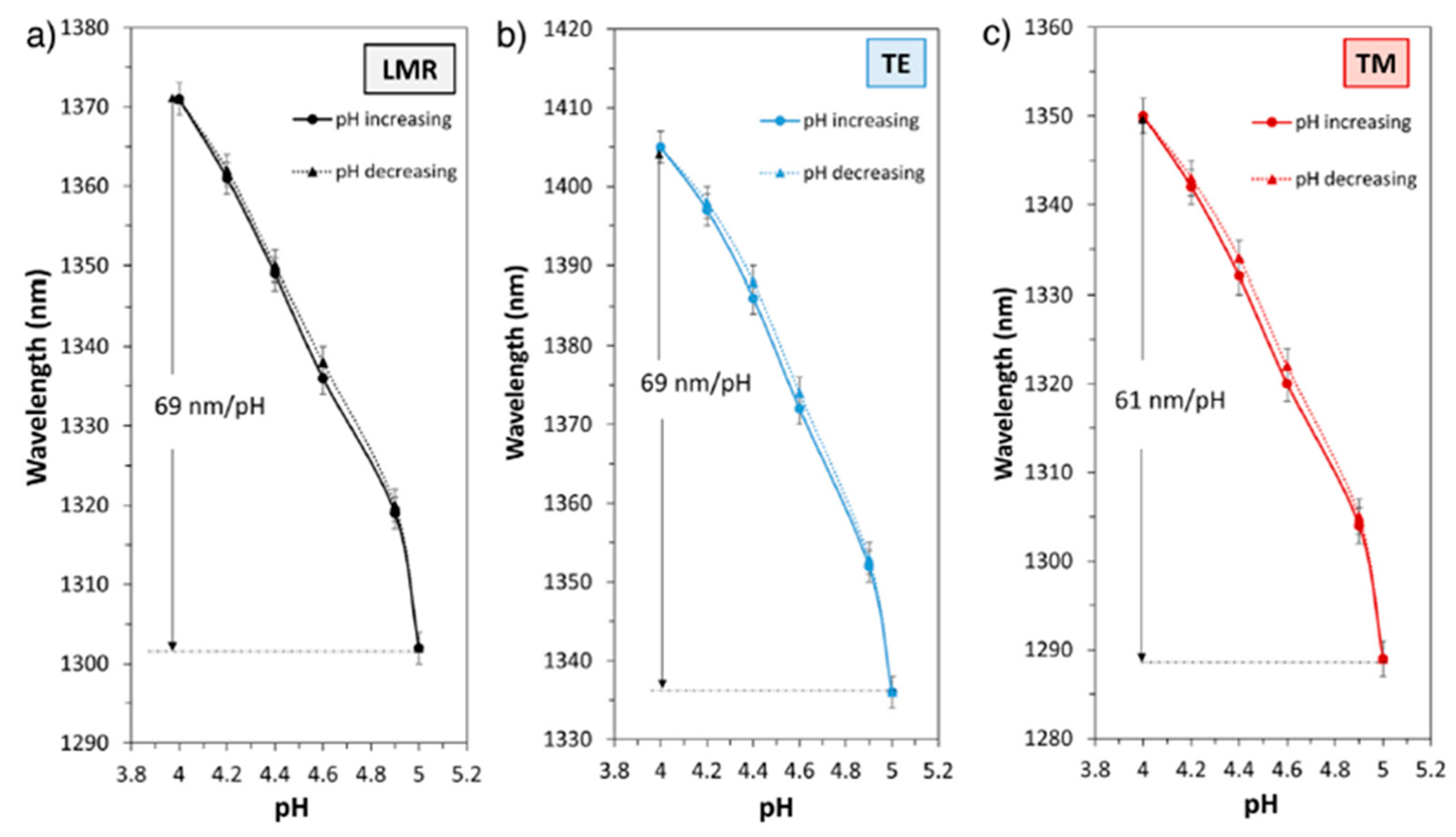
- Zubiate, P.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Del Villar, I.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Tunable Optical Fiber pH Sensors Based on TE and TM Lossy Mode Resonances (LMRs). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 231, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Villar, I.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Hernaez, M.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Lossy Mode Resonance Generation with Indium-Tin-Oxide-Coated Optical Fibers for Sensing Applications. J. Lightwave Technol. 2010, 28, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Goicoechea, J.; Hernaez, M.; Socorro, A.B.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Optical Fiber Resonance-Based pH Sensors using Gold Nanoparticles into Polymeric Layer-by-Layer Coatings. Microsyst. Technol. 2016, 22, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socorro, A.B.; Rivero, P.J.; Hernaez, M.; Goicoechea, J.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Optical fiber pH sensor based on gold nanoparticles into polymeric coatings. In Smart Sensors, Actuators and MEMS VII; and Cyber Physical Systems; The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9517. [Google Scholar]
- Liz-Marzán, L.M. Nanometals: Formation and Color. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corres, J.M.; Matias, I.R.; del Villar, I.; Arregui, F.J. Design of pH Sensors in Long-Period Fiber Gratings Using Polymeric Nanocoatings. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goicoechea, J.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Matías, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Study on white light optical fiber interferometry for pH sensor applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors, Atlanta, GA, USA, 28–31 October 2007; pp. 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Surre, F.; Lyons, B.; Sun, T.; Grattan, V.; O’Keeffe, S.; Lewis, E.; Elosua, C.; Hernaez, M.; Barian, C. U-Bend Fibre Optic pH Sensors using Layer-by-Layer Electrostatic Self-Assembly Technique. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2009; Volume178, p. 012046. [Google Scholar]
- Raoufi, N.; Surre, F.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K.T.V.; Rajarajan, M. Improvement of optical properties of pH-sensitive nanolayers coating deposited using Layer-by-Layer technique. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors, Taipei, Taiwan, 28–31 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Raoufi, N.; Surre, F.; Sun, T.; Rajarajan, M.; Grattan, K.T.V. Wavelength Dependent pH Optical Sensor Using the Layer-by-Layer Technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 169, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoufi, N.; Surre, F.; Rajarajan, M.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K.T.V. Fiber Optic pH Sensor Using Optimized Layer-by-Layer Coating Approach. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goicoechea, J.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Minimizing the Photobleaching of Self-Assembled Multilayers for Sensor Applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 126, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.Y.; Yin, M.J.; Tam, H.Y.; Albert, J. Fiber optic pH sensor with self-assembled multilayer nanocoatings on tilted FBG. In Proceedings of the OFS2012 22nd International Conference on Optical Fiber Sensors; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8421, p. 84216A. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, Z.; Qian, J.; Yin, M.; An, Q.; Gu, B.; Zhang, A. A Novel Fast Response Fiber-Optic pH Sensor Based on Nanoporous Self-Assembled Multilayer Films. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7754–7760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Gu, B.; Zhao, Q.; Qian, J.; Zhang, A.; An, Q.; He, S. Highly Sensitive and Fast Responsive Fiber-Optic Modal Interferometric pH Sensor Based on Polyelectrolyte Complex and Polyelectrolyte Self-Assembled Nanocoating. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 3623–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Yin, M.; Zhang, A.P.; Qian, J.; He, S. Biocompatible Fiber-Optic pH Sensor Based on Optical Fiber Modal Interferometer Self-Assembled with Sodium alginate/polyethylenimine Coating. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G. Detection of Hazardous Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) by Metal Oxide Nanostructures-Based Gas Sensors: A Review. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 15119–15141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewski, B.; Kesy, M.; Ligor, T.; Amann, A. Human Exhaled Air Analytics: Biomarkers of Diseases. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broza, Y.Y.; Haick, H. Nanomaterial-Based Sensors for Detection of Disease by Volatile Organic Compounds. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 785–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, J.; Segrè, D. The Effect of Oxygen on Biochemical Networks and the Evolution of Complex Life. Science 2006, 311, 1764–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, A. Oxygen Indicators and Intelligent Inks for Packaging Food. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005, 34, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Zhao, H. A Portable Photoelectrochemical Probe for Rapid Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand in Wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7810–7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, S.; Hosoki, A.; Nishiyama, M.; Seki, A.; Watanabe, K. Optical fiber oxygen sensor using layer-by-layer stacked porous composite membranes. In Photonic Instrumentation Engineering III; The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9754, p. 97540F. [Google Scholar]
- Elosua, C.; De Acha, N.; Lopez-Torres, D.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Luminescent optical fiber oxygen sensor following layer-by-layer method. Procedia Eng. 2014, 87, 987–990. [Google Scholar]
- Elosua, C.; De Acha, N.; Hernaez, M.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Layer-by-Layer Assembly of a Water-Insoluble Platinum Complex for Optical Fiber Oxygen Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Acha, N.; Elosúa, C.; Martínez, D.; Hernáez, M.; Matías, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Comparative Study of Polymeric Matrices Embedding Oxygen-Sensitive Fluorophores by Means of Layer-by-Layer Nanosassembly. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Acha, N.; Elosúa, C.; Matías, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Enhancement of Luminescence-Based Optical Fiber Oxygen Sensors by Tuning the Distance between Fluorophore Layers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 248, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasu, P.T.; Noor, A.S.M.; Shabaneh, A.A.; Girei, S.H.; Mahdi, M.A.; Lim, H.N.; Abdul Rashid, H.A.; Yaacob, M.H. Absorbance Properties of Gold Coated Fiber Bragg Grating Sensor for Aqueous Ethanol. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. 2014, 9, 14018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Lin, N.B.; Chai, X.S.; Li, Z.; Barnes, D.G. A Rapid Method for Simultaneously Determining Ethanol and Methanol Content in Wines by Full Evaporation Headspace Gas Chromatography. Food Chem. 2015, 183, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
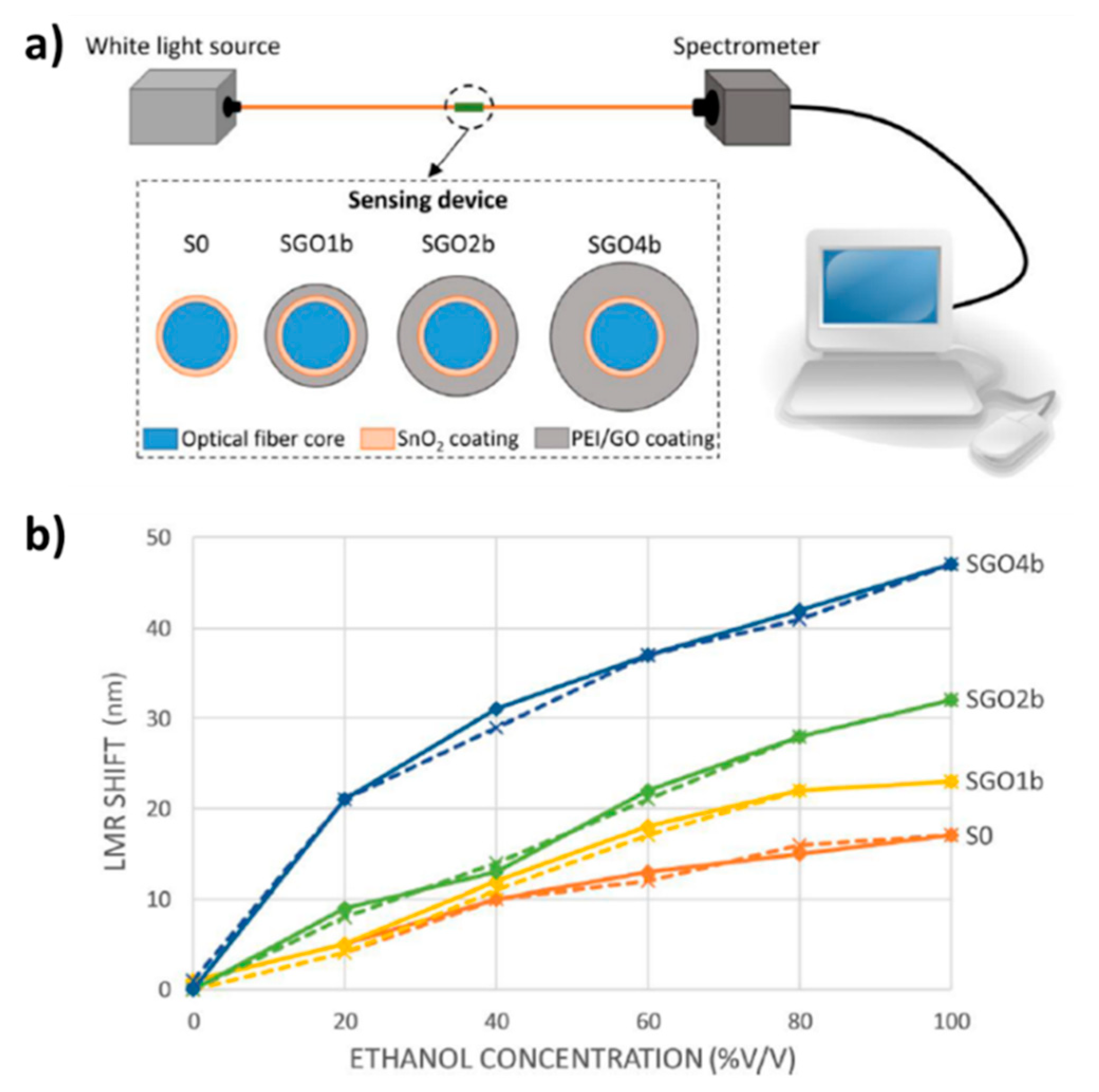
- Hernaez, M.; Mayes, A.G.; Melendi-Espina, S. Sensitivity enhancement of lossy mode resonance-based ethanol sensors by graphene oxide coatings. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors, Glasgow, UK, 29 October–1 November 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Hernaez, M.; Mayes, A.G.; Melendi-Espina, S. Graphene Oxide in Lossy Mode Resonance-Based Optical Fiber Sensors for Ethanol Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elosúa, C.; Vidondo, I.; Arregui, F.J.; Bariain, C.; Luquin, A.; Laguna, M.; Matías, I.R. Lossy Mode Resonance Optical Fiber Sensor to Detect Organic Vapors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 187, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elosua, C.; Arregui, F.J.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Bariain, C.; Luquin, A.; Laguna, M.; Matias, I.R. Volatile Organic Compounds Optical Fiber Sensor Based on Lossy Mode Resonances. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 173, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, H.; Wang, T.; Lee, S.W. Selective Methanol Gas Detection using a U-Bent Optical Fiber Modified with a Silica Nanoparticle Multilayer. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 2017, 100, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korposh, S.; Kodaira, S.; Lee, S.W.; Batty, W.J.; James, S.W.; Tatam, R.P. Deposition of SiO2/Polymer Nanoporous thin films on long-period grating (LPG) optical fibres and dramatic Enhancement of the resonance bands. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Sensing Technology, ICST 2008, Tainan, Taiwan, 30 November–3 December 2008; pp. 666–669. [Google Scholar]
- Bevc, S.; Mohorko, E.; Kolar, M.; Brglez, P.; Holobar, A.; Kniepeiss, D.; Podbregar, M.; Piko, N.; Hojs, N.; Knehtl, M.; Ekart, R.; Hojs, R. Measurement of Breath Ammonia for Detection of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Nephrol. 2017, 88, S14–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.Z.; Lin, Y.L.; Lin, H.C.; Zan, H.W.; Chang, K.T.; Meng, H.F.; Liao, J.W.; Tsai, M.J.; Cheng, H. Highly Sensitive Ammonia Sensor with Organic Vertical Nanojunctions for Noninvasive Detection of Hepatic Injury. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3110–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Wang, T.; Selyanchyn, R.; Korposh, S.; James, S.W. Optical fiber sensing of human skin emanations. In Fifth Asia-Pacific Optical Sensors Conference; The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9655. [Google Scholar]
- Korposh, S.; Kodaira, S.; Selyanchyn, R.; Ledezma, F.H.; James, S.W.; Lee, S.W. Porphyrin-Nanoassembled Fiber-Optic Gas Sensor Fabrication: Optimization of Parameters for Sensitive Ammonia Gas Detection. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 101, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korposh, S.; Okuda, H.; Wang, T.; James, S.W.; Lee, S.W. U-shaped evanescent wave optical fibre sensor based on a porphyrin anchored nanoassembled thin film for high sensitivity ammonia detection. In Fifth Asia-Pacific Optical Sensors Conference; The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9655. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Korposh, S.; Wong, R.; James, S.; Tatam, R.; Lee, S.W. A Novel Ammonia Gas Sensor Using a Nanoassembled Polyelectrolyte Thin Film on Fiber-Optic Long-Period Gratings. Chem. Lett. 2012, 41, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Korposh, S.; James, S.; Tatam, R.; Lee, S.W. Optical Fiber Long Period Grating Sensor with a Polyelectrolyte Alternate Thin Film for Gas Sensing of Amine Odors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 185, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Korposh, S.; James, S.; Tatam, R.; Lee, S.W. Polyelectrolyte multilayer nanothin film coated long period grating fiber optic sensors for ammonia gas sensing. In Proceedings of the 2013 13th IEEE International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO 2013), Beijing, China, 5–8 August 2013; pp. 505–508. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Tao, C.; Guo, X.; Bao, H.; Yin, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y. An in-Line Mach-Zehnder Interferometer using Thin-Core Fiber for Ammonia Gas Sensing with High Sensitivity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korposh, S.; Selyanchyn, R.; James, S.; Tatam, R.; Lee, S. Identification and Quality Assessment of Beverages Using a Long Period Grating Fibre-Optic Sensor Modified with a Mesoporous Thin Film. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2014, 1, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korposh, S.; Davis, F.; James, S.W.; Wang, T.; Lee, S.W.; Higson, S.; Tatam, R.P. Detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) using an optical fibre long period grating with a calixarene anchored mesoporous thin film. In Fifth European Workshop on Optical Fibre Sensors; The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013; Volume 8794. [Google Scholar]
- Hromadka, J.; Korposh, S.; Partridge, M.; James, S.W.; Davis, F.; Crump, D.; Tatam, R.P. Volatile Organic Compounds Sensing Using Optical Fibre Long Period Grating with Mesoporous Nano-Scale Coating. Sensors 2017, 17, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, S.L.; Cibulskis, K.; Helman, E.; McKenna, A.; Shen, H.; Zack, T.; Laird, P.W.; Onofrio, R.C.; Winkler, W.; Weir, B.A.; et al. Absolute Quantification of Somatic DNA Alterations in Human Cancer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kathariou, S. Listeria Monocytogenes Virulence and Pathogenicity, a Food Safety Perspective. J. Food Protection 2002, 65, 1811–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cooper, K.L.; Xu, J.; Wang, A.; Tu, Z. Label-free DNA detection on the surface of an optical fiber tip. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Lon Beach, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Cooper, K.L.; Wang, A.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, Z. Label-Free DNA Sequence Detection using Oligonucleotide Functionalized Optical Fiber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 163901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamarreno, C.R.; Zubiate, P.; Sanchez, P.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J.; Ramos-Arroyo, M.A.; Moreno-Igoa, M.; Hernandez-Charro, B. Single strand DNA detection by means of lossy mode resonance-based optical fiber devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 October–3 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Lang, T.; Jin, J.; Chen, J. An optical fiber biosensor based on layer-by-layer electrostatic self-assembly for rapid detection of HIgG. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Optical Communications and Networks, Hangzhou, China, 24–27 September 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Xu, S.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W. Optical Fiber LSPR Biosensor Prepared by Gold Nanoparticle Assembly on Polyelectrolyte Multilayer. Sensors 2010, 10, 3585–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socorro, A.B.; Corres, J.M.; Del Villar, I.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Fiber-Optic Biosensor Based on Lossy Mode Resonances. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 174, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, P.S.; Kaul, S.; Chinnayelka, S.; McShane, M.J. Fiber Optic Biosensors Comprising Nanocomposite Multilayered Polymer and Nanoparticle Ultrathin Films. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Cancun, Mexico, 17–21 September 2003; pp. 2987–2990. [Google Scholar]
- Kaul, S.; Chinnayelka, S.; McShane, M.J. Self-assembly of polymer/nanoparticle films for fabrication of fiber-optic sensors based on SPR. In Optical Fibers and Sensors for Medical Applications IV; The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5317, pp. 224–233. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Marques, L.; Correia, R.; Morgan, S.P.; Lee, S.W.; Tighe, P.; Fairclough, L.; Korposh, S. Human IgM detection using an optical fibre long period grating sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors, Glasgow, UK, 29 October–1 November 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Marques, L.; Correia, R.; Morgan, S.P.; Lee, S.W.; Tighe, P.; Fairclough, L.; Korposh, S. Highly Sensitive Label-Free Antibody Detection Using a Long Period Fibre Grating Sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 271, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W.; Erson, J.; Crudge, P.; Smith, H. Acute Myelopathy Associated with Primary Infection with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Brit. Med. J. 1987, 294, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, L.; Hernandez, F.U.; James, S.W.; Morgan, S.P.; Clark, M.; Tatam, R.P.; Korposh, S. Highly Sensitive Optical Fibre Long Period Grating Biosensor Anchored with Silica Core Gold Shell Nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Heflin, J.R.; Vancott, K.; Stolen, R.H.; Ramachandran, S.; Ghalmi, S. Sensitivity of long period fiber gratings to nanoscale ionic self-assembled multilayers. In Nanophotonic Materials and Systems II; The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5925, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, M.; Luo, P.; Jin, J.; Xing, J.; Wang, Z.; Wong, S.T.C. Fabrication of Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Fiber Probes using Ionic Self-Assembled Gold Nanoparticles. Sensors 2010, 10, 6477–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrutia, A.; Bojan, K.; Marques, L.; Mullaney, K.; Goicoechea, J.; James, S.; Clark, M.; Tatam, R.; Korposh, S. Novel Highly Sensitive Protein Sensors Based on Tapered Optical Fibres Modified with Au-Based Nanocoatings. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 8129387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Guang, J.; Peng, W. Gold nano sphere based fiber optic LSPR probe for biosensing measurement. In Nanophotonics and Micro/Nano Optics III; The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 10027. [Google Scholar]
- Del Villar, I.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J.; Corres, J.M. Fiber Optic Glucose Biosensor. Opt. Eng. 2006, 45, 104401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socorro, A.B.; Del Villar, I.; Corres, J.M.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Spectral Width Reduction in Lossy Mode Resonance-Based Sensors by Means of Tapered Optical Fibre Structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 200, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubiate, P.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Sánchez, P.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. High Sensitive and Selective C-Reactive Protein Detection by Means of Lossy Mode Resonance Based Optical Fiber Devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubiate, P.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Sánchez, P.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Lossy mode resonances biosensor for the detection of C-reactive protein. In Asia-Pacific Optical Sensors Conference; Optical Society of America: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; p. W4A-23. [Google Scholar]








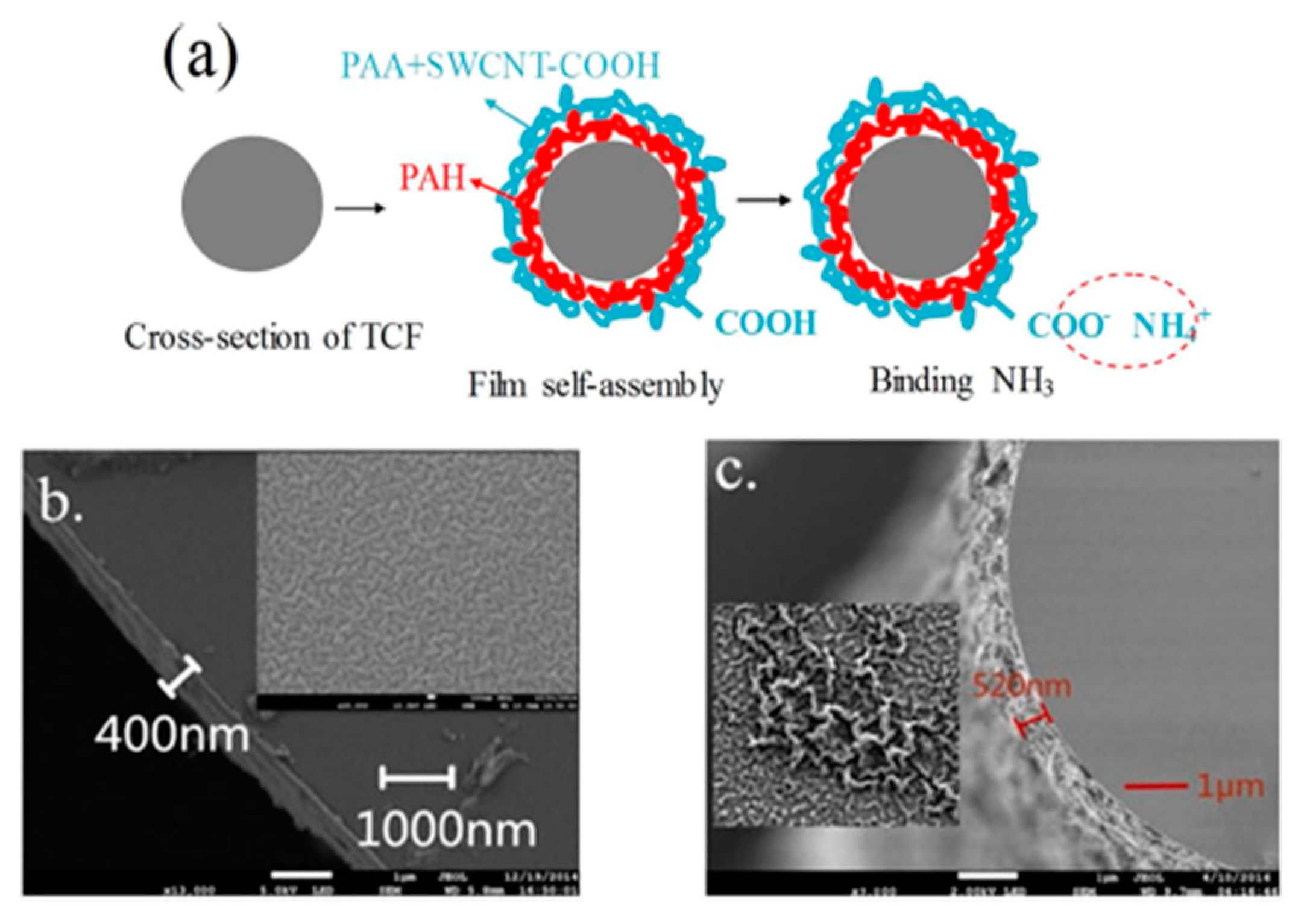
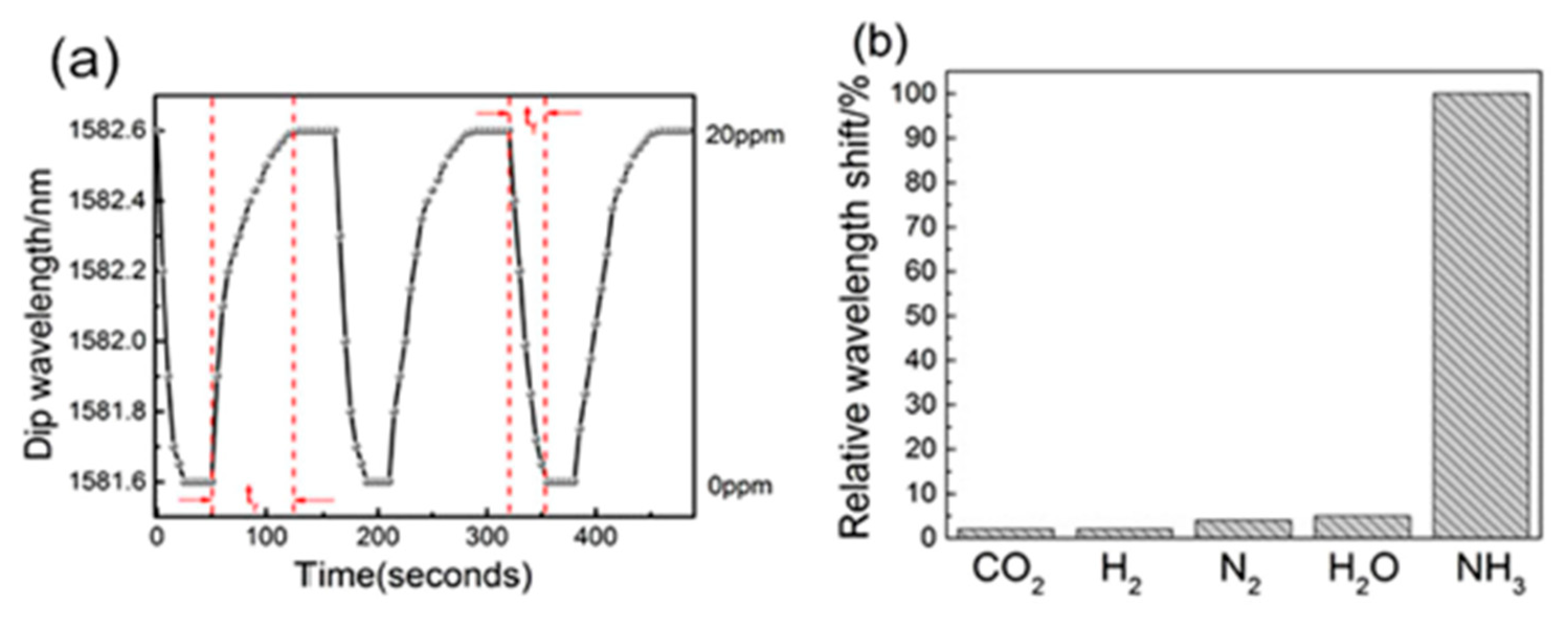
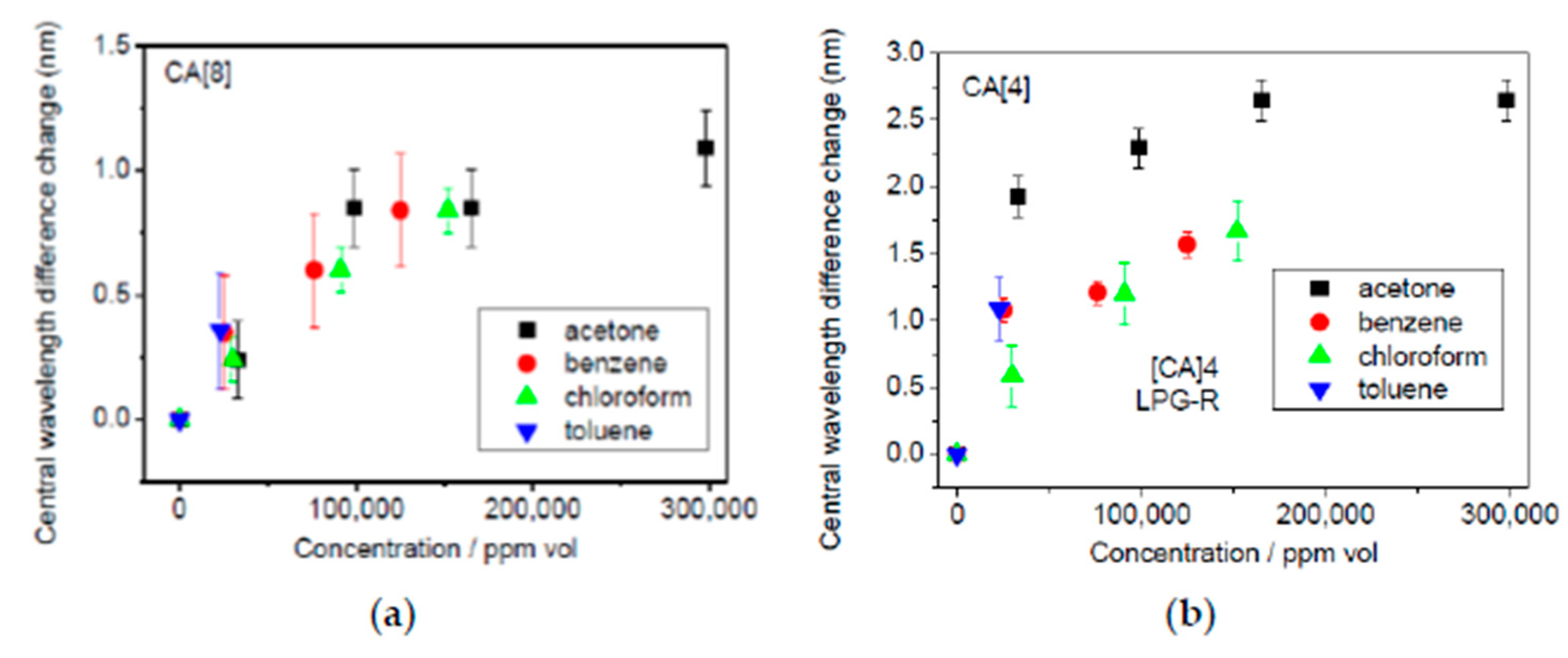
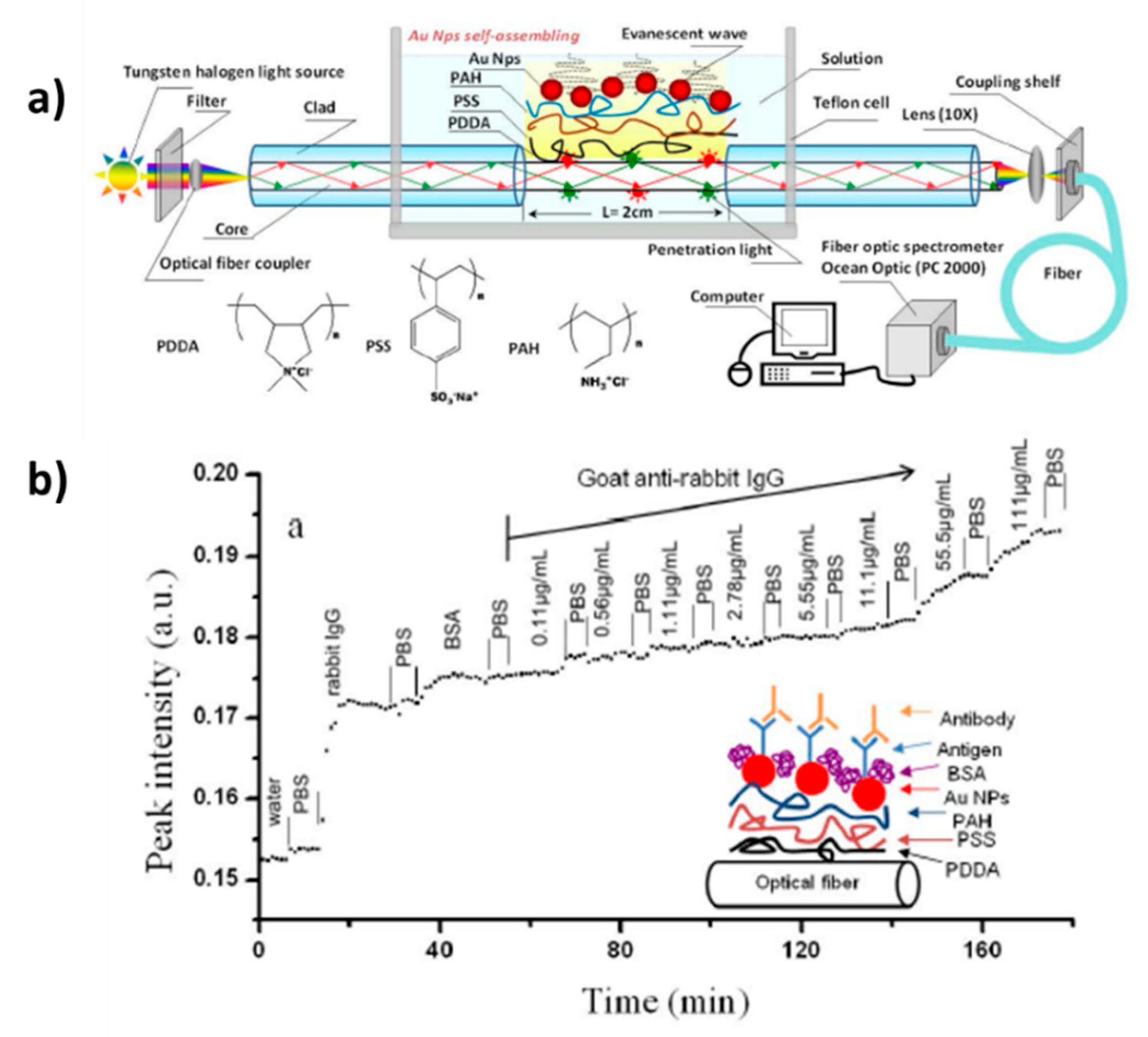
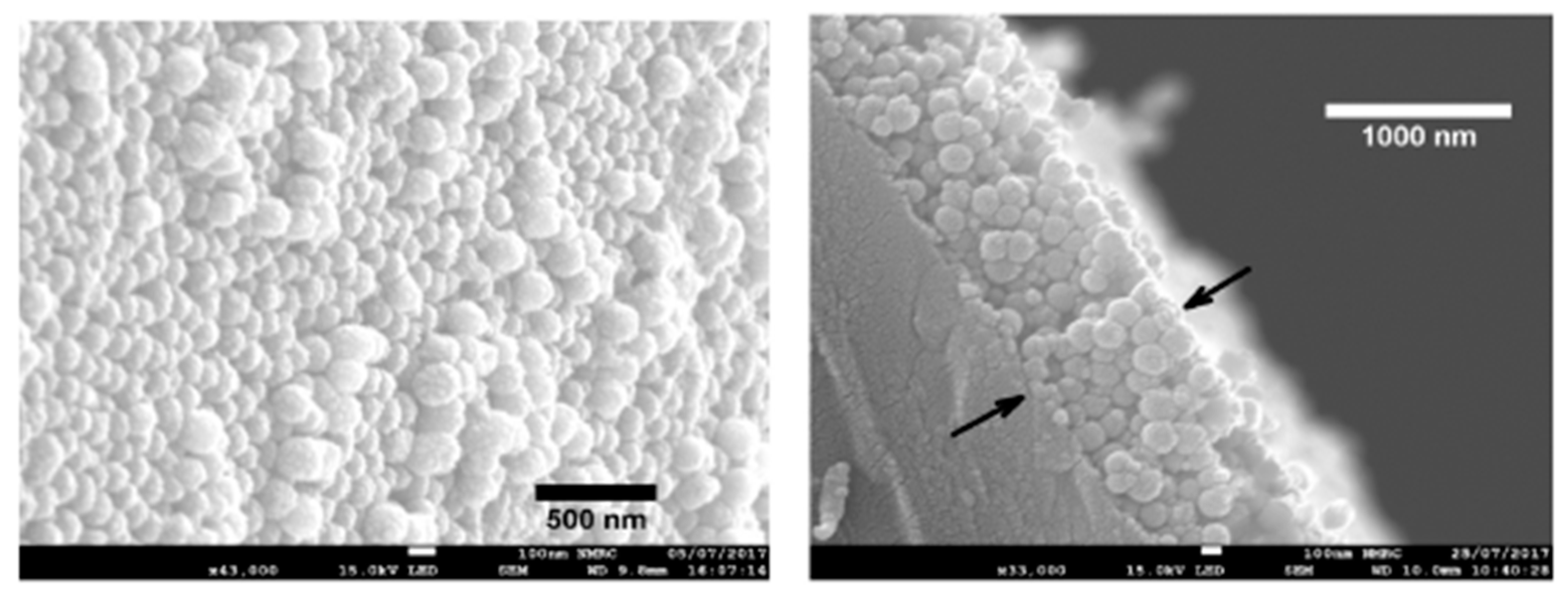

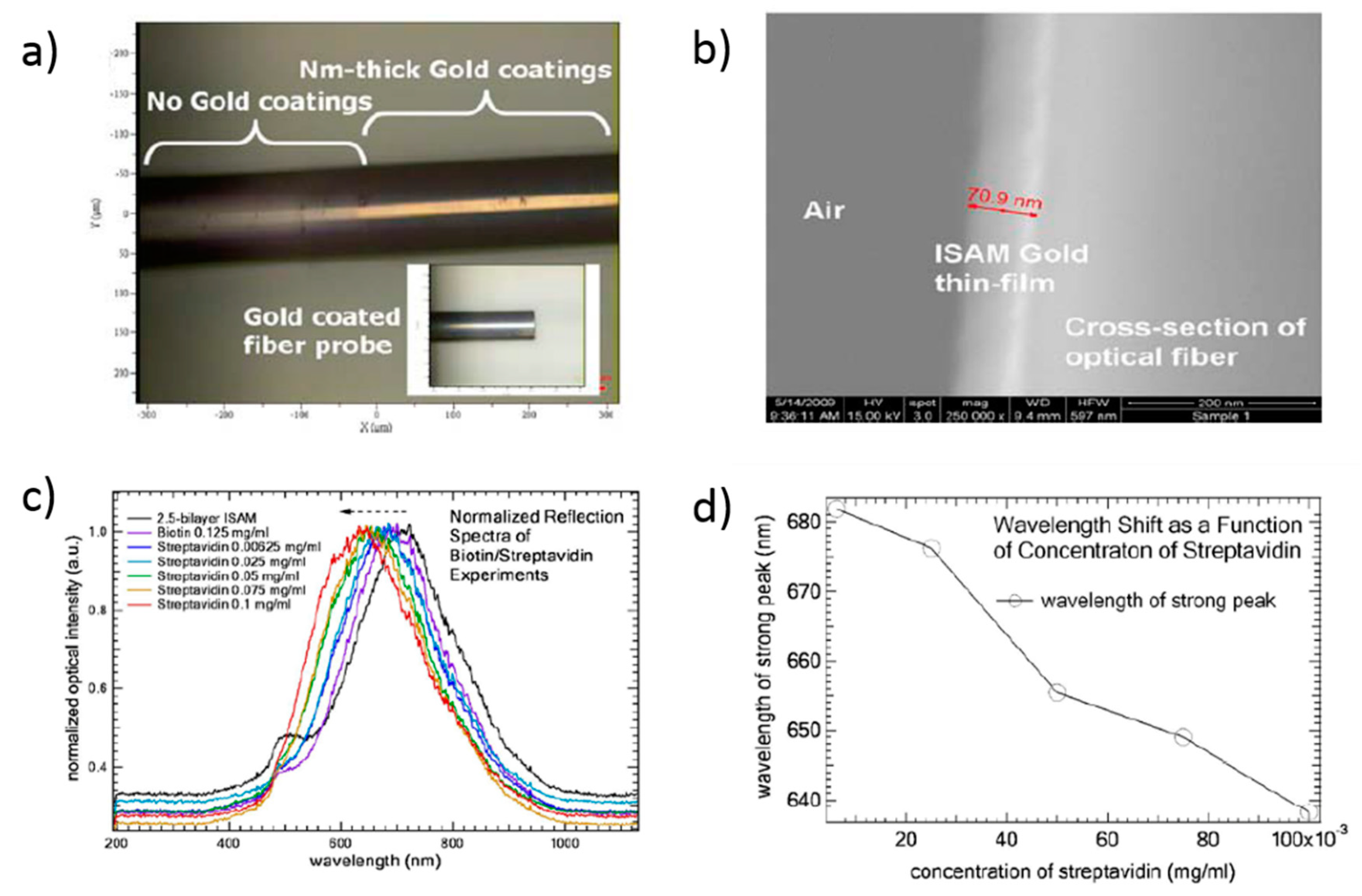


| Sensitive Coating | Optical Structure | Sensing Mechanism | pH Range | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [PAH/PAA] | Reflection | Absorbance | 3–9 | [76] |
| [PAH/PAA] | Transmission | LMR | 3–6 | [81] |
| [PAH/PAA] | Taper | LMR | 4–6 | [84] |
| [PAH/PAA] | D-shape | LMR | 4–5 | [86] |
| [PAH/PAA] | D-shape | LMR | 6–7 | [86] |
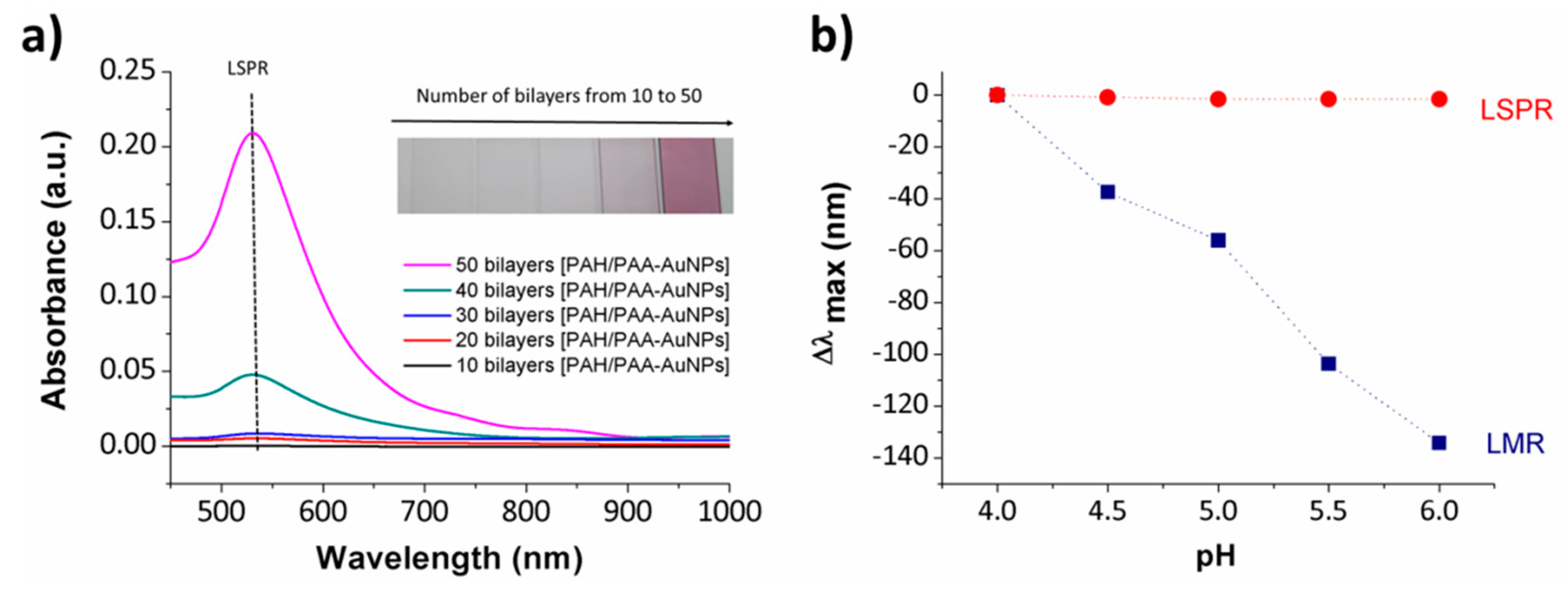
| [PAH/PAA-AuNPs] | Transmission | LSPR and LMR | 4–6 | [88] |
| [PAH+PB/PAA] | LPGs | Wavelength shift | 4–7 | [91] |
| [PAH + NR/PAA] | U-bend | Absorbance | 5–10 | [93] |
| [NR/PAA] | Reflection | Absorbance | 3–9 | [76] |
| [NR/PAA] | Reflection | Wavelength shift | 5.5–7.5 | [94] |
| [PAH/BY] | Reflection | Wavelength shift | 6.80–9 | [95] |
| [PAH/BY] | U-bend and straight | Wavelength shift | 7–9 | [96] |
| [PAH/PAA+HPTS] | Taper | Fluorescence | 3–7 | [75] |
| [PAH/SiO2] + [PAH/PAA+HPTS] | Taper | Fluorescence | 3–7 | [75] |
| [PAH+DABCO/PAA+HPTS+DABCO] | Taper | Fluorescence | 3–7 | [97] |
| [PDDA/PAA] | TFBG | Absorbance | 4.66–6.02 | [98] |
| [PDDA/PAA] | MZ | Wavelength shift | 4.48–5.66 | [99] |
| [PVPMC+PDDA/PAA] | MZ | Wavelength shift | 4.48–5.66 | [99] |
| [PDDA/PSS + PDDA/PEC−] | MZ | Wavelength shift | 2–11 | [100] |
| [PEI/SA] | MZ | Wavelength shift | 2–11 | [101] |
| Sensitive Coating | Optical Structure | Sensing Mechanism | Parameter Detection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [PAH + porous glass beads/PAA] | Reflection | Fluorescence | Oxygen | [108] |
| [PAH/SDS-Pt-TFPP] | Reflection | Fluorescence | Oxygen | [109] |
| [PAH/SDS-Pt-TFPP] | Reflection | Fluorescence | Oxygen | [110] |
| [PDDA/SDS-Pt-TFPP] [PEI/SDS-Pt-TFPP] [PAH/SDS-Pt-TFPP] | Reflection | Fluorescence | Oxygen | [111] |
| [P(+)/SDS-Pt-TFPP] [P(+)/SDS-Pt-TFPP/(P(+)/PAA)N]4+[P(+)/SDS-Pt-TFPP] N = 1, 2, 3 and P(+) = PAH, PDDA, PEI | Reflection | Fluorescence | Oxygen | [112] |
| [PEI/GO] | Transmission | LMR | Ethanol | [115] |
| [PEI/GO] | Transmission | LMR | Ethanol | [116] |
| [PAH/[Au2Ag2(C6F5)4(C6H5C≡CC6H5)2]n | Transmission | LMR | Methanol Ethanol Isopropanol | [117] |
| [PAH/PAA/[Au2Ag2(C6F5)4(NH3)2]n/PAA | Transmission | LMR | Methanol Ethanol Isopropanol | [118] |
| TSPP-infused PAH/SiO2 | U-bend | Intensity | Methanol | [119] |
| TSPP-infused PDDA/SiO2 | LPG | Intensity | Ammonia | [120] |
| [PAH/TSPP] | Transmission | Intensity | Skin emanation | [123] |
| [PDDA/TSPP] | Transmission | Intensity | Ammonia | [124] |
| [PDDA/TSPP] | U-bend | Intensity | Ammonia | [125] |
| [PDDA/PAA] | LPG | Wavelength shift | Ammonia | [126] |
| [PAH/PAA] | LPG | Wavelength shift | Ammonia | [127] |
| [PAH/PAA] [PDDA/PAA] | LPG | Wavelength shift | Ammonia | [128] |
| [PAH/PAA]+[PAH/(PAA+SWCNTsCOOH)] | MZ | Wavelength shift | Ammonia | [129] |
| [PAH/SiO2] | LPG | Wavelength shift | Carboxylic acids in beverages | [130] |
| Calix[4]arene-infused PAH/SiO2 | LPG | Intensity | Chloroform Benzene | [131] |
| Calix[4]arene-infused PAH/SiO2 Calix[8]arene-infused PAH/SiO2 | LPG | Wavelength shift | Chloroform Benzene Toluene Acetone | [132] |
| Sensitive Coating | Optical Structure | Sensing Mechanism | Parameter Detection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [PAH/PSS] | Transmission | Fiber cavity thickness | DNA | [135] |
| [PAH/PSS] | Transmission | Fiber cavity thickness | DNA | [136] |
| [PAH/PSS] | Transmission | LMR | DNA | [137] |
| [PDDA/PSS] | MZ | Wavelength shift | HIgG | [138] |
| [PDDA/PSS/PAH/AuNPs] | Transmission | LSPR intensity | Goat anti-rabbit IgG | [139] |
| [PAH/PSS] | Reflection | LMR | IgG | [140] |
| [PAH/PSS] + [PAH/AuNPs] | Reflection | Refractive index changes | IgG | [141] |
| [PAH/PSS] + [PAH/AgNPs or AuNPs (variable size of 10 and 20 nm)] | Reflection | Wavelength shift | IgG | [142] |
| [PAH/SiO2@AuNPs] | LPG | Wavelength shift | HIgM | [143] |
| [PAH/SiO2@AuNPs] | LPG | Wavelength separation | HIgM | [144] |
| [PAH/SiO2@AuNPs] | LPG | Wavelength shift | Streptavidin | [144] |
| [PAH/SiO2@AuNPs] | LPG | Wavelength shift | Streptavidin | [146] |
| [PAH/PCBS] | LPG | Wavelength shift | Streptavidin | [147] |
| [PAH/AuNPs] | Reflection | Wavelength shift | Streptavidin | [148] |
| [PAH/SiO2NPs] + [AuNPs/PSS] | Taper | Wavelength shift | Streptavidin | [149] |
| [PDDA/PSS/PAH] + AuNPs | Transmission | LSPR intensity | Con A | [150] |
| [PAH+PB/GOx] | Reflection | Fabry-Perot cavity | Glucose | [151] |
| [PAH/PAA] + [PAH/PSS] | Taper | LMR | Anti-gliadin antibodies | [152] |
| [PAH/PSS] | D-shaped | LMR | C-reactive protein | [153] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivero, P.J.; Goicoechea, J.; Arregui, F.J. Layer-by-Layer Nano-assembly: A Powerful Tool for Optical Fiber Sensing Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030683
Rivero PJ, Goicoechea J, Arregui FJ. Layer-by-Layer Nano-assembly: A Powerful Tool for Optical Fiber Sensing Applications. Sensors. 2019; 19(3):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030683
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivero, Pedro J., Javier Goicoechea, and Francisco J. Arregui. 2019. "Layer-by-Layer Nano-assembly: A Powerful Tool for Optical Fiber Sensing Applications" Sensors 19, no. 3: 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030683
APA StyleRivero, P. J., Goicoechea, J., & Arregui, F. J. (2019). Layer-by-Layer Nano-assembly: A Powerful Tool for Optical Fiber Sensing Applications. Sensors, 19(3), 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030683







